

新疆农业科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (5): 1121-1130.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.05.009
收稿日期:2024-10-07
出版日期:2025-05-20
发布日期:2025-07-09
通信作者:
刘易(1983-),男,河北保定人,副研究员,博士研究生,研究方向为作物栽培育种,(E-mail)liuyun_5511@163.com作者简介:王亚玲(1994-),女,新疆乌鲁木齐人,助理研究员,博士研究生,研究方向为马铃薯抗逆育种,(E-mail)yalingwangx@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Yaling( ), JIANG Yinghong, SUN Hui, LIU Yi(
), JIANG Yinghong, SUN Hui, LIU Yi( )
)
Received:2024-10-07
Published:2025-05-20
Online:2025-07-09
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究与马铃薯耐盐性相关的候选基因,为马铃薯耐盐性鉴定与评价和耐盐基因的挖掘提供理论依据。【方法】以耐盐品种晋薯16号及盐敏感品种冀张薯12号为试材,采用0%、0.5%、1%和1.5% NaCl溶液进行盐胁迫处理,在第8 d时,分析植株表型和生理生化指标,随后选择1%的盐浓度处理,分析2个品种进行转录组测序和生物信息学。【结果】相较于冀张薯12号,晋薯16号在盐胁迫条件下,具有较低的丙二醛含量。植物激素信号转导途径和类黄酮代谢途径在2个马铃薯品种中显示出明显的差异。【结论】筛选出与植物激素信号转导和类黄酮代谢相关的差异表达基因。
中图分类号:
王亚玲, 江应红, 孙慧, 刘易. 不同马铃薯耐盐性转录组比较及耐盐基因的挖掘[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1121-1130.
WANG Yaling, JIANG Yinghong, SUN Hui, LIU Yi. Comparative transcriptome analysis between two potato varieties with different salt-tolerance and further identification of potato salt-tolerance genes[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(5): 1121-1130.
| 基因号 Gene ID | 上游引物 Up-stream primer | 下游引物 Down-stream primer |
|---|---|---|
| PGSC0003DMT400016742 | CTGTTGTGGCCGTCCTAACT | ATCAGGCTTGTGGTCAGTGG |
| PGSC0003DMT400018004 | ATGGAAGAGATGTTTCCAGCACT | GCAAGCTAGTCGTATTCGGG |
| PGSC0003DMT400027196 | GTGCGACTTCGGTATGTGGA | AGCCATGGCCATCGTAAACA |
| PGSC0003DMT400029264 | AAGTCGGTGGAGACTTATGCTT | AGCACGGATTAAAGCCCTC |
| StEF1a | GATGTTGTGCCAAAGGATGT | AACTTGTGGTCAATGCGAGA |
表1 实时荧光定量PCR引物
Tab.1 qRT-PCR primers
| 基因号 Gene ID | 上游引物 Up-stream primer | 下游引物 Down-stream primer |
|---|---|---|
| PGSC0003DMT400016742 | CTGTTGTGGCCGTCCTAACT | ATCAGGCTTGTGGTCAGTGG |
| PGSC0003DMT400018004 | ATGGAAGAGATGTTTCCAGCACT | GCAAGCTAGTCGTATTCGGG |
| PGSC0003DMT400027196 | GTGCGACTTCGGTATGTGGA | AGCCATGGCCATCGTAAACA |
| PGSC0003DMT400029264 | AAGTCGGTGGAGACTTATGCTT | AGCACGGATTAAAGCCCTC |
| StEF1a | GATGTTGTGCCAAAGGATGT | AACTTGTGGTCAATGCGAGA |
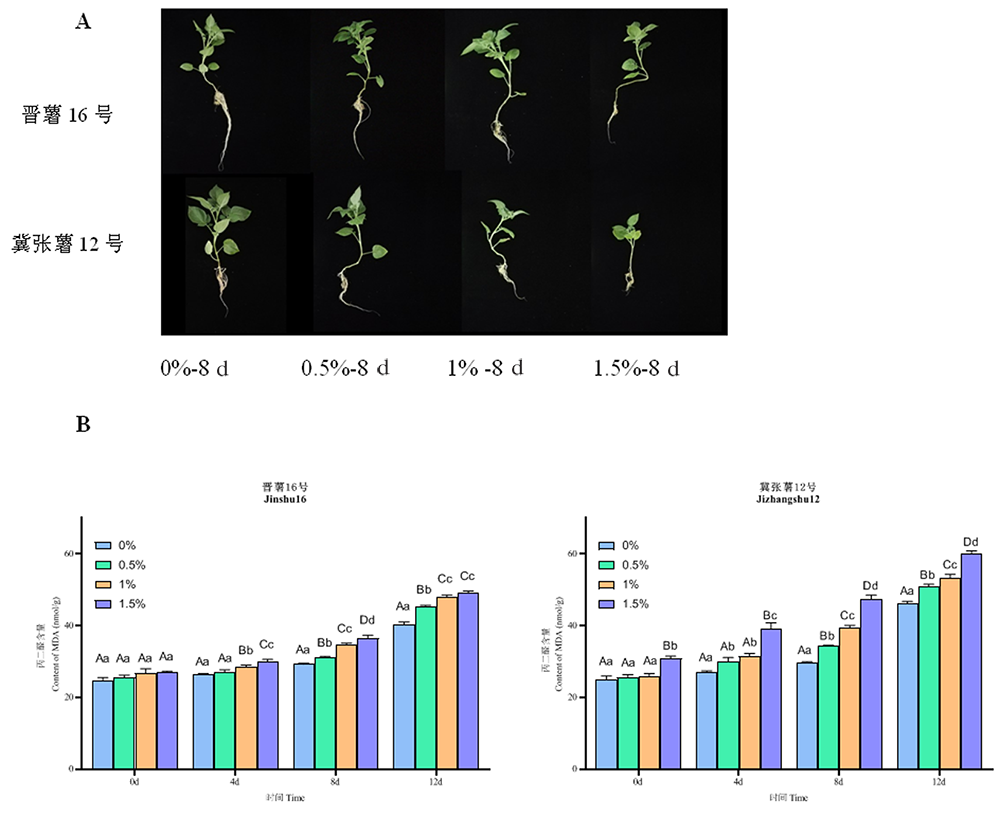
图1 (A)不同NaCl浓度的盐胁迫下晋薯16号和冀张薯12号马铃薯幼苗生长的变化(B)不同NaCl浓度(0%、0.5%、1%、1.5%)和胁迫时间(0、4、8、12 d)下晋薯16号和冀张薯12号的丙二醛含量的变化
Fig.1 (A) Changes of salt stress with different NaCl concentrations on the growth of potato seedlings in Jinshu 16 and Jizhangshu 12. (B) The malondialdehyde content of Jinshu 16 and Jizhangshu 12 were measured at different NaCl concentrations (0%, 0.5%, 1%, 1.5%) and stress times (0, 4, 8, 12 days)
| 样品 Sample | 有效 序列 Clean reads | 有效 碱基(G) Clean bases | Q30 含量 Q30 content (%) | GC 含量 GC content (%) | 比对效率 Mapped reads ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC | 42058489 | 6.27 | 93.89 | 43.89 | 80.01 |
| JT | 41683414 | 6.26 | 93.67 | 43.98 | 85.13 |
| ZC | 41728022 | 6.22 | 93.62 | 43.36 | 87.58 |
| ZT | 41015686 | 6.12 | 93.71 | 43.95 | 87.72 |
表2 测序数据的统计与质量评估
Tab.2 Statistics and assessment of sequencing data
| 样品 Sample | 有效 序列 Clean reads | 有效 碱基(G) Clean bases | Q30 含量 Q30 content (%) | GC 含量 GC content (%) | 比对效率 Mapped reads ratio (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC | 42058489 | 6.27 | 93.89 | 43.89 | 80.01 |
| JT | 41683414 | 6.26 | 93.67 | 43.98 | 85.13 |
| ZC | 41728022 | 6.22 | 93.62 | 43.36 | 87.58 |
| ZT | 41015686 | 6.12 | 93.71 | 43.95 | 87.72 |
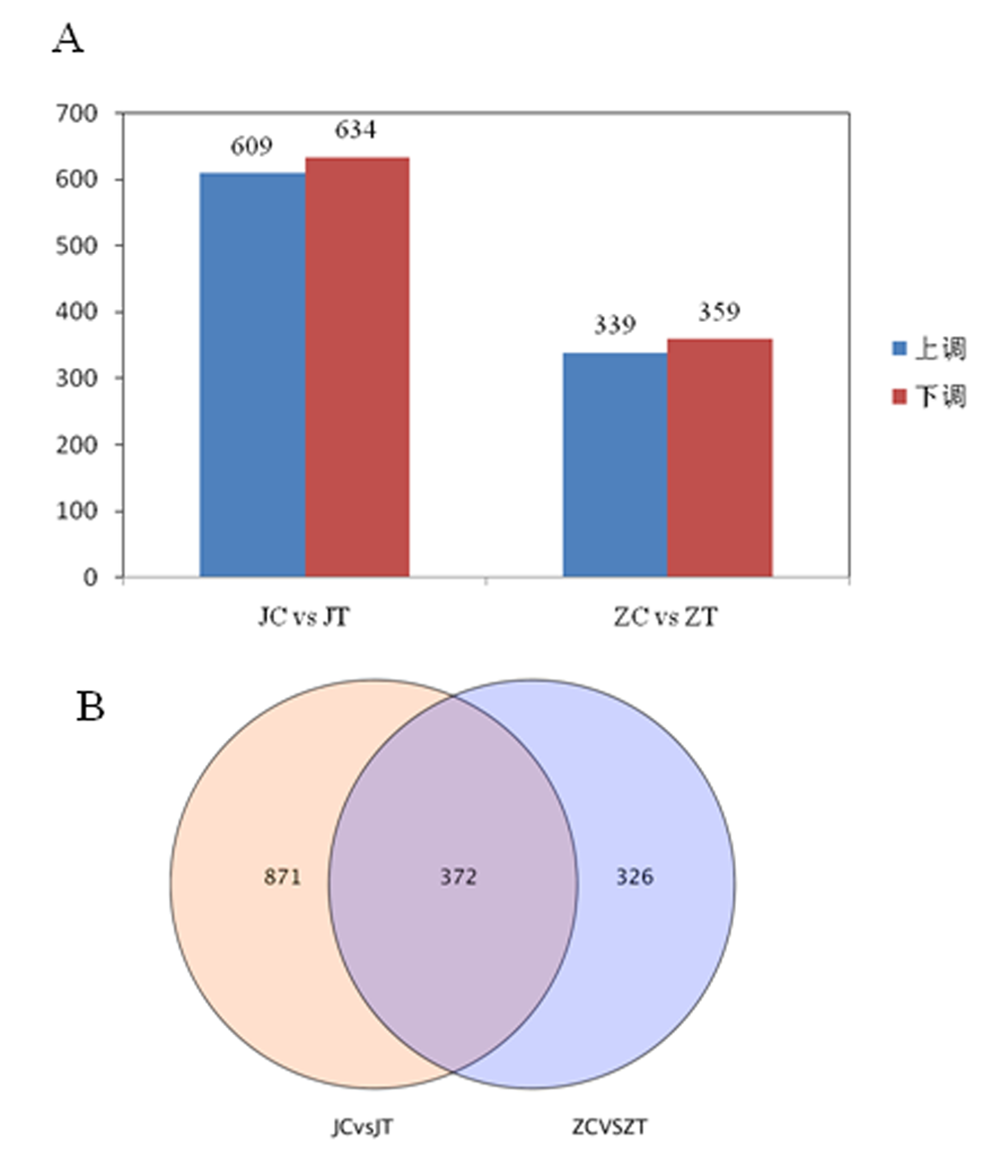
图2 耐盐马铃薯晋薯16号和盐敏感马铃薯冀张薯12号差异表达基因 注:(A)差异表达基因统计;(B)差异表达基因韦恩图
Fig.2 Analysis of differentially expressed genes between salt tolerant Jinshu16 and salt sensitive Jizhangshu 12 groups Notes:(A) Differential expression gene statistics; (B) Differential expression gene Venn diagram

图3 盐胁迫下马铃薯差异表达基因前20个显著富集GO条目 注:(A) JC vs JT,(B) ZC vs ZT
Fig.3 The top 20 significantly enriched GO entries of DEGs in potato under salt stress Notes:(A) JC vs JT, (B) ZC vs ZT

图4 盐胁迫下马铃薯差异表达基因的前20个显著富集的KEGG通路 注:(A) JC vs JT,(B) ZC vs ZT
Fig.4 The top 20 significantly enriched KEGG pathway maps of DEGs in potato under salt stress Notes:(A) JC vs JT, (B) ZC vs ZT
| 名称 Name | 基因ID Gene ID | 表达模式 Expression pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase | PGSC0003DMG400003790 PGSC0003DMG400009843 PGSC0003DMG400014064 PGSC0003DMG400015666 PGSC0003DMG400017943 PGSC0003DMG400018840 PGSC0003DMG400019720 PGSC0003DMG400021993 PGSC0003DMG401019681 PGSC0003DMG402029906 | 下调 Down |
| PP2C Protein phosphatase 2C | PGSC0003DMG400002573 PGSC0003DMG400009112 PGSC0003DMG400016742 PGSC0003DMG400018004 PGSC0003DMG400019604 PGSC0003DMG400027196 PGSC0003DMG400030332 | 上调UP |
| 生长素转运蛋白 Auxin transporter- like protein 3 | PGSC0003DMG400006550 | UP上调 |
| ABF ABRE binding factor | PGSC0003DMG400008011 | UP上调 |
| 脱落酸受体 Abscisic acid receptor protein | PGSC0003DMG400011033 PGSC0003DMG400015897 PGSC0003DMG400023949 | DOWN下调 |
| 脱落酸-不敏感蛋白 ABSCISIC ACID- INSENSITIVE 5- like protein 4 | PGSC0003DMG400025889 | UP上调 |
| 生长素应答蛋白 Auxin-responsive protein | PGSC0003DMG400026010 PGSC0003DMG402002635 | UP上调 UP上调 |
| 吲哚-3-乙酸酰 胺合成酶 Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | PGSC0003DMG401018368 PGSC0003DMG402018368 | DOWN下调 DOWN下调 |
| MYC4转录因子 Transcription factor MYC4 | PGSC0003DMG400005525 PGSC0003DMG401010822 PGSC0003DMG402010822 | DOWN下调 |
表3 晋薯16号在盐胁迫下参与植物激素信号转导途径的DEGs
Tab.3 Analysis of DEGs involved in plant hormone signal transduction pathway under salt stress in Jinshu16
| 名称 Name | 基因ID Gene ID | 表达模式 Expression pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 蛋白激酶 Protein kinase | PGSC0003DMG400003790 PGSC0003DMG400009843 PGSC0003DMG400014064 PGSC0003DMG400015666 PGSC0003DMG400017943 PGSC0003DMG400018840 PGSC0003DMG400019720 PGSC0003DMG400021993 PGSC0003DMG401019681 PGSC0003DMG402029906 | 下调 Down |
| PP2C Protein phosphatase 2C | PGSC0003DMG400002573 PGSC0003DMG400009112 PGSC0003DMG400016742 PGSC0003DMG400018004 PGSC0003DMG400019604 PGSC0003DMG400027196 PGSC0003DMG400030332 | 上调UP |
| 生长素转运蛋白 Auxin transporter- like protein 3 | PGSC0003DMG400006550 | UP上调 |
| ABF ABRE binding factor | PGSC0003DMG400008011 | UP上调 |
| 脱落酸受体 Abscisic acid receptor protein | PGSC0003DMG400011033 PGSC0003DMG400015897 PGSC0003DMG400023949 | DOWN下调 |
| 脱落酸-不敏感蛋白 ABSCISIC ACID- INSENSITIVE 5- like protein 4 | PGSC0003DMG400025889 | UP上调 |
| 生长素应答蛋白 Auxin-responsive protein | PGSC0003DMG400026010 PGSC0003DMG402002635 | UP上调 UP上调 |
| 吲哚-3-乙酸酰 胺合成酶 Indole-3-acetic acid-amido synthetase | PGSC0003DMG401018368 PGSC0003DMG402018368 | DOWN下调 DOWN下调 |
| MYC4转录因子 Transcription factor MYC4 | PGSC0003DMG400005525 PGSC0003DMG401010822 PGSC0003DMG402010822 | DOWN下调 |
| 名称 Name | 基因ID Gene ID | 表达模式 Expression pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 查尔酮合成酶 Chalcone synthase G | PGSC0003DMG400008633 PGSC0003DMG400019110 PGSC0003DMG400029620 | UP上调 UP上调 DOWN下调 |
| 乙酰辅酶A苄醇 乙酰转移酶 Acetyl-CoA-benzylalcohol acetyltransferase-like | PGSC0003DMG400029256 PGSC0003DMG400029262 | DOWN下调 |
| 黄烷酮3-羟化酶 Flavanone 3-hydroxylase | PGSC0003DMG400003563 PGSC0003DMG400011929 | DOWN下调 UP上调 |
| ECERIFERUM 1 蛋白 protein ECERIFERUM 1 | PGSC0003DMG400002049 | DOWN下调 |
表4 冀张薯12号在盐胁迫下参与类黄酮代谢途径的DEGs
Tab.4 Analysis of DEGs involved in flavonoid metabolism pathway under salt stress in Jizhangshu 12
| 名称 Name | 基因ID Gene ID | 表达模式 Expression pattern |
|---|---|---|
| 查尔酮合成酶 Chalcone synthase G | PGSC0003DMG400008633 PGSC0003DMG400019110 PGSC0003DMG400029620 | UP上调 UP上调 DOWN下调 |
| 乙酰辅酶A苄醇 乙酰转移酶 Acetyl-CoA-benzylalcohol acetyltransferase-like | PGSC0003DMG400029256 PGSC0003DMG400029262 | DOWN下调 |
| 黄烷酮3-羟化酶 Flavanone 3-hydroxylase | PGSC0003DMG400003563 PGSC0003DMG400011929 | DOWN下调 UP上调 |
| ECERIFERUM 1 蛋白 protein ECERIFERUM 1 | PGSC0003DMG400002049 | DOWN下调 |
| [1] | Birch P R J, Bryan G, Fenton B, et al. Crops that feed the world 8: potato: are the trends of increased global production sustainable?[J]. Food Security, 2012, 4(4): 477-508. |
| [2] |
Jaarsma R, de Boer A H. Salinity tolerance of two potato cultivars (Solanum tuberosum) correlates with differences in vacuolar transport activity[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2018, 9: 737.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Arif Y, Singh P, Siddiqui H, et al. Salinity induced physiological and biochemical changes in plants: an omic approach towards salt stress tolerance[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, 156: 64-77.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Ju Y L, Min Z, Zhang Y, et al. Transcriptome profiling provide new insights into the molecular mechanism of grapevine response to heat, drought, and combined stress[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2021, 286: 110076. |
| [5] |
Zhang Y J, Li D H, Zhou R, et al. Transcriptome and metabolome analyses of two contrasting sesame genotypes reveal the crucial biological pathways involved in rapid adaptive response to salt stress[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2019, 19(1): 66.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | Wu F H, Chen Z T, Zhang F N, et al. Identification and transcriptome analysis of genes related to membrane lipid regulation in sweet Sorghum under salt stress[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022, 23(10): 5465. |
| [7] | Hussain Q, Asim M, Zhang R, et al. Transcription factors interact with ABA through gene expression and signaling pathways to mitigate drought and salinity stress[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(8): 1159. |
| [8] | 张龙. 近二十年新疆灌区盐碱地变化情况分析和对策研究[J]. 水资源开发与管理, 2020, 6(6): 72-76. |
| ZHANG Long. Analysis and countermeasure research on saline-alkali land change in Xinjiang irrigation area in recent 20 years[J]. Water Resources Development and Management, 2020, 6(6): 72-76. | |
| [9] |
Draper H H, Hadley M. 43] Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid Peroxidation[J]. Methods in Enzymology, 1990, 186: 421-431.
PMID |
| [10] |
Kim D, Paggi J M, Park C, et al. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2019, 37(8): 907-915.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Mortazavi A, Williams B A, McCue K, et al. Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-seq[J]. Nature Methods, 2008, 5(7): 621-628.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Love M I, Huber W, Anders S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2[J]. Genome Biology, 2014, 15(12): 550. |
| [13] | 李飞, 徐建飞, 刘杰, 等. 冷驯化前后野生马铃薯Solanum acaule内参基因的筛选[J]. 西南农业学报, 2012, 25(5): 1592-1595. |
| LI Fei, XU Jianfei, LIU Jie, et al. Selection of reference genes from wild potato Solanum acaule before and after cold acclimation[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012, 25(5): 1592-1595. | |
| [14] |
Cavaiuolo M, Cocetta G, Ferrante A. The antioxidants changes in ornamental flowers during development and senescence[J]. Antioxidants, 2013, 2(3): 132-155.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Iwashina T. Flavonoid function and activity to plants and other organisms[J]. Uchu Seibutsu Kagaku, 2003, 17(1): 24-44.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Pourcel L, Routaboul J M, Cheynier V, et al. Flavonoid oxidation in plants: from biochemical properties to physiological functions[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2007, 12(1): 29-36.
DOI PMID |
| [17] |
Zhang P P, Du H Y, Wang J, et al. Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9-mediated metabolic engineering increases soya bean isoflavone content and resistance to soya bean mosaic virus[J]. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2020, 18(6): 1384-1395.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Munns R, James R A, Läuchli A. Approaches to increasing the salt tolerance of wheat and other cereals[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2006, 57(5): 1025-1043.
DOI PMID |
| [19] | 江应红, 冯怀章, 孙慧, 等. 不同基质对马铃薯原原种生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 农村科技, 2018(4): 9-10. |
| JIANG Yinghong, FENG Huaizhang, SUN Hui, et al. Effects of different substrates on the growth and yield of potato original seed[J]. Rural Science & Technology, 2018(4): 9-10. | |
| [20] | Zlatev Z S, Lidon F C, Ramalho J C, et al. Comparison of resistance to drought of three bean cultivars[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2006, 50(3): 389-394. |
| [21] | Zhou X Y, Zhang N, Yang J W, et al. Functional analysis of StDWF4 gene in response to salt stress in potato[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 125: 63-73. |
| [22] | Xu N, Chu Y L, Chen H L, et al. Rice transcription factor OsMADS25 modulates root growth and confers salinity tolerance via the ABA-mediated regulatory pathway and ROS scavenging[J]. PLoS Genetics, 2018, 14(10): e1007662. |
| [23] |
董明, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 吕芃, 等. 高粱苗期耐盐性转录组分析和基因挖掘[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(22): 3987-4001.
DOI |
|
DONG Ming, Zaituniguli Kuerban, LYU Peng, et al. Transcriptome analysis and gene mining of salt tolerance in Sorghum seedlings(Sorghum bicolor L. moench)[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(22): 3987-4001.
DOI |
|
| [24] | Park S Y, Fung P, Nishimura N, et al. Abscisic acid inhibits type 2C protein phosphatases via the PYR/PYL family of START proteins[J]. Science, 2009, 324(5930): 1068-1071. |
| [25] |
Zou M J, Guan Y C, Ren H B, et al. A bZIP transcription factor, OsABI5, is involved in rice fertility and stress tolerance[J]. Plant Molecular Biology, 2008, 66(6): 675-683.
DOI PMID |
| [26] | Hernández M M, Pesquera-Alegría C, Manso-Martínez C, et al. Antioxidant capacity and flavanol composition of seed extracts from a Grenache × Tempranillo population: Effect of sex and color[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2021, 161: 113177. |
| [27] | Khan A L, Kang S M, Dhakal K H, et al. Flavonoids and amino acid regulation in Capsicum annuum L. by endophytic fungi under different heat stress regimes[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2013, 155: 1-7. |
| [28] | Jan R, Kim N, Lee S H, et al. Enhanced flavonoid accumulation reduces combined salt and heat stress through regulation of transcriptional and hormonal mechanisms[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2021, 12: 796956. |
| [29] | 李爽, 孙亮亮, 白丽丽, 等. 类黄酮参与调控中亚滨藜幼苗对盐胁迫的耐受性[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2017, 25(9): 1345-1350. |
| LI Shuang, SUN Liangliang, BAI Lili, et al. Flavonoid is associated with salt stress tolerance in Atriplex centralasiatica seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2017, 25(9): 1345-1350. |
| [1] | 樊德鹏, 陈玉鹏, 石洁, 琚艳君, 邢斌德, 江应红, 刘易, 赵多勇. 新疆不同马铃薯品种品质性状的综合分析与评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1111-1120. |
| [2] | 古丽娜尔·巴合提别克, 刘文静, 麻井彪, 张国胜, 郭启平, 袁杰, 张燕红, 安万刚, 萨吉代木·玉苏甫, 潘建明, 任磊. 盐胁迫下水稻种子萌发特性及其耐盐性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(4): 858-868. |
| [3] | 杨茹薇, 刘易, 古丽米拉·热合木土拉, 孙慧, 江应红. 不同基质、扦插密度及追肥次数对马铃薯微型薯生产的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(4): 869-875. |
| [4] | 弓兆星, 韩鹏程, 李泽森, 李桂真, 王玉祥, 张博. 盐胁迫下接种AM真菌对野生无芒雀麦生理的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 129-136. |
| [5] | 孙彩琴, 吴佳, 黄海, 郭家鑫, 闵伟, 郭慧娟. 不同盐碱胁迫对棉花根系蛋白质组的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 146-160. |
| [6] | 董志多, 徐菲, 付秋萍, 黄建, 祁通, 孟阿静, 付彦博, 开赛尔·库尔班. 不同类型盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [7] | 奚瑞, 陈怡佳, 李宁, 余庆辉, 王强, 秦勇. 外源2, 4-表芸苔素内酯对盐胁迫下不同盐敏感型番茄种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1983-1992. |
| [8] | 洪飞, 贾丰莲, 刘易, 吴燕, 杨茹薇, 孙慧, 李广悦. 新疆马铃薯黑痣病病原菌的分离及定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1766-1771. |
| [9] | 刘易, 李江涛, 江应红, 杨茹薇, 孙慧, 吴燕. NaCl胁迫下外源亚精胺对马铃薯幼苗生理特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 336-344. |
| [10] | 欧源, 罗莎莎, 王如月, 孙雅丽, 虎海防. 盐胁迫对美国黑核桃幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 393-401. |
| [11] | 刘会芳, 王强, 韩宏伟, 庄红梅, 王浩, 常亚南. 盐、碱及复合盐碱胁迫对番茄幼苗光合特性及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2658-2666. |
| [12] | 杨茹薇, 刘易, 古丽米拉·热合木土拉, 孙慧, 江应红. 马铃薯病毒病实时荧光定量PCR检测技术[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2484-2490. |
| [13] | 徐李娟, 陈勇, 王则玉, 王博, 艾尼江·尔斯满, 郭瑞, 李克梅, 宋素琴. 新疆拜城县马铃薯疮痂病病原菌的分离鉴定及生物学特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2258-2265. |
| [14] | 来汉林, 沈煜洋, 陈利, 杨红, 李月, 雷钧杰, 李广阔, 高海峰. 温度和盐胁迫对播娘蒿种子萌发特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1326-1334. |
| [15] | 王兴州, 时晓磊, 张恒, 曲可佳, 耿洪伟, 丁孙磊, 张金波, 严勇亮. 引进春小麦品种萌发期耐盐性鉴定及评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1353-1362. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||