

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (1): 1-10.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.01.001
• 作物遗传育种 · 耕作栽培 · 种质资源 · 生理生化 • 上一篇 下一篇
张红霞1( ), 雍晓宇1, 何飞1, 夏军1, 李慧琴2, 王潭刚2(
), 雍晓宇1, 何飞1, 夏军1, 李慧琴2, 王潭刚2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-23
出版日期:2023-01-20
发布日期:2023-03-07
通信作者:
王潭刚(1984-),男,甘肃平凉人,副研究员,研究方向为棉花栽培,(E-mail)381762798@qq.com作者简介:张红霞(1995-),女,甘肃通渭人,硕士研究生,研究方向为作物高产栽培, (E-mail) 2635172750@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Hongxia1( ), YONG Xiaoyu1, HE Fei1, XIA Jun1, LI Huiqin2, WANG Tangang2(
), YONG Xiaoyu1, HE Fei1, XIA Jun1, LI Huiqin2, WANG Tangang2( )
)
Received:2022-04-23
Published:2023-01-20
Online:2023-03-07
Correspondence author:
WANG Tangang (1984 -), male, associate researcher, research direction is cotton cultivation technology, (E-mail)381762798@qq.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究不同浓度盐胁迫对早熟棉花种子萌发特性及关键酶活性的影响。【方法】以新陆早45号和新陆早65号为试材,设置不同浓度的盐胁迫处理,测定棉种萌发过程中种胚相对含水量、发芽势、发芽率以及脯氨酸(Pro)、可溶性蛋白(SP)、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)、丙二醛(MDA)含量的变化。【结果】随盐胁迫处理时间的延长,0~15 h内相对含水量持续上升,15~60 h逐渐平缓,63 h时相对含水量有上升趋势。新陆早45号种子的相对含水量在不同盐浓度下表现为:0.2%比对照的相对含水量高,0.8%相对含水量最低;新陆早65号的不同浓度处理间无明显差异。吸水速率新陆早65号>新陆早45号,且相对含水量新陆早65号>新陆早45号;随盐浓度的增加,2个品种的发芽势均有下降;处理前60 h在0.2%、0.4%、0.6%和0.8%盐浓度处理下,新陆早65号的平均超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)活性较新陆早45号分别高出15%、19%、2%和13%,相同NaCl浓度胁迫的80 h内,新陆早65号过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性、游离脯氨酸(Pro)含量在0.2%、0.4%、0.6%和0.8%NaCl浓度下均比新陆早45号高,且均呈先增后减的趋势,可溶性蛋白(SP)呈增加趋势;相同浓度NaCl胁迫下,新陆早45号种子丙二醛含量均高于新陆早65号,且随NaCl浓度的增加丙二醛含量逐渐增加。新陆早45号和新陆早65号的SOD、CAT的载荷值较高。耐盐性新陆早65号>新陆早45号。【结论】盐胁迫下棉种可通过提高种胚超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化氢酶(CAT)酶活性和降低丙二醛(MDA)含量来提高耐盐性,减轻盐胁迫对其出苗的伤害。
中图分类号:
张红霞, 雍晓宇, 何飞, 夏军, 李慧琴, 王潭刚. 早熟陆地棉种萌发中种胚保护性酶活性对盐胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(1): 1-10.
ZHANG Hongxia, YONG Xiaoyu, HE Fei, XIA Jun, LI Huiqin, WANG Tangang. Effects of Different Concentrations of NaCl Stress on Seed Embryo Protective Enzyme Activity during Cotton Germination[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(1): 1-10.
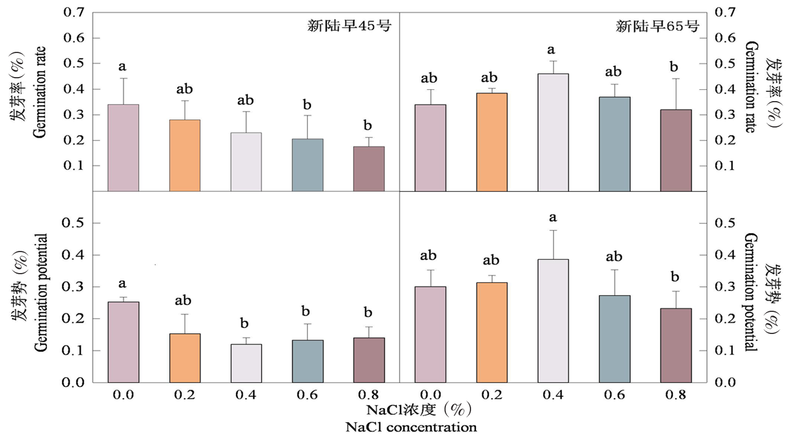
图2 不同NaCl胁迫下2棉花品种的相对发芽率、相对发芽势变化
Fig.2 Comparison between the relative germination rate and the relative germination potential of the two cotton varieties under different concentrations of NaCl stress
| NaCl浓度 NaCl concen tration (%) | 盐害指数 Salt damage index | 盐害级别 Salt damage level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新陆 早45号 Xinlu zao 45 | 新陆 早65号 Xinlu zao 65 | 新陆 早45号 Xinlu zao 45 | 新陆 早65号 Xinlu zao 65 | |
| 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 | 0.26 0.40 0.46 0.63 | 0 0 0 0.3 | 2 2 3 4 | 无盐害 无盐害 无盐害 2 |
表1 不同棉花品种盐害指数和盐害级别
Table 1 Salt damage index and salt harm level of different cotton varieties
| NaCl浓度 NaCl concen tration (%) | 盐害指数 Salt damage index | 盐害级别 Salt damage level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新陆 早45号 Xinlu zao 45 | 新陆 早65号 Xinlu zao 65 | 新陆 早45号 Xinlu zao 45 | 新陆 早65号 Xinlu zao 65 | |
| 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 | 0.26 0.40 0.46 0.63 | 0 0 0 0.3 | 2 2 3 4 | 无盐害 无盐害 无盐害 2 |
| 棉花品种 Cotton varieties | 新陆早45号 Xinluzao 45 | 新陆早65号 Xinluzao 65 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参数 Paramter | 提取成分 Extracted component | 提取成分 Extracted component | ||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| SP | -0.559 57 | 0.086 63 | -0.512 07 | 0.318 25 |
| Pro | -0.501 11 | 0.439 58 | 0.411 08 | -0.260 71 |
| SOD | 0.339 83 | 0.595 14 | 0.431 93 | 0.602 95 |
| CAT | 0.310 07 | 0.613 75 | 0.456 78 | 0.472 09 |
| MDA | 0.473 43 | -0.261 5 | -0.416 64 | 0.494 29 |
表2 参数矩阵
Table 2 Parameter matrix analysis
| 棉花品种 Cotton varieties | 新陆早45号 Xinluzao 45 | 新陆早65号 Xinluzao 65 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 参数 Paramter | 提取成分 Extracted component | 提取成分 Extracted component | ||
| PC1 | PC2 | PC1 | PC2 | |
| SP | -0.559 57 | 0.086 63 | -0.512 07 | 0.318 25 |
| Pro | -0.501 11 | 0.439 58 | 0.411 08 | -0.260 71 |
| SOD | 0.339 83 | 0.595 14 | 0.431 93 | 0.602 95 |
| CAT | 0.310 07 | 0.613 75 | 0.456 78 | 0.472 09 |
| MDA | 0.473 43 | -0.261 5 | -0.416 64 | 0.494 29 |
| [1] |
Zhu J K. Plant salt tolerance[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2001, 6(2):66-71.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | 刘国强, 鲁黎明, 刘金定, 等. 棉花品种资源耐盐性鉴定研究[J]. 作物品种资源, 1993, (2): 21-22. |
| LIU Guoqiang, LU Liming, LIU Jinding, et al. Research on the identification of salt tolerance of cotton variety resources[J]. Crop Variety Resources, 1993,(2): 21-22. | |
| [3] |
肖爽, 韩雨辰, 号宇然, 等. 聚乙二醇引发对盐胁迫下棉种萌发及生理特性的影响[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35 (1):202-210.
DOI |
| XIAO Shuang, HAN Yuchen, HAO Yuran, et al. Effects of polyethylene glycol priming on Germination and physiological characteristics of cottonseeds under salt stress[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(1): 202-210. | |
| [4] | 新疆维吾尔自治区农业厅. 新疆土壤[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996:304-336. |
| Department of Agriculture of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Xinjiang Soil[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996: 304-336. | |
| [5] | 田长彦, 周宏飞, 刘国庆, 等. 21世纪新疆土壤盐渍化调控与农业持续发展研究建议[J]. 干旱区地理, 2000, 23(2):177-181. |
| TIAN Changyan, ZHOU Hongfei, LIU Guoqin, et al. The Proposal on Control of Soil Salinizing and Agricultural Sustaining Developmentn in 21st Century In Xinjiang[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2000, 23(2):177-181. | |
| [6] |
Greenway H, Munns R A. Mechanisms of Salt Tolerance in Nonhalophytes[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology, 1980, 31(4):149-190.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Koyro H W. Effect of salinity on growth, photosynthesis, water relations and solute composition of the potential cash crop halophyte Plantago coronopus (L.)[J]. Environmental & Experimental Botany, 2006, 56(2):136-146. |
| [8] | 丁顺华, 邱念伟, 杨洪兵, 等. 小麦耐盐性生理指标的选择[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2001, 37(2):98-102. |
| DING Shunhua, QIU Nianwei, YANG Hongbing, et al. Selection of physiological indicators for salt tolerance in wheat[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2001, 37(2): 98-102. | |
| [9] | 周桃华. NaCI胁迫对棉子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 中国棉花, 1995, 22(4): 11-12. |
| ZHOU Taohua. The effect of NaCI stress on cottonseed germination and seedling growth[J]. China Cotton, 1995, 22(4): 11-12. | |
| [10] | 柯玉琴, 潘廷国. 鉴定水稻发芽种子成苗过程中耐盐性的NaCl琼脂固定法[J]. 植物生理学报, 2001, 37(5):432-434. |
| KE Yuqin, PAN Tingguo. A Identifying Method for Salt-Tolerance in Germinating Seeds and Seedling of Rice Using NaCl Agar Fixation[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2001, 37(5):432-434. | |
| [11] | 白灯莎·买买提艾力, 李寒暝, 张少民, 等. 不同棉花品种种子萌发阶段耐盐性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(1):18-24. |
| Baidengsha Maimaitiaili, LI Hanming, ZHANG Shaomin, et al. Assesment on the Salt Resistance of Seven Cotton Varieties(Gossypium hirsutum L.)During Germination Stage[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 48(1):18-24. | |
| [12] |
Bowler C, Slooten L, Vandenbranden S, et al. Manganese superoxide dismutase can reduce cellular damage mediated by oxygen radicals in transgenic plants.[J]. Embo Journal, 1991, 10(7):1723-1732.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | 蔡天革, 王鹏, 唐凤德, 等. 盐胁迫对燕麦种子萌发和幼苗抗氧化酶的影响[J]. 辽宁大学学报, 2016, 43(1): 75-78. |
| CAI Tiange, WANG Peng, TAN Fengdei, et al. The Effects of the Salt Stresses on Germination of Oat Seeds and Anti-oxidation Enzyme of their Seedling Growth[J]. Journal of Liaoning University, 2016, 43(1): 75-78. | |
| [14] | 史树德. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京, 中国林业出版社, 2011:74-75. |
| SHI S D. Experimental Guidance of Plant Physiology[M]. Beijing, China Forestry Press, 2011: 74-75. | |
| [15] | 李玲. 植物生理学模块实验指导[M]. 北京, 农业出版社, 2009:97-98. |
| LI Ling. Experimental guidance of plant physiology module[M]. Beijing, Agricultural Press, 2009: 97-98. | |
| [16] | 李合生. 植物生理生化实验原理和技术[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006:164-167 |
| LI Hesheng. Experimental principles and techniques of plant physiology and biochemistry[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006: 164-167 | |
| [17] |
陈玉珍, 李凤兰. 低温锻炼对绵头雪莲花组织培养苗抗寒性及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 植物生理与分子生物学学报, 2005, 31(4): 437-440.
PMID |
|
CHEN Yuzhen, LI Fenglan. Effects of Cold-hardening on Freezing Tolerance and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Plantlets of Saussurea laniceps Hand.-Mazz.[J]. Journal of Plant Physiology and Molecular Biology, 2005, 31(4): 437-440.
PMID |
|
| [18] | 方婧雯, 邬燕, 刘志华, 等. 盐胁迫对罗布麻种子萌发及生理特性的影响[J]. 作物杂志, 2018,(4): 167-174. |
| FANG Jingwen, WU Yan, LIU Zhihua, et al. Effects of salt stress on seed germination and physiological characteristics of Apocynum venetum[J]. Crops, 2018,(4): 167-174. | |
| [19] | 孙小芳, 郑青松, 刘友良, 等. NaCl胁迫对棉花种子萌发和幼苗生长的伤害植物[J]. 资源与环境学报, 2000, 9(3): 22-25. |
| SUN Xiaofang, ZHENG Qinsong, LIU Youliang, et al. Salinity injury to germination and growth of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) at emergence and seedling stages[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2000, 9(3): 22-25. | |
| [20] | 朱毅, 范希峰, 刘吉利, 等. 盐胁迫对柳枝稷种子萌发的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2014, 36(4):38-43. |
| ZHU Yi, FAN Xifeng, LIU Jili, et al. Effects of salt stress on Switchgrass Germination[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2014, 36(4): 38-43. | |
| [21] |
张国伟, 路海玲, 张雷陈, 等. 棉花萌发期和苗期耐盐性评价及耐盐指标筛选[J]. 应用生态学报, 2011, 22(8): 2045-2053.
PMID |
|
ZANG Guowei, LU Hailing, ZHANG Leichen, et al. Salt tolerance evaluation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) at its germinating and seedling stages and selection of related indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2011, 22(8): 2045-2053.
PMID |
|
| [22] |
Khan M N, Siddiqui M H, Mohammad F, et al. Interactive role of nitric oxide and calcium chloride in enhancing tolerance to salt stress[J]. Nitric Oxide, 2012, 27(4):210-218.
DOI PMID |
| [23] | 李彦, 张英鹏, 孙明, 等. 盐分胁迫对植物的影响及植物耐盐机理研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008,(1):258-265. |
| LI Yan, ZHANG Yingpeng, SUN Ming, et al. Effects of salt stress on plants and research progress of salt tolerance mechanism of plants[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008,(1):258-265. | |
| [24] | 吕有军, 等. 盐胁迫下棉花生长发育特性与耐盐机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2005. |
| LV Youjun. Cotton growth and development characteristics and salt tolerance mechanism under salt stress[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2005. | |
| [25] | 陈立松, 刘星辉, 等. 果树逆境生理[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2003: 261-267. |
| CHEN Lisong, LIU Xinhui, et al. Fruit Tree Adversity Physiology[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2003: 261-267. | |
| [26] | 郭艳超, 孙昌禹, 王文成, 等. NaCl胁迫对芙蓉葵种子萌发和种苗生长的影响, 西北农业学报, 2012, 21(3): 158-163. |
| GUO Yanchao, SUN Changyu, WANG Wencheng, et al. Effects of NaCl Stress on Seed Germination and Plants Growth of Hibiscus moscheutos[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2012, 21(3): 158-163. | |
| [27] | 郇树乾, 刘国道, 张绪元, 等. NaCl胁迫对刚果臂形草种子萌发及幼苗生理效应的研究[J]. 中国草地, 2004, 26(6): 45-49. |
| XUN Suqian, LIU Guodao, ZHANG Wuxuan, et al. Physiological Responses to the NaCl Stress in the Stage of Seed Germination and Seedlings of Bachiaria ruziziensis[J]. Grassland of China, 2004, 26(6): 45-49. | |
| [28] |
Bowler C, Slooten L, Vandenbranden S, et al. Manganese superoxide dismutase can reduce cellular damage mediated by oxygen radicals in transgenic plants[J]. Embo Journal, 1991, 10(7):1723-1732.
DOI PMID |
| [29] | 史宝胜, 刘冬云, 陈书明, 等. 盐胁迫对盐蒿种子萌发及保护酶活性的影响[J]. 河北林果研究, 2007, 22(1): 7-10. |
| SHI Baosheng, LIU Dongyun, CHEN Shuming, et al. Germination effect of Artemisia halodendron under salt stress[J]. Hebei Journal of Forestry and Orchard Research, 2007, 22(1): 7-10. | |
| [30] | 闫永庆, 朱虹, 刘兴亮, 等. 盐胁迫对紫穗槐生长发育及生理特性的影响[J]. 东北农业大学学报, 2008, 39(12): 31-35. |
| YAN Yongqin, ZHU Hong, LIU Xinliang, et al. Effects of salt stress on the growth, development and physiological characteristics of Amorpha pseudoacacia[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural University, 2008, 39(12): 31-35. | |
| [31] | 於丽华, 博士学位论文, NaCl胁迫下甜菜的生理响应及其耐盐机理研究[D] 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2015. |
| YU Lihua. The physiological response of sugar beet and its salt tolerance mechanism under NaCl stress[D]. Shenyan: Shenyan Agricultural University, 2015. | |
| [32] | 张海艳, 赵延明. NaCl胁迫对糯玉米种子发芽和幼苗生长的影响[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2010, 46(3): 291-293. |
| ZHANG Haiyan, ZHAO Yanming. Effects of NaCl stress on seed germination and seedling growth of waxy corn[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2010, 46(3): 291-293. |
| [1] | 巩雪花, 王小武, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 乔小燕, 叶晓琴, 郭文超, 丁新华. 新疆绿洲灌区玉米田杂草种子库及环境因子对杂草种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 49-59. |
| [2] | 张帆, 陈晓露, 王洁, 侯献飞, 贾东海, 顾元国, 苗昊翠, 李强. 混合盐碱胁迫对花生种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2168-2182. |
| [3] | 董志多, 徐菲, 付秋萍, 黄建, 祁通, 孟阿静, 付彦博, 开赛尔·库尔班. 不同类型盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [4] | 候丽丽, 王伟, 崔新菊, 周大伟. 有机无机肥配施对冬小麦产量和土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1845-1852. |
| [5] | 奚瑞, 陈怡佳, 李宁, 余庆辉, 王强, 秦勇. 外源2, 4-表芸苔素内酯对盐胁迫下不同盐敏感型番茄种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1983-1992. |
| [6] | 刘慧杰, 王俊豪, 龚照龙, 梁亚军, 王俊铎, 李雪源, 郑巨云, 王冀川. 197份陆地棉品种萌发期耐盐性鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1574-1581. |
| [7] | 强立栋, 冯宽, 朱长安, 赵云, 李召锋, 李卫华. 花后高温胁迫对小麦籽粒萌发及相关酶活性影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1345-1351. |
| [8] | 杨君妍, 闫淼, 吴海波, 杨文莉, 王豪杰, 毛建才, 翟文强, 李俊华. 高温对不同厚皮甜瓜品种种子萌发的影响及其耐热性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1386-1396. |
| [9] | 张宏芝, 王立红, 时佳, 孔德鹏, 王重, 高新, 李剑峰, 王春生, 夏建强, 樊哲儒, 张跃强. 土壤水分对不同抗旱性春小麦品种叶片保护性酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1041-1047. |
| [10] | 李肖, 陈永成, 黄嵘峥, 许平珠, 张凡凡, 马春晖. 向日葵副产物中优势乳酸菌和纤维素分解菌的生理生化特征分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 607-614. |
| [11] | 巴哈依丁·吾甫尔, 阿布来克·尼牙孜, 胡西旦·买买提, 吕小龙, 王浩淼, 马会勤. 60Co-γ射线对不同无花果品种一年生枝条的辐射效应分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 373-381. |
| [12] | 欧源, 罗莎莎, 王如月, 孙雅丽, 虎海防. 盐胁迫对美国黑核桃幼苗生长和生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 393-401. |
| [13] | 周小云, 张军高, 梁晶, 龚静云, 周广威, 张少民, 雷斌. 低温和水分胁迫条件下萎锈灵对棉花种子萌发及幼苗生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 3051-3060. |
| [14] | 刘会芳, 王强, 韩宏伟, 庄红梅, 王浩, 常亚南. 盐、碱及复合盐碱胁迫对番茄幼苗光合特性及抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2658-2666. |
| [15] | 廖彩云, 马贵, 周炎炎, 丁家富, 周悦, 毕可心, 孙蓉, 李有花. 微塑料作用下锌对玉米种子萌发与生长影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2713-2721. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||