

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (3): 615-622.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.03.011
收稿日期:2023-07-19
出版日期:2024-03-20
发布日期:2024-04-19
通信作者:
于辉(1976- ),男,黑龙江齐齐哈尔人,副教授,硕士,西瓜种植资源及育种,(E-mail)yh1166@sina.com作者简介:张伟(1984- ),男,内蒙古包头人,讲师,硕士,研究方向园艺植物遗传育种,(E-mail)weizhang880310@126.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Wei1( ), YANG Guohui2, YU Hui1(
), YANG Guohui2, YU Hui1( )
)
Received:2023-07-19
Published:2024-03-20
Online:2024-04-19
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 研究外源2,4-表油菜素内酯(2,4-epibrassinolide,EBR)对干旱胁迫条件下西瓜幼苗生长以及相关基因表达的影响,为西瓜抗旱研究提供理论基础。【方法】 以西瓜品种齐红1号为材料,利用15%聚乙二醇(PEG6000)模拟干旱胁迫,设置3个处理CK(清水)、PEG和PEG+EBR,其中EBR的浓度为0.01 mg/L。检测不同处理后西瓜幼苗的生物量、光合作用指标、叶绿素含量、抗氧化酶活性以及相关基因的表达量。【结果】 喷施外源EBR可以缓解干旱胁迫对西瓜幼苗生长发育的抑制和损害程度,还可以通过增加应答基因的表达量,激活EBR信号转导途径,提高西瓜幼苗的耐旱性。喷施外源EBR西瓜幼苗株高、根长、地上鲜重、地下鲜重较PEG胁迫分别增加了2.41%、36.76%、1.88%和3.42%;而且也增强光合作用各项指标,抗氧化酶(POD和SOD)活性。油菜素内酯(BRs)信号转导途径关键应答基因BRI1、BIN2 、BES1 和DWF4的表达量也呈现不同程度变化,抗旱相关基因CDSP32和MYB101的表达量也有显著变化。【结论】 外源EBR能够有效缓解干旱胁迫对西瓜幼苗造成的损害,从而提高西瓜幼苗的抗旱性。
中图分类号:
张伟, 杨国慧, 于辉. 2,4-表油菜素内酯对干旱胁迫下西瓜幼苗生长及相关基因表达的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 615-622.
ZHANG Wei, YANG Guohui, YU Hui. Effects of 2,4-epibrassinolide on growth and related genes expression of watermelon seedlings under drought Stress[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 615-622.
| 西瓜基因 Watermelon gene | 同源基因名称 Homologous gene name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cla97C05G101410 | BRI1 | F:ATCTCCTCTCCCACCTTCCT R:CTTGCTCGGTAATCTCGCAC | BRI1激酶抑制剂 |
| Cla97C07G136530 | BIN2 | F:GGTTGCCATTGGTGTTGTCT R:CCGACTGACCAAAGCTAACG | DNA结合蛋白 |
| Cla97C08G158860 | BES1 | F:GACCTCAGCTCCATACTCCC R:GGTCAGCAGGTTTCACAAGG | BR信号转导 |
| Cla97C09G163730 | DWF4 | F:AATTGTACCCGCGTATTGGC R:TACCCTGCTTCCCACCAAAA | 油菜素类固醇生物合成 |
| Cla97C08G157590 | CDSP32 | F:TCCGACGGTGATAAAGCTGT R:TCTCCTTTACCGGACCCAAC | 硫氧还蛋白 |
| Cla97C10G189540 | MYB101 | F:ACCACGCCGCAGTTAATTTT R:CTGGGTTGATGAAGGGAGGT | MYB相关转录因子 |
| β-Actin | F:GTCGTACAACAGGTATTGTG R:AAGGTCCAGACGGAGGATAG | 内参基因 |
表1 西瓜抗旱基因相关信息
Tab.1 Information on drought resistance genes in watermelon
| 西瓜基因 Watermelon gene | 同源基因名称 Homologous gene name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') | 基因功能 Gene function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cla97C05G101410 | BRI1 | F:ATCTCCTCTCCCACCTTCCT R:CTTGCTCGGTAATCTCGCAC | BRI1激酶抑制剂 |
| Cla97C07G136530 | BIN2 | F:GGTTGCCATTGGTGTTGTCT R:CCGACTGACCAAAGCTAACG | DNA结合蛋白 |
| Cla97C08G158860 | BES1 | F:GACCTCAGCTCCATACTCCC R:GGTCAGCAGGTTTCACAAGG | BR信号转导 |
| Cla97C09G163730 | DWF4 | F:AATTGTACCCGCGTATTGGC R:TACCCTGCTTCCCACCAAAA | 油菜素类固醇生物合成 |
| Cla97C08G157590 | CDSP32 | F:TCCGACGGTGATAAAGCTGT R:TCTCCTTTACCGGACCCAAC | 硫氧还蛋白 |
| Cla97C10G189540 | MYB101 | F:ACCACGCCGCAGTTAATTTT R:CTGGGTTGATGAAGGGAGGT | MYB相关转录因子 |
| β-Actin | F:GTCGTACAACAGGTATTGTG R:AAGGTCCAGACGGAGGATAG | 内参基因 |
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 地上鲜重 Fresh weight above ground (mg) | 地下鲜重 Fresh weigh underground (mg) | 地上干重 Dry weight above ground (mg) | 地下干重 Dry weight underground (mg) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.67±0.10c | 16.49±0.07c | 8.55±0.02b | 3.64±0.17b | 3.52±0.06b | 0.34±0.01b | 0.09±0.04a |
| PEG | 18.49±0.05a | 11.27±0.03a | 7.27±0.03a | 3.02±0.02a | 2.78±0.09a | 0.26±0.01a | 0.10±0.03b |
| PEG+EBR | 18.94±0.06b | 15.41±0.22b | 7.40±0.14a | 3.12±0.02a | 2.73±0.02a | 0.28±0.01a | 0.10±0.01b |
表2 不同外源EBR干旱胁迫下西瓜幼苗生物量变化
Tab.2 Effects of exogenous EBR on the biomass of watermelon seedlings under drought stress
| 处理 Treatment | 株高 Plant height (cm) | 根长 Root length (cm) | 地上鲜重 Fresh weight above ground (mg) | 地下鲜重 Fresh weigh underground (mg) | 地上干重 Dry weight above ground (mg) | 地下干重 Dry weight underground (mg) | 根冠比 Root-shoot ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 19.67±0.10c | 16.49±0.07c | 8.55±0.02b | 3.64±0.17b | 3.52±0.06b | 0.34±0.01b | 0.09±0.04a |
| PEG | 18.49±0.05a | 11.27±0.03a | 7.27±0.03a | 3.02±0.02a | 2.78±0.09a | 0.26±0.01a | 0.10±0.03b |
| PEG+EBR | 18.94±0.06b | 15.41±0.22b | 7.40±0.14a | 3.12±0.02a | 2.73±0.02a | 0.28±0.01a | 0.10±0.01b |
| 处理 Treatment | 净光合作用速率Pn Photosynthetic rate (μmol CO2/(m2·s)) | 气孔导度Gs Conductance to H2O (mmol/(m2·s)) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci Intercellular CO2 concentration(μL/L) | 蒸腾速率Tr Transpiration (mmol H2O/(m2·s)) | 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.80±0.36c | 0.62±0.02c | 458.00±8.18a | 6.59±0.17b | 18.23±0.12a |
| PEG | 13.03±0.21a | 0.27±0.03a | 504.00±7.21c | 4.96±0.18a | 21.50±0.06b |
| PEG+EBR | 18.90±0.20b | 0.34±0.01b | 486.00±9.17b | 5.05±0.05a | 20.58±0.34b |
表3 不同外源EBR 干旱胁迫下西瓜幼苗光合作用指标变化
Tab.3 Effects of exogenous EBR on photosynthetic indexes of watermelon seedlings under drought stress
| 处理 Treatment | 净光合作用速率Pn Photosynthetic rate (μmol CO2/(m2·s)) | 气孔导度Gs Conductance to H2O (mmol/(m2·s)) | 胞间CO2浓度Ci Intercellular CO2 concentration(μL/L) | 蒸腾速率Tr Transpiration (mmol H2O/(m2·s)) | 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 20.80±0.36c | 0.62±0.02c | 458.00±8.18a | 6.59±0.17b | 18.23±0.12a |
| PEG | 13.03±0.21a | 0.27±0.03a | 504.00±7.21c | 4.96±0.18a | 21.50±0.06b |
| PEG+EBR | 18.90±0.20b | 0.34±0.01b | 486.00±9.17b | 5.05±0.05a | 20.58±0.34b |
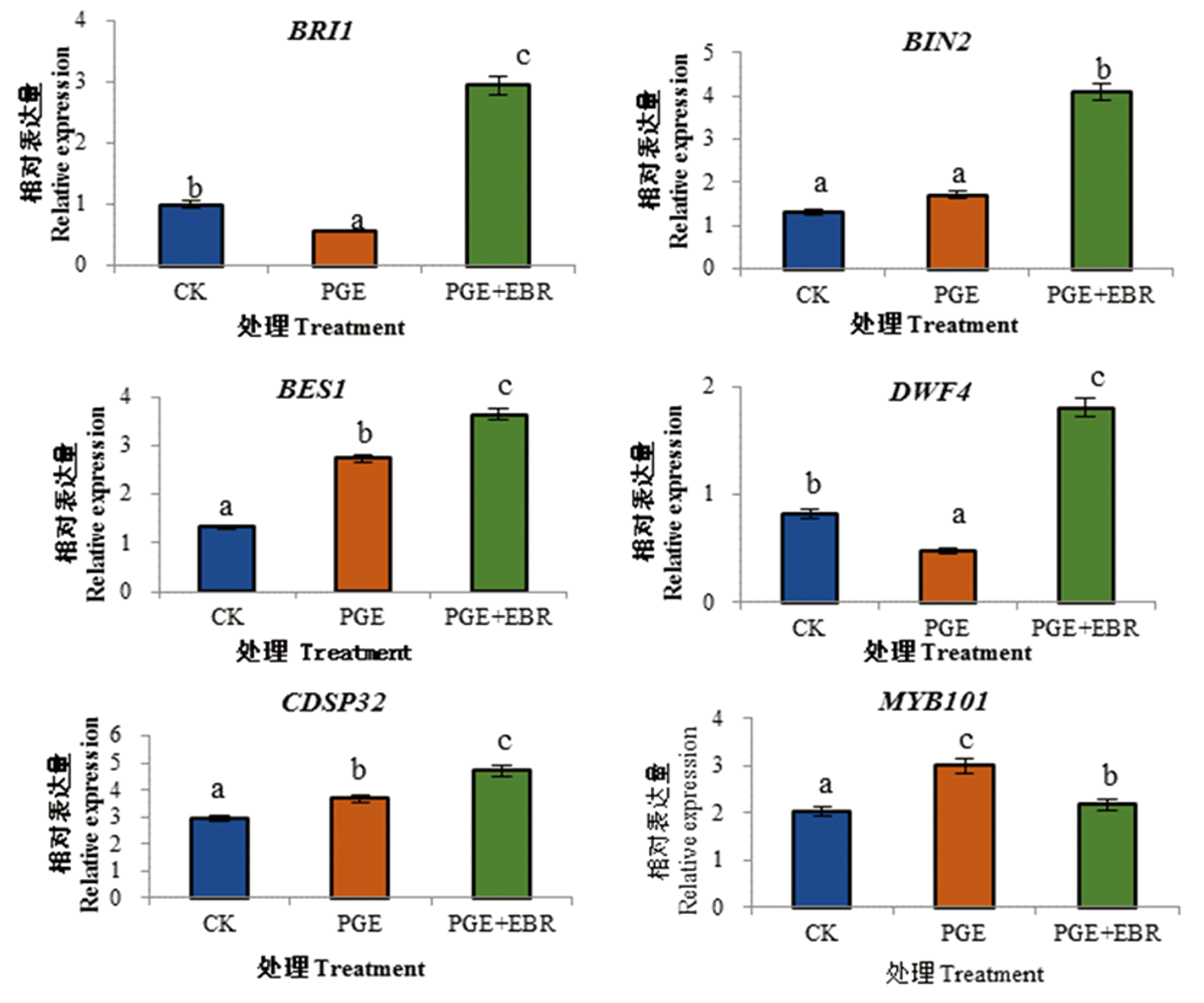
图2 不同外源EBR干旱胁迫下西瓜苗期抗旱相关基因表达量变化
Fig.2 Effects of exogenous EBR on the expression of drought resistance related genes of watermelon seedlings under drought stress
| [1] |
Chandra P, Wunnava A, Verma P, et al. Strategies to mitigate the adverse effect of drought stress on crop plants—influences of soil bacteria: a Review[J]. Pedosphere, 2021, 31(3): 496-509.
DOI URL |
| [2] | 何亚萍, 王春霞, 闫星, 等. 9份西瓜种质苗期抗旱性鉴定[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2020, 33(12): 14-21. |
| HE Yaping, WANG Chunxia, YAN Xing, et al. Screening of drought resistance of nine watermelon germplasm at seedling stage[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2020, 33(12): 14-21. | |
| [3] | 贾斌, 高龙飞, 张卫华, 等. 西瓜苗期干旱胁迫下的代谢组学分析[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(21):7161-7170. |
| JIA Bing, GAO Longfei, ZHANG Weihua, et al. Metabolomics analysis of watermelon seedlings under drought stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(21):7161-7170. | |
| [4] |
Grove M D, Spencer G F, Rohwedder W K, et al. Brassinolide,a plant growth-promoting steroid isolated from Brassica napus pollen[J]. Nature, 1979, 281(5728): 216-217.
DOI |
| [5] | Sreeramulu S, Mostizky Y, Sunitha S, et al. BSKs are partially redundant positive regulators of brassinosteroid signaling in Arabidopsis.[J]. Plant Journal for Cell & Molecular Biology, 2013, 74(6): 905-919. |
| [6] |
Sharma I, Bhardwaj R, Pati P K. Exogenous application of 28-homobrassinolide modulates the dynamics of salt and pesticides induced stress responses in an elite rice variety pusa basmati-1[J]. Journal of Plant Growth Regulation, 2015, 34(3): 509-518.
DOI URL |
| [7] | Li J, Yang P, Kang J G, et al. Transcriptome analysis of pepper (capsicum annuum) revealed a role of 24-epibrassinolide in response to chilling[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2016, 29(7):1281. |
| [8] | 李启程, 余学军. 外源油菜素内酯对毛竹实生苗生理特性的影响[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2021, 38(1): 120-127. |
| LI Qicheng, YU Xuejun. Effects of exogenous BR on physiological characteristics of phyllostachys edulis seedlings[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A&F University, 2021, 38(1): 120-127. | |
| [9] | 胡勇军, 韩德复, 郭继勋. 油菜素内酯对羊草人工草地产量及其品质的影响[J]. 长春师范学院学报, 2007, 26(4): 61-64. |
| HU Yongjun, HAN Defu, GUO Jixun. Effect of Brassinolide (BR) on the quality and the yield of leymus chinensis growing in the sown grassland[J]. Journal of Changchun Normal University, 2007, 26(4): 61-64. | |
| [10] | 丁丹阳, 张璐翔, 朱智威, 等. 叶面喷施2,4-表油菜素内酯对烟草抗旱性的影响[J]. 中国烟草科学, 2018, 39(4): 50-57. |
| DING Danyang, ZHANG Luxiang, ZHU Zhiwei, et al. Effect of leaf spray 2,4-epibrassinolide on drought resistance of tobacco[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2018, 39(4): 50-57. | |
| [11] |
雷阳, 乔宁, 白扬, 等. 表油菜素内酯对重度镉胁迫下辣椒幼苗生理特性及抗逆基因的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2021, 36(5): 99-106.
DOI |
| LEI Yang, QIAO Ning, BAI Yang, et al. Effects of Epibrassinolide on Physiological Characteristics and Resistance Genes of Pepper Seedlings under Severe Cadmium Stress[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2021, 36(5): 99-106. | |
| [12] |
Xia X J, Wang Y J, Zhou Y H, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Are Involved in Brassinosteroid-induced Stress Tolerance in Cucumber[J]. Plant Physiology, 2009, 150(2): 801-814.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Bajguz A, Hayat S. Effects of brassinosteroids on the plant responses to environmental stresses[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2009, 47(1): 1-8.
DOI PMID |
| [14] | 范小玉, 张显. 油菜素内酯对低温弱光胁迫下西瓜幼苗耐冷性的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2012,(7): 5-8. |
| FAN Xiaoyu, ZHANG Xian. The effect of brassinolide on chilling resistance of watermelon seedlings under low temperature and poor light stress[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2012,(7): 5-8. | |
| [15] |
Sakamoto T, Morinaka Y, Ohnishi T, et al. Erect leaves caused by brassinosteroid deficiency increase biomass production and grain yield in rice[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2006, 24(1): 105-109.
DOI PMID |
| [16] |
Chono M, Honda I, Zeniya H, et al. A semi dwarf phenotype of barley uzu results from a nucleotide substitution in the gene encoding a putative brassinosteriod receptor.[J]. Plant Physiology, 2003, 133(3):1209-1219.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Kir G, Ye H X, Nelissen H, et al. RNA interference knockdown of brassinosteroid insensitive1 in maize reveals novel functions for brassinosteroid signaling in controlling plant architecture[J]. Plant Physiology, 2015, 169(1):826-839.
DOI PMID |
| [18] |
Montoya T, Nomura T, Farrar K, et al. Cloning the tomato Curl3 gene highlights the putative dual role of the leucine-rich repeat receptor kinase Tbri1/sr160 in plant steroid hormone and peptide hormone signaling[J]. Plant Cell, 2002, 14(12): 3163-3176.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Kim S Y, Kim B H, Lim C J, et al. Constitutive activation of stress-inducible genes in a brassinosteroid-insensitive 1 (bri1) mutant results in higher tolerance to cold[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2010, 138(2): 191-204.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Martins S, Dohmann E M N, Cayrel A, et al. Internalization and vacuolar targeting of the brassinosteroid hormone receptor BRI1 are regulated by ubiquitination[J]. Nature Communications, 2015, 6: 6151.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Goddard R, Peraldi A, Ridout C, et al. Enhanced disease resistance caused by bri1 mutation is conserved between brachypodium distachyon and barley (hordeum Vulgare).[J]. Molecular Plant Microbe Interactions: MPMI, 2014, 27(10):1095-1106.
DOI URL |
| [22] | 王斐, 何伟, 闫海芳. 油菜素甾醇信号转导的调控机制[J]. 植物生理学报, 2013, 49(12): 1309-1318. |
| WANG Fei, HE Wei, YAN Haifang. Regulation mechanism of brassinosteroids signal transduction[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 2013, 49(12): 1309-1318. | |
| [23] |
Yang J N, Thames S, Best N B, et al. Brassinosteroids modulate meristem fate and differentiation of unique inflorescence morphology in setaria viridis[J]. Plant Cell, 2018, 30(1):48-66.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Yin Y H, Wang Z Y, Mora-Garcia S, et al. BES1 accumulates in the nucleus in response to brassinosteroids to regulate gene expression and promote stem elongation[J]. Cell, 2002, 109(2):181-191.
DOI PMID |
| [25] |
Bancoş S Nomura T, Sato T, et al. Regulation of transcript levels of the arabidopsis cytochrome p450 genes involved in brassinosteroid biosynthesis[J]. Plant Physiology, 2002, 130(1): 504-513.
DOI PMID |
| [26] |
Eymery F, Rey P. Immunocytolocalization of CDSP 32 and CDSP 34,two chloroplastic drought-induced stress proteins in solanum tuberosum plants[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 1999, 37(4): 305-312.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Broin M, Cuiné S, Eymery F, et al. The plastidic 2-cysteine peroxiredoxin is a target for a thioredoxin involved in the protection of the photosynthetic apparatus against oxidative damage[J]. The Plant Cell, 2002, 14(6): 1417-1432.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Zhang F G, Xiao X, Yan G X, et al. Association mapping of cadmium-tolerant QTLs in Brassica Napus L.and insight into their contributions to phytoremediation[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2018, 155: 420-428.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
An R, Liu X Y, Wang R, et al. The over-expression of two transcription factors,ABS5/BHLH30 and ABS7/MYB101,leads to upwardly curly leaves[J]. Plos One, 2014, 9(9):e107637.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Gong H J, Zhu X Y, Chen K M, et al. Silicon alleviates oxidative damage of wheat plants in pots under drought[J]. Plant Science, 2005, 169(2):313-321.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Broin M, Rey P. Potato plants lacking the CDSP32 plastidic thioredoxin exhibit overoxidation of the BAS1 2-cysteine peroxiredoxin and increased lipid peroxidation in thylakoids under photooxidative stress[J]. Plant Physiology, 2003, 132(3):1335-1343.
PMID |
| [32] |
Guo S G, Shu H G, Zhang H Y, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis of cultivated and wild watermelon during fruit development[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(6):e0130267.
DOI URL |
| [33] | 樊正球. 干旱环境胁迫下的植物分子适应机理及其应用研究[D]. 上海: 复旦大学, 2004. |
| FAN Zhengqiu. Study on plant molecular adaptation to drought stress and its application[D]. Shanghai: Fudan University, 2004. | |
| [34] | 赵小强, 任续伟, 张金乾, 等. 外源2,4-表油菜素内酯对干旱胁迫下青贮玉米幼苗生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 分子植物育种, 2023, 21(10),3371-3382. |
| ZHAO Xiaoqiang, REN Xuwei, ZHANG Jinqian, et al. Effects of exogenous 2,4-epibrassinolide on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of Silage Maize Seedlings under drought stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2023, 21(10),3371-3382. | |
| [35] |
Choudhary S P, Yu J Q, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, et al. Benefits of Brassinosteroid Crosstalk[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2012, 17(10):594-605.
DOI PMID |
| [36] |
Clouse D, Sasse M. Brassionsteroids: Essential Regulators of Plant Growth and Development[J]. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol, 1998, 49:427-451.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 许金亮, 谢鹏飞, 向世鹏, 等. 喷施外源EBR和H2O2对低温胁迫烟苗恢复生长期生理特性的影响[J]. 中国烟草学报, 2022, 28(3):44-51. |
| XU Jinliang, XIE Pengfei, XIANG Shipeng, et al. Effects of exogenous EBR and H2O2 on physiological characteristics of tobacco seedlings under low temperature stress[J]. Chinese Tobacco Science, 2022, 28(3):44-51. | |
| [38] |
Mahesh K, Balaraju P, Ramakrishna B, et al. Effect of brassinosteroids on germination and seedling growth of radish (Raphanus SativusL.) under PEG-6000 induced water stress[J]. American Journal of Plant Sciences, 2013, 4(12): 2305-2313.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
吴志勇, 顾红, 程大伟, 等. 油菜素内酯调控植物根系发育机制研究进展[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2022, 24(2): 68-76.
DOI |
|
WU Zhiyong, GU Hong, CHENG Dawei, et al. Advances in regulatory mechanism of brassinolide on plant root development[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology, 2022, 24(2): 68-76.
DOI |
|
| [40] | 周晔, 赵璇, 王璐, 等. 植物BZR家族基因调控非生物胁迫应答和生长发育的研究进展[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2020, 42(4): 499-511. |
|
ZHOU Ye, ZHAO Xuan, WANG Lu, et al. Research advances on plant BZR family genes in regulating abiotic stress response and development[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2020, 42(4): 499-511.
DOI |
|
| [41] |
Jia D D, Chen L G, Yin G M, et al. Brassinosteroids regulate outer ovule integument growth in part via the control of inner no outer by brassinozole-resistant family transcription factors[J]. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology, 2020, 62(8): 1093-1111.
DOI URL |
| [42] | 兰彩耘, 宋洪元. 超量表达DWF4基因对芥菜生长发育的影响[J]. 西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 43(12): 26-37. |
| LAN Caiyun, SONG Hongyuan. Effect of DWF4 Gene Overexpression on Growth and Development in Brassica juncea[J]. Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Ed.), 2021, 43(12): 26-37. |
| [1] | 曾婉盈, 耿洪伟, 程宇坤, 李思忠, 钱松廷, 高卫时, 张立明. 甜菜品系叶丛快速生长期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [2] | 阿热孜姑·吐逊, 高杰. 干旱胁迫和播种密度对洋葱小鳞茎生理特性及产出鳞茎个数的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2211-2222. |
| [3] | 鞠乐, 齐军仓, 牛银亭, 石培春, 宋瑞娇, 宋凌宇, 阴志刚, 陈培育, 强学兰. 基于RNA-seq的大麦苗期抗旱相关基因的挖掘与分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1077-1084. |
| [4] | 王凯迪, 高晨旭, 裴文锋, 杨书贤, 张文庆, 宋吉坤, 马建江, 王莉, 于霁雯, 陈全家. 陆地棉TRM基因家族的鉴定及纤维品质相关优异单倍型分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 521-536. |
| [5] | 程云霞, 谭占明, 郭玲, 李雯雯, 杜佳庚. 不同干旱胁迫对野生山杏和人工栽培山杏品种根茎叶解剖结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2684-2692. |
| [6] | 邵疆, 赵云, 胡相伟, 刘杰, 纳斯如拉·克热木, 石书兵, 冯国郡. 不同时期干旱胁迫对谷子产量及干物质积累的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2388-2395. |
| [7] | 王晓雨, 王小平, 史文宇, 刘美艳, 马健, 郭云鹏, 宋瑞欣, 王清涛. 拔节期冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累和产量对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2163-2172. |
| [8] | 向莉, 王仙, 董裕生, 郭小玲, 方伏荣, 陈智军, 马艳明, 苗雨. 外源丁酸对干旱胁迫下大麦产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2173-2181. |
| [9] | 米尔扎提·木塔力甫, 石秀楠, 柏军兵, 祖拜代·阿布都克日木, 吾勒加勒哈斯·阿扎提, 石书兵. 不同脱绒方式及PEG胁迫下对棉花种子活力及幼苗性状的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1561-1568. |
| [10] | 曲可佳, 时晓磊, 张恒, 王兴州, 耿洪伟, 丁孙磊, 张金波, 严勇亮. PEG处理下引进春小麦品种苗期抗旱性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1363-1371. |
| [11] | 邵盘霞, 赵准, 邵武奎, 郝晓燕, 高升旗, 李建平, 胡文冉, 黄全生. 玉米ZmCDPK22基因在干旱胁迫下的表达分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1372-1378. |
| [12] | 江柱, 张江辉, 白云岗, 杨鹏年, 刘洪波, 肖军, 刘旭辉. 膜下咸水滴灌水肥盐调控对棉花生长及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1389-1397. |
| [13] | 汤东, 安玉光, 程平, 李宏, 杨建军, 王凯. 天山北坡前山带典型灌木光合特性对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1531-1539. |
| [14] | 刘衍晨, 刘志刚, 白新慧, 乔鹏, 徐诚, 白慧敏, 张娟. 蛭石复混基质对辣椒育苗的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1190-1199. |
| [15] | 唐碧徽, 张俐华, 李海英, 张冲, 蒋廷浩, 赵晓钰, 蒋腾, 丁雅文, 吴盈萍, 赵全庄. 伊犁鹅和霍尔多巴吉鹅在繁殖性能、血清激素水平和基因表达量的比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1271-1280. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 58
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 122
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||