

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (4): 992-1002.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.04.025
程利华1,2( ), 杨红兰2(
), 杨红兰2( ), 马清倩1, 史莹3, 张大伟4, Alisher A. Abdullaev5, 张道远2(
), 马清倩1, 史莹3, 张大伟4, Alisher A. Abdullaev5, 张道远2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-08-19
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-05-06
通信作者:
张道远(1973-),女,安徽合肥人,研究员,研究方向为干旱区资源保育与分子生物学,(E-mail)zhangdy@ms.xjb.ac.cn;作者简介:程利华(1995-),女,河南商丘人,硕士研究生,研究方向为植物分子育种,(E-mail)chenglh5258@163.com
基金资助:
CHENG Lihua1,2( ), YANG Honglan2(
), YANG Honglan2( ), MA Qingqian1, SHI Ying3, ZHANG Dawei4, Alisher A. Abdullaev5, ZHANG Daoyuan2(
), MA Qingqian1, SHI Ying3, ZHANG Dawei4, Alisher A. Abdullaev5, ZHANG Daoyuan2( )
)
Received:2022-08-19
Published:2023-04-20
Online:2023-05-06
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Daoyuan(1973-), female, researcher. Her research interest is resource conservation and molecular biology in arid region, (E-mail)zhangdy@ms.xjb.ac.cn;Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究陆地棉种质黄萎病抗性及生理鉴定,为棉花黄萎病抗性品种选育提供数据支持。【方法】以10份国外棉花种质(Gossypium hirsutum)为材料对室内盆栽棉花接种大丽轮枝菌(Verticillium dahliae Kleb),菌液浓度为107 CFU/mL,接菌14 d后,观察并记录表型发病情况;采用荧光定量PCR检测叶片的菌含量;测定棉花叶片的木质素、过氧化氢(H2O2)、苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PAL)、丙二醛(MDA)和脯氨酸(PRO)等生理生化指标,结合相关性、主成分、隶属函数和聚类分析等方法,综合评价棉花的5个生理指标抗性。【结果】03804、A-6、04841和05189发病较轻;03804和A-6病菌DNA含量最少;在病菌侵染过程中,这些品种对PAL、PRO、木质素等的依赖程度不同,呈现出品种间差异;当棉花受到V. dahliae侵染后,MDA与H2O2呈极显著正相关,与PAL和PRO呈极显著负相关;五项抗病指标通过简化得到2个主成分,贡献率分别为64.951%,20.386%;10份材料根据棉花抗病综合指标可划分为1份抗病(03804)、5份耐病(05160、A-6、A-688、A-91、A-924)和4份易感病(04219、04841、A-1139、05189)材料。【结论】筛选出1份抗病、5份耐病和4份易感病的陆地棉种质。
中图分类号:
程利华, 杨红兰, 马清倩, 史莹, 张大伟, Alisher A. Abdullaev, 张道远. 陆地棉种质黄萎病抗性生理鉴定分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 992-1002.
CHENG Lihua, YANG Honglan, MA Qingqian, SHI Ying, ZHANG Dawei, Alisher A. Abdullaev, ZHANG Daoyuan. Physiological identification and analysis of Verticillium wilt resistance of 10 foreign cotton germplasm resources[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 992-1002.
| 编号 Code | 原名称 Original name | 来源国家 Original country |
|---|---|---|
| 03804 | Ryad 285 | 土库曼斯坦 |
| 04219 | Acal Shafter P18C | 美国 |
| 04841 | Qalla lot 361 | 澳大利亚 |
| 05160 | Lightning express | 阿塞拜疆 |
| 05189 | Acala India | 阿塞拜疆 |
| A-1139 | C-1211 | 乌兹别克斯坦 |
| A-6 | no name | 秘鲁 |
| A-688 | Chimbayski 1086 | 乌兹别克斯坦 |
| A-91 | #4F Upland | 美国 |
| A-924 | C-1472 | 乌兹别克斯坦 |
表1 棉花种质资源信息
Tab.1 Information of cotton germplasm resources
| 编号 Code | 原名称 Original name | 来源国家 Original country |
|---|---|---|
| 03804 | Ryad 285 | 土库曼斯坦 |
| 04219 | Acal Shafter P18C | 美国 |
| 04841 | Qalla lot 361 | 澳大利亚 |
| 05160 | Lightning express | 阿塞拜疆 |
| 05189 | Acala India | 阿塞拜疆 |
| A-1139 | C-1211 | 乌兹别克斯坦 |
| A-6 | no name | 秘鲁 |
| A-688 | Chimbayski 1086 | 乌兹别克斯坦 |
| A-91 | #4F Upland | 美国 |
| A-924 | C-1472 | 乌兹别克斯坦 |
| 试剂 Reagent | 使用量 Usage(μL) |
|---|---|
| SYBR PremixEx TAqTMⅡ(TliRNAseHPlus) | 10 |
| PCR-ForwArd Primer(10 μM) | 0.5 |
| PCR-Reverse Primer(10 μM) | 0.5 |
| DNA溶液 | 2.0 |
| 灭菌水 | 7.0 |
| Total | 20 |
表2 实时荧光定量PCR体系
Tab.2 Real time PCR system
| 试剂 Reagent | 使用量 Usage(μL) |
|---|---|
| SYBR PremixEx TAqTMⅡ(TliRNAseHPlus) | 10 |
| PCR-ForwArd Primer(10 μM) | 0.5 |
| PCR-Reverse Primer(10 μM) | 0.5 |
| DNA溶液 | 2.0 |
| 灭菌水 | 7.0 |
| Total | 20 |
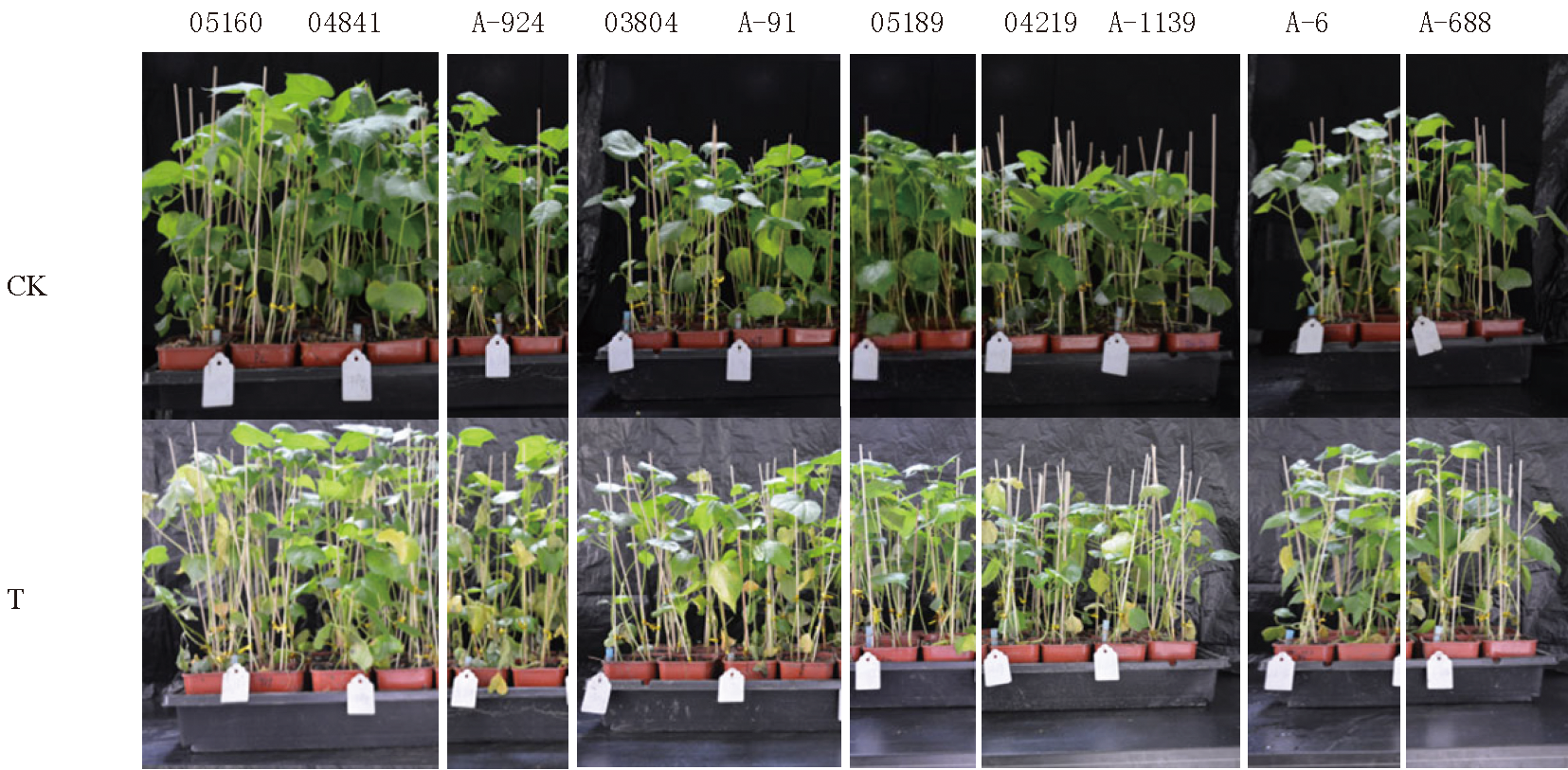

图1 棉苗在大丽轮枝菌(菌液107 个/mL)接菌后0、14 d的表型动态
Fig.1 Dynamic phenotype observation of cotton seedlings at 0 d and 14 d after inoculation with Verticillium dahliae Kleb(bacterial solution 107CFU/mL)
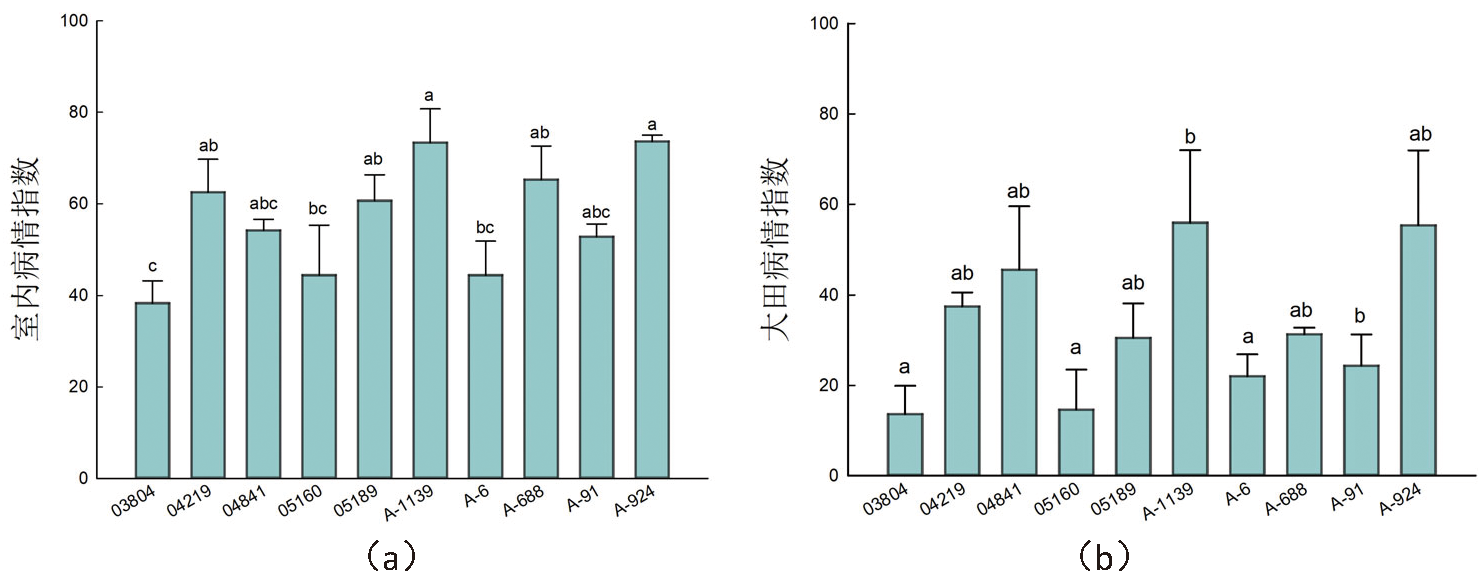
图2 室内和病田棉花黄萎病病情指数 注:(a)室内棉苗接大丽轮枝菌14 d病情指数,(b)大田病情指数;CK:对照组,T:处理组;不同字母(a,b…)代表各种质组间在0.05水平上差异显著,P<0.05,下同
Fig.2 Verticillium wilt disease index of indoor and diseased fields Note: (a) Verticillium wilt disease index of indoor cotton seedlings exposed to R. dahliae for 14 days, (b) Disease index of Daejeon;CK:the control group, T: the treatment group; Different letters (a, b...) It means that there were significant differences among all quality groups at 0.05 level, P<0.05, the same as below

图3 棉花叶片含菌量qPCR分析 注: (a) 接大丽轮枝菌菌液14d叶片含菌量qPCR分析 (b)qPCR标曲
Fig.3 Real-time PCR analysis of bacterial content in leaves of cotton Note: (a)Real-time PCR analysis of V. dahliae content in leaves after 14 days post inoculation of Verticillium dahliae Kleb (b) Real-time PCR scale-up
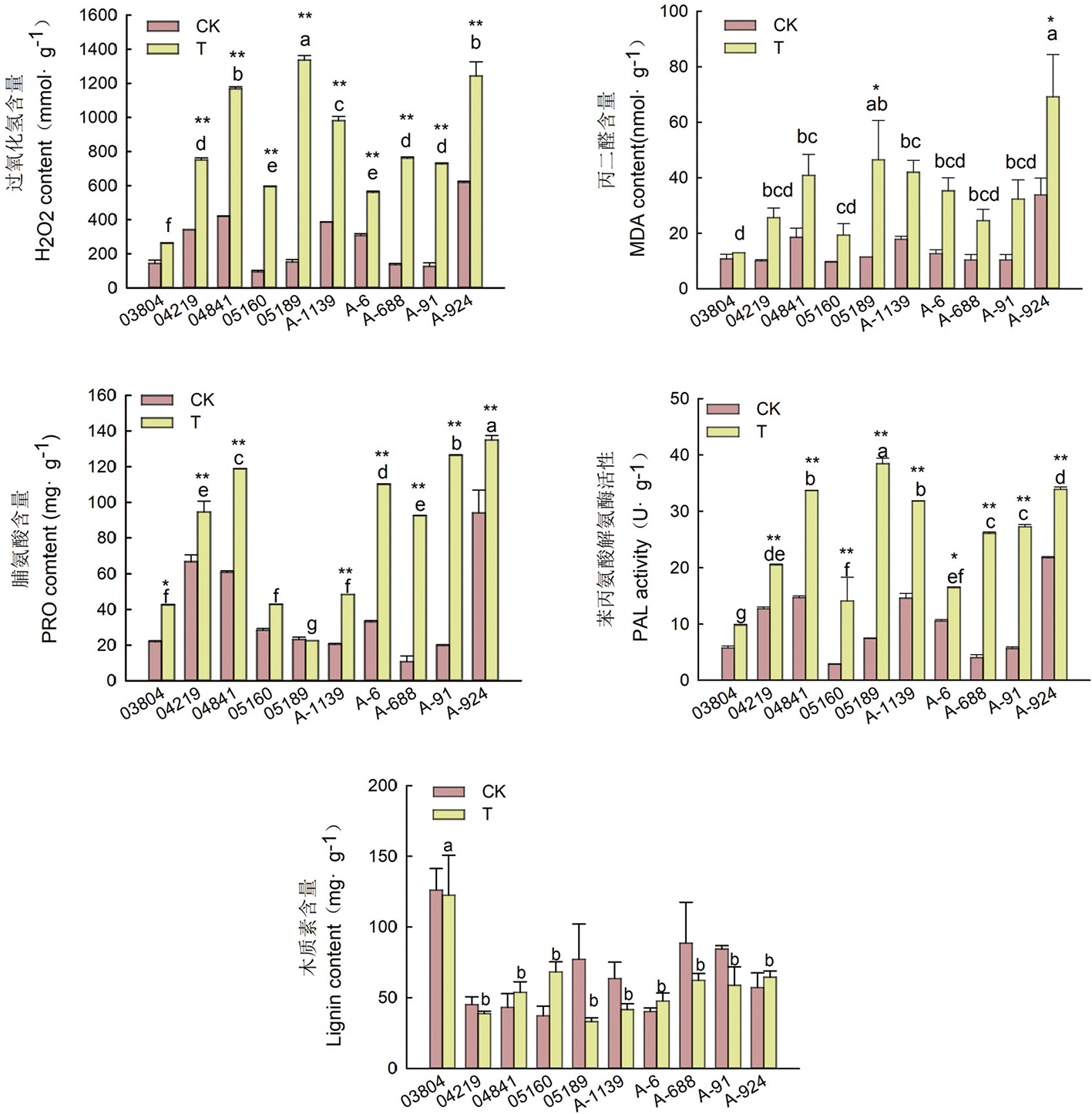
图4 棉苗接大丽轮枝菌菌液14 d后的生理生化指标 注:CK:对照组,T:处理组;‘*’‘ **’:分别表示种质组内P<0.05和P<0.01,下同
Fig.4 Physiological and biochemical indexes of 10 cotton seedlings at 14 days after inoculation of Verticillium dahliae Kleb Note: CK:the control group, T: the treatment group; "*" "**" respectively represent P < 0.05 and P < 0.01 within germplasm group, the same as below
| 项目 Item | 丙二醛含量 MDA content | 过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content | 苯丙氨酸 解氨酶活性 PAL activity | 木质素含量 Lignin content | 游离脯氨酸含量 PRO content | 发病率 Incidencet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content | 0.833** | |||||
| 苯丙氨酸解氨酶活性 PAL activity | 0.782** | 0.954** | ||||
| 木质素含量 Lignin content | -0.454 | -0.638* | -0.615 | |||
| 游离脯氨酸含量 PRO content | 0.383 | 0.134 | 0.17 | -0.129 | ||
| 发病率 Incidence | 0.639* | 0.813** | 0.839** | -0.829** | 0.367 | |
| 含菌量 Bacterial content | -0.322 | 0.109 | 0.013 | -0.333 | -0.25 | 0.283 |
表3 棉花黄萎病抗性指标的相关系数矩阵
Tab.3 Correlation coefficient matrix of cotton Verticillium wilt resistance index
| 项目 Item | 丙二醛含量 MDA content | 过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content | 苯丙氨酸 解氨酶活性 PAL activity | 木质素含量 Lignin content | 游离脯氨酸含量 PRO content | 发病率 Incidencet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content | 0.833** | |||||
| 苯丙氨酸解氨酶活性 PAL activity | 0.782** | 0.954** | ||||
| 木质素含量 Lignin content | -0.454 | -0.638* | -0.615 | |||
| 游离脯氨酸含量 PRO content | 0.383 | 0.134 | 0.17 | -0.129 | ||
| 发病率 Incidence | 0.639* | 0.813** | 0.839** | -0.829** | 0.367 | |
| 含菌量 Bacterial content | -0.322 | 0.109 | 0.013 | -0.333 | -0.25 | 0.283 |
| 成分 Component | 特征值 Eigen value | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.457 | 64.951 | 64.951 |
| 2 | 1.427 | 20.386 | 85.337 |
| 3 | 0.56 | 8.005 | 93.342 |
| 4 | 0.381 | 5.442 | 98.784 |
| 5 | 0.054 | 0.765 | 99.550 |
| 6 | 0.025 | 0.357 | 99.906 |
| 7 | 0.007 | 0.094 | 100 |
表4 棉花黄萎病各综合指标的特征值、贡献率及累计贡献率
Tab.4 Characteristic values, contribution andcumulative contribution of each comprehensive index of cotton after Verticillium wilt pathogen infection
| 成分 Component | 特征值 Eigen value | 贡献率 Contribution rate (%) | 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.457 | 64.951 | 64.951 |
| 2 | 1.427 | 20.386 | 85.337 |
| 3 | 0.56 | 8.005 | 93.342 |
| 4 | 0.381 | 5.442 | 98.784 |
| 5 | 0.054 | 0.765 | 99.550 |
| 6 | 0.025 | 0.357 | 99.906 |
| 7 | 0.007 | 0.094 | 100 |
| 主成分 Princial component | 丙二醛含量 MDA content | 过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content | 苯丙氨酸 解氨酶活性 PAL Activity | 木质素含量 Lignin content | 游离脯氨酸 含量 PRO content | 发病率 Incidence | 含菌量 Bacterial content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一主成分 PC1 | 0.936 | 0.985 | -0.867 | 0.879 | -0.344 | 0.978 | 0.317 |
| 第二主成分 PC2 | -0.265 | 0.065 | -0.041 | 0.139 | 0.791 | 0.032 | 0.8 |
表5 棉花黄萎病抗性各生理指标的主成分矩阵
Tab.5 Principal component coefficients of each physiological index in cotton after Verticillium wilt pathogen infection
| 主成分 Princial component | 丙二醛含量 MDA content | 过氧化氢含量 H2O2 content | 苯丙氨酸 解氨酶活性 PAL Activity | 木质素含量 Lignin content | 游离脯氨酸 含量 PRO content | 发病率 Incidence | 含菌量 Bacterial content |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一主成分 PC1 | 0.936 | 0.985 | -0.867 | 0.879 | -0.344 | 0.978 | 0.317 |
| 第二主成分 PC2 | -0.265 | 0.065 | -0.041 | 0.139 | 0.791 | 0.032 | 0.8 |
| 品种(系) Variety(line) | Y1 | Y2 | U(X1) | U(X2) | D值 D value | 综合评价 Comprehensive evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 03804 | 5.330 | 0.020 | 1.000 | 0.437 | 0.866 | 抗 |
| A-6 | 0.630 | 1.860 | 0.340 | 1.000 | 0.498 | 耐 |
| 05160 | 1.420 | -1.410 | 0.451 | 0.000 | 0.343 | 耐 |
| A-91 | -0.580 | 1.240 | 0.170 | 0.810 | 0.323 | 耐 |
| A-924 | -1.490 | 1.560 | 0.042 | 0.908 | 0.249 | 耐 |
| A-688 | -0.140 | -0.510 | 0.232 | 0.275 | 0.242 | 耐 |
| 04219 | -0.590 | -0.720 | 0.169 | 0.211 | 0.179 | 敏 |
| 04841 | -1.530 | 0.160 | 0.037 | 0.480 | 0.143 | 敏 |
| A-1139 | -1.260 | -0.830 | 0.074 | 0.177 | 0.099 | 敏 |
| 05189 | -1.790 | -1.380 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 敏 |
| 权重Weight | 0.761 | 0.239 |
表6 棉花各品种黄萎病抗性的综合指标值Y、权重、U(Xj)、D值及综合评价
Tab.6 Value of each comprehensive index(CI), index weight, U(Xj)and comprehensive evaluation value (D value) of cotton after Verticillium wilt pathogen infection
| 品种(系) Variety(line) | Y1 | Y2 | U(X1) | U(X2) | D值 D value | 综合评价 Comprehensive evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 03804 | 5.330 | 0.020 | 1.000 | 0.437 | 0.866 | 抗 |
| A-6 | 0.630 | 1.860 | 0.340 | 1.000 | 0.498 | 耐 |
| 05160 | 1.420 | -1.410 | 0.451 | 0.000 | 0.343 | 耐 |
| A-91 | -0.580 | 1.240 | 0.170 | 0.810 | 0.323 | 耐 |
| A-924 | -1.490 | 1.560 | 0.042 | 0.908 | 0.249 | 耐 |
| A-688 | -0.140 | -0.510 | 0.232 | 0.275 | 0.242 | 耐 |
| 04219 | -0.590 | -0.720 | 0.169 | 0.211 | 0.179 | 敏 |
| 04841 | -1.530 | 0.160 | 0.037 | 0.480 | 0.143 | 敏 |
| A-1139 | -1.260 | -0.830 | 0.074 | 0.177 | 0.099 | 敏 |
| 05189 | -1.790 | -1.380 | 0.000 | 0.009 | 0.002 | 敏 |
| 权重Weight | 0.761 | 0.239 |
| [1] | 石磊岩. 我国棉花黄萎病研究进展[J]. 棉花学报, 1995,(4):243-245, 251. |
| SHI Leiyan. Advances in research on Verticillium wilt of cotton in China[J]. Cotton Science, 1995,(4):243-245, 251. | |
| [2] | A. Aguado, B. De Los Santos, D. Gamane, et al. Gene effects for cotton-fiber traits in cotton plant (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under Verticillium conditions[J]. Field Crops Research, 2009, 116(3): |
| [3] | 张兴华, 李捷. 棉黄萎病发生和研究进展[J]. 江西农业学报, 2006,(1):99-104. |
| ZHANG Xinghua, LI Jie. Research Progress of Verticillium wilt in Cotton[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2006,(1):99-104. | |
| [4] | 李凤瑞, 史加亮, 杨秀凤. 棉花抗黄萎病研究进展及前景展望[J]. 山东农业科学, 2009,(9):57-59. |
| LI Fengrui, SHI Jialiang, YANG Xiufeng. Avances y perspectivas de la resistencia del algodón al Verticillium[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2009,(9):57-59. | |
| [5] | 简桂良, 邹亚飞, 马存. 棉花黄萎病连年流行的原因及对策[J]. 中国棉花, 2003,(3):13-14. |
| JIAN Guiliang, ZOU Yafei, MA Cun. Causes and Countermeasures of Verticillium wilt Epidemic in Cotton[J]. China Cotton, 2003,(3):13-14. | |
| [6] |
崔淑芳, 李俊兰, 金卫平, 等. 棉花抗黄萎病种质资源的选育与鉴定[J]. 华北农学报, 2006,(S2):180-182.
DOI |
| CUI Shufang, LI Junlan, JIN Weiping, et al. Breeding and identification of germplasm resources resistant to Verticillium wilt in cotton[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2006,(S2):180-182. | |
| [7] | 邢宏宜, 贺道华, 易永华, 等. 陕西棉花抗枯黄萎病种质资源评价[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008,(10):222-227. |
| XING Hongyi, HE Daohua, YI Yonghua, et al. Evaluation of germplasm resources for resistance to Verticillium wilt in cotton in Shaanxi[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008,(10):222-227. | |
| [8] | Wang Yiqin, Liang Chengzhen, Wu Shenjie, et al. Significant Improvement of Cotton Verticillium wilt Resistance by Manipulating the Expression of Gastrodia Antifungal Proteins.[J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(10): |
| [9] |
Zhao Y L, Zhou T T, Guo H S. Hyphopodium-Specific VdNoxB/VdPls1-Dependent ROS-Ca2+ Signaling Is Required for Plant Infection by Verticillium dahliae[J]. PLoS Pathogens, 2016, 12(7):e1005793.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Zhang Tao, Jin Yun, Zhao Jianhua, et al. Host-Induced Gene Silencing of the Target Gene in Fungal Cells Confers Effective Resistance to the Cotton Wilt Disease Pathogen Verticillium dahliae[J]. Molecular Plant, 2016, 9(6): 939-942.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Zhang T, Zhao Y L, Zhao J H, et al. Cotton plants export microRNAs to inhibit virulence gene expression in a fungal pathogen[J]. Nature Plants, 2016, 2(10):16153.
DOI PMID |
| [12] |
Xu J, Xu X, Tian L, et al. Discovery and identification of candidate genes from the chitinase gene family for Verticillium dahliae resistance in cotton[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6:29022.
DOI |
| [13] |
Zhang Z, Zhao J, Ding L, et al. Constitutive expression of a novel antimicrobial protein, Hcm1, confers resistance to both Verticillium and Fusarium wilts in cotton[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1):20773.
DOI |
| [14] | 程红梅, 简桂良, 倪万潮, 等. 转几丁质酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶基因提高棉花对枯萎病和黄萎病的抗性[J]. 中国农业科学, 2005,(6):1160-1166. |
| CHENG Hongmei, JIAN Guiliang, NI Wanchao, et al. Transgenic chitinase and β-1, 3-glucanase genes improve resistance of cotton to Fusarium wilt and Verticillium wilt[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2005,(6):1160-1166. | |
| [15] | Tohidfar M, Hossaini R, Bashir N S, et al. Enhanced resistance to Verticillium dahliae in transgenic cotton expressing an endochitinase gene from Phaseolus vulgaris[J]. Czech Journal of Genetics & Plant Breeding, 2012, 48(1):33-41. |
| [16] |
吴家和, 张献龙, 罗晓丽, 等. 转几丁质酶和葡聚糖酶基因棉花的获得及其对黄萎病的抗性[J]. 遗传学报, 2004,(2):183-188.
PMID |
|
WU Jiahe, ZHANG Xianlong, LUO X iaoli, et al. Effects of chitinase and glucanase genes on resistance to Verticillium wilt in cotton[J]. Acta Genetica Sinica, 2004,(2):183-188.
PMID |
|
| [17] | Miss C. B.. Sulochana. B-Vitamins in root exudates of cotton[J]. Plant and Soil, 1962, 16(3): |
| [18] | Yao Z, Badawi, et al. Overexpression of StRboh A in Arabidopsis thaliana enhances defense responses against Verticillium dahliae[J]. Physiological & Molecular Plant Pathology, 2015. |
| [19] |
Zhang B, Tremousaygue D, Denancé D, et al. PIRIN2 stabilizes cysteine protease XCP2 and increases susceptibility to the vascular pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Journal, 2015, 79(6):1009-1019.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Buhtz A, Witzel K, Strehmel N, et al. Perturbations in the Primary Metabolism of Tomato and Arabidopsis thaliana Plants Infected with the Soil-Borne Fungus Verticillium dahliae[J]. Plos One, 2015, 10(9):e0138242.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Mo H, Wang X, Zhang Y, et al. Cotton polyamine oxidase is required for spermine and camalexin signalling in the defence response to Verticillium dahliae[J]. Plant Journal, 2015, 83(6). |
| [22] | 蒋明义, 郭绍川, 张学明. 氧化胁迫下稻苗体内积累的脯氨酸的抗氧化作用[J]. 植物生理学报, 1997,(4):347-352. |
| JING Mingyi, GUO Shaochuan, ZHANG Xueming. Antioxidant effects of proline accumulation in rice seedlings under oxidative stress[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 1997,(4):347-352. | |
| [23] | 刘丽霞. 海岛棉抗黄萎病基因GbVe抗病机制研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2013. |
| LIU Lixia. Research on resistance mechanism of Verticillium wilt resistance gene GBVE in island cotton[D]. Baoding: Agricultural University of Hebei, 2013. | |
| [24] | 王省芬, 马峙英. 一种新的棉花黄萎病抗性鉴定方法[J]. 棉花学报, 2002,(4):231-233. |
| WANG Shengfen, MA Zhiying. A new method for identification of Verticillium wilt resistance in cotton[J]. Cotton Science, 2002,(4):231-233. | |
| [25] | 郭秀华. 分子标记辅助聚合陆地棉不同抗黄萎病QTL材料创制与鉴定[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2014. |
| GUO Xiuhua. Development and identification of QTLs for resistance to Verticillium wilt in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.)[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014. | |
| [26] | 朱荷琴, 吴征彬, 邹奎, 等. 国家棉花品种区域试验抗枯黄萎病鉴定方法[J]. 中国棉花, 2007,(11):9-10. |
| ZHU Heqin, WU Zhengbin, ZOU Kui, et al. Identification of resistance to Verticillium wilt in national cotton cultivars in regional tests[J]. China Cotton, 2007,(11):9-10. | |
| [27] | 南英子. 实证分析中运用主成分分析法应注意的几个问题[J]. 统计与决策, 2009,(21):155-156. |
| NAN Yingzi. Several problems in the application of principal component analysis in empirical analysis[J]. Statistics and Decision, 2009,(21):155-156. | |
| [28] | 吴殿廷, 吴迪. 用主成分分析法作多指标综合评价应该注意的问题[J]. 数学的实践与认识, 2015, 45(20):143-150. |
| WU Dianting, WU Di. Problems that should be paid attention to when using principal component analysis as multi-index comprehensive evaluation[J]. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2015, 45(20):143-150. | |
| [29] | 何团结, 程福如, 江本利, 等. 棉花区试黄萎病田间调查抽样技术研究[J]. 中国棉花, 2010, 37(7):15-18. |
| HE Tuanjie, CHENG Furu, JIANG Benli, et al. Study on sampling technique of Verticillium wilt in cotton field test[J]. China Cotton, 2010, 37(7):15-18. | |
| [30] | 王瑞卿, 张旭, 王景怀, 等. 影响我国棉花黄萎病发生的综合因素分析[A]. 中国农学会棉花分会.中国棉花学会 2007年年会论文汇编[C].中国农学会棉花分会:中国农学会棉花分会, 2007. |
| WANG Ruiqing, ZHANG Xu, WANG Jinghuai, et al. Analysis of comprehensive factors affecting cotton Verticillium wilt occurrence in China[A]. Cotton Branch of Chinese Society of Agronomic Society. Cotton Branch of Chinese Society of Agronomy: Cotton Branch of Chinese Society of Agronomy, 2007. | |
| [31] | 李琼芳, 谭永久, 叶鹏盛, 等. 棉花抗枯、黄萎病性早期鉴定方法的研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 1994,(1):49-54. |
| LI Qiongfang, TAN Yongjiu, YE Pengsheng, et al. Study on early Identification of Resistance to Blight and Verticillium wilt in Cotton[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 1994, (1):49-54. | |
| [32] |
Gayoso C, Pomar F, Novo-Uzal E, et al. The Ve-mediated resistance response of the tomato to Verticillium dahliae involves H2O2, peroxidase and lignins and drives PAL gene expression[J]. BMC Plant Biology, 2010, 10(1):232-232.
DOI |
| [33] |
Qiao Z, Dixon R A. Transcriptional networks for lignin biosynthesis: more complex than we thought[J]. Trends in Plant Science, 2011, 16(4):227-233.
DOI PMID |
| [34] | Boudet A M. Lignins and lignification: Selected issues[J]. Plant Physiology & Biochemistry, 2000, 38(1-2):81-96. |
| [35] | 宋喜贵, 佘小平. 植物体内过氧化氢的产生及其生理作用[J]. 连云港师范高等专科学校学报, 2010, 27(4):99-103. |
| SONG Xigui, SHE Xiaoping. The Generation and the Role of Hydrogen Peroxide in Plant[J]. Journal of Lianyungang Teachers College, 2010, 27(4):99-103. | |
| [36] | 陈贵, 胡文玉, 谢甫绨, 等. 提取植物体内MDA的溶剂及MDA作为衰老指标的探讨[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1991,(1):44-46. |
| CHEN Gui, HU Wenyu, XIE Fudi, et al. Solvent for Extracting Malondialdehyde in Plant as an Index of Senescence[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1991,(1):44-46. | |
| [37] | 张江涛, 段光明, 于泽英. 苯丙氨酸解氨酶(PaL)与水稻抗稻瘟病的关系[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1987,(6):34-37. |
| ZHANG Jiangtao, DUAN Guangming, YU Zeying. Relationship between phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) and rice blast resistance[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1987,(6):34-37. | |
| [38] | 侯丽娟, 李卫, 刘燕霞, 等. 棉花黄萎病菌毒素对棉花生化代谢的影响[J]. 西北农业学报, 2010, 19(12):63-67. |
| HOU Lijuan, LI Wei, LIU Yanxia, et al. Effects of Verticillium dahliae toxin on cotton biochemical metabolism[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 19(12):63-67. | |
| [39] | 王玉, 刘维信, 孙令强, 等. 南瓜幼苗叶片感染白粉病菌后一些酶活性的变化[J]. 西北农业学报, 2009, 18(4):103-105. |
| WANG Yu, LIU Weixin, SUN Lingqiang, et al. Effects of powdery mildew on the enzymatic activity of pumpkin seedlings[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2009, 18(4):103-105. | |
| [40] | 全先庆, 张渝洁, 单雷, 等. 脯氨酸在植物生长和非生物胁迫耐受中的作用[J]. 生物技术通讯, 2007,(1):159-162. |
| QUAN Xianqing, ZHANG Yujie, SHAN Lei, et al. Effects of proline on plant growth and Abiotic Stress tolerance[J]. Biotechnology Letters, 2007,(1):159-162. | |
| [41] | 宋凤鸣, 郑重. 细胞壁羟脯氨酸和游离脯氨酸与棉花对枯萎病抗性的关系[J]. 植物生理学报, 1995,(3):235-241. |
| SONG Fengming, ZHENG Zheng. Relationship between Cell Wall Hydroxyproline and Free ProLine and Resistance to Fusarium wilt of Cotton[J]. Plant Physiology Journal, 1995,(3):235-241. | |
| [42] | 冯洁, 陈其煐, 石磊岩. 枯萎菌诱导棉花细胞壁富含羟脯氨酸糖蛋白积累与枯萎病抗性间的关系[J]. 植物病理学报, 1995,(2):133-138. |
| FENG Jie, CHEN Qiying, SHI Leiyan. Effects of Fusarium oxysporum (Fu sarium oxysporum) on resistance to Fusarium oxysporum[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Pathology, 1995,(2):133-138. | |
| [43] | 王军, 周美学, 许如根, 等. 大麦耐湿性鉴定指标和评价方法研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2007, 40(10):2145-2152. |
| WANG Jun, ZHOU Meixue, XU Rugen, et al. Studies on Selecting Indices and Evaluation Methods for Barley's (Hordeum vulgare L.)Waterlogging Tolerance[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2007, 40(10):2145-2152. | |
| [44] | 赵晓军. 利用主成分分析法评价6个燕麦品种[J]. 养殖与饲料, 2020, 19(7):32-34. |
| ZHAO Xiaojun. Evaluation of six oat varieties by principal component analysis[J]. Animals Breeding and Feed, 2020, 19(7):32-34. | |
| [45] | 葛礼姣, 方馨妍, 张云月, 等. 菊花苗期氮高效品种资源筛选及氮效率评价体系建立[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2021, 4(6): 2054-2062. |
| GE Lijiao, FANG Xinyan, ZHANG Yunyue, et al. Screening of nitrogen efficient varieties and its assessment system construction at seedling stage of chrysanthemum[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021, 4(6): 2054-2062. |
| [1] | 苗红萍, 王晓伟, 田聪华, 李志, 张玉新, 戴俊生. 塔里木河流域棉花生产与布局演变特征及驱动因素分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 217-226. |
| [2] | 王俊铎, 崔豫疆, 梁亚军, 龚照龙, 郑巨云, 李雪源. 新疆棉花生产优势区域分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 60-69. |
| [3] | 郑巨云, 龚照龙, 梁亚军, 耿世伟, 孙丰磊, 阳妮, 李雪源, 王俊铎. 新疆机采棉花生产关键技术模式[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 70-74. |
| [4] | 李杰, 刘佳, 王亮, 张娜, 杨延龙, 郑子漂, 魏鑫, 王萌, 周子馨, 阳妮, 龚照龙, 侯献飞, 黄启秀, 阿不都卡地尔·库尔班, 张济鹏, 张鹏忠. “棉、油、糖”科技成果转化现状及应用分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 89-94. |
| [5] | 扁青永, 付彦博, 祁通, 黄建, 蒲胜海, 孟阿静, 哈丽哈什·依巴提. 新疆南疆盐碱地棉花出苗影响因素及保苗措施分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 95-100. |
| [6] | 李永泰, 高阿香, 李艳军, 张新宇. 脱叶剂对不同敏感性棉花品种生理特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2094-2102. |
| [7] | 张泽华, 叶含春, 王振华, 李文昊, 李海强, 刘健. 等氮配施脲酶抑制剂对滴灌棉花生长发育和产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [8] | 陈瑞杰, 罗林毅, 阮向阳, 冶军. 腐植酸对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [9] | 黄铂轩, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 庞朝友, 徐文修, 董合林. 不同氮素抑制剂对棉花生长发育、氮素利用与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [10] | 王超, 徐文修, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 冯卫娜, 邵晶晶, 董合林. 棉花苗期生长发育对土壤速效钾水平的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2132-2139. |
| [11] | 阿热孜姑·吐逊, 高杰. 干旱胁迫和播种密度对洋葱小鳞茎生理特性及产出鳞茎个数的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2211-2222. |
| [12] | 张庭军, 李字辉, 崔豫疆, 孙孝贵, 陈芳. 微生物菌剂对棉花生长及土壤理化性质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2269-2276. |
| [13] | 董志多, 徐菲, 付秋萍, 黄建, 祁通, 孟阿静, 付彦博, 开赛尔·库尔班. 不同类型盐碱胁迫对棉花种子萌发的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1831-1844. |
| [14] | 袁莹莹, 赵经华, 迪力穆拉提·司马义, 杨庭瑞. 基于apriori算法对盆栽春小麦生理指标及产量的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [15] | 赖成霞, 杨延龙, 李春平, 玛依拉·玉素音, 王燕, 杨栋, 阳妮, 葛风伟, 汪鹏龙, 马君. 落叶型棉花黄萎病的生物学特征及药剂防治分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2034-2042. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 70
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||