

新疆农业科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (12): 2909-2923.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.12.006
收稿日期:2021-12-18
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2023-01-30
通信作者:
闵伟(1986-),男,安徽太和人,副教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为土壤肥力与调控,(Email)minwei555@126.com基金资助:
GUO Xiaowen, DU Siyao, WANG Fangxia, YE Yang, YANG Maoqi, MIN Wei( )
)
Received:2021-12-18
Published:2022-12-20
Online:2023-01-30
Correspondence author:
MIN Wei(1986-), male, associate professor, research interest: soil fertility and regulation, (E-mail)minwei555@126.comSupported by:摘要: 【目的】 研究长期咸水灌溉对棉田土壤理化性质、细菌和真菌群落结构多样性的影响。【方法】 设3个灌溉水盐度处理为0.35、4.61和8.04 dS/m,分别代表淡水、微咸水、咸水3种灌溉水质,采用高通量测序法测定土壤中细菌和真菌群落结构多样性。【结果】 与淡水灌溉相比,微咸水和咸水灌溉显著提高了土壤盐分和土壤容重,但降低了土壤pH、有机质和全氮含量。微咸水和咸水灌溉显著增加细菌OTUs,而咸水灌溉显著降低真菌OTUs。咸水灌溉显著增加细菌Chao1和ACE指数,降低Shannon指数,降低真菌Chao1和ACE 指数,增加Simpson指数。微咸水和咸水灌溉显著降低细菌RB41、H16、Haliangium、硝化螺旋菌属、溶杆菌属、苔藓杆菌属、酸杆菌属和真菌被孢霉属、粉褶菌属、Tetracladium的相对丰度,但显著增加细菌鞘脂单胞菌属、芽单胞菌属、Gaiella、Ilumatobacter、Solirubrobacter、Nocardioides和真菌弯孢菌属、球腔菌属的相对丰度。随着灌溉水盐度的增加,细菌群落潜在生物标志物的数量逐渐减少,为4个、2个和1个,真菌群落潜在生物标志物数量在微咸水灌溉最高12个,咸水灌溉最低5个。细菌群落结构的改变与土壤含水量,容重和盐度的变化密切相关,而真菌群落结构的改变仅与土壤含水量显著相关。【结论】 盐分是驱动土壤细菌和真菌群落组成变化的主要因素。土壤细菌和真菌群落通过调节物种组成来适应盐胁迫,不同灌溉水盐度胁迫下土壤细菌和真菌群落会形成显著差异的物种。
中图分类号:
郭晓雯, 杜思垚, 王芳霞, 叶扬, 杨茂琪, 闵伟. 长期咸水滴灌对棉田土壤细菌和真菌群落结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(12): 2909-2923.
GUO Xiaowen, DU Siyao, WANG Fangxia, YE Yang, YANG Maoqi, MIN Wei. Effects of Long-Term Saline Water Irrigation on Soil Bacteria and Fungi Community Structure in Cotton Field[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(12): 2909-2923.
| 处理 Treatment | 含水量 Soil water content(%) | 容重 Bulk density | 电导率 ECe (dS/m) | pH (1∶2.5) | 有机质 SOM (g/kg) | 全氮 TN (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWN 360 | 13.35c | 1.27b | 3.01c | 7.96a | 17.83a | 0.74a |
| BWN 360 | 14.63b | 1.34a | 7.35b | 7.76b | 17.21b | 0.70b |
| SWN 360 | 18.23a | 1.38a | 11.61a | 7.75b | 16.97b | 0.65c |
表1 不同处理下土壤理化性质变化
Table 1 Effects of different treatments on soil physical and chemical properties
| 处理 Treatment | 含水量 Soil water content(%) | 容重 Bulk density | 电导率 ECe (dS/m) | pH (1∶2.5) | 有机质 SOM (g/kg) | 全氮 TN (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWN 360 | 13.35c | 1.27b | 3.01c | 7.96a | 17.83a | 0.74a |
| BWN 360 | 14.63b | 1.34a | 7.35b | 7.76b | 17.21b | 0.70b |
| SWN 360 | 18.23a | 1.38a | 11.61a | 7.75b | 16.97b | 0.65c |
| 处理 Treatment | 测序片段 Reads | 物种分类单元 OTUs | 覆盖度 Coverage(%) | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWN 360 | 80 088a | 1 889c | 99.55ab | 1 952b | 1 968b | 0.002 8a | 6.64b |
| BWN 360 | 80 053a | 2 000a | 99.62a | 2 048a | 2 058a | 0.002 8a | 6.69a |
| SWN 360 | 80 181a | 1 950b | 99.51b | 2 025a | 2 047a | 0.003 0a | 6.60c |
表2 不同处理下土壤细菌群落丰富度和多样性指数变化
Table 2 Richness and diversity index of soil bacterial community in different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 测序片段 Reads | 物种分类单元 OTUs | 覆盖度 Coverage(%) | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWN 360 | 80 088a | 1 889c | 99.55ab | 1 952b | 1 968b | 0.002 8a | 6.64b |
| BWN 360 | 80 053a | 2 000a | 99.62a | 2 048a | 2 058a | 0.002 8a | 6.69a |
| SWN 360 | 80 181a | 1 950b | 99.51b | 2 025a | 2 047a | 0.003 0a | 6.60c |
| 处理 Treatment | 测序片段 Reads | 物种分类单元 OTUs | 覆盖度 Coverage(%) | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWN 360 | 63 910a | 426a | 0.999 5a | 439a | 445a | 0.052 6c | 3.86a |
| BWN 360 | 63 007a | 435a | 0.999 5a | 447a | 448a | 0.062 7b | 3.83a |
| SWN 360 | 63 568a | 408b | 0.999 5a | 419b | 421b | 0.069 1a | 3.68a |
表3 不同处理的土壤真菌群落丰富度和多样性指数
Table 3 Richness and diversity index of soil fungal community in different treatments
| 处理 Treatment | 测序片段 Reads | 物种分类单元 OTUs | 覆盖度 Coverage(%) | ACE指数 ACE index | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWN 360 | 63 910a | 426a | 0.999 5a | 439a | 445a | 0.052 6c | 3.86a |
| BWN 360 | 63 007a | 435a | 0.999 5a | 447a | 448a | 0.062 7b | 3.83a |
| SWN 360 | 63 568a | 408b | 0.999 5a | 419b | 421b | 0.069 1a | 3.68a |
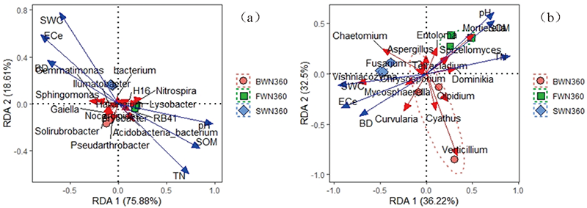
图7 细菌(a)和真菌(b)群落结构与土壤理化性质间RDA
Fig.7 Redundancy analysis (RDA) of correlations between soil physicochemical properties and the community structure of bacteria(a), fungi(b)
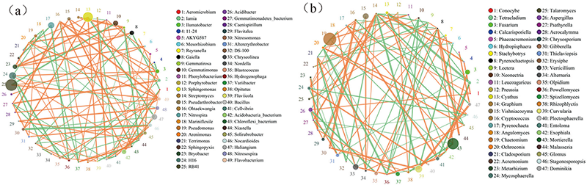
图8 细菌和真菌间的相关性网络注:不同颜色的圆圈代表物种,圆圈大小代表物种的丰度,线条代表两物种间相关,线的粗细代表相关性的强弱程度,橙色连线代表正相关,绿色连线代表负相关。
Fig.8 Correlation network of bacteria and fungi Note:The circles in different colors represent species, the size of the circles represents the abundance of species, the lines represent the comrelation between the two species, the thickness of the lines represents the degree of corelation, the orange lines reptesent positive corelation, and thegreen lines represent negative correlation
| [1] | 刘雪艳, 丁邦新, 白云岗, 等. 微咸水膜下滴灌对棉花生长及产量的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2020, 37(6): 1627-1634. |
| LIU Xueyan, DING Bangxin, BAI Yungang, et al. Effect of drip irrigation under brackish water film on cotton growth and yield[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2020, 37(6):1627-1634. | |
| [2] |
Zhang P, Xu S, Zhang G, et al. Carbon cycle in response to residue management and fertilizer application in a cotton field in arid Northwest China[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2019, 18(5): 1103-1119.
DOI URL |
| [3] | 刘静, 高占义. 中国利用微咸水灌溉研究与实践进展[J]. 水利水电技术, 2012, 43(1): 101-104. |
| LIU Jing, GAO Zhanyi. Advances in study and practice of brackish water irrigation in China[J]. Water Resources and Hydropower Engineering, 2012, 43(1):101-104. | |
| [4] | 祁通, 孙阳讯, 黄建, 等. 两种盐生植物在南北疆地区的适生性及吸盐能力[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017, (1): 144-148. |
| QI Tong, SUN Yangxun, HUANG Jian, et al. The adaptability and salt absorption ability of two kinds of halophyte in southern and northern of Xinjiang[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017,(1): 144-148. | |
| [5] | 王娟娟, 王倩, 姜爱霞, 等. 黄河三角洲盐生植被演替对土壤真菌碳源代谢多样性的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2018, 55(5):1264-1275. |
| WANG Juanjuan, WANG Qian, JIANG Aixia, et al. Effects of Succession of Halophytic Vegetation on Carbon Metabolism Diversityof Fungi in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2018, 55(5): 1264-1275. | |
| [6] | 周际海, 郜茹茹, 魏倩, 等. 旱地红壤不同土地利用方式对土壤酶活性及微生物多样性的影响差异[J]. 水土保持学报, 2020, 34(1): 327-332. |
| ZHOU Jihai, GAO Ruru, WEI Qian, et al. Effects of different land use patterns on enzyme activities and microbial diversity in upland red soil[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2020, 34(1):327-332. | |
| [7] | 郭仁松, 林涛, 徐海江, 等. 微咸水滴灌对绿洲棉田水盐运移特征及棉花产量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2017, 31(1): 211-216. |
| GUO Rensong, LIN Tao, XU Haijiang, et al. Effects of saline water drip irrigation on water and salt transport features and cotton yield in oasis cotton field[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2017, 31(1):211-216. | |
| [8] | 唐超超, 张坤, 周祥, 等. 微咸水膜下滴灌对土壤盐分离子变化及玉米产量的影响[J]. 科技视界, 2017, (6): 57-58. |
| TANG Chaochao, ZHANG Kun, ZHOU Xiang, et al. Effects of drip irrigation with brackish water under plastic film on soil salinity and maize yield[J]. Science & Technology Vision, 2017,(6): 5758. | |
| [9] | 郑智, 刘琛, 傅庆林, 等. 盐分和水分对滨海盐土微生物组成及多样性的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2015, 27(2): 240-248. |
| ZHENG Zhi, LIU Chen, FU Qinglin, et al. Effects of salinity and soil moisture on microbial composition and community diversity in acoastal saline soil[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2015, 27(2): 240-248. | |
| [10] | 冯棣, 张俊鹏, 孙池涛, 等. 长期咸水灌溉对土壤理化性质和土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2014, 28(3): 171-176. |
| FENG Di, ZHANG Junpeng, SUN Chitao, et al. Effects of long-term irrigation with saline water on soil physical-chemical properties and activities of soil enzyme[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 28(3): 171-176. | |
| [11] |
Wong V N L, Greene R S B, Dalal R C, et al. Soil carbon dynamics in saline and sodic soils: a review[J]. Soil Use and Management, 2010, 26(1): 2-11.
DOI URL |
| [12] | 李丹, 万书勤, 康跃虎, 等. 滨海盐碱地微咸水滴灌水盐调控对番茄生长及品质的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39(7): 39-50. |
| LI Dan, WAN Shuqin, KANG Yuehu, et al. Effects of water-salt regulation on tomato growth and quality under drip irrigation with brackish water in coastal saline-alkali soil[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2020, 39(7): 39-50. | |
| [13] | 牛世全, 杨婷婷, 李君锋, 等. 盐碱土微生物功能群季节动态与土壤理化因子的关系[J]. 干旱区研究, 2011, 28(2):328-334. |
| NIU Shiquan, YANG Tingting, LI Junfeng, et al. Seasonal trends of microbial functional groups in saline-alkali soil and their relationship with soil physicochemical factors in the east Hexi corridor[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2011, 28(2): 328-334. | |
| [14] | 赵娇, 谢慧君, 张建. 黄河三角洲盐碱土根际微环境的微生物多样性及理化性质分析[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(3):1449-1455. |
| ZHAO Jiao, XIE Huijun, ZHANG Jian. Microbial diversity and physicochemical properties of rhizosphere microenvironment in saline-alkali soils of the yellow river delta[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(3):1449-1455. | |
| [15] | 马丽娟, 张慧敏, 侯振安, 闵伟. 长期咸水滴灌对土壤氨氧化微生物丰度和群落结构的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(12):2797-2807. |
| MA Lijuan, ZHANG Huimin, HOU Zhenan, MIN Wei. Effects of long-term saline water drip irrigation on the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizer[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(12): 2797-2807. | |
| [16] | 井大炜, 马海林, 刘方春, 等. 盐胁迫环境下接种根际促生细菌对碱蓬根际土壤微环境特征的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018, (4): 34-39. |
| JING Dawei, MA Hailin, LIU Fangchun, et al. Effects of inoculating plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria on the micro-environmental characteristics of the rhizospheresoil of Suaeda glauce Bge under salt stress[J]. Soil and Fertilizer in China, 2018,(4):34-39. | |
| [17] | 徐丽慧, 曾蓉, 高士刚, 等. 土壤真菌多样性对土传病害影响的研究进展[J]. 上海农业学报, 2017, 33(3): 161-165. |
| XU Lihui, ZENG Rong, GAO Shigang, et al. Review on the effect of soil fungal communities on soil-borne diseases[J]. Acta Agriculturae Shanghai, 2017, 33(3):161-165. | |
| [18] | 孙佳, 夏江宝, 苏丽, 等. 黄河三角洲盐碱地不同植被模式的土壤改良效应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(4): 1323-1332. |
| SUN Jia, XIA Jiangbao, SU Li, et al. Soil ameliorationof different vegetation on types in saline-alkali land of Yellow River Delta, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(4): 1323-1332. | |
| [19] | 田平雅, 沈聪, 赵辉, 等. 银北盐碱区植物根际土壤酶活性及微生物群落特征[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(1) :217-226. |
| TIAN Pingya, SHEN Cong, ZHAO Hui, et al. Enzyme activities and microbial communities in rhizospheres of plants in salinized soil in north Yinchuan,China[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(1):217-226. | |
| [20] |
潘媛媛, 黄海鹏, 孟婧, 等. 松嫩平原盐碱地中耐(嗜)盐菌的生物多样性[J]. 微生物学报, 2012, 52(10): 1187-1194.
PMID |
|
PAN Yuanyuan, HUANG Haipeng, MENG Jing, et al. Biodiversity of culturable halotolerant and halophilicbacteria isolated from saline-alkaline soils in Songnen Plain[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2012, 52(10): 1187-1194.
PMID |
|
| [21] | 梁悦萍, 李科江, 张俊鹏, 等. 咸水灌溉棉田休耕期土壤胞外酶活性和微生物多样性研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2018, 37(4): 732-740. |
| LIANG Yueping, LI Kejiang, ZHANG Junpeng, et al. Extracellular enzyme activity and microbial diversity of saline-irrigated cotton field soil during the fallow period[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2018, 37(4): 732-740. | |
| [22] | 马中昇, 谭军利, 魏童. 中国微咸水利用的地区和作物适应性研究进展[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2019, 38(3):70-75. |
| MA Zhongsheng, TAN Junli, WEI Tong. The variation of salt-tolerance of crops in different regions irrigated with brackish water in china[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2019, 38(3):70-75. | |
| [23] | Pang H C, Li Y Y, Yang J S, Liang Y S. Effect of brackish water irrigation and straw mulching on soil salinity and crop yields under monsoonal climatic conditions[J]. Agricultural Water Management, 2010, (97): 1971-1977. |
| [24] |
Malash N M, Flowers T J, Ragab R. Effect of irrigation methods, management and salinity of irrigation water on tomato yield, soil moisture and salinity distribution[J]. Irrigation Science, 2008, 26(4): 313-323.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 吴雨晴, 郑春莲, 孙景生, 等. 长期咸水灌溉对棉田土壤水稳性团聚体的影响[J]. 灌溉排水学报, 2020, 39(9): 58-64, 107. |
| WU Yuqing, ZHENG Chunlian, SUN Jingsheng, et al. The Effects of long-term saline water irrigation on stability of soil aggregates in a cotton field[J]. Journal of Irrigation and Drainage, 2020, 39(9): 58-64, 107. | |
| [26] | 孙慧, 张建锋, 许华森, 等. 余姚滨海不同盐碱度土壤微生物群落组成及土壤酶活性的变化[J]. 应用生态学报, 2016, 27(10): 3361-3370. |
| SUN Hui, ZHANG Jianfeng, XU Huasen, et al. Variations of soil microbial community composition and enzyme activities with different salinities on Yuyao coast,Zhejiang,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2016, 27(10): 3361-3370. | |
| [27] | 仙旋旋, 孔范龙, 朱梅珂, 等. 水盐梯度对滨海湿地土壤养分指标和酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2019, 39(1): 65-71. |
| XIAN Xuanxuan, KONG Fanlong, ZHU Meike, et al. Effects of water and salt gradient on soil nutrients indices and enzyme activities in coastal wetland[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 39(1): 65-71. | |
| [28] |
Rietz D N, Haynes R J. Effects of irrigation-induced salinity and sodicity on soil microbial activity[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2003, 35(6): 845-854.
DOI URL |
| [29] | 胡敏, 屈忠义, 王丽萍, 等. 不同改良剂对河套灌区盐渍化土壤性状和葵花生长特性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2019, 33(5): 316-322. |
| HU Min, QU Zhongyi, WANG Liping, et al. Effects of different ameliorants on the properties of salinized and sunflower growth in Hetao irrigation district[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2019, 33(5): 316-322. | |
| [30] | 杨赛, 俞冰倩, 胡信玉, 等. 东北苏打盐碱土壤微生物群落对植被进展演替的响应[J]. 土壤通报, 2019, 50(3): 632-640. |
| YANG Sai, YU Bingqian, HU Xinyu, et al. Response of microbial community to vegetation succession in soda saline- alkali soil in northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2019, 50(3): 632-640. | |
| [31] | 李新. 不同盐碱程度盐碱土壤微生物多样性研究[D]. 呼和洁特: 内蒙古师范大学, 2015. |
| LI Xin. Study on soil microbial community structure diversity in different degrees saline-alkaline soil[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Normal University, 2015. | |
| [32] |
张慧敏, 郭慧娟, 侯振安. 不同盐碱胁迫对土壤细菌群落结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(6):1074-1084.
DOI |
|
ZHANG Huimin, GUO Huijuan, HOU Zhenan. Effects of saline and alkaline stress on soil bacterial community structure[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(6): 1074-1084.
DOI |
|
| [33] |
Yang H, Hu J, Long X, et al. Salinity altered root distribution and increased diversity of bacterial communities in the rhizosphere soil of Jerusalem artichoke[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6(1): 1-10.
DOI URL |
| [34] | 李明, 毕江涛, 王静. 宁夏不同地区盐碱化土壤细菌群落多样性分布特征及其影响因子[J]. 生态学报, 2020, 40(4): 1316-1330. |
| LI Ming, BI Jiangtao, WANG Jing. Bacterial community structure and key influence factors in saline soil of different sites of Ningxia[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2020, 40(4): 1316-1330. | |
| [35] | 沈琦, 郝雅荞, 徐潇航, 等. 基于高通量测序技术的盐地碱蓬根际细菌群落多样性分析[J]. 浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 43(5): 671-677. |
| SHEN Qi, HAO Yaxiao, XU Xiaohang, et al. Analysis of rhizosphere bacterial diversity in Suaeda glauca bunge based on high-throughput sequencing[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Sci-Tech University (Natural Sciences Edi.), 2020, 43(5): 671-677. | |
| [36] | 侯梅锋, 何士龙, 李栋, 等. 连云港海底底泥及青海湖底泥细菌多样性研究[J]. 环境科学, 2011, 32(9): 2681-2688. |
| HOU Meifeng, HE Shilong, LI Dong, et al. Bacterial diversity in Lianyungang marine sediments and Qinghai Lake sediment[J]. Environmental Science, 2011, 32(9): 2681-2688. | |
| [37] |
Li X, Rui J, Xiong J, et al. Functional Potential of Soil Microbial Communities in the Maize Rhizosphere[J]. Plos One, 2014, 09(11): e112609.
DOI URL |
| [38] | 何小丽, 朱义, 崔心红. 盐胁迫下沼泽小叶桦土壤细菌数量及种类的变化特征[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2017, 58(9): 1600-1601. |
| HE Xiaoli, ZHU Yi, CUI Xinhong. Variation characteristics of bacterial quantity and species in betula microphylla soil under salt Stress[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 58(9): 1600-1601. | |
| [39] | 张科, 李臻, 郑瑶, 等. 河南叶县岩盐可培养中度嗜盐菌的多样性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(12): 3987-3997. |
| ZHANG Ke, LI Zhen, ZHENG Yao, et al. Biodiversity of culturable moderate halophilic bacteria of rocksalt in Yexian county, Henan province[J]. Microbiology China, 2020, 47(12): 3987-3997. | |
| [40] | 王巍琦, 杨磊, 程志博, 等. 干旱区不同类型盐碱地土壤微生物碳源代谢活性研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019, 33(6):158-166. |
| WANG Weiqi, YANG Lei, CHENG Zhibo, et al. Study on soil microbial biomass carbon source metabolism in different types of sodic saline-alkali soil in arid area[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2019, 33(6): 158-166. | |
| [41] | 徐扬, 张冠初, 丁红, 等. 干旱与盐胁迫对花生根际土壤细菌群落结构和花生产量的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(4): 1305-1313. |
| XU Yang, ZHANG Guanchu, DING Hong, et al. Effects of salt and drought stress on rhizosphere soil bacterial community structure and peanut yield[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(4): 1305-1313. | |
| [42] |
Brockett B F T, Prescott C E, Grayston S J. Soil moisture is the major factor influencing microbial community structure and enzyme activities across seven biogeoclimatic zones in western Canada[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2012, 44(1): 9-20.
DOI URL |
| [43] | 张玥, 姜爱霞, 郭笃发. 基于16S rDNA基因文库的黄河三角洲盐生植被土壤细菌群落多样性研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(13):55-57, 164. |
| ZHANG Yue, JIANG Aixia, GUO Dufa. Analysis of saline vegetation diversity of soil bacterial community in the yellow river delta based on 16S rDNA gene Library[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(13): 55-57, 164. | |
| [44] | 张晓丽, 张宏媛, 卢闯, 等. 河套灌区不同秋浇年限对土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 中国农业科学, 2019, 52(19): 3380-3392. |
| ZHANG Xiaoli, ZHANG Hongyuan, LU Chuang, et al. Effects of different autumn irrigation years on soil bacterial community in Hetao irrigation district[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2019, 52(19):3380-3392. | |
| [45] | 林耀奔, 杨建辉, 叶艳妹. 盐碱地不同土地利用方式下土壤细菌群落结构多样性差异分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(4): 1266-1273. |
| LIN Yaoben, YANG Jianhui, YE Yanmei. Analysis on diversity of soil bacterial community under different land use patterns in saline-alkali land[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(4): 1266-1273. | |
| [46] | 向君亮, 刘权, 申永瑞, 等. 松嫩草原盐碱土细菌多样性分析[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(2): 62-68. |
| XIANG Junliang, LIU Quan, SHEN Yongrui, et al. Variation of bacterial communities in the saline-alkalinesoil of meadow on Songnen Plain[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(2): 62-68. | |
| [47] | 黄艳飞, 吴庆丽, 万群, 等. 丛枝菌根真菌的研究进展[J]. 现代农业, 2019,(12): 9-12. |
| HUANG Yanfei, WU Qingli, WAN Qun, et al. Research progress of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi[J]. Modern Agriculture, 2019,(12): 9-12. | |
| [48] | 王芳, 图力古尔. 土壤真菌多样性研究进展[J]. 菌物研究, 2014, 12(3): 178-186. |
| WANG Fang, Tuligur. Research advances in the diversity of soil fungal[J]. Journal of Fungal Research, 2014, 12(3):178-186. | |
| [49] | Cortés-Lorenzo C, González-Martínez A, Smidt H, et al. Influence of salinity on fungal communities in a submerged fixed bed bioreactor for wastewater treatment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, (285): 562-572. |
| [50] | 赵君, 姚彤, 李明, 等. 生物炭对干旱胁迫下蓝盆花生长及根际土壤真菌丰度的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2019, (14): 93-99. |
| ZHAO Jun, YAO Tong, LI Ming, et al. Effects of biochar on growth of blue potted flower and fungal abundance of rhizosphere soil under drought stress[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2019,(14): 93-99. | |
| [51] | 王诗慧, 常顺利, 李鑫, 等. 天山林区土壤真菌多样性及其群落结构[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(1): 124-134. |
| WANG Shihui, CHANG Shunli, LI Xin, et al. Soil fungal diversity and its community structure in Tianshan forest[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(1):124-134. | |
| [52] | 邵璐, 姜华. 辽宁碱蓬根际土壤真菌多样性的季节变化及其耐盐性[J]. 生态学报, 2016, 36(4): 1050-1057. |
| SHAO Lu, JIANG Hua. Effect of seasonal and variation in salinity on the rhizosphere fungal diversity of Suaeda liaotungensis[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2016, 36(4):1050-1057. | |
| [53] | 孙倩, 吴宏亮, 陈阜, 等. 宁夏中部干旱带不同作物根际土壤真菌群落多样性及群落结构[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(11):2963-2972. |
| SUN Qian, WU Hongliang, CHEN Fu, et al. Fungal community diversity and structure in rhizosphere soil of different crops in the arid zone of central Ningxia[J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(11):2963-2972. | |
| [54] | 高玉峰, 贺字典. 影响土壤真菌多样性的土壤因素[J]. 中国农学通报, 2010, 26(10):177-181. |
| GAO Yufeng, HE Zidian. Study on soil effect factors to fungal diversity in Hebei Province[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2010, 26(10):177-181. | |
| [55] | 张建峰, 吉丽, 蔺朝龙, 等. 盐碱胁迫下大豆根际土壤真菌多样性分析[J]. 福建农业学报, 2017, 32(10):1130-1134. |
| ZHANG Jianfeng, JI Li, LIN Chaolong, et al. Fungal diversity in rhizosphere soil of soybean fields under saline-alkali stress[J]. Fujian Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 32(10):1130-1134. | |
| [56] | 萨如拉, 杨恒山, 邰继承, 等. 玉米秸秆还田对盐碱地土壤真菌多样性的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2017, 48(4):937-942. |
| SA Rula, YANG Hengshan, TAI Yi, et al. Effects of maize straw returning on soil fungal diversity in salinealkali soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2017, 48(4):937-942. | |
| [57] |
顾美英, 徐万里, 张志东, 等. 施用棉秆炭连作棉花根际土壤真菌多样性与土壤理化性质及黄萎病的相关性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(9):1698-1709.
DOI |
|
GU Meiying, XU Wanli, ZHANG Zhidong, et al. Relationships between fungi diversity,physicochemical properties and verticillium wilt in continuous cropping cotton rhizosphere soil with cotton stover biochar[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(9):1698-1709.
DOI |
|
| [58] | 王海英, 郭守玉, 黄满荣, 等. 子囊菌较担子菌具有更快的进化速率和更高的物种多样性[J]. 中国科学(生命科学) 2010, 40(8):731-737, 765-772. |
| WANG Haiying, GUO Shouyu, HUANG Manrong, et al. Ascomycota has faster evolutionary rate and higher species diversity than Basidiomycota (Fungi).[J]. Scientia Sinica (Vitae), 2010, 40(8):731-737, 765-772. | |
| [59] | 刘珊珊, 刘元元, 余彬彬, 等. 新疆巴音布鲁克草原白蘑蘑菇圈土壤真菌多样性分析[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(11):2909-2918. |
| LIU Shanshan, LIU Yuanyuan, YU Binbin, et al. Soil fungi diversity analysis of Tricholoma mongolicum mushroomring in Bayinbuluke grassland, Xinjiang[J]. Bulletin of Microbiology, 2019, 46(11):2909-2918. | |
| [60] |
王艳云, 郭笃发. 黄河三角洲盐碱地土壤真菌多样性及其与土壤理化性质的关系[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2016, 28(11):1901-1907.
DOI |
|
WANG Yanyun, GUO Dufa. Soil fungal diversity and its relationship with soil physical and chemical properties in the Yellow River Delta[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2016, 28(11):1901-1907.
DOI |
| [1] | 王丹丹, 李燕, 张庆银, 李世东, 庞永超, 马琨芝, 马龙, 牛瑞生, 钟增明, 齐连芬, 师建华. 不同微生物菌处理对番茄土壤微生物多样性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2248-2257. |
| [2] | 岳丽, 王卉, 山其米克, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 涂振东. 基于高通量测序的甜高粱青贮饲料中微生物群落分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2742-2750. |
| [3] | 李春艳, 刘芳婷, 张王斌. 基于高通量测序对引起苹果外观异常病原的鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(1): 171-177. |
| [4] | 李选文, 熊智, 王金华, 周艺萍, 熊忠平. 思茅松毛虫成虫肠道细菌多样性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(9): 2276-2287. |
| [5] | 艾海白尔·卡斯木, 樊永红, 迪拉热·海米提. 盐碱地白刺不同部位微生物群落高通量分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2562-2573. |
| [6] | 张星星, 黄新, 韩猛立, 蒋烈戈, 张倩, 高攀, 刘鹏, 吴桐忠, 钟发刚. 放牧与舍饲条件下夏洛莱牛肠道微生物多样性及差异分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(9): 1729-1739. |
| [7] | 翟亚萍, 王绍明, 刘鸯, 杨盼, 张霞, 赵祥, 刘丹. 不同种植地苜蓿根际土壤细菌群落结构多样性差异分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(5): 955-964. |
| [8] | 迪拉热·海米提, 樊永红, 王伟楠, 喻文丽, 艾海白尔·卡斯木. 盐穗木叶片及根际土壤微生物群落高通量分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(4): 731-740. |
| [9] | 刘建成, 曾军, 丁峰, 许先查, 窦晶晶, 陈开旭, 李凤鸣, 高雁. 再生固体牛粪垫料中细菌多样性分析及评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2334-2341. |
| [10] | 刘海洋, 王伟, 张仁福, 雷斌, 姚举. 施用生物菌剂对棉田土壤细菌群落多样性及种群结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2256-2264. |
| [11] | 杨洁萍, 周丽, 马丽, 全绍文, 覃阳, 牛建新. 基于高通量测序的技术检测梨树病毒[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(8): 1503-1513. |
| [12] | 王伟, 布丽根·加冷别克, 胡晓东, 夏俊芳, 张志东, 顾美英, 武运. 基于高通量测序技术的酿酒葡萄产区土壤微生物多样性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(5): 859-868. |
| [13] | 王志方,陈竞,代金平,古丽努尔·艾合买提,王小武,秦新政,李晨华,杨新平. 棉秸秆自然腐解过程中细菌菌群多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(1): 111-119. |
| [14] | 顾美英, 徐万里, 张志东, 唐光木, 刘洪亮, 李志强, 刘晓伟, 蒲胜海, 冯雷, 张计峰. 施用棉秆炭连作棉花根际土壤真菌多样性与土壤理化性质及黄萎病的相关性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(9): 1698-1709. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 81
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 358
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||