

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2021, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (11): 2122-2132.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2021.11.019
• Facility Agriculture·Agricultural Product Analysis and Detection • Previous Articles Next Articles
SU Lihe( ), ZHANG Fanfan, WANG Xuzhe, SONG Lei, YU Xue, HE Tingting, MA Chunhui(
), ZHANG Fanfan, WANG Xuzhe, SONG Lei, YU Xue, HE Tingting, MA Chunhui( )
)
Received:2020-10-20
Online:2021-11-20
Published:2021-12-16
Correspondence author:
MA Chunhui
Supported by:
苏力合( ), 张凡凡, 王旭哲, 宋磊, 俞雪, 贺婷婷, 马春晖(
), 张凡凡, 王旭哲, 宋磊, 俞雪, 贺婷婷, 马春晖( )
)
通讯作者:
马春晖
作者简介:苏力合(1995-),女,新疆塔城人,硕士研究生,研究方向为饲草生产与加工,(E-mail) 949366910@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
SU Lihe, ZHANG Fanfan, WANG Xuzhe, SONG Lei, YU Xue, HE Tingting, MA Chunhui. Effects of Natural Snow Cover on Winter Survival Rate and Cold Resistance of Five Different Fall Dormancy Alfalfa[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(11): 2122-2132.
苏力合, 张凡凡, 王旭哲, 宋磊, 俞雪, 贺婷婷, 马春晖. 自然覆雪对5个不同秋眠级紫花苜蓿越冬率及抗寒性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(11): 2122-2132.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: http://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2021.11.019
| 月份(月) Month (M) | 平均温度 Average temperature (℃) | 极端低温 Minimum temperature (℃) | 覆雪厚度 Snowfall (cm) | 降水量 Precipitation (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年 | 9 | 18 | 6 | - | 16 |
| 10 | 9 | -3 | - | 18 | |
| 11 | -2 | -19 | 8 | 19 | |
| 12 | -10 | -17 | 14 | 15 | |
| 2020年 | 1 | -12 | -20 | 19 | 9 |
| 2 | -7 | -19 | 24 | 8 | |
| 3 | 3 | -15 | 20 | 13 | |
| 4 | 16 | 1 | - | 25 | |
| 5 | 20 | 7 | - | 23 | |
Table 1 Weather conditions for the trial year (September 2019-may 2020)
| 月份(月) Month (M) | 平均温度 Average temperature (℃) | 极端低温 Minimum temperature (℃) | 覆雪厚度 Snowfall (cm) | 降水量 Precipitation (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年 | 9 | 18 | 6 | - | 16 |
| 10 | 9 | -3 | - | 18 | |
| 11 | -2 | -19 | 8 | 19 | |
| 12 | -10 | -17 | 14 | 15 | |
| 2020年 | 1 | -12 | -20 | 19 | 9 |
| 2 | -7 | -19 | 24 | 8 | |
| 3 | 3 | -15 | 20 | 13 | |
| 4 | 16 | 1 | - | 25 | |
| 5 | 20 | 7 | - | 23 | |
| 品种 Variety | 秋眠级 FD rate | 秋眠类型 FD type | 种子来源 Seed sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 肇东 Zhaodong | 1 | 秋眠型 | 黑龙江省农业科学院草业研究所 |
| 中苜2号 Zhongmu2 | 3 | 秋眠型 | 中国农科院北京畜牧研究所 |
| Archer | 5 | 半秋眠型 | 蓝德雷(北京)贸易有限公司 |
| 渝苜1号 Yumu1 | 7 | 非秋眠型 | 西南大学 |
| WL903 | 9 | 非秋眠型 | 北京正道生态科技有限公司 |
Table 2 Fall dormancy rate and type of alfalfa variety
| 品种 Variety | 秋眠级 FD rate | 秋眠类型 FD type | 种子来源 Seed sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| 肇东 Zhaodong | 1 | 秋眠型 | 黑龙江省农业科学院草业研究所 |
| 中苜2号 Zhongmu2 | 3 | 秋眠型 | 中国农科院北京畜牧研究所 |
| Archer | 5 | 半秋眠型 | 蓝德雷(北京)贸易有限公司 |
| 渝苜1号 Yumu1 | 7 | 非秋眠型 | 西南大学 |
| WL903 | 9 | 非秋眠型 | 北京正道生态科技有限公司 |
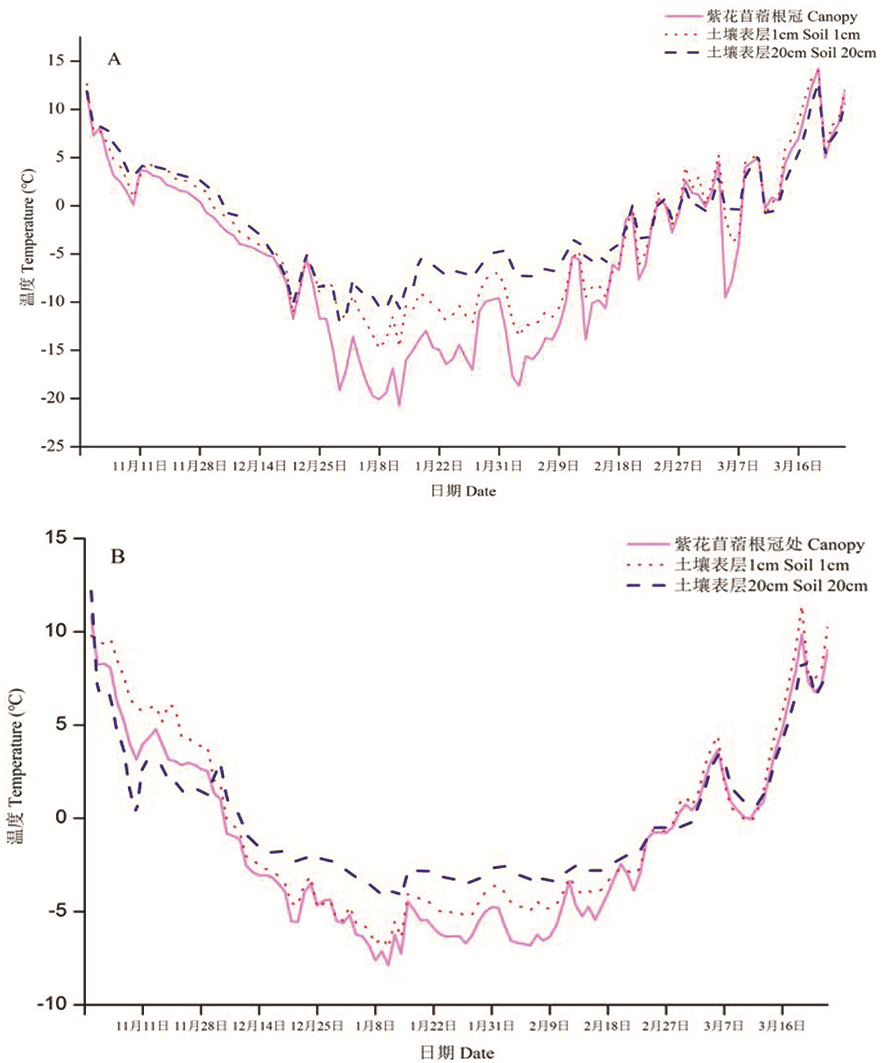
Fig.1 Effect of snow cover and no-cover treatment on temperature of alfalfa canopy level and soil depths (1-20 cm) Note: 1A: no-snow cover;1B: natural snowfall
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 8.84±0.15d | 24.96±1.91a | 21.79±0.81b | 22.32±1.47b | 16.03±0.83c | 10.12±0.58d |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 8.84±0.15e | 24.96±1.91b | 30.85±2.00a | 26.42±1.56b | 21.81±1.62c | 12.48±1.03d |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 8.85±0.21f | 25.43±0.87a | 23.62±1.89b | 15.58±0.76d | 20.31±0.90c | 10.00±0.48e |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 8.85±0.21e | 25.43±0.87ab | 26.06±0.58a | 24.80±0.60b | 16.28±0.91c | 11.86±0.39d |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 8.93±0.02e | 18.69±0.64b | 17.69±0.94b | 24.98±1.13a | 14.23±1.22c | 9.30±0.72d |
| 自然降雪 | 8.93±0.02e | 18.69±0.64c | 26.98±0.30b | 29.65±1.13a | 17.16±1.38d | 12.30±0.68e | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 7.82±0.47e | 19.80±1.85b | 15.93±1.22c | 24.50±1.23a | 12.72±0.73d | 11.29±0.50d |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 7.82±0.47d | 19.80±1.85b | 26.70±0.39a | 27.18±0.85a | 13.48±0.42c | 12.26±1.46c |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 7.99±0.32f | 19.49±0.67c | 27.77±0.25a | 23.19±0.45b | 14.91±0.91d | 9.50±0.15e |
| 自然降雪 | 7.99±0.32e | 19.49±0.67c | 30.98±0.99a | 25.39±0.39b | 17.62±0.99c | 11.47±0.75d | |
Table 3 Changes of water soluble carbon content in alfalfa roots(% DM)
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 8.84±0.15d | 24.96±1.91a | 21.79±0.81b | 22.32±1.47b | 16.03±0.83c | 10.12±0.58d |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 8.84±0.15e | 24.96±1.91b | 30.85±2.00a | 26.42±1.56b | 21.81±1.62c | 12.48±1.03d |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 8.85±0.21f | 25.43±0.87a | 23.62±1.89b | 15.58±0.76d | 20.31±0.90c | 10.00±0.48e |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 8.85±0.21e | 25.43±0.87ab | 26.06±0.58a | 24.80±0.60b | 16.28±0.91c | 11.86±0.39d |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 8.93±0.02e | 18.69±0.64b | 17.69±0.94b | 24.98±1.13a | 14.23±1.22c | 9.30±0.72d |
| 自然降雪 | 8.93±0.02e | 18.69±0.64c | 26.98±0.30b | 29.65±1.13a | 17.16±1.38d | 12.30±0.68e | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 7.82±0.47e | 19.80±1.85b | 15.93±1.22c | 24.50±1.23a | 12.72±0.73d | 11.29±0.50d |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 7.82±0.47d | 19.80±1.85b | 26.70±0.39a | 27.18±0.85a | 13.48±0.42c | 12.26±1.46c |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 7.99±0.32f | 19.49±0.67c | 27.77±0.25a | 23.19±0.45b | 14.91±0.91d | 9.50±0.15e |
| 自然降雪 | 7.99±0.32e | 19.49±0.67c | 30.98±0.99a | 25.39±0.39b | 17.62±0.99c | 11.47±0.75d | |
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 6.32±0.33d | 7.72±0.35c | 15.12±1.34a | 10.88±1.27b | 7.23±0.21cd | 2.66±0.64e |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 6.32±0.33de | 7.72±0.35d | 18.55±0.89a | 14.44±1.45b | 11.83±1.14c | 5.27±0.85e |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 2.60±0.21d | 6.00±0.65c | 16.09±1.49a | 9.27±0.21b | 7.97±1.30b | 2.90±1.12d |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 2.60±0.21d | 6.00±0.65c | 14.23±1.55a | 11.56±0.83b | 10.65±0.65b | 3.86±1.05d |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 5.15±0.40d | 6.02±0.72cd | 14.40±1.49a | 12.71±0.66b | 7.38±0.52c | 4.72±1.29d |
| 自然降雪 | 5.15±0.40de | 6.02±0.72d | 18.72±0.82a | 14.41±0.85b | 9.14±0.96c | 4.12±0.43e | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 4.96±0.53cd | 6.84±0.68b | 14.25±1.25a | 12.75±0.59a | 6.18±0.41bc | 3.95±1.38d |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 4.96±0.53e | 6.84±0.68d | 17.80±1.55a | 13.59±1.32b | 8.77±0.66c | 4.62±0.74e |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 5.60±0.48b | 6.63±0.45b | 12.07±3.59a | 10.67±1.15a | 6.53±0.44b | 5.07±0.31b |
| 自然降雪 | 5.60±0.48e | 6.63±0.45e | 18.71±2.40a | 13.73±0.39b | 10.61±1.50c | 8.76±0.30d | |
Table 4 Changes of soluble protein content in alfalfa roots(mg/g DM)
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 6.32±0.33d | 7.72±0.35c | 15.12±1.34a | 10.88±1.27b | 7.23±0.21cd | 2.66±0.64e |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 6.32±0.33de | 7.72±0.35d | 18.55±0.89a | 14.44±1.45b | 11.83±1.14c | 5.27±0.85e |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 2.60±0.21d | 6.00±0.65c | 16.09±1.49a | 9.27±0.21b | 7.97±1.30b | 2.90±1.12d |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 2.60±0.21d | 6.00±0.65c | 14.23±1.55a | 11.56±0.83b | 10.65±0.65b | 3.86±1.05d |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 5.15±0.40d | 6.02±0.72cd | 14.40±1.49a | 12.71±0.66b | 7.38±0.52c | 4.72±1.29d |
| 自然降雪 | 5.15±0.40de | 6.02±0.72d | 18.72±0.82a | 14.41±0.85b | 9.14±0.96c | 4.12±0.43e | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 4.96±0.53cd | 6.84±0.68b | 14.25±1.25a | 12.75±0.59a | 6.18±0.41bc | 3.95±1.38d |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 4.96±0.53e | 6.84±0.68d | 17.80±1.55a | 13.59±1.32b | 8.77±0.66c | 4.62±0.74e |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 5.60±0.48b | 6.63±0.45b | 12.07±3.59a | 10.67±1.15a | 6.53±0.44b | 5.07±0.31b |
| 自然降雪 | 5.60±0.48e | 6.63±0.45e | 18.71±2.40a | 13.73±0.39b | 10.61±1.50c | 8.76±0.30d | |
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 45.27±1.59e | 348.24±4.05cd | 808.91±0.77a | 405.69±9.91c | 706.49±8.18b | 310.62±11.00d |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 45.27±1.59e | 348.24±4.05d | 1 066.93±8.38a | 627.86±4.90c | 800.51±3.41b | 450.58±4.56d |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 77.08±0.58e | 378.43±12.29bc | 341.80±2.80c | 426.08±2.45b | 700.43±2.24a | 146.51±8.98d |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 77.08±0.58f | 378.43±12.29e | 1 384.43±7.03a | 967.42±1.76b | 771.88±6.96c | 529.92±9.73d |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 94.56±1.15d | 322.06±8.77c | 910.02±0.53a | 536.91±5.63b | 561.73±8.98b | 398.18±6.47c |
| 自然降雪 | 94.56±1.15e | 322.06±8.77d | 1 111.96±0.54a | 713.24±6.75b | 768.57±0.84b | 476.74±2.50c | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 88.03±1.89d | 349.96±3.88b | 353.65±0.52b | 395.03±3.56a | 271.89±1.74c | 373.56±4.07ab |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 88.03±1.89e | 349.96±3.88d | 803.66±0.19a | 480.40±11.16bc | 547.87±1.79b | 427.03±7.15cd |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 187.32±0.18d | 750.22±3.47b | 1 145.21±3.04a | 467.68±5.20c | 750.78±3.62b | 421.85±8.04c |
| 自然降雪 | 187.32±0.18d | 750.22±3.47c | 1 287.30±9.07a | 962.65±6.03b | 1 192.00±5.46a | 589.97±9.08c | |
Table 5 Changes of proline content in alfalfa roots(μg/g DM)
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 45.27±1.59e | 348.24±4.05cd | 808.91±0.77a | 405.69±9.91c | 706.49±8.18b | 310.62±11.00d |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 45.27±1.59e | 348.24±4.05d | 1 066.93±8.38a | 627.86±4.90c | 800.51±3.41b | 450.58±4.56d |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 77.08±0.58e | 378.43±12.29bc | 341.80±2.80c | 426.08±2.45b | 700.43±2.24a | 146.51±8.98d |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 77.08±0.58f | 378.43±12.29e | 1 384.43±7.03a | 967.42±1.76b | 771.88±6.96c | 529.92±9.73d |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 94.56±1.15d | 322.06±8.77c | 910.02±0.53a | 536.91±5.63b | 561.73±8.98b | 398.18±6.47c |
| 自然降雪 | 94.56±1.15e | 322.06±8.77d | 1 111.96±0.54a | 713.24±6.75b | 768.57±0.84b | 476.74±2.50c | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 88.03±1.89d | 349.96±3.88b | 353.65±0.52b | 395.03±3.56a | 271.89±1.74c | 373.56±4.07ab |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 88.03±1.89e | 349.96±3.88d | 803.66±0.19a | 480.40±11.16bc | 547.87±1.79b | 427.03±7.15cd |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 187.32±0.18d | 750.22±3.47b | 1 145.21±3.04a | 467.68±5.20c | 750.78±3.62b | 421.85±8.04c |
| 自然降雪 | 187.32±0.18d | 750.22±3.47c | 1 287.30±9.07a | 962.65±6.03b | 1 192.00±5.46a | 589.97±9.08c | |
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 74.54±2.45c | 62.80±3.08d | 52.82±3.49d | 146.27±12.23a | 92.96±12.07b | 77.91±3.35c |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 74.54±2.45c | 62.80±3.08d | 41.68±3.69e | 135.50±0.23a | 83.46±7.19b | 70.87±1.41c |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 92.04±9.07c | 46.63±2.93e | 74.69±1.98d | 137.10±2.40a | 109.09±9.65b | 99.22±2.09bc |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 92.04±9.07b | 46.63±2.93d | 61.13±3.15c | 111.99±5.80a | 90.15±8.24b | 82.62±2.42b |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 92.68±4.04c | 42.09±4.59e | 58.89±1.81d | 174.76±8.63a | 119.73±7.83b | 98.14±4.80c |
| 自然降雪 | 92.68±4.04bc | 42.09±4.59e | 52.40±2.80d | 137.75±4.46a | 97.30±4.63b | 86.20±5.94c | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 66.76±2.32d | 53.90±7.60e | 63.38±4.15d | 162.34±0.23a | 129.96±5.65b | 106.24±0.78c |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 66.76±2.32c | 53.90±7.60cd | 44.10±2.43d | 151.71±5.69a | 102.49±11.00b | 92.32±9.52b |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 80.05±1.29c | 69.03±5.32c | 72.32±3.66c | 221.54±4.27a | 119.03±6.40b | 109.53±2.01b |
| 自然降雪 | 80.05±1.29cd | 69.03±5.32d | 46.87±3.78e | 185.79±9.14a | 106.97±0.61b | 89.01±2.07c | |
Table 6 Changes of malondialdehyde content in alfalfa roots(μmol/g DM)
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 74.54±2.45c | 62.80±3.08d | 52.82±3.49d | 146.27±12.23a | 92.96±12.07b | 77.91±3.35c |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 74.54±2.45c | 62.80±3.08d | 41.68±3.69e | 135.50±0.23a | 83.46±7.19b | 70.87±1.41c |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 92.04±9.07c | 46.63±2.93e | 74.69±1.98d | 137.10±2.40a | 109.09±9.65b | 99.22±2.09bc |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 92.04±9.07b | 46.63±2.93d | 61.13±3.15c | 111.99±5.80a | 90.15±8.24b | 82.62±2.42b |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 92.68±4.04c | 42.09±4.59e | 58.89±1.81d | 174.76±8.63a | 119.73±7.83b | 98.14±4.80c |
| 自然降雪 | 92.68±4.04bc | 42.09±4.59e | 52.40±2.80d | 137.75±4.46a | 97.30±4.63b | 86.20±5.94c | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 66.76±2.32d | 53.90±7.60e | 63.38±4.15d | 162.34±0.23a | 129.96±5.65b | 106.24±0.78c |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 66.76±2.32c | 53.90±7.60cd | 44.10±2.43d | 151.71±5.69a | 102.49±11.00b | 92.32±9.52b |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 80.05±1.29c | 69.03±5.32c | 72.32±3.66c | 221.54±4.27a | 119.03±6.40b | 109.53±2.01b |
| 自然降雪 | 80.05±1.29cd | 69.03±5.32d | 46.87±3.78e | 185.79±9.14a | 106.97±0.61b | 89.01±2.07c | |
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 160.45±13.24c | 281.70±4.63a | 141.32±3.01c | 153.47±16.10c | 275.49±2.89a | 236.95±2.49b |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 160.45±13.24d | 281.704.63b | 191.66±4.12c | 168.96±4.19cd | 343.63±7.67a | 264.14±7.59b |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 197.40±0.93c | 252.40±8.37a | 169.12±6.22d | 188.48±7.09cd | 250.22±2.87a | 226.21±4.30b |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 197.40±0.93d | 252.40±8.37c | 209.51±2.78d | 262.78±4.80bc | 362.28±5.77a | 291.77±0.42b |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 152.73±6.28c | 239.45±9.81b | 147.23±4.12c | 140.66±3.43c | 302.06±2.98a | 256.64±11.39b |
| 自然降雪 | 152.73±6.28d | 239.45±9.81c | 176.05±2.87d | 155.62±7.20d | 334.72±2.42a | 294.13±3.24b | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 217.38±7.01d | 236.27±9.73c | 151.07±6.37e | 139.52±4.81e | 283.86±1.59b | 302.79±8.86a |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 217.38±7.01cd | 236.27±9.73c | 194.98±2.56d | 210.96±3.51cd | 352.66±7.72a | 321.47±4.06b |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 205.99±3.80b | 227.22±5.47ab | 146.46±9.56c | 142.70±4.21c | 261.31±1.54a | 190.38±7.22b |
| 自然降雪 | 205.99±3.80cd | 227.22±5.47bc | 157.56±8.92e | 186.85±7.36d | 322.60±9.90a | 249.69±11.00b | |
Table 7 Changes of superoxide dismutase content in alfalfa roots(U/g FW)
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 160.45±13.24c | 281.70±4.63a | 141.32±3.01c | 153.47±16.10c | 275.49±2.89a | 236.95±2.49b |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 160.45±13.24d | 281.704.63b | 191.66±4.12c | 168.96±4.19cd | 343.63±7.67a | 264.14±7.59b |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 197.40±0.93c | 252.40±8.37a | 169.12±6.22d | 188.48±7.09cd | 250.22±2.87a | 226.21±4.30b |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 197.40±0.93d | 252.40±8.37c | 209.51±2.78d | 262.78±4.80bc | 362.28±5.77a | 291.77±0.42b |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 152.73±6.28c | 239.45±9.81b | 147.23±4.12c | 140.66±3.43c | 302.06±2.98a | 256.64±11.39b |
| 自然降雪 | 152.73±6.28d | 239.45±9.81c | 176.05±2.87d | 155.62±7.20d | 334.72±2.42a | 294.13±3.24b | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 217.38±7.01d | 236.27±9.73c | 151.07±6.37e | 139.52±4.81e | 283.86±1.59b | 302.79±8.86a |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 217.38±7.01cd | 236.27±9.73c | 194.98±2.56d | 210.96±3.51cd | 352.66±7.72a | 321.47±4.06b |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 205.99±3.80b | 227.22±5.47ab | 146.46±9.56c | 142.70±4.21c | 261.31±1.54a | 190.38±7.22b |
| 自然降雪 | 205.99±3.80cd | 227.22±5.47bc | 157.56±8.92e | 186.85±7.36d | 322.60±9.90a | 249.69±11.00b | |
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 80.05±8.88e | 184.07±16.05d | 353.55±6.92b | 427.57±9.69a | 291.74±7.58c | 149.35±6.68d |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 80.05±8.88d | 184.07±16.05c | 465.24±7.06b | 540.30±3.50a | 498.63±4.49ab | 180.43±6.40c |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 62.10±5.65d | 159.08±5.29c | 366.71±6.98b | 456.34±2.55a | 335.56±3.35b | 151.88±9.72c |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 62.10±5.65d | 159.08±5.29c | 479.84±4.21b | 554.80±1.18a | 517.65±1.60ab | 190.00±4.71c |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 83.95±5.34d | 159.54±2.59c | 255.57±2.76b | 322.34±9.90a | 276.13±0.27b | 129.38±2.65c |
| 自然降雪 | 83.95±5.34e | 159.54±2.59d | 452.70±5.63c | 561.15±9.38a | 491.52±9.98b | 153.40±2.94d | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 47.41±5.29d | 129.84±4.75c | 270.53±1.03b | 380.67±3.66a | 282.94±4.44b | 130.64±2.46c |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 47.41±5.29e | 129.84±4.75d | 409.02±9.90b | 495.42±2.21a | 436.76±10.19b | 175.47±5.19c |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 78.97±11.46d | 156.74±0.38c | 323.52±5.10b | 400.18±4.16a | 264.49±1.17b | 137.93±3.17cd |
| 自然降雪 | 78.9711.46d | 156.74±0.38c | 435.79±8.00b | 552.94±9.25a | 460.17±7.28b | 175.46±2.02c | |
Table 8 Changes of peroxidase content in alfalfa roots([μ/(g·min)] FW)
| 品种 Variety | 覆雪处理 Snow depth | 采样期 Year-month | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019年9月 | 2019年10月 | 2019年11月 | 2019年12月 | 2020年1月 | 2020年5月 | ||
| 肇东 | 无覆雪 | 80.05±8.88e | 184.07±16.05d | 353.55±6.92b | 427.57±9.69a | 291.74±7.58c | 149.35±6.68d |
| Zhaodong | 自然降雪 | 80.05±8.88d | 184.07±16.05c | 465.24±7.06b | 540.30±3.50a | 498.63±4.49ab | 180.43±6.40c |
| 中苜2号 | 无覆雪 | 62.10±5.65d | 159.08±5.29c | 366.71±6.98b | 456.34±2.55a | 335.56±3.35b | 151.88±9.72c |
| Zhongmu2 | 自然降雪 | 62.10±5.65d | 159.08±5.29c | 479.84±4.21b | 554.80±1.18a | 517.65±1.60ab | 190.00±4.71c |
| Archer | 无覆雪 | 83.95±5.34d | 159.54±2.59c | 255.57±2.76b | 322.34±9.90a | 276.13±0.27b | 129.38±2.65c |
| 自然降雪 | 83.95±5.34e | 159.54±2.59d | 452.70±5.63c | 561.15±9.38a | 491.52±9.98b | 153.40±2.94d | |
| 渝苜1号 | 无覆雪 | 47.41±5.29d | 129.84±4.75c | 270.53±1.03b | 380.67±3.66a | 282.94±4.44b | 130.64±2.46c |
| Yumu1 | 自然降雪 | 47.41±5.29e | 129.84±4.75d | 409.02±9.90b | 495.42±2.21a | 436.76±10.19b | 175.47±5.19c |
| WL903 | 无覆雪 | 78.97±11.46d | 156.74±0.38c | 323.52±5.10b | 400.18±4.16a | 264.49±1.17b | 137.93±3.17cd |
| 自然降雪 | 78.9711.46d | 156.74±0.38c | 435.79±8.00b | 552.94±9.25a | 460.17±7.28b | 175.46±2.02c | |

Fig.2 Effect of snow depth on the winter surviving rate of alfalfa with different fall dormancy Note:The different lower case letters means the significiant differences at 0.05 level
| 覆雪厚度 Snow depth | 品种 Cultivar | 秋眠级 Rating | 可溶性糖 SS | 可溶性 蛋白 SP | 游离脯 氨酸 Pro | 丙二醛 MDA | 超氧化物 歧化酶 SOD | 过氧化 物酶 POD | 越冬率 WSR | 平均值 Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无覆雪 | 肇东 | 1 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.75 |
| 中苜2号 | 3 | 0.87 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 0.59 | |
| Archer | 5 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.42 | |
| 渝苜1号 | 7 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.32 | |
| WL903 | 9 | 1.00 | 0.31 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.39 | |
| 自然降雪 | 肇东 | 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 0.27 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.79 |
| 中苜2号 | 3 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.69 | |
| Archer | 5 | 0.36 | 0.57 | 0.35 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.49 | |
| 渝苜1号 | 7 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 0.81 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.35 | |
| WL903 | 9 | 0.59 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.46 |
Table 9 Membership function analysis of cold resistance and overwintering rate of alfalfa of fall dormancy grade under snow cover and no snow cover
| 覆雪厚度 Snow depth | 品种 Cultivar | 秋眠级 Rating | 可溶性糖 SS | 可溶性 蛋白 SP | 游离脯 氨酸 Pro | 丙二醛 MDA | 超氧化物 歧化酶 SOD | 过氧化 物酶 POD | 越冬率 WSR | 平均值 Average |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 无覆雪 | 肇东 | 1 | 0.76 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 1.00 | 0.48 | 0.75 | 1.00 | 0.75 |
| 中苜2号 | 3 | 0.87 | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.69 | 0.70 | 1.00 | 0.78 | 0.59 | |
| Archer | 5 | 0.11 | 1.00 | 0.52 | 0.52 | 0.41 | 0.00 | 0.38 | 0.42 | |
| 渝苜1号 | 7 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 0.00 | 0.53 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.07 | 0.32 | |
| WL903 | 9 | 1.00 | 0.31 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.44 | 0.00 | 0.39 | |
| 自然降雪 | 肇东 | 1 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.28 | 1.00 | 0.27 | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.79 |
| 中苜2号 | 3 | 0.33 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.86 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.69 | |
| Archer | 5 | 0.36 | 0.57 | 0.35 | 0.64 | 0.01 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.49 | |
| 渝苜1号 | 7 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.61 | 0.81 | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.35 | |
| WL903 | 9 | 0.59 | 0.99 | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.62 | 0.00 | 0.46 |
| [1] | 王晓龙, 米福贵, 李红, 等. 不同秋眠级苜蓿产量、品质及越冬率比较[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(6):7-13. |
| WANG Xiaolong, MI Fugui, LI Hong, et al. Comparison of yield,nutrition quality and winter surviving rate of alfalfa varieties with different fall dormancy levels[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Sciences Ed.), 2019, 47(6):7-13. | |
| [2] | 段保宁, 张晶晶. 苜蓿产业发展现状及展望[J]. 今日畜牧兽医, 2019, 35(6):74-75. |
| DUAN Baoning, ZHANG Jingjing. The development status and prospect of alfalfa industry[J]. Today Animay Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 35(6):74-75. | |
| [3] | Mervi M Seppnen, Alitalo V, Hanna B?ckstr?m , et al. Growth,freezing tolerance and yield performance of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars grown under controlled and field conditions in the northern latitudes[J]. Revue Canadienne De Phytotechnie, 2018, 98(5). |
| [4] | 刘志英, 李西良, 李峰, 等. 越冬紫花苜蓿根系性状与秋眠性的关系及其抗寒效应[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(9):1689-1701. |
| LIU Zhiying, LI Xiliang, LI Feng, et al. Response of alfalfa root traits to fall dormancy and its effect on winter hardiness.[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(9):1689-1701. | |
| [5] | Volenec J J, Cunningham S M, Haagenson D M, et al. Physiological genetics of alfalfa improvement: past failures,future prospects[J]. Field Crops Research, 2002, 75(2-3):100-110. |
| [6] |
Castonguay Y, Réal Michaud, Nadeau P, et al. An Indoor Screening Method for Improvement of Freezing Tolerance in Alfalfa[J]. Crop Science, 2009, 49(3):809-818.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Schwab P M, Barnes D K, Sheaffer C C, et al. Factors Affecting a Laboratory Evaluation of Alfalfa Cold Tolerance[J]. Crop Science, 1996, 36(2):318-324.
DOI URL |
| [8] | 岳亚飞, 王旭哲, 苗芳, 等. 覆雪厚度对不同秋眠级苜蓿抗寒性及越冬率的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(8):98-106. |
| YUE Yafei, WANG Xuzhe, MIAO Fang, et al. Effect of snow cover thickness on cold resistance and winter surviving rates in alfalfa cultivars with different fall dormancies.[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2009, 25(8):98-106. | |
| [9] | 李如来, 申晓慧, 姜成, 等. 积雪覆盖对苜蓿越冬及返青生长的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2016, 38(1):67-73,92. |
| LI Rulai, SHEN Xiaohui, JIANG Cheng, et al. Effects of Snow Cover on Alfalfa Over-wintering and Turning Green.[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2016, 38(1):67-73,92. | |
| [10] | 于辉, 刘惠青, 王静. 灌水、覆盖对阿尔冈金苜蓿越冬率及田间土壤温湿度的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2015, 37(6):107-111. |
| YU Hui, LIU Huiqing, WANG Jing. Effects of Cover and Irrigation on Winter Surviving Rate,Soil Temperature and Soil Moisture of Algonquin Alfalfa[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2015, 37(6):107-111. | |
| [11] |
刘志英, 李西良, 李峰, 等. 紫花苜蓿秋眠性对低温驯化过程与越冬耐寒适应的作用机理[J]. 植物生态学报, 2015, 39(6):635-648.
DOI |
|
LIU Zhiying, LI Xiliang, LI Feng, et al. Mechanisms underlying the effects of fall dormancy on the cold acclimation and winter hardiness ofMedicago sativa[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2015, 39(6):635-648.
DOI |
|
| [12] | 付强, 侯仁杰, 王子龙, 等. 积雪覆盖下土壤热状况及其对气象因素的响应研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2015, 46(7):154-161. |
| FU Qiang, HOU Renjie, WANG Zilong, et al. Soil Thermal Regime under Snow Cover and Its Response to Meteorological Factors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(7):154-161. | |
| [13] | Cunningham S M, Gana J A, Volenec J J, et al. Winter Hardiness,Root Physiology,and Gene Expression in Successive Fall Dormancy Selections from 'Mesilla' and 'CUF 101' Alfalfa[J]. Crop Science, 2015, 41(4). |
| [14] | 方强恩, 张勃, 李宇泊, 等. 紫花苜蓿根颈芽越冬期间幼叶细胞超微结构的适应性变化[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(3):96-107. |
| FANG Qiangen, ZHANG Bo, LI Yubo, et al. Adaptive changes in the young leaf cell ultrastructure of crown buds inMedicago sativa (Leguminosae) during overwintering[J]. Acta PratacuLPurae Sinica, 2016, 25(3):96-107. | |
| [15] |
Castonguay, Y P, Nadeauand P. Lechasseur. Different accumulation of carbohydrates in alfalfa cultivars of contrasting winter hardiness[J]. Crop Science, 1995, 35:509-516.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Cunningham S M, Nadeau P, Castonguay Y, et al. Raffinose and Stachyose Accumulation,Galactinol Synthase Expression, and Winter Injury of Contrasting Alfalfa Germplasms[J]. Crop Science, 2003, 43(2):562-570.
DOI URL |
| [17] | 申晓慧, 姜成, 冯鹏, 等. 寒区6个紫花苜蓿品种根系中MDA含量及抗氧化酶活性的比较研究[J]. 作物杂志, 2015(4):88-91. |
| SHEN Xiaohui, JIANG Cheng, FENG Peng, et al. Comparison of MDA Content and Antioxidant Enzymes Activity of Several Alfafa Roots in Cold Region[J]. Crops, 2015,(4):88-91. | |
| [18] | 张璐, 石凤翎, 熊梅, 等. 苜蓿属三种牧草主要贮藏物质含量的变化[J]. 中国草地学报, 2014, 36(6):103-107. |
| ZHANG Lu, SHI Fengling, XIONG Mei, et al. Changes of Main Storage Substance Contents of ThreeMedicago Forage[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2014, 36(6):103-107. | |
| [19] | Mervi M Seppänen, Alitalo V, Hanna K, B?ckstr?m , et al. Growth,freezing tolerance and yield performance of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) cultivars grown under controlled and field conditions in the Northern latitudes[J]. Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2018, 98(5). |
| [20] | 南丽丽, 师尚礼, 朱新强, 等. 田间越冬期不同根型苜蓿根系的生理生化特性[J]. 核农学报, 2011, 25(2):369-374. |
| NAN Lili, SHI Shangli, ZHU Xinqiang, et al. Physiological and biochemical characteristics of root in different root type alfalfa cultivars in field during overwintering period[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 25(2):369-374. | |
| [21] | 陶雅, 孙启忠. 不同紫花苜蓿品种可溶性糖、全氮、丙二醛含量动态变化及其与抗寒性关系研究[J]. 中国农业科技导报, 2008,(S1):56-60. |
| TAO Ya, SUN Qizhong. Dynamic Variation of Soluble Sugar,Total Nitrogen and Malondialdehyde in Alfalfa Varieties and Their Effect on Alfalfa Cold Resistance.[J]. Journal of Agricultural Sciences and Technology, 2008,(S1):56-60. | |
| [22] | 张仲鹃. 6份苜蓿材料生物学特性及生理特性研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院硕士学位论文, 2019. |
| ZHANG Zhongjuan. Study on Biological and Physiological Characteristics of 6 Alfalfa Materials[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019. | |
| [23] | Bertrand A, Bipfubusa Mc, Claessens A, et al. Effect of photoperiod prior to cold acclimation on freezing tolerance and carbohydrate metabolism in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.)[J]. Plant Science An International Journal of Experimental Plant Biology, 2017, 264:122. |
| [1] | MA Mingjie, ZHAO Jinghua, LI Dongmin, YANG Shengchun, WANG Kexian, LI Chi. Effects of alflfa different irrigation methods on soil moisture and irrigation water use efficiency [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2306-2313. |
| [2] | LIU Min, JIN Juan, Abudoukayoumu Ayimaiti, FAN Dingyu, HAO Qing, YANG Lei, ZHAO Xiaomei, GENG Wenjuan. Evaluation of cold resistance of three fresh edible jujube cultivars in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(4): 916-924. |
| [3] | MA Hong, MENG Jie, LI Ning. Effects of Phosphorus Levels on Root Morphology and Plant Growth of Alfalfa Seedlings [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(3): 750-756. |
| [4] | ZHONG Xinnian, LIANG Qigan, XU Jianwei, XU Mengke, TANG Kaixiu, LI Zhibo. Effect of Low Temperature Stress in Bud Stage on Cotton Growth and Development [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(3): 551-557. |
| [5] | WANG Dongmei, PAN Hongsheng, LI Haiqiang, DING Ruifeng, Akedan Wuwaishi, LIU Jian, LI Haobin. Quantitatively Evaluate the Control Function of Predatory Natural Enemies on Cotton Aphids by DNA Molecular Detection Technology [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(11): 2661-2667. |
| [6] | ZHAI Yaping, WANG Shaoming, LIU Yang, YANG Pan, ZHANG Xia, ZHAO Xiang, LIU Dan. Study on Structural Diversity of Bacterial Community in Rhizosphere Soil of Alfalfa in Parts of Northern Foot of Tianshan Mountains [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(5): 955-964. |
| [7] | MA Tiecheng, ZHANG Hui. Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphate Fertilizer Application Rates on Growth Indicators and Yield of Alfalfa from Awei Irrigation District [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(8): 1535-1541. |
| [8] | SHI You, CHEN Shuying, LIU Jun, LUO Bingyu , WANG Jin. Study on Cold Resistance of Apple Dwarf Rootstock [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(3): 485-491. |
| [9] | DOU Xiaoli, HU Wenjing, LIU Fan, LIN Caiying, LI Kemei. Biological Characteristics of Pathogens Causing of Two Alfalfa Leaf Spot in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(10): 1863-1870. |
| [10] | Zaoreguli Reheman, Yeerlan Duishanbieke, WAN Jiang-chun, Aibibula Yimamu. Effects of Defect Fragrant Pear Juice Residue on Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(6): 1136-1141. |
| [11] | LI Yan-hong, Nuermaimaiti Aimeiti, Xiarepati Aizezi, Qiman Yunus. Comparative Study on Cold Resistance of Different Hippophae rhamnoides L. Varieties in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(12): 2289-2295. |
| [12] | ZHANG Ling, XI Lin-qiao, ZHANG Fan-fan, WANG Xu-zhe, MA Chun-hui. Dynamics of Microorganism, Fermentation and Nutritional Quality in Alfalfa Silage with Inferior Jujube Powder [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(10): 1929-1938. |
| [13] | Ablah Niyaz, LI Chao-hai, ZHANG Shi-kui, Amangul Osman, TANG Zhang-hu, DONG Sheng-li. Study on the Cold Resistance of F1 Generation Korla Fragrant Pear × Hesejujuli [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(4): 674-681. |
| [14] | ZHANG Na, HU Xin, FU Dai-hui, DING Jin-peng, LI Qun. Cloning and Expression Analysis of Cold Resistance Genes in Lepidium apetalum [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(4): 689-696. |
| [15] | CAO Biao, BAI Yun-gang, CHEN Jun-ke, XIAO Jun. Experimental Study on Alfalfa Leaf Area Index with Different Irrigation Treatments in Cold and Arid Regions [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(4): 737-745. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||