

新疆农业科学 ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (8): 2038-2045.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.08.026
李志强( ), 陈昱东, 吕光辉(
), 陈昱东, 吕光辉( ), 王金龙, 蒋腊梅, 王恒方, 李韩鹏, 张磊
), 王金龙, 蒋腊梅, 王恒方, 李韩鹏, 张磊
收稿日期:2022-11-07
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-08-14
通信作者:
吕光辉(1963-),男,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为生物多样性,(E-mail)ler@xju.edu.cn作者简介:李志强(1996-),男,新疆巴州人,硕士研究生,研究方向为生物多样性与生物保护,(E-mail)1458219167@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Zhiqiang( ), CHEN Yudong, LYU Guanghui(
), CHEN Yudong, LYU Guanghui( ), WANG Jinlong, JIANG Lamei, WANG Hengfang, LI Hanpeng, ZHANG Lei
), WANG Jinlong, JIANG Lamei, WANG Hengfang, LI Hanpeng, ZHANG Lei
Received:2022-11-07
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-08-14
Correspondence author:
LYU Guanghui(1963-), Male,doctor, professor, the research direction is global change and biodiversity, (E-mail)ler@xju.edu.cnSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究植物功能性状间的关系及其随土壤水、盐梯度的变化规律。【方法】以新疆艾比湖荒漠草本群落为对象,调查120个草本植物群落样方,并选中8个植物功能性状进行群落权重均值(CWM)计算,采用K-means聚类法将土壤水、盐含量聚类成3个梯度,利用多元因子分析法(MFA)、单因素方差分析、灰色关联度分析、CSR生态策略等方法,分析土壤水盐对植物功能性状的影响以及植物生态策略。【结果】(1)综合3个梯度变化,株高(H),冠幅(S)随土壤盐分升高表现出亲水性。(2)土壤水分对单个群落植物功能性状的影响在低水低盐梯度最强,土壤盐分对单个群落植物功能性状的影响在高水高盐梯度最强。(3)荒漠草本植物在土壤高水高盐和中水中盐梯度中植被倾向于C/CR,在土壤低水低盐梯度中更倾向于CSR策略。(4)植物S和叶面积(LA)在生态策略和土壤群落梯度间差异性最大。【结论】(1)植物冠幅面积和株高对土壤水分具有较强的敏感性,土壤盐分含量增加会造成草本植物对土壤水分更加依赖。(2)荒漠土壤对植物的影响并非是随土壤水、盐协同变化,土壤高水盐群落由盐胁迫主导,土壤低水盐群落由干旱胁迫主导,并且干旱胁迫对植物生长发育的影响更强烈。(3)受环境影响,艾比湖荒漠区草本植物主要形成了C/CR、C/CSR和CSR 3种生态策略,并且是受干旱胁迫影响,植物功能性状在土壤水盐梯度的变化中S和LA对3种生态策略响应最强烈。
中图分类号:
李志强, 陈昱东, 吕光辉, 王金龙, 蒋腊梅, 王恒方, 李韩鹏, 张磊. 荒漠草本植物功能性状的土壤水盐响应特征及生态策略[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2038-2045.
LI Zhiqiang, CHEN Yudong, LYU Guanghui, WANG Jinlong, JIANG Lamei, WANG Hengfang, LI Hanpeng, ZHANG Lei. Soil water-salt response characteristics and ecological strategies for functional traits of desert herbaceous plants[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(8): 2038-2045.
| 水盐梯度 Water and salt gradient | 样方数 Plots | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content (%) | 土壤含盐量 Soil salt content (g/kg) | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高High | 26 | 4.325±1.645a | 3.585±0.941a | 碱蓬、猪毛菜、小獐毛 |
| 中Middle | 58 | 1.719±0.421b | 2.538±0.529b | 碱蓬、沙漠绢蒿、小獐毛、对节刺 |
| 低Low | 36 | 0.843±0.202c | 1.584±0.448c | 碱蓬、沙漠绢蒿,对节刺、刺沙蓬 |
表1 样方水分、盐分聚类
Tab.1 Sample soil water and salt clustering and statistical parameters
| 水盐梯度 Water and salt gradient | 样方数 Plots | 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content (%) | 土壤含盐量 Soil salt content (g/kg) | 优势种 Dominant species |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 高High | 26 | 4.325±1.645a | 3.585±0.941a | 碱蓬、猪毛菜、小獐毛 |
| 中Middle | 58 | 1.719±0.421b | 2.538±0.529b | 碱蓬、沙漠绢蒿、小獐毛、对节刺 |
| 低Low | 36 | 0.843±0.202c | 1.584±0.448c | 碱蓬、沙漠绢蒿,对节刺、刺沙蓬 |
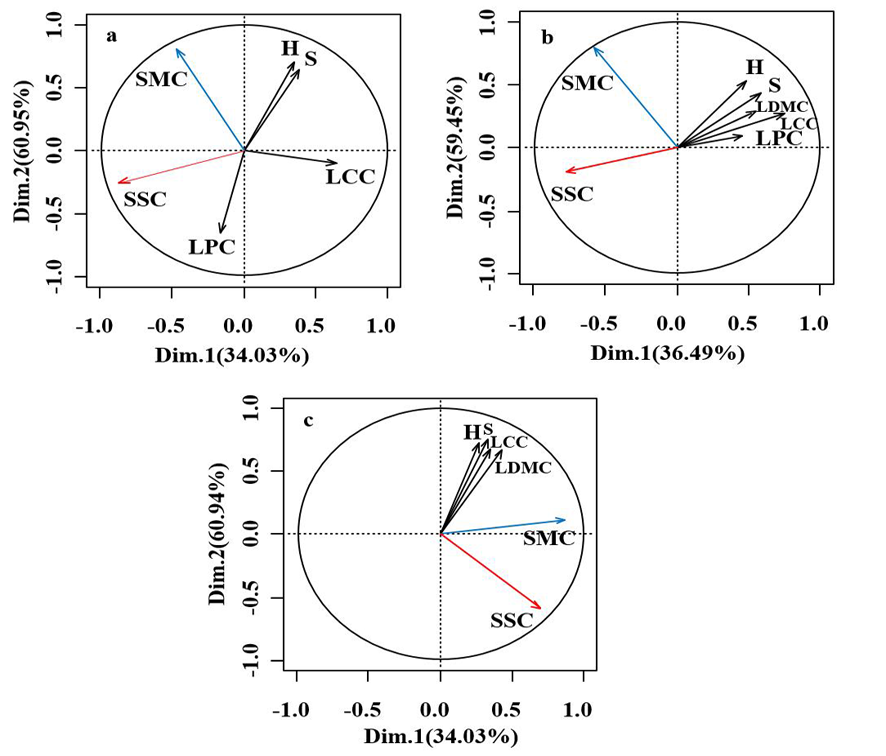
图1 功能性状与土壤水盐多元因子 注:小写字母a,b,c分别表示高、中、低水盐梯度
Fig.1 Multiple factor analysis of functional traits and soil water & salt Note: Lowercase letters a, b and c represent high, medium and low water salt gradients, respectively
| 性状 Trait | 土壤水分Soil water | 土壤盐分Soil salt | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Middle | Low | High | Middle | Low | |
| 比叶面积SLA Specific leaf area | 0.598 | 0.622 | 0.716 | 0.681 | 0.543 | 0.483 |
| 叶片干物质含量LDMC Leaf dry matter content | 0.583 | 0.482 | 0.699 | 0.647 | 0.553 | 0.437 |
| 冠幅面积S Grown area | 0.396 | 0.435 | 0.453 | 0.447 | 0.335 | 0.358 |
| 叶片碳含量LCC Leaf carbon content | 0.620 | 0.535 | 0.689 | 0.666 | 0.530 | 0.340 |
| 叶片氮含量LNC Leaf nitrogen content | 0.568 | 0.523 | 0.639 | 0.627 | 0.477 | 0.409 |
| 叶片磷含量LPC Leaf phosphorus content | 0.627 | 0.546 | 0.703 | 0.685 | 0.508 | 0.449 |
| 株高H Height | 0.554 | 0.533 | 0.648 | 0.653 | 0.556 | 0.498 |
| 叶面积LA Leaf area | 0.500 | 0.459 | 0.715 | 0.976 | 0.499 | 0.953 |
表2 功能性状与土壤水盐灰色关联度
Tab.2 Grey relational grade analysis between functional traits and soil water and salt
| 性状 Trait | 土壤水分Soil water | 土壤盐分Soil salt | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Middle | Low | High | Middle | Low | |
| 比叶面积SLA Specific leaf area | 0.598 | 0.622 | 0.716 | 0.681 | 0.543 | 0.483 |
| 叶片干物质含量LDMC Leaf dry matter content | 0.583 | 0.482 | 0.699 | 0.647 | 0.553 | 0.437 |
| 冠幅面积S Grown area | 0.396 | 0.435 | 0.453 | 0.447 | 0.335 | 0.358 |
| 叶片碳含量LCC Leaf carbon content | 0.620 | 0.535 | 0.689 | 0.666 | 0.530 | 0.340 |
| 叶片氮含量LNC Leaf nitrogen content | 0.568 | 0.523 | 0.639 | 0.627 | 0.477 | 0.409 |
| 叶片磷含量LPC Leaf phosphorus content | 0.627 | 0.546 | 0.703 | 0.685 | 0.508 | 0.449 |
| 株高H Height | 0.554 | 0.533 | 0.648 | 0.653 | 0.556 | 0.498 |
| 叶面积LA Leaf area | 0.500 | 0.459 | 0.715 | 0.976 | 0.499 | 0.953 |
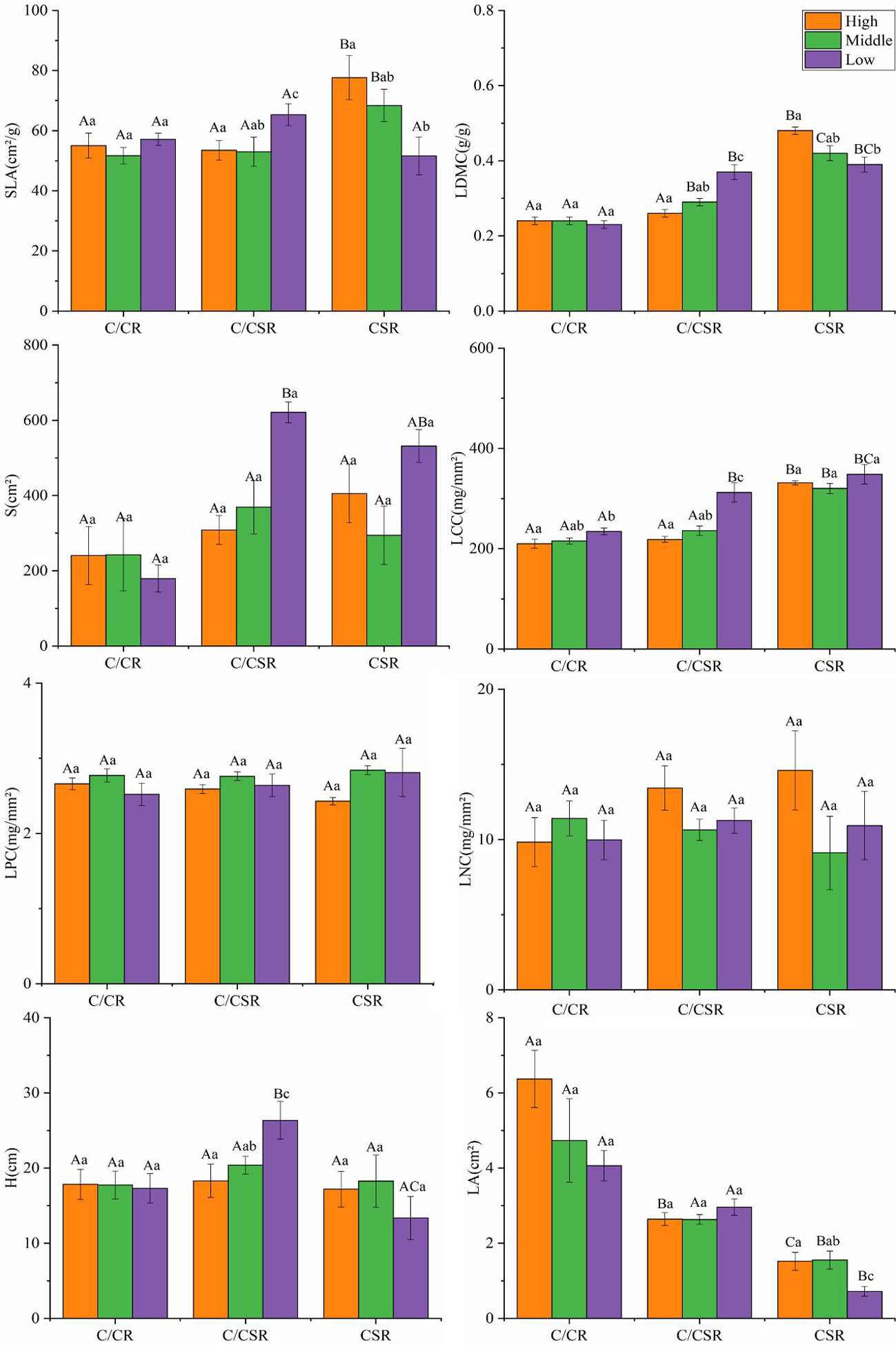
图3 3个水盐梯度功能性状植物生态策略方差 注:(P<0.05)。A,B,C,a,b,c表示差异性显著,大写字母为功能性状在同一水盐梯度群落下不同生态策略之间的差异,小写字母为相同生态策略中不同水盐梯度群落之间的差异
Fig.3 Analysis of variance of ecological strategies of three plants with water and salt gradient functional traits Note: (P<0.05).A, B, C, a, b and c represent significant difference.Uppercase letters represent the difference of functional traits among different ecological strategies in the same water-salt gradient community, and lowercase letters represent the difference between communities with different water-salt gradient in the same ecological strategy
| [1] |
何芸雨, 郭水良, 王喆. 植物功能性状权衡关系的研究进展[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(12): 1021-1035.
DOI |
|
HE Yunyu, GUO Shuiliang, WANG Zhe. Advances in research on functional trait trade-off relationships in plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2019, 43(12): 1021-1035.
DOI |
|
| [2] |
DÌaz S, Kattge J, Cornelissen J, et al. The global spectrum of plant form and function[J]. Nature, 2016, 529(7585): 167-171.
DOI |
| [3] |
Blonder B, Kapas R E, Dalton R M, et al. Microenvironment and functional-trait context dependence predict alpine plant community dynamics[J]. Journal of Ecology, 2018, 106(4): 1323-1337.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 张国庆, 杨雨玲, 唐爱国, 等. 新安江流域(屯溪段)浮游植物群落结构及其与环境因子的关系[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(2): 527-540. |
| ZHANG Guoqinng, YANG Yuling, TANG Aiguo, et al. Phytoplankton community structure and its relationship with environmental factors in the Xin’an River Basin (Tunxi Section)[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(2): 527-540. | |
| [5] | 栾志慧. 植物子叶生长及其功能性状研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2015. |
| LUAN Zhihui. Research on plant cotyledon growth and its functional traits[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2015. | |
| [6] |
杨锐, 张博睿, 王玲玲, 等. 元谋干热河谷植物功能性状组合的海拔梯度响应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2015, 24(1): 49-56.
DOI |
| YANG Rui, ZHANG Borui, WANG Lingling, et al. Altitudinal gradient response of plant functional trait assemblages in the Yuanmou Dry Heat Valley[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2015, 24(1): 49-56. | |
| [7] | 刘晓娟, 马克平. 植物功能性状研究进展[J]. 中国科学:生命科学, 2015, 45(4): 325-339. |
| LIU Xiaojuan, MA Keping. Advances in the study of functional traits in plants[J]. China Science: Life Sciences, 2015, 45(4): 325-339. | |
| [8] | 孙雪娇, 常顺利, 张毓涛, 等. 天山森林植物功能性状与碳库沿海拔梯度的变化[J] .生态学报, 2018, 38(14): 4994-5005. |
| SUN Xuejiao, CHANG Shunli, ZHANG Yutao, et al. Changes in plant functional traits and carbon pools along an altitudinal gradient in Tianshan forests[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(14): 4994-5005. | |
| [9] |
Palma E, Catford J A, Corlett R T, et al. Functional trait changes in the floras of 11 cities across the globe in response to urbanization[J]. Ecography, 2016, 40(7): 875-886.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Blonder B, Salinas N, Bentley L P, et al. Predicting trait-environment relationships for venation networks along an Andes-Amazon elevation gradient[J]. Ecology, 2017, 98(5): 1239-1255.
DOI PMID |
| [11] |
Grime J P. Vegetation classification by reference to strategies[J]. Nature, 1974, 250(5461): 26-31.
DOI |
| [12] |
Burton J I, Perakis S S, Mckenzie S C, et al. Intraspecific variability and reaction norms of forest understory plant species traits[J]. Functional Ecology, 2017, 31: 1881-1893.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Kattenborn T, Fassnacht F E, Pierce S, et al. Linking plant strategies and plant traits derived by radiative transfer modeling[J]. Journal of Vegetation Science, 2017, 28: 717-727.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Hodgson J G, Santini B A, Montserrat M G, et al. Trade-offs between seed and leaf size (seed-phytomer-leaf theory): Functional glue linking regenerative with life history strategies and taxonomy with ecology[J]. Annals of Botany, 2017, 120 (5): 633-652.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Guo W, Kleunen M V, Winter M, et al. The role of adaptive strategies in plant naturalization[J]. Ecology Letters, 2018, 21 (9): 1380-1389.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Pierce S, Negreiros D, Cerabolini B E L, et al. A global method for calculating plant CSR ecological strategies applied across biomes world-wide[J]. Functional Ecology, 2017, 31: 444-457.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Grime J P. Evidence for the existence of three primary strategies in plants and its relevance to ecological and evolutionary theory[J]. The American Naturalist, 1977, 111(982): 1169-1194.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Pierce S, Brusa G, Sartori M, et al. Combined use of leaf size and economics traits allows direct comparison of hydrophyte and terrestrial herbaceous adaptive strategies[J]. Annals of Botany, 2012, 109(5): 1047-1053.
DOI PMID |
| [19] |
Pierce S, Brusa G, Vagge I, et al. Allocating CSR plant functional types: The use of leaf economics and size traits to classify woody and herbaceous vascular plants[J]. Functional Ecology, 2013, 27 (4): 1002-1010.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
龚雪伟, 吕光辉. 艾比湖流域杜加依林荒漠植物群落多样性及优势种生态位[J]. 生物多样性, 2017, 25(1): 34-45.
DOI |
|
GONG Xuewei, LYU Guanghui. Diversity of desert plant communities and ecological niches of dominant species in the Dugai Forest of the Lake Ebeye Basin[J]. Biodiversity Science, 2017, 25(1): 34-45.
DOI |
|
| [21] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第三版)[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| BAO Shidan. Soil Agrochemical Analysis (3rd ed.)[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. | |
| [22] |
戚德辉, 温仲明, 杨士梭, 等. 基于功能性状的铁杆蒿对环境变化的响应与适应[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(7): 1921-1927.
PMID |
|
QI Dehui, WEN Zhongming, YANG Shisuo, et al. Trait-based responses and adaptation of Artemisia sacrorum to environmental changes[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(7): 1921-1927.
PMID |
|
| [23] |
韩玲, 赵成章, 冯威, 等. 张掖湿地芨芨草叶脉密度和叶脉直径的权衡关系对3种生境的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2017, 41(8): 872-881.
DOI |
|
HAN Ling, ZHAO Chengzhang, FENG Wei, et al. Trade-offs between leaf vein density and leaf vein diameter inAchnathernmsplendens in Zhangye wetland in response to three habitats[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2017, 41(8): 872-881.
DOI |
|
| [24] |
Wang R, Huang W, Chen L, et al. Anatomical and physiological plasticity in Leymuschinensis (Poaceae) along large-scale longitudinal gradient in northeast China[J]. Plos One, 2011, 6(11): e26209.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 王羽梅, 任安祥, 潘春香, 等. 长时间盐胁迫对苋菜叶片细胞结构的影响[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2004, 40(3): 27-30. |
| WANG Yumei, REN Anxiang, PAN Chunxiang, et al. Effects of prolonged salt stress on the cell structure of Amaranthus leaves[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2004, 40(3): 27-30. | |
| [26] | 李琪, 於虹, 王支虎, 等. 醋糟对土壤改良及兔眼蓝浆果幼苗生长的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2017, 26(4): 25-31. |
| LI Qi, YU Hong, WANG Zhihu, et al. Effect of vinegar residue on soil amelioration and seedling growth of Vacciniumashei[J]. Journal of Plant Resources and Environment, 2017, 26(4): 25-31. | |
| [27] | 魏瑞锋. 土壤水分含量对梨枣树光合特性以及果实品质的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2012. |
| WEI Ruifeng. Effect of soil moisture content on photosynthetic characteristics and fruit quality of pear and date palm[D]. Yangling: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University of Science and Technology, 2012. | |
| [28] | 王擎运, 何咏霞, 陈景, 等. 秸秆或粉煤灰添加对砂姜黑土持水性及小麦抗干旱胁迫的影响[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(2): 95-102. |
| WANG Qingyun, HE Yongxia, CHEN Jing, et al. Effect of straw or fly ash addition on water retention and drought stress resistance of wheat in sand ginger black soil[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(2): 95-102. | |
| [29] | Grime J P, Pierce S. The Evolutionary Strategies That Shape Ecosystems[M].Wiley-Blackwell, 2012. |
| [30] |
Osnas J L D, Lichstein I W, Reich P B. et al. Global leaf trait relationships mass, area and the leaf economics spectrum[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6133): 741-744.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Szmeja J, Galka A. Phenotypic responses to water flow and wave exposure in aquatic plants[J]. Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae, 2008, 77(1): 59-65.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Robionek A, Banas K, Chmara R, et al. The avoidance strategy of environmental constraints by an aquatic plant Potamogetonalpinus in running waters[J]. Ecology & Evolution, 2015, 5(16): 3327-3337. |
| [1] | 胡文聪, 潘存德, 赵善超, 宋梦真, 童海麦, 田晨阳. 天山北坡中部天山云杉1 a生天然更新幼苗存活数量与功能性状的微生境分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 454-463. |
| [2] | 陈昱东, 吕光辉, 张磊, 蒋腊梅, 王恒方. 荒漠植物功能性状和生物量对土壤水盐环境的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2574-2584. |
| [3] | 申吴燕, 吐尔逊娜依·热依木, 雪热提江·麦提努日, 邓婷婷, 黄长福, 王梦, 马伊王利, 麻浩. 12种植物萌发期耐盐性筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(10): 1912-1920. |
| [4] | 曹靖;杨晓东;吕光辉;王庭权;赵晓英;刘薇;刘志东. 盐分对白刺光合作用及其叶功能性状的影响[J]. , 2015, 52(11): 2065-2075. |
| [5] | 马晓瑜;孟晖;潘存德;张国林. 天山中部不同年龄和海拔高度天山云杉天然更新幼苗茎干功能性状[J]. , 2014, 51(7): 1238-1245. |
| [6] | 朱玉伟;陈启民;刘茂秀;桑巴叶. 准噶尔盆地南缘人工封育促进天然植被恢复的研究[J]. , 2009, 46(5): 1144-1148. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||