

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (2): 393-400.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.02.016
• Plant Protection·Microbes • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Ruixingyue( ), SUN Yingying, JI Yuxing, MA Deying(
), SUN Yingying, JI Yuxing, MA Deying( )
)
Received:2024-08-10
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-04-17
Correspondence author:
MA Deying
Supported by:通讯作者:
马德英
作者简介:张瑞星月(1998-),女,新疆克拉玛依人,硕士研究生,研究方向为农业昆虫与害虫防治,(E-mail)Zhangrxy1102@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Ruixingyue, SUN Yingying, JI Yuxing, MA Deying. Dynamics analysis and comparison of Aleyrodes proletella L. and its associated population Aleyrodes sp.on different host plants[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(2): 393-400.
张瑞星月, 孙颖颖, 吉宇星, 马德英. 欧洲甘蓝粉虱Aleyrodes proletella L.和伴生种群Aleyrodes sp.在不同寄主植物上种群消长动态的比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(2): 393-400.
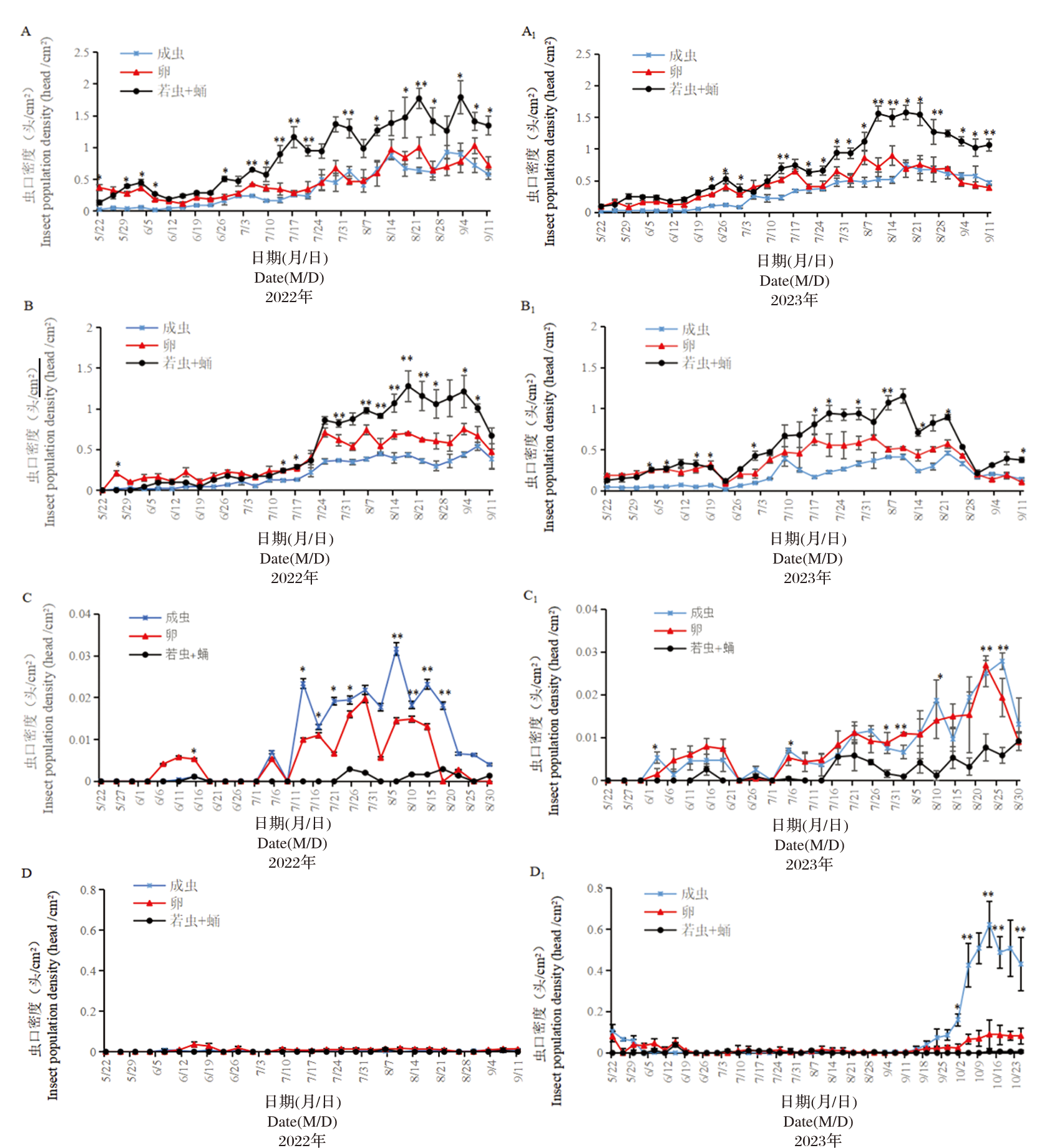
Fig.3 Dynamics of two Aleyrodes mixed population on four host plants. Notes:The * above the line graph indicates a significant difference (*:P<0.05;**:P<0.01);A: Lactuca serriola L.;B: Lactuca sativa var.longifolia Lam ;C:Brassica chinensis var.chinensisv ;D:Brassica oleracea L.
| [1] | Mound L A, Halsey S H. Whitefly of the world: a systematic catalogue of the Aleyrodidae (Homoptera) with host plant and natural enemy data[M]. London: British Museum (Natural History), 1978. |
| [2] | Hill D S. Agricultural insect pests of temperate regions and their control[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1987. |
| [3] | Muñiz M, Nebreda M. Differential variation in host preference of Aleyrodes proletella(L) on some cauliflower cultivars[J]. Aleyrodes Proletella Host Preference, 2003. |
| [4] | Ramsey A D, Ellis P R. Resistance in wild brassicas to the cabbage whitefly, Aleyrodes proletella[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 1996,(407): 507-514. |
| [5] | Richter E, Hirthe G. Hibernation and migration of Aleyrodes proletella in Germany[J]. Bulletin Oepp/eppo Bulletin, 2014, 107:143-149. |
| [6] | Spencer C. The biology and ecology of Aleyrodes proletella, the cabbage whitefly: a pest of Brassica crops[D]. Coventry, West Midlands, UK: University of Warwick, 2016 |
| [7] | 张桂芬, 冼晓青, 张金良, 等. 甘蓝粉虱入侵中国大陆[J]. 生物安全学报, 2014, 23(1): 66-70. |
| ZHANG Guifen, XIAN Xiaoqing, ZHANG Jinliang, et al. Cabbage whitefly, Aleyrodes proletella(L.)(Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae), invaded China’s mainland[J]. Journal of Biosafety, 2014, 23(1): 66-70. | |
| [8] | Trdan S, Kac M, Bobnar A, et al. Research on the efficacy of the yellow sticky boards to control the cabbage whitefly (Aleyrodes proletella L. Aleyrodidae) on Brussels sprouts[J]. Kmetijstvo, 2003, 81(1):171-177. |
| [9] | Nebreda M, Nombela G, Muñiz M. Comparative host suitability of some Brassica cultivars for the whitefly, Aleyrodes proletella (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae)[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2005, 34(1): 205-209. |
| [10] | Trdan S, Papler U. Susceptibility of four different vegetable brassicas to cabbage whitefly (Aleyrodes Proletella L., Aleyrodidae) attack[J]. Mededelingen (Rijksuniversiteit Te Gent Fakulteit Van de Landbouwkundige En Toegepaste Biologische Wetenschappen), 2002, 67(3): 531-535. |
| [11] | Chen C H, Kumar Dubey A, Ko C C. Comparative morphological studies on two species of Aleyrodes (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae)[J]. The Pan-Pacific Entomologist, 2007, 83(3): 244-254. |
| [12] | De Barro P J, Carver M. Cabbage whitefly, Aleyrodes proletella (L.) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae), newly discovered in Australia[J]. Australian Journal of Entomology, 1997, 36(3): 255-256. |
| [13] | Bale J S, Masters G J, Hodkinson I D, et al. Herbivory in global climate change research: direct effects of rising temperature on insect herbivores[J]. Global Change Biology, 2002, 8(1): 1-16. |
| [14] | Curnutte L B, Simmons A M, Abd-Rabou S. Climate change and Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae): impacts of temperature and carbon dioxide on life history[J]. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 2014, 107(5): 933-943. |
| [15] | Porter J H, Parry M L, Carter T R. The potential effects of climatic change on agricultural insect pests[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 1991, 57(1/2/3): 221-240. |
| [16] |
Springate S, Colvin J. Pyrethroid insecticide resistance in British populations of the cabbage whitefly, Aleyrodes proletella[J]. Pest Management Science, 2012, 68(2): 260-267.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Łabanowski G.S. Cabbage whitefly—Aleyrodes proletella (L. 1758)—pest of Brassica vegetables in Poland[J]. Zesz. Nauk. Inst. Ogrod, 2015 23: 49-61. |
| [18] |
Martin J H, Mifsud D, Rapisarda C. The whiteflies (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) of Europe and the Mediterranean Basin[J]. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 2000, 90(5): 407-448.
PMID |
| [19] | Tomlinson J A, Webb M J W, Faithfull E M. Studies on broccoli necrotic yellows virus[J]. Annals of Applied Biology, 1972, 71(2): 127-134. |
| [20] | Kuwan A, Zhang G F, Li J H, et al. Morphological, genetic and biological differences in two populations of Aleyrodes proletella from Northwestern China[J]. Entomologia Generalis, 2021, 41(1): 27-37. |
| [21] | Dale P S, Hayes J C, Johannesson J. New records of plant pests in New Zealand[J]. New Zealand Journal of Agricultural Research, 1976, 19(2): 265-269. |
| [22] | Iheagwam E U. Photoperiodism in the cabbage whitefly, Aleyrodes brassicae[J]. Physiological Entomology, 1977, 2(3): 179-184. |
| [23] | Lenteren J C, Noldus L. Whitefly-plant relationships: behavioural and ecological aspects[J]. In Gerling, D. (ed.), Whiteflies: their Bionomics, Pest Status and Management. Intercept Ltd., Andover, UK., 1990 |
| [24] | Coudriet D L, Prabhaker N, Kishaba A N, et al. Variation in developmental rate on different hosts and overwintering of the sweetpotato whitefly, Bemisia tabaci (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae)[J]. Environmental Entomology, 1985, 14(4): 516-519. |
| [25] | Campos O R, Crocomo W B, Labinas A M. Comparative biology of the whitefly Trialeurodes vaporariorum (West.) (Hemiptera - Homoptera: Aleyrodidae) on soybean and bean cultivars[J]. Neotropical Entomology, 2003, 32(1): 133-138. |
| [26] |
Manzano M R, van Lenteren J C. Life history parameters of Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Westwood) (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) at different environmental conditions on two bean cultivars[J]. Neotropical Entomology, 2009, 38(4): 452-458.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | Lorenzo M E, Grille G, Basso C, et al. Host preferences and biotic potential of Trialeurodes vaporariorum and Bemisia tabaci (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) in tomato and pepper[J]. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 2016, 10(4): 293-301. |
| [28] | Askoul K, Richter E, Vidal S, et al. Life history parameters of Aleyrodes proletella (Hemiptera: Aleyrodidae) on different host plants[J]. Journal of Economic Entomology, 2019, 112(1): 457-464. |
| [29] | 吉宇星, 帕提玛·乌木尔汗, 张瑞星月, 等. 两个欧洲甘蓝粉虱种群的线粒体基因组与寄主选择性[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2022, 45(6): 474-479. |
| JI Yuxing, Patima Wumuerhan, ZHANG Ruixingyue, et al. Mitochondrial genome and host selectivity of two populations of European cabbage whitefly[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022, 45(6): 474-479. | |
| [30] | Broekgaarden C, Riviere P, Steenhuis G, et al. Phloem-specific resistance in Brassica oleracea against the whitefly Aleyrodes proletella[J]. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 2012, 142(2): 153-164. |
| [31] | Butler C. On the ecology of Aleurodes brassicae Walk.(Hemiptera)[D]. Cambridge: Cambridge University, 1938. |
| [32] | Mound L A, Halsey S H. Whitefly of the world: a systematic catalogue of the Aleyrodidae (Homoptera) with host plant and natural enemy data[M]. London: British Museum (Natural History), 1978. |
| [33] | Ramsey A D, Ellis P R. Resistance in wild brassicas to the cabbage whitefly, Aleyrodes proletella[J]. Acta Horticulturae, 1996,(407): 507-514. |
| [34] | Broekgaarden C, Pelgrom K T B, Bucher J, et al. Combining QTL mapping with transcriptome and metabolome profiling reveals a possible role for ABA signaling in resistance against the cabbage whitefly in cabbage[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(11): e0206103. |
| [1] | ZHANG Yiran, Yeerjiang Baiketuerhan, Baihetiguli Kayier, QI Zhiying. Spatial distribution pattern and prediction of Rhus typhina L. roots sucker in urban green space system [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2023-2033. |
| [2] | TIAN Wenqiang, DONG Yanxue, SHI Yongqing, LEI Junjie, SUN Ganggang, WANG Hongyi, NIE Lingfan, GOU Fei, AI Hongyu, SHI Shubing, ZHANG Jinshan. Effects of sowing date on stem traits and population dynamics of ultra late winter wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1301-1307. |
| [3] | SHEN Yuyang, LAI Ning, FAN Guiqiang, CUI Yanhua, YANG Hong, LAI Hailin, LIN Min, LEI Junjie, LI Guangkuo, GAO Haifeng. Effects of wheat late sowing and organic fertilizer replaced nitrogen fertilizer on the population dynamics of Sitobion avenae [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(5): 1082-1087. |
| [4] | Amire Yashengjiang, Adili Shataer. Screening of Plant-Derived Attractants and Clayworm Plates for Ash Borer Adults and Their Development Dynamics [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(10): 2532-2537. |
| [5] | MA Zhilong,YAO Yanxia, Adili Sattar. Study on Dynamics of Agrilus mali Matsumura Population and Selection of Sustained-Release Vials in Yili Wild Fruit Forest Area [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(2): 304-312. |
| [6] | TANG Rui, SUN Xianyin, ZHUO Fuyan, ZHU Jingquan, GUO Rong. Investigation and Research on the Dynamic Occurrence of Major Crop Diseases and Pests and the Succession of Control Strategy in China During 2015-2019 [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(12): 2208-2219. |
| [7] | ZHANG Hongzhi, GAO Yonghong, WANG Lihong, KONG Depeng, ZHANG Yueqiang, LI Jianfeng, WANG Zhong, GAO Xin, SHI Jia, ZHAO QI, FAN Zheru. Differences in Population Dynamics, Dry Matter Accumulation and Distribution of High-Yield Winter Wheat [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(12): 2157-2163. |
| [8] | Aziguli Abulizi, Aibibaimu Yiming, Sajidamu Aizezi, WANG Gan-cheng, Yasen Shali. Effects of Main Meteorological Factors on the Population Fluctuation of Loxostege sticticalis:Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)in Habahe County [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(3): 509-517. |
| [9] | MA Jiang-xia;DANG Rui;JIAO Li;XIE Zhi-sheng;DUAN Cheng-ren;YANG Kun-ming;GUO Ai-min;YUE Cheng. Research on Population Dynamics of Lota lota's Diplostomum mergi in the Irtysh River, Xinjiang [J]. , 2017, 54(6): 1160-1166. |
| [10] | WANG Pan-pan;Abdusattor Saidov;Anvar Jalilov;Adili Wubier;Haliti Hashan;LIU Zhao-hai;MA Ying-jie;L(U) Zhao-zhi. Occurrence Generation and Preliminary Comparison of Population Dynamics of Cutworm (Agrotis segetum) in Xinjiang of China and in Tajikistan [J]. , 2017, 54(5): 918-924. |
| [11] | LI Chao;DING Xin-hua;WANG Xiao-wu;GUO Wen-chao;Tuerxun Ahemaiti;HE Jiang. Effect of Neighboring Crops Distribution Patterns and Film Mulching on the Population Dynamics of Colorado Potato Beetle, Leptinotarsa decemlineata in Xinjiang [J]. , 2017, 54(1): 117-123. |
| [12] | HE Wei;XU Jian-jun;YANG Hua;CUI Yuan-yu;SUN Xiao-jun. Study on Pest Species and Population Dynamics Based on Application of Insect Sex Lures in Processing Tomato Fields [J]. , 2016, 53(9): 1618-1624. |
| [13] | CHEN Sheng-Ao;YAO Na;WANG Zhi-Chao;LIU Jie-ya;MA Bao-Shan;XIE Cong-Xin. Studies on the Population Dynamics of Triplophysa (Hedinichthys) yarkandensis (Day) in the Tarim River [J]. , 2015, 52(10): 1917-1925. |
| [14] | Adil·Sattar;LIU Heng;LI Hong. Preliminary Study on Population Metastasis Rule of Tetranychus truncatus Ehara in Fruit Trees and Crop Intercropping in the Aksu Region [J]. , 2014, 51(3): 471-478. |
| [15] | JIAO Xu-dong;GUO Yan-lan;XIA Wei;SONG Chang-gui;ZHANG Jian-ping. Study on the Occurrence Characteristics and Population Dynamics of the Main Insect Pests in Bazhou of Xinjiang [J]. , 2013, 50(7): 1254-1259. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 8
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 38
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||