

新疆农业科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (11): 2661-2667.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.11.008
王冬梅( ), 潘洪生(
), 潘洪生( ), 李海强, 丁瑞丰, 阿克旦・吾外士, 刘建, 李号宾
), 李海强, 丁瑞丰, 阿克旦・吾外士, 刘建, 李号宾
收稿日期:2021-12-24
出版日期:2022-11-20
发布日期:2022-12-28
通信作者:
潘洪生(1982-),男,研究员,博士,研究方向为棉花害虫综合防控,(E-mail)panhongsheng0715@163.com作者简介:王冬梅(1969-),女,新疆人,研究员,研究方向为转基因安全性评价,(E-mail)wdm872@sina.com
基金资助:
WANG Dongmei( ), PAN Hongsheng(
), PAN Hongsheng( ), LI Haiqiang, DING Ruifeng, Akedan Wuwaishi, LIU Jian, LI Haobin
), LI Haiqiang, DING Ruifeng, Akedan Wuwaishi, LIU Jian, LI Haobin
Received:2021-12-24
Published:2022-11-20
Online:2022-12-28
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】利用DNA分子检测技术定量评价新疆棉田重要捕食性天敌对棉蚜的控害作用,为有效发挥捕食性天敌在棉田害虫生物防治中的作用提供支撑。【方法】田间系统调查棉蚜种群数量,运用DNA分子检测技术定量分析的捕食性天敌中肠棉蚜检出率并分析相关性,以棉蚜检出率为依据研究新疆棉田优势捕食性天敌,基于棉田和邻近苜蓿条带采集捕食性瓢虫的中肠对棉蚜和三叶草彩斑蚜的检出率分析捕食性瓢虫的取食偏好习性。【结果】2019~2021年,棉田棉蚜种群数量和捕食性天敌中肠棉蚜检出率均密切相关,Pearson相关系数分别为0.921和0.839;多异瓢虫是新疆棉田优势捕食性天敌。2019年当捕食性瓢虫采自苜蓿条带时,三叶草彩斑蚜在6月、7月和8月的检出率分别为52.50 %、73.70 %和27.95 %,棉蚜在6月、7月和8月的检出率分别为0、21.10 %和38.71 %;当捕食性瓢虫采自棉田时,棉蚜在6月、7月和8月的检出率分别为18.11%、75.52 %和49.53 %,三叶草彩斑蚜在6月、7月和8月的检出率分别为92.12 %、29.60 %和5.61 %。当棉蚜种群数量较少时,捕食性瓢虫以取食苜蓿条带的三叶草彩斑蚜为主,当棉蚜和三叶草彩斑蚜同时发生时,捕食性瓢虫以取食栖息生境的蚜虫种类为主。【结论】利用DNA分子检测技术可以定量评估捕食性天敌对棉蚜的控害作用。邻近棉田的苜蓿条带可以为捕食性天敌提供替代食物,对其具有重要的保育作用。
中图分类号:
王冬梅, 潘洪生, 李海强, 丁瑞丰, 阿克旦・吾外士, 刘建, 李号宾. DNA分子检测技术定量评估捕食性天敌对棉蚜的控害功能[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(11): 2661-2667.
WANG Dongmei, PAN Hongsheng, LI Haiqiang, DING Ruifeng, Akedan Wuwaishi, LIU Jian, LI Haobin. Quantitatively Evaluate the Control Function of Predatory Natural Enemies on Cotton Aphids by DNA Molecular Detection Technology[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(11): 2661-2667.
| 蚜虫种类 Aphid species | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 退火温度 Annealing temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| 棉蚜 | AG-F5R2F | CCACCCTCATTAATAATAATAATTTGC | 57℃ |
| A. gossypii | AG-F5R2R | GTAATAGCACCAGCTAATACAGGTAAG | |
| 三叶草彩斑蚜 | Thet-F1 | TGGTAATTGATTAATCCCTC | 50℃ |
| T. trifolii | Thet-R1 | TAAAGTTAATAGCTCCTAAG |
表1 棉蚜和三叶草彩斑蚜的引物序列和退火温度
Table 1 Primer sequence and annealing temperature of Aphis gossypii and Therioaphis trifolii
| 蚜虫种类 Aphid species | 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列 Primer sequence(5'-3') | 退火温度 Annealing temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| 棉蚜 | AG-F5R2F | CCACCCTCATTAATAATAATAATTTGC | 57℃ |
| A. gossypii | AG-F5R2R | GTAATAGCACCAGCTAATACAGGTAAG | |
| 三叶草彩斑蚜 | Thet-F1 | TGGTAATTGATTAATCCCTC | 50℃ |
| T. trifolii | Thet-R1 | TAAAGTTAATAGCTCCTAAG |
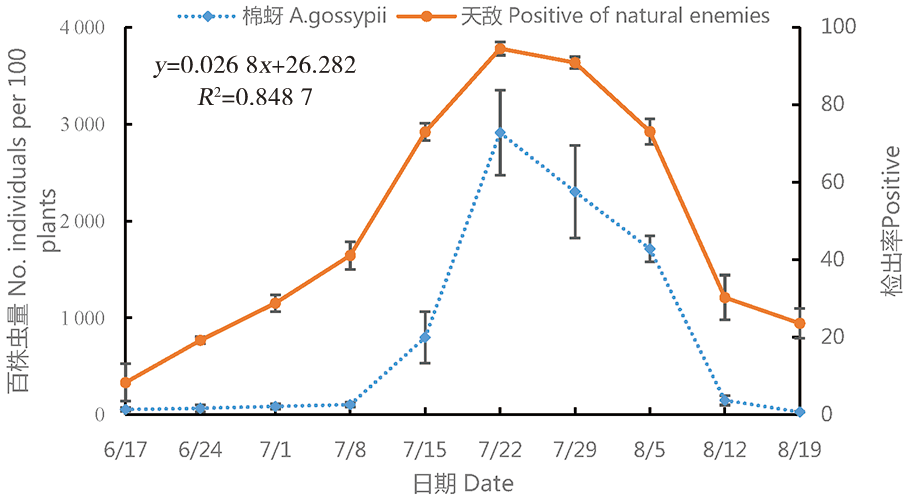
图1 棉蚜种群数量与捕食性天敌中肠检出率的动态变化(2019年)
Fig.1 Dynamic changes of population number of cotton aphids and its detection rate in the midgut of predatory natural enemies during 2019
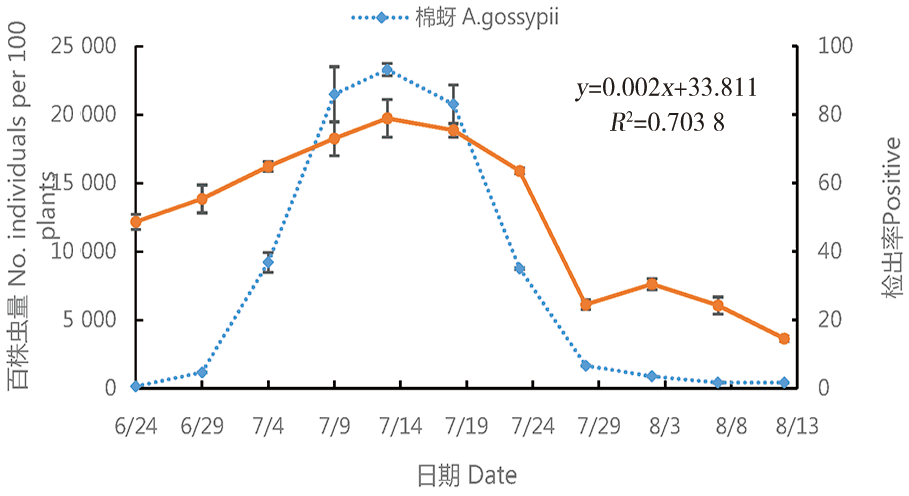
图2 棉蚜种群数量与捕食性天敌中肠检出率的动态变化(2021年)
Fig.2 Dynamic changes of population number of cotton aphids and its detection rate in the midgut of predatory natural enemies during 2021
| 天敌种类 Natural enemy species | 2019年 | 2021年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总检测数 Total | 检出数 Number | 检出率 Positive (%) | 总检测数 Total | 检出数 Number | 检出率 Positive (%) | |
| 多异瓢虫(成虫) H. variegate(adult) | 957 | 584 | 61.06 | 1 035 | 520 | 50.24 |
| 方斑瓢虫(成虫) P. quatuordecimpunctata(adult) | 33 | 9 | 27.24 | 167 | 49 | 29.34 |
| 菱斑巧瓢虫(成虫) O. conglobate (adult) | 72 | 12 | 16.65 | 167 | 38 | 22.75 |
| 七星瓢虫(成虫) C. septempunctata(adult) | 6 | 0 | 0.00 | |||
| 食蚜蝇类成虫Hover flyadults | 5 | 0 | 0.00 | |||
| 瓢虫类幼虫Ladybeetle larvae | 798 | 524 | 65.71 | 532 | 314 | 59.02 |
| 草蛉类幼虫Lacewing larvae | 123 | 69 | 56.03 | 58 | 28 | 48.95 |
| 合计Total | 1 988 | 1 198 | 60.26 | 1 964 | 949 | 48.32 |
表2 不同捕食性天敌中肠棉蚜的检出率
Table 2 Detection rate of cotton aphids in the midgut of different predatory natural enemies
| 天敌种类 Natural enemy species | 2019年 | 2021年 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 总检测数 Total | 检出数 Number | 检出率 Positive (%) | 总检测数 Total | 检出数 Number | 检出率 Positive (%) | |
| 多异瓢虫(成虫) H. variegate(adult) | 957 | 584 | 61.06 | 1 035 | 520 | 50.24 |
| 方斑瓢虫(成虫) P. quatuordecimpunctata(adult) | 33 | 9 | 27.24 | 167 | 49 | 29.34 |
| 菱斑巧瓢虫(成虫) O. conglobate (adult) | 72 | 12 | 16.65 | 167 | 38 | 22.75 |
| 七星瓢虫(成虫) C. septempunctata(adult) | 6 | 0 | 0.00 | |||
| 食蚜蝇类成虫Hover flyadults | 5 | 0 | 0.00 | |||
| 瓢虫类幼虫Ladybeetle larvae | 798 | 524 | 65.71 | 532 | 314 | 59.02 |
| 草蛉类幼虫Lacewing larvae | 123 | 69 | 56.03 | 58 | 28 | 48.95 |
| 合计Total | 1 988 | 1 198 | 60.26 | 1 964 | 949 | 48.32 |
| 日期 Date (D/M) | 苜蓿条带Alfalfa strips | 棉田Cotton fields | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 棉蚜 A. gossypii | 三叶草 彩斑蚜 T. trifolii | 棉蚜 A. gossypii | 三叶草 彩斑蚜 T. trifolii | |
| 14/6 | 0.00 | 42.11 | 8.33 | 91.67 |
| 22/6 | 0.00 | 78.26 | 19.13 | 92.17 |
| 6月平均 Average in June | 0.00 | 52.50 | 18.11 | 92.12 |
| 1/7 | 0.00 | 90.00 | 28.95 | 71.00 |
| 8/7 | 0.00 | 92.54 | 41.43 | 50.00 |
| 13/7 | 0.00 | 92.06 | 72.73 | 38.57 |
| 22/7 | 47.92 | 52.86 | 94.21 | 24.79 |
| 29/7 | 60.00 | 53.85 | 91.04 | 17.16 |
| 7月平均 Average in July | 21.10 | 73.70 | 75.52 | 29.60 |
| 5/8 | 84.62 | 33.33 | 73.08 | 11.92 |
| 12/8 | 18.75 | 21.88 | 30.77 | 1.54 |
| 19/8 | 22.86 | 14.29 | 24.14 | 6.90 |
| 8月平均 Average in August | 38.71 | 27.95 | 49.53 | 5.61 |
表3 棉蚜和三叶草彩斑蚜在捕食性天敌中肠的检出率
Table 3 Detection rate of A. gossypii and T. trifolii in the midgut of predatory natural enemies
| 日期 Date (D/M) | 苜蓿条带Alfalfa strips | 棉田Cotton fields | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 棉蚜 A. gossypii | 三叶草 彩斑蚜 T. trifolii | 棉蚜 A. gossypii | 三叶草 彩斑蚜 T. trifolii | |
| 14/6 | 0.00 | 42.11 | 8.33 | 91.67 |
| 22/6 | 0.00 | 78.26 | 19.13 | 92.17 |
| 6月平均 Average in June | 0.00 | 52.50 | 18.11 | 92.12 |
| 1/7 | 0.00 | 90.00 | 28.95 | 71.00 |
| 8/7 | 0.00 | 92.54 | 41.43 | 50.00 |
| 13/7 | 0.00 | 92.06 | 72.73 | 38.57 |
| 22/7 | 47.92 | 52.86 | 94.21 | 24.79 |
| 29/7 | 60.00 | 53.85 | 91.04 | 17.16 |
| 7月平均 Average in July | 21.10 | 73.70 | 75.52 | 29.60 |
| 5/8 | 84.62 | 33.33 | 73.08 | 11.92 |
| 12/8 | 18.75 | 21.88 | 30.77 | 1.54 |
| 19/8 | 22.86 | 14.29 | 24.14 | 6.90 |
| 8月平均 Average in August | 38.71 | 27.95 | 49.53 | 5.61 |
| [1] | 戈峰. 害虫区域性生态调控的理论、方法及实践[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2001, 38(5):337-341 |
| GE Feng. The principles, methods and practices of regional ecological regulation and management of pests[J]. Entomological Knowledge, 2001, 38(5):337-341. | |
| [2] | 陆庆光. 国外天敌引种与外来有害生物的持续控制[J]. 植物保护, 1996, 22(6):44-45. |
| LU Qingguang. Introductionof foreign natural enemies and continuous control of alien pests[J]. Plant Protection, 1996, 22(6):44-45. | |
| [3] |
LI Jiancheng, YAN Fengming, Coudron T A, et al. Field release of the parasitoid Microplitis mediator(hymenoptera:Braconidae) for control of Helicoverpa armigera (lepidoptera:Noctuidae) incotton fields in northwestern China’s Xinjiang province[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2006, 35(3):694-699.
DOI URL |
| [4] | 郑书文, 刘学谦, 李明贵, 等. 中华通草蛉幼虫对绣线菊蚜捕食作用的研究[J]. 山东农业科学, 2008,(6):50-52. |
| ZHENG Shuwen, LIU Xueqian, LI Minggui, et al. Predacious function of Chrysoperla sinica larvae to Aphis citricola[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2008,(6):50-52. | |
| [5] | 戈峰. 昆虫生态学原理与方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2008. |
| GE Feng. Principle and method of insect ecology[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2008. | |
| [6] | 王丽丽, 陆宴辉, 吴孔明. 绿盲蝽捕食棉铃虫卵的COI标记检测方法[J]. 应用昆虫学报, 2010, 47(6): 1248-1252. |
| WANG Lili, LU Yanhui, WU Kongming. The method of COI marker for detecting predation of Apolygus lucorum on Helicoverpa armigera eggs[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Entomology, 2010, 47(6):1248-1252. | |
| [7] | Staudacher K, Jonsson M, Traugott M. Diagnostic PCR assays to unravel food web interactions in cereal crops with focus on biological control of aphids[J]. Journal of Pest Science, 2016, (89): 281-293. |
| [8] | Rowley C, Cherrill Aj, Leathersr, et al. PCR-based gut content analysis to identifyarthropod predators of Haplodiplosis marginata[J]. Biological Control, 2017, (115): 112-118. |
| [9] | 宋新元, 丛斌, 钱海涛, 等. 大豆蚜捕食性天敌捕食行为的COI基因标记检测[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(9):2881-2888. |
| SONG Xinyuan, CONG Bin, QIAN Haitao, et al. Identification of the key predators of Aphis glycines Matsumura (Homoptera: Aphididae) using COI gene markers[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(9):2881-2888. | |
| [10] | 杨静. 北疆棉区非棉田生境对捕食性天敌的保育功能[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2016. |
| YANG Jing. Conservation functions of non-cotton habitat on predatory natural enemies in northern Xinjiang[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2016. | |
| [11] | 李雪玲. 碱蓬对棉田多异瓢虫的保育作用[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2019. |
| LI Xueling. Conservation effect of Suaeda strip on the Hippodamia variegata in adjacent cotton fields[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2019. | |
| [12] | 潘洪生, 姜玉英, 王佩玲, 等. 新疆棉花害虫发生演替与综合防治研究进展[J]. 植物保护, 2018, 44(5):47-55. |
| PAN Hongsheng, JIANG Yuying, WANG Peiling, et al. Research progress in the status evolution and intergrated control of cotton pests in Xinjiang[J]. Plant Protection, 2018, 44(5):47-55. | |
| [13] | 冯宏祖, 王兰, 熊仁慈, 等. 多异瓢虫种群动态及捕食功能的研究[J]. 昆虫知识, 2000, 37(4):223-226. |
| FENG Hongzu, WANG Lan, XIONG Renci, et al. A study on the population dynamics and predacious function of Hippodamia (Adonia) variegate[J]. Entomological Knowledge, 2000, 37(4):223-226. | |
| [14] | 姚举, 姬华, 王东, 等. 棉田优势天敌多异瓢虫成虫对棉蚜捕食功能的研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2005, 42(4):262-264. |
| YAO Ju, JI Hua, WANG Dong, et al. Study on predation of Aphis gossypii by adult Hippodamia variegate[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2005, 42(4):262-264. | |
| [15] | 潘洪生, 李号宾, 丁瑞丰, 等. 多异瓢虫对棉黑蚜的捕食能力[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2020, 36(4):628-631. |
| PAN Hongsheng, LI Haobin, DING Ruifeng, et al. Predation capacity of Adonia variegata to Aphis atrata[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2020, 36(4):628-631. | |
| [16] | 俞晓平, 胡萃, Heong KL. 非作物生境对农业害虫及其天敌的影响[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 1996, 12(3):130-133. |
| YU Xiaoping, HU Cui, Heong K L. The effects of non-crop habitat on crop pests and their natural enemies[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 1996, 12(3):130-133. | |
| [17] |
Rand T A, Tylianakis J M, Tscharntket. Spillover edge effects: the dispersal of agriculturally subsidized insect natural enemies into adjacent natural habitats[J]. Ecology Letters, 2010, 9(5): 603-614.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Cottrell T E, Yeargan K V. Factors influencing dispersal of larval Coleomegilla maculata from the weed Acalypha ostryaefolia to sweet corn[J]. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 1999, 90(3): 313-322.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 吕昭智, 田长彦, 胡明芳, 等. 棉田及其边缘杂草对天敌的影响[J]. 植物保护, 2002, 28(5):22-24. |
| LV Zhaozhi, TIAN Changyan, HU Mingfang, et al. The influence of cotton fields and their weeds on natural enemies[J]. Plant Protection, 2002, 28(5): 22-24. | |
| [20] |
李雪玲, 罗延亮, 李辉, 等. 田埂碱蓬带对棉田多异瓢虫种群发生的调控作用[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(1):13-22.
DOI |
|
LI Xueling, LUO Yanliang, LI Hui, et al. Regulation and control effects of Suaeda strips on the population occurrence of Hippomidia variegata in cotton fields[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(1):13-22.
DOI |
|
| [21] |
罗延亮, 李雪玲, 李辉, 等. 苦豆子条带对棉田捕食性天敌发生的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(1):74-83.
DOI |
|
LUO Yanliang, LI Xueling, LI Hui, et al. Effects of Sophorastrips on the population occurrence of predators in cotton fields[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(1):13-22.
DOI |
|
| [22] | 杨惠玲. 七星瓢虫对松大蚜和棉蚜的选择效应[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2010, 38(8):149-150. |
| YANG Huiling. Selective effect of Coccinella septempunctata to Cinara pintabula eformis and Aphis gossypii[J] .Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2010, 38(8):149-150. | |
| [23] | 朱冠雄. 异色瓢虫对苹果绵蚜和绣线菊蚜的捕食功能反应研究[J]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2019. |
| ZHU Guanxiong. Functional response of Harmonia axyridis to Eriosoma lanigerm and Aphis citricola[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2019. | |
| [24] |
ZHANG Runzhi, LIANG Hongbin, TIANChangyan, et al. Biological mechanism of controlling cotton aphid(homoptera:aphididae) by the marginal alfalfa zone surrounding cotton field[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2000, 45(4):355-357.
DOI URL |
| [25] | 杨帆, 刘冰, 陆宴辉. DNA 分子检测技术在节肢动物食物网结构解析中的应用[J]. 植物保护学报,https://doi.org/10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2022.2022821. |
| YANG Fan, LIU Bing, LU Yanhui. Application of DNA-based molecular detection techniques in arthropod food web structure analyses[J]. Journal of Plant Protection,https://doi.org/10.13802/j.cnki.zwbhxb.2022.2022821. |
| [1] | 周欣, 刘旋峰, 姜羽晗, 张海春, 杨豫新, 叶尔波拉提·铁木尔, 蒋永新, 张丽. 新疆棉田废旧地膜机械化回收及资源化利用现状及发展趋势[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 131-141. |
| [2] | 付鑫法, 吕廷波, 王久龙, 李港强, 宋仁友, 刘一凡. 春灌定额对棉田水温盐分布及棉花苗期生长发育的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1336-1344. |
| [3] | 柳萍, 张凯, 马超, 张慧, 杨川. 有机物料对不同磷肥用量条件下棉田综合效益评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2521-2531. |
| [4] | 马彬, 王帅, 吴依衍, 姜艳. 干旱荒漠区农田防护林正负效应及其影响机制[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(9): 2232-2239. |
| [5] | 高倩, 王亚梅, 吴平凡, 张红美, 周岭. 基于近红外光谱的果树残枝纤维组分含量分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(8): 2025-2032. |
| [6] | 张栋海, 魏俊梅, 陈兵, 吉光鹏, 王凡, 牛蛉磊. 无人机播前喷施除草剂防除棉田杂草效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(12): 3022-3029. |
| [7] | 李江余, 赵强, 吴雪琴, 马春梅, 任若飞, 许豆豆, 田阳青. 塑型剂对棉花农艺性状及产量品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2352-2357. |
| [8] | 高文翠, 杨卫君, 史春玲, 陈磊. 膜下滴灌连作棉田土壤有机碳及其活性变化分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(9): 1603-1609. |
| [9] | 朱玉永, 赵冰梅, 张强, 丁丽丽, 马江锋, 李贤超, 田英, 王林, 王雪祎, 焦文锴. 添加不同喷雾助剂对早熟棉区除草剂减量增效的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(7): 1291-1296. |
| [10] | 吴依衍, 马彬, 姜艳. 典型荒漠农田防护林对棉田土壤水盐动态的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(6): 1012-1020. |
| [11] | 耿亚玲, 李耀发, 浑之英, 王华, 田婷婷, 王玲慧, 贾宏军, 袁立兵. 冀南棉田杂草发生种类及防治药剂筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(10): 1876-1881. |
| [12] | 王树林, 王燕, 董明, 祁虹, 冯国艺, 雷晓鹏, 梁青龙, 张谦. 磷肥用量定位6年对土壤和棉株磷素吸收及棉花产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(10): 1882-1886. |
| [13] | 王方斌, 刘凯, 孙嘉璘, 殷星, 侯振安. 氮肥减施对滴灌棉田NH3挥发及棉花养分吸收和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(9): 1746-1753. |
| [14] | 徐丽娜, 吴晨源, 胡飞, 周子燕, 胡本进. 四唑虫酰胺对棉田斜纹夜蛾的防治效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(6): 1090-1094. |
| [15] | 张谦, 王树林, 祁虹, 李岩, 王燕, 冯国艺, 梁青龙, 雷晓鹏, 林永增. 助剂对精喹禾灵防治棉田杂草的减量增效作用[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(6): 1159-1165. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||