

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (S1): 35-48.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.S1.005
袁梓涵( ), 赵雯慧, 王小武, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 丁新华, 张帅, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 郭文超(
), 赵雯慧, 王小武, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 丁新华, 张帅, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 郭文超( )
)
收稿日期:2024-07-05
出版日期:2024-10-10
发布日期:2024-11-15
通信作者:
郭文超(1966-),男,新疆乌鲁木齐人,研究员,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为农业昆虫与害虫防治(E-mail)gwc1966@163.com作者简介:袁梓涵(1998-),女,重庆涪陵人,硕士研究生,研究方向为农业昆虫与害虫防治, (E-mail)3187203383@qq.com
基金资助:
YUAN Zihan( ), ZHAO Wenhui, WANG Xiaowu, Tuerxun Ahemaiti, DING Xinhua, ZHANG Shuai, FU Kaiyun, JIA Zunzun, GUO Wenchao(
), ZHAO Wenhui, WANG Xiaowu, Tuerxun Ahemaiti, DING Xinhua, ZHANG Shuai, FU Kaiyun, JIA Zunzun, GUO Wenchao( )
)
Received:2024-07-05
Published:2024-10-10
Online:2024-11-15
Correspondence author:
GUO Wenchao (1966 -), male, from Hebei, researcher, Ph.D.,masterand doctoral's supervisor, research direction: integrated control of agricultural pests, (E-mail)gwc1966@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】筛选防治玉米茎腐病有效的生防菌,并评价其效果,获得高效防治玉米茎腐病的生防菌株。【方法】采用平板对峙法和菌丝生长速率法,以轮枝镰刀菌Fusarium verticillioides、胶孢镰刀菌Fusarium subglutinans、木贼镰刀菌Fusarium equiseti、层出镰孢菌Fusarium proliferatum、拟轮枝镰孢菌Fusarium sporotrichioides、变红镰刀菌Fusarium lateritium、禾谷镰刀菌Fusarium graminearum、尖孢镰刀菌Fusarium oxysporum 8株玉米茎腐病病原菌为指示菌,通过4株候选菌株发酵滤液浸种试验,检测其发酵滤液对玉米种子萌发的影响。【结果】6株生防真菌中里氏木霉Trichoderma reesei的抑菌效果最好,其对8株病原菌的抑菌率达41.43%~60.29%,绿木霉Trichoderma viride的抑菌率次之,为11.55%~54.93%,粉红粘帚菌Gliocladium roseum抑菌率最差为1.61%-38.63%。6株生防真菌对8株病原菌的拮抗系数均为Ⅱ级,菌落均能占据平板的2/3以上。8株病原菌分生孢子在各生防菌发酵滤液中的萌发率均显著低于对照(P< 0.05),其中,里氏木霉发酵滤液处理8株病原菌的孢子萌发率最低,仅为8.44%~13.56%。11种生防细菌中解淀粉芽孢杆菌Bacillus amyloliquefaciens IK-5抑菌效果最佳,其对8株病原菌的抑菌率达47.04%~90.48%,解淀粉芽孢杆菌2#次之,为65.98%~76.71%,枯草芽孢杆菌Bacillus subtilis ACB0043最差,仅为1.89%~51.53%。里氏木霉、绿木霉、解淀粉芽孢杆菌IK-5和解淀粉芽孢杆菌2#发酵滤液对玉米种子具有促生作用,绿木霉对玉米种子的萌发和生长促进效果最佳。【结论】菌株里氏木霉、绿木霉、解淀粉芽孢杆菌IK-5、解淀粉芽孢杆菌2#对玉米茎腐病具有较好的拮抗活性和促生能力,在玉米茎腐病防控中具有潜在的应用价值。
中图分类号:
袁梓涵, 赵雯慧, 王小武, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 丁新华, 张帅, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 郭文超. 玉米茎腐病生防菌的筛选及生防效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 35-48.
YUAN Zihan, ZHAO Wenhui, WANG Xiaowu, Tuerxun Ahemaiti, DING Xinhua, ZHANG Shuai, FU Kaiyun, JIA Zunzun, GUO Wenchao. Screening of Corn Stalk Rot control bacteria and evaluation of control effects[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(S1): 35-48.
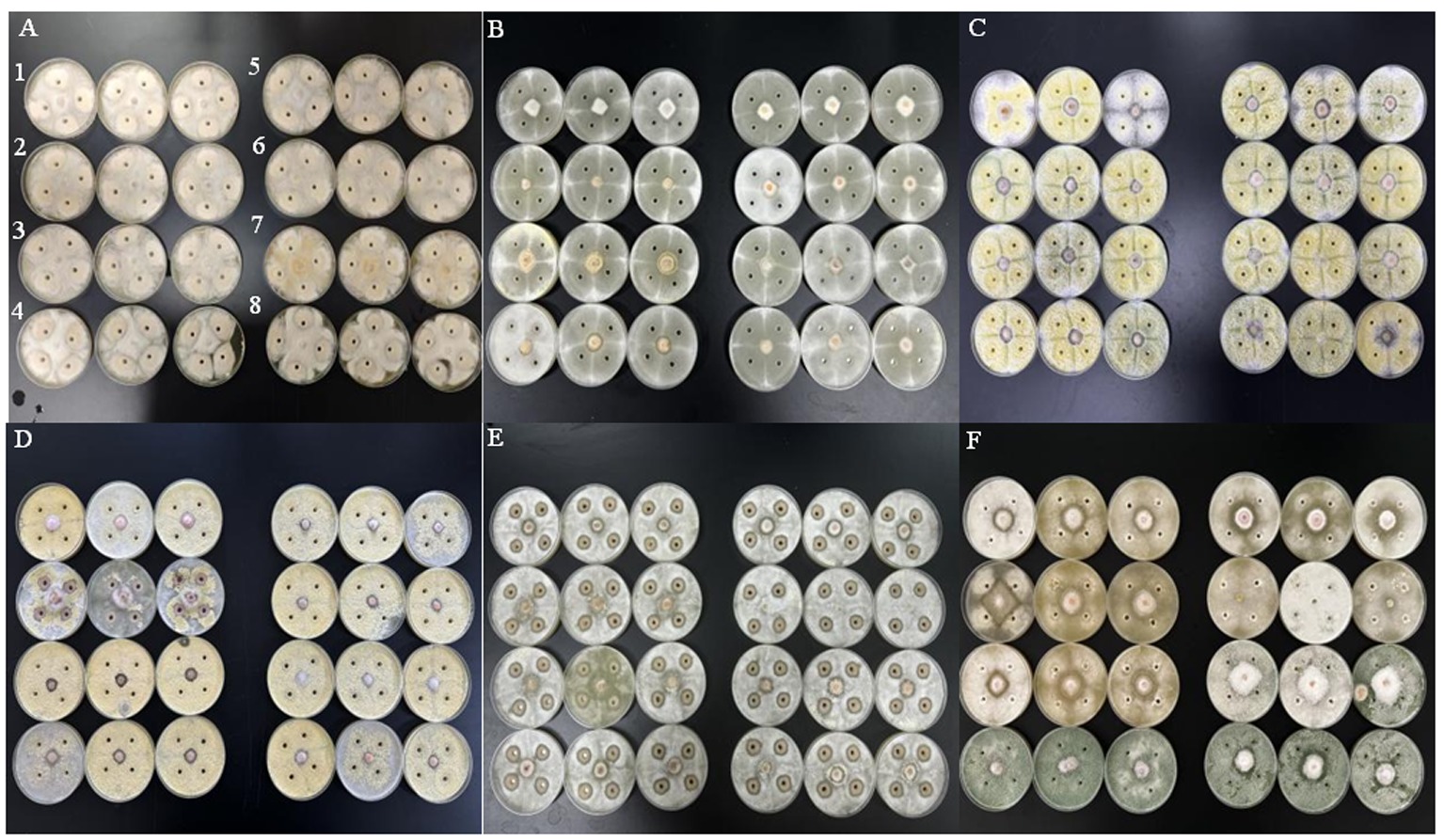
图1 6株生防真菌与8株病原菌的对峙培养对比 注:A、B、C、D、E、F分别为粉红粘帚菌、哈茨木霉、棘孢木霉、里氏木霉、绿木霉和长枝木霉处理。A中的1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8分别为胶孢镰刀菌88、木贼镰刀菌120、拟轮枝镰孢菌280、尖孢镰刀菌22、轮枝镰刀菌16、层出镰孢菌40、禾谷镰刀菌51、变红镰刀菌15,B、C、D、E、F中的1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8同A
Fig.1 Comparions of confrontation cultures of six strains of biocontrol fungi with eight strains of pathogens Note: A, B, C, D, E and F are treatments of G.roseum, T.harzianum, T.asperellum, T.reesei, T.viride and T.longibrachiatum, respectively.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 in A are treatments of F.subglutinans 88, F.equiseti 120, F.sporotrichioides 280, F.oxysporum 22, F.verticillioides 16, and F.proliferatum 40, F.graminearum 51, F.lateritium 15, respectively, and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 in B, C, D, E, F are the same as A
| 生防菌 Biocontrol microbe | 拮抗系数Antagonistic coefficient | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 层出镰 孢菌 F.prolifer atum 40 | 变红镰 刀菌 F. lateritium 15 | 拟轮枝 镰孢菌 F. sporotrichioides 280 | 胶孢镰 刀菌 F. subglutinans 88 | 尖孢镰 刀菌 F. oxysporum 22 | 轮枝镰 刀菌 F. verticillioides 16 | 木贼镰 刀菌 F. equiseti 120 | 禾谷镰 刀菌 F. graminearum 51 | |
| 棘孢木霉 T.asperellum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 哈茨木霉 T.harzianum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 长枝木霉 T.longibrachiatum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 绿木霉 T.viride | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 里氏木霉 T.reesei | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 粉红粘帚菌 G.roseum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
表2 生防真菌抑制病原菌的拮抗系数比较
Tab.2 Comparions of antagonistic coefficient for inhibition of pathogenic fungi by biocontrol fungi
| 生防菌 Biocontrol microbe | 拮抗系数Antagonistic coefficient | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 层出镰 孢菌 F.prolifer atum 40 | 变红镰 刀菌 F. lateritium 15 | 拟轮枝 镰孢菌 F. sporotrichioides 280 | 胶孢镰 刀菌 F. subglutinans 88 | 尖孢镰 刀菌 F. oxysporum 22 | 轮枝镰 刀菌 F. verticillioides 16 | 木贼镰 刀菌 F. equiseti 120 | 禾谷镰 刀菌 F. graminearum 51 | |
| 棘孢木霉 T.asperellum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 哈茨木霉 T.harzianum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 长枝木霉 T.longibrachiatum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 绿木霉 T.viride | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 里氏木霉 T.reesei | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
| 粉红粘帚菌 G.roseum | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 | Ⅱ级 |
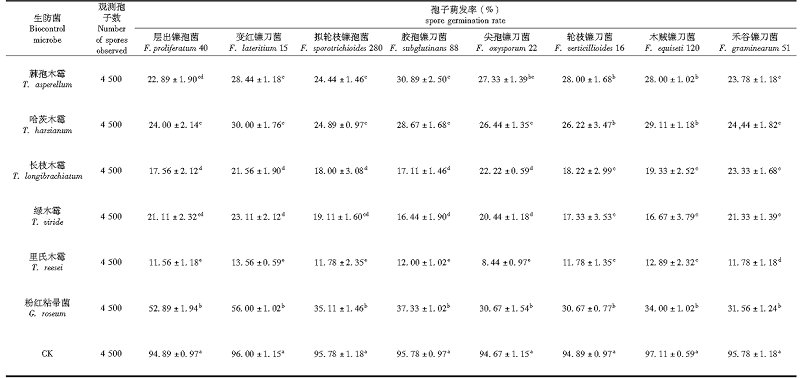 |
表3 8株病原菌分生孢子在6株生防真菌发酵滤液中的萌发率比较
Tab.3 Comparions of germination rate of conidia of eight strains of pathogenic fungi in the fermentation filtrate of six strains of bioprophy lactic fungi
 |
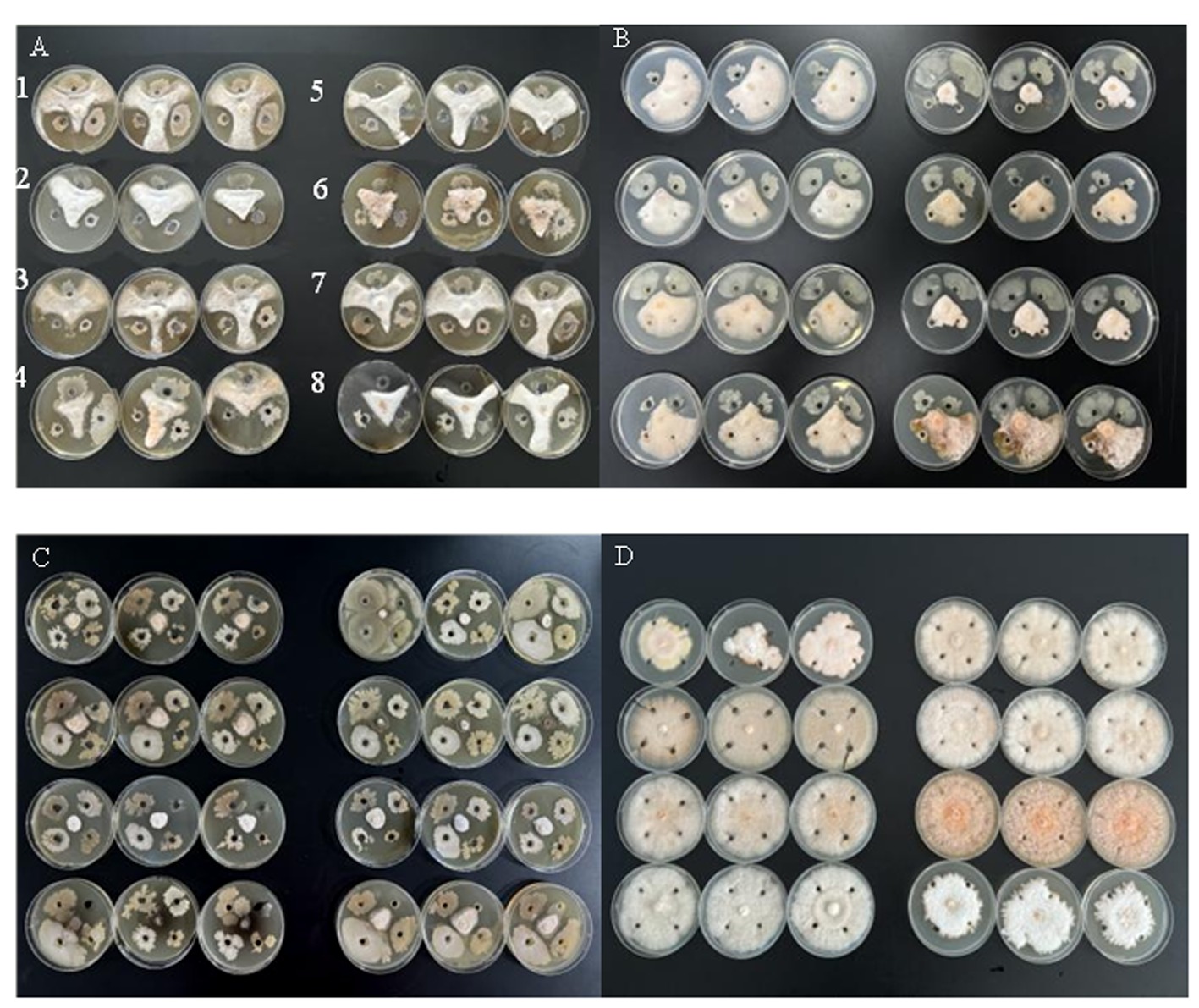
图2 11株生防细菌与8株病原菌的初筛对比 注:A上孔是解淀粉芽孢杆菌BNCC336388,左下孔是解淀粉芽孢杆菌2#,右下孔是解淀粉芽孢杆菌IK-5;B图中左上孔是贝莱斯芽孢杆菌J/C,右上孔是枯草芽孢杆菌 ACB0043,左下孔是贝莱斯芽孢杆菌W38,右下孔是苏云金芽孢杆菌ACB10410;C图中左上孔是枯草芽孢杆菌Z-4,右上孔是贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BH229,左下孔是贝莱斯芽孢杆菌BLS-9,右下孔是贝莱斯芽孢杆菌B.velezensis AL7;D是无菌水对照。A中的1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8分别为胶孢镰刀菌88、木贼镰刀菌120、拟轮枝镰孢菌280、尖孢镰刀菌22、轮枝镰刀菌16、层出镰孢菌40、禾谷镰刀菌51、变红镰刀菌15,B、C、D中的1、2、3、4、5、6、7、8同A。
Fig.2 Comparions of initial screening results of 11 strains of bioprophilic bacteria and 8 strains of pathogenic bacteria Notes: A, the upper hole is B.amyloliquefaciens BNCC336388, the lower left hole is B.amyloliquefaciens 2#, and the lower right hole is B.amyloliquefaciens IK-5; in figure B, the upper left hole is B.velezensis J/C, the upper right hole is B.subtilis ACB0043, the lower left hole is B.velezensis W38, and the lower right hole is B.thuringiensis ACB10410; in figure C the upper left hole is B.subtilis Z-4, the upper right hole is B.velezensis BH229, the lower left hole is B.velezensis BLS-9, and the lower right hole is B.velezensis AL7; D is the sterile water control.1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 in A are F.subglutinans 88, F.equiseti 120, F.sporotrichioides 280, F.oxysporum 22, F.verticillioides 16, and F.proliferatum 40, F.graminearum 51, F.lateritium 15, respectively, and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 in B, C, and D are as in A.
| 处理 Treatments | 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | 胚芽长度 Germ length (cm) | 胚根长度 Radicle length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 绿木霉T.viride | 92.83±1.22a | 5.48±0.12a | 8.53±0.18a |
| 里氏木霉T.reesei | 92.00±0.86a | 5.38±0.16a | 7.45±0.11b |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌IK-5B.amyloliquefaciens | 93.83±0.95a | 4.82±0.10b | 7.53±0.16b |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌2#B.amyloliquefaciens | 93.33±1.12a | 5.13±0.10ab | 6.92±0.12c |
| 对照CK | 88.00±1.03b | 3.52±0.17c | 4.72±0.15d |
表 5 4种候选发酵液处理的玉米种子发芽性状的比较
Tab.5 Comparions of germination traits of maize seeds treated with four candidate fermentation broths
| 处理 Treatments | 发芽率 Germination rate (%) | 胚芽长度 Germ length (cm) | 胚根长度 Radicle length (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 绿木霉T.viride | 92.83±1.22a | 5.48±0.12a | 8.53±0.18a |
| 里氏木霉T.reesei | 92.00±0.86a | 5.38±0.16a | 7.45±0.11b |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌IK-5B.amyloliquefaciens | 93.83±0.95a | 4.82±0.10b | 7.53±0.16b |
| 解淀粉芽孢杆菌2#B.amyloliquefaciens | 93.33±1.12a | 5.13±0.10ab | 6.92±0.12c |
| 对照CK | 88.00±1.03b | 3.52±0.17c | 4.72±0.15d |
| [1] | 刘晓燕, 金继运, 何萍, 等. 氯化钾抑制玉米茎腐病发生与土壤微生物关系初探[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007, (2): 279-285. |
| LIU Xiaoyan, JIN Jiyun, HE Ping, et al. Relationship between inhibition of maize stem rot by potassium chloride and soil microorganisms[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilisation, 2007, (2): 279-285. | |
| [2] | 杨洋, 郭成, 孙素丽, 等. 玉米抗腐霉茎腐病种质标记基因型鉴定与遗传多样性分析[J]. 植物遗传资源学报, 2019, 20(6): 1418-1427. |
| YANG Yang, GUO Cheng, SUN Suli, et al. Genotypic identification and genetic diversity analysis of germplasm markers for rot-resistant stem rot in maize[J]. Journal of Plant Genetic Resources, 2019, 20(6): 1418-1427. | |
| [3] | 丁新华, 宋子硕, 蒋旭东, 等. 新疆绿洲灌溉玉米产区玉米茎腐病优势病原菌分离与鉴定[J]. 植物保护学报, 2023, 50(3): 733-743. |
| DING Xinhua, SONG Zishuo, JIANG Xudong, et al. Isolation and characterisation of the dominant pathogen of maize stem rot in irrigated maize production areas in Xinjiang oasis[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2023, 50(3): 733-743. | |
| [4] |
宋子硕, 杨杰, 丁新华, 等. 荒漠绿洲生态区玉米茎腐病发生分布与危害[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(4): 950-956.
DOI |
| SONG Zishuo, YANG Jie, DING Xinhua, et al. Distribution and damage of maize stem rot in desert oasis ecological zones[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Science, 2022, 59(4): 950-956. | |
| [5] | 佟昀铮. 玉米茎腐病生防菌鉴定及其绿色防控关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021. |
| TONG Yunzheng. Identification of maize stem rot bacteria and key technologies for green prevention and control[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021. | |
| [6] | 代真林, 何洪磊, 姚秀英, 等. 抗生素溶杆菌13-6对玉米小斑病的生防作用机制初步研究[J]. 植物病理学报, 2021, 51(3): 393-402. |
| DAI Zhenlin, HE Honglei, YAO Xiuying, et al. Preliminary study on the mechanism of biocontrol of small blotch disease of maize by the antibiotic Bacillus thuringiensis 13-6[J]. Journal of Plant Pathology, 2021, 51(3): 393-402. | |
| [7] | 马佳, 范莉莉, 傅科鹤, 等. 哈茨木霉SH2303防治玉米小斑病的初步研究[J]. 中国生物防治学报, 2014, 30(1): 79-85. |
| MA Jia, FAN Lili, FU Kehe, et al. Preliminary study on the control of maize small blotch disease by Aspergillus oryzae SH2303[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control, 2014, 30(1): 79-85. | |
| [8] | 杨冰娟, 陶睿泽, 林丽, 等. 芽孢杆菌抑制玉米茎腐病菌禾谷镰孢菌和拟轮枝镰孢菌的研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2023, 51(12): 42-49. |
| YANG Bingjuan, TAO Ruize, LIN Li, et al. Inhibition of Fusarium graminearum and Fusarium verticillioides by Bacillus sphaericus on maize stem rot[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Science, 2023, 51(12): 42-49. | |
| [9] | 刘彦策. 抗玉米茎腐病复合菌剂CAP的创制与应用效果[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2020. |
| LIU Yanze. Creation and application of CAP against maize stem rot[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [10] |
郭成, 王宝宝, 王春明, 等. 甘肃玉米镰孢茎腐病病原菌种群多样性分析[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(11): 2521-2527.
DOI |
| GUO Cheng, WANG Baobao, WANG Chunming, et al. Analysis of the diversity of Fusarium stalk rot pathogen in Gansu[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, 2021, 35(11): 2521-2527. | |
| [11] |
Anle He, Jianan Sun, Xinhua Wang, et al. Reprogrammed endophytic microbial community in maize stalk induced by Trichoderma asperellum biocontrol agent against Fusarium diseases and mycotoxin accumulation[J]. Fungal Biology, 2019, 123 (6):448-455.
DOI PMID |
| [12] | Kandasamy Saravanakumar, Yaqian Li, Chuanjin Yu, et al. Effect of Trichoderma harzianum on maize rhizosphere microbiome and biocontrol of Fusarium Stalk rot[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7 (1). |
| [13] | Qiong Wu, Ruiyan Sun, Ni M, et al. Identification of a novel fungus, Trichoderma asperellum GDFS1009, and comprehensive evaluation of its biocontrol efficacy[J]. PLOS ONE, 2017, 12 (6). |
| [14] |
Xingkai Cheng, Xiaoxue Ji, Yanzhen Ge, et al. Characterization of Antagonistic Bacillus methylotrophicus Isolated From Rhizosphere and Its Biocontrol Effects on Maize Stalk Rot[J]. Phytopathology, 2019, 109 (4): 571-581.
DOI PMID |
| [15] | 霍宪起, 陈京元. 拮抗菌C23对松苗猝倒病原菌的抑制效果及在松苗根际的定殖[J]. 山西农业科学, 2009, 37(11): 33-36. |
| HUO Xianqi, CHEN Jingyuan. Inhibitory effect of the antagonist bacterium C23 on the pathogen Sudden Fall of pine seedlings and its colonisation in the inter-root zone of pine seedlings[J]. Shanxi Agricultural Science, 2009, 37(11): 33-36. | |
| [16] | 李晶, 杨谦. 生防枯草芽孢杆菌的研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2008, (1): 106-111,132. |
| LI Jing, Yang Qian. Research progress of biocontrol of Bacillus subtilis[J]. Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2008, (1): 106-111,132. | |
| [17] | 李志普. 玉米镰孢茎腐病生防菌株的筛选鉴定与菌剂研发[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2023. |
| LI Zipu. Screening and identification of Fusarium oxysporum stem rot control strains in maize and development of fungicides[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| [18] | 郭佳月, 徐素娟, 赵晓霞, 等. 玉米茎腐病拮抗放线菌的筛选及抑菌促生活性鉴定[J]. 玉米科学, 2022, 30(3): 169-177. |
| GUO Jiayue, XU Sujuan, ZHAO Xiaoxia, et al. Screening of antagonistic actinomycetes against maize stem rot and identification of bacteriostatic activity[J]. Maize Science, 2022, 30(3): 169-177. | |
| [19] | 吴沁. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌OR2-30对禾谷镰孢菌的抑菌机理研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2022. |
| WU Qin. Inhibition mechanism of Fusarium graminearum by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens OR2-30[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| [20] |
梁晓洁, 刘志华, 张平, 等. 抗油桐枯萎病木霉菌的分离鉴定及抑菌作用研究[J]. 菌物学报, 2020, 39(5): 795-805.
DOI |
| LIANG Xiaojie, LIU Zhihua, ZHANG Ping, et al. Isolation, identification and inhibitory effect of Xylomycetes resistant to oil tree wilt[J]. Journal of Mycology, 2020, 39(5): 795-805. | |
| [21] | 朱廷恒, 邢小平, 孙顺娣. 木霉T_(97)菌株对几种植物病原真菌的拮抗作用机制和温室防治试验[J]. 植物保护学报, 2004, (2): 139-144. |
| ZHU Tingheng, XING Xiaoping, SUN Shundi. Mechanism of antagonistic action of Aspergillus oryzae T_(97) strain on several plant pathogenic fungi and greenhouse control experiments[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2004, (2): 139-144. | |
| [22] | 方中达. 植病研究法(第3版)[D]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1998. |
| FANG Zhongda. Phytophthora (3rd ed.)[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 1998. | |
| [23] |
郭宁, 孙华, 马红霞, 等. 玉米腐霉茎腐病生防木霉菌株的筛选、鉴定及防治效果分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2023, 56(22): 4453-4466.
DOI |
| GUO Ning, SUN Hua, MA Hongxia, et al. Screening, identification and control effect analysis of biocontrol strains of Xylella spp. on corn stem rot[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science, 2023, 56(22): 4453-4466. | |
| [24] | Jung Won Shin, Jiye Han, Ju Kyong Lee, et al. Characterization of the Maize Stalk Rot Pathogens Fusarium subglutinans and F.temperatum and the Effect of Fungicides on Their Mycelial Growth and Colony Formation[J]. Plant pathology journal (Suwon), 2014, 30 (4): 397-406. |
| [25] | 叶旻硕, 俞键烽, 马艳, 等. 不同微生物菌剂对辣椒疫病的防控效果及对土壤性状的影响[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2019, 35(4): 811-817. |
| YE Minshuo, YU Jianfeng, MA Yan, et al. Effect of different microbial agents on the prevention and control of chilli blight and on soil properties[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agriculture, 2019, 35(4): 811-817. | |
| [26] | Nguyễn Hoàng Lộc, Nguyễn Đức Huy, Hoàng Tấn Quảng, et al. Characterisation and antifungal activity of extracellular chitinase from a biocontrol fungus, Trichoderma asperellum PQ34[J]. Mycology, 2019, 11 (1): 38-48. |
| [27] | 杨合同, 肖性龙, 徐砚珂, 等. 植病生防木霉菌的RAPD分析[J]. 山东科学, 2004, (3): 17-21. |
| YANG Hetong, XIAO Xinglong, XU Yanke, et al. RAPD analysis of Phytophthora parasitica[J]. Shandong Science, 2004, (3): 17-21. | |
| [28] |
张小杰, 周天旺, 王春明, 等. 长枝木霉TS-1的分离鉴定、拮抗作用及固体发酵条件初探[J]. 中国农学通报, 2021, 37(27): 105-111.
DOI |
| ZHANG Xiaojie, ZHOU Tianwang, WANG Chunming, et al. Identification, antagonism and solid-state fermentation conditions of Trichoderma longibrachiatum TS-1[J]. Chinese Agronomy Bulletin, 2021, 37(27): 105-111. | |
| [29] | 刘佳, 张悦, 沈志彦, 等. 长枝木霉T6菌株对美洲南瓜枯萎病菌的抑制作用[J]. 西北农业学报, 2020, 29(12): 1891-1897. |
| LIU Jia, ZHANG Yue, SHEN Zhiyan, et al. Inhibitory effect of Trichoderma longibrachiatum T6 strain on American pumpkin wilt[J]. Northwest Journal of Agriculture, 2020, 29(12): 1891-1897. | |
| [30] | Danielson R M, Davey C B. Carbon and nitrogen nutrition of Trichoderma[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 1973, 5(5): 505-515. |
| [31] | 肖烈. 内生放线菌S-42的鉴定及对黄瓜枯萎病拮抗效果研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2010. |
| Xiao Lie. Identification of endophytic actinomycete S-42 and its antagonistic effect on cucumber wilt[D]. Ya’an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2010. | |
| [32] | 沈冰冰. 玉米茎腐病和大斑病生防菌的筛选及其促生作用的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2019. |
| Shen Bingbing. Screening of biocontrol fungi against maize stem rot and big blotch disease and research on their growth-promoting effects[D]. Harbin:Northeast Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| [33] |
Jung Yeop Lee, Byung Kook Hwang. Diversity of antifungal actinomycetes in various vegetative soils of Korea[J]. Canadian Journal of Microbiology, 2002, 48 (5): 407-417.
PMID |
| [34] | 连玲丽. 芽孢杆菌的生防菌株筛选及其抑病机理[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2007. |
| LIAN Lingli. Screening of biocontrol strains of Bacillus subtilis and its disease suppression mechanism[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2007. | |
| [35] | 李全胜, 谢宗铭, 张国丽, 等. 棉花黄萎病拮抗芽孢杆菌S12的筛选鉴定及拮抗机制的分析[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2015, 38(3): 402-408. |
| LI Quansheng, XIE Zongming, ZHANG Guoli, et al. Screening and identification of antagonistic Bacillus sphaericus S12 against cotton yellow wilt and analysis of antagonistic mechanism[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2015, 38(3): 402-408. | |
| [36] | 李想, 王欢欢, 郭秋翠, 等. 玉米茎腐病病原禾谷镰孢拮抗菌筛选及分子鉴定[J]. 玉米科学, 2020, 28(5): 169-175. |
| LI Xiang, WANG Huanhuan, GUO Qiu Cui, et al. Screening and molecular identification of Fusarium graminearum antagonist bacteria as the causal agent of maize stem rot[J]. Maize Science, 2020, 28(5): 169-175. | |
| [37] | 刘芳婷. 玉米茎腐病生防菌株筛选及应用[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2023. |
| LIU Fangting. Screening and application of biocontrol strains of maize stem rot[D]. Tai'an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2023. | |
| [38] | Shuang Wang, Lina Sun, Wu Zhang, et al. Bacillus velezensis BM21, a potential and efficient biocontrol agent in control of corn stalk rot caused by Fusarium graminearum[J]. Egyptian Journal of Biological Pest Control, 2020, 30 (1):0-0. |
| [39] | 谢红辉. 桑毛色二孢根腐病的病原、发生规律及其防治研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2016. |
| Xie Honghui. Research on the pathogen, occurrence law and its control of mulberry hairy discolouration root rot[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2016. | |
| [40] | 崔文艳, 何朋杰, 尚娟, 等. 解淀粉芽孢杆菌B9601-Y2对玉米的防病促生长效果研究[J]. 玉米科学, 2015, 23(5): 153-158. |
| CUI Wenyan, HE Pengjie, SHANG Juan, et al. Study on disease prevention and growth promotion effect of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens B9601-Y2 on maize[J]. Maize Science, 2015, 23(5): 153-158. | |
| [41] | I.Pertot, Oscar Giovannini, Maddalena Benanchi, et al. Combining biocontrol agents with different mechanisms of action in a strategy to control Botrytis cinerea on grapevine[J]. Crop Protection, 2017, 97 (0): 85-93. |
| [1] | 张帅, 高国文, 吴莉莉, 赵海燕, 王小武, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 丁新华, 李克梅, 郭文超. 增效剂及微肥与种衣剂协同施用评价玉米茎腐病的防效[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 19-27. |
| [2] | 耿松毅, 孙洪涛, 赵伟琦, 王梅, 芦屹, 马荣. 苹果树腐烂病发生及新型防治药剂筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1461-1467. |
| [3] | 曹竹君, 张振宇, 康宁, 赵倩, 胡红英. 新疆西天山野果林杏鬃球蚧寄生蜂资源调查[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 971-983. |
| [4] | 孟卓, 唐小雯, 张广杰, 徐安东, 颜宇, 付娆, 羌松, 蒋平安, 马德英. 虫砂复合微生物菌剂2种施用方式对棉花生长发育及防控黄萎病的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2861-2871. |
| [5] | 文霞, 田立超, 高桂珍. 四斑月瓢虫对紫薇长斑蚜的捕食功能反应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2266-2272. |
| [6] | 杨海涛, 席欧彦, 赵倩, 曹竹君, 胡红英. 朝鲜球坚蚧成虫寄生蜂资源调查[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2273-2280. |
| [7] | 宋素琴, 高海峰, 吕卓, 唐琦勇, 顾美英, 张志东, 楚敏, 朱静, 王玮. 马铃薯疮痂病病原菌的分离鉴定及其生长特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(8): 1999-2006. |
| [8] | 李艳兵, 郭小虎, 努尔什瓦克·阿达力别克, 帕提玛·乌木尔汗, 马德英. 人工助迁多异瓢虫和化防2种模式对棉蚜的防效及天敌种群动态影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1173-1179. |
| [9] | 高宇洁, 詹发强, 陈澄, 包慧芳, 杨蓉, 王宁, 侯新强, 侯敏, 史应武, 龙宣杞. 黑曲霉拮抗菌Xenorhabdus bovienii445筛选、鉴定及发酵优化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1203-1215. |
| [10] | 赵莹莹, 张军高, 李进, 梁晶, 高翔宇, 顾爱星, 雷斌. 枯草芽孢杆菌KXZ-33与化学药剂协同防控棉花枯萎病的效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1216-1222. |
| [11] | 宋子硕, 杨杰, 丁新华, 付开赟, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 何江, 郭文超. 荒漠绿洲生态区玉米茎腐病发生分布与危害[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(4): 950-956. |
| [12] | 丁新华, 宋子硕, 杨杰, 高国文, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 郭文超. 玉米种质对腐霉茎腐病和镰孢茎腐病抗性鉴定与评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(12): 3047-3056. |
| [13] | 鲁晏宏, 郝金辉, 詹发强, 王宁, 侯新强, 杨蓉, 包慧芳, 龙宣杞. 香梨黑斑病病原菌分离及拮抗菌筛选鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2538-2545. |
| [14] | 刘海洋, 王伟, 张仁福, 温切木·阿布列孜, 姚举. 利用生防菌防治棉花黄萎病效果的制约因素[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 155-161. |
| [15] | 杜鹏程, 刘海洋, 张军高, 李进, 周小云, 刘梦丽, 雷斌, 郭庆元. 棉花苗期根腐类病害生防细菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(4): 686-693. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 18
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 89
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||