

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (9): 2330-2340.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.09.030
• 植物保护·微生物·畜牧兽医·土壤肥料 • 上一篇
李金瑶1( ), 徐贵青2(
), 徐贵青2( ), 王立生3, 吕平3, 石东方4, 郑伟华5
), 王立生3, 吕平3, 石东方4, 郑伟华5
收稿日期:2024-02-15
出版日期:2024-09-20
发布日期:2024-10-09
通信作者:
徐贵青(1976-),男,新疆人,副研究员,博士,硕士生导师,研究方向干旱区植物生理生态学,(E-mail)xugq@ms.xjb.ac.cn作者简介:李金瑶(1998-),女,河南人,在读硕士研究生,研究方向植物生理学。(E-mail)865268214@qq.com
基金资助:
LI Jinyao1( ), XU Guiqing2(
), XU Guiqing2( ), WANG Lisheng3, LU Ping3, SHI Dongfang4, ZHENG Weihua5
), WANG Lisheng3, LU Ping3, SHI Dongfang4, ZHENG Weihua5
Received:2024-02-15
Published:2024-09-20
Online:2024-10-09
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】探索施用氮肥对提高植物抗旱性的影响。【方法】以干旱区重要造林树种头状沙拐枣(Calligonum caput-medusae)幼苗为研究对象,采用盆栽试验,设置两组水分处理(亏缺供水和正常供水)和两组氮肥处理(未施氮和施氮),测定幼苗同化枝的生理生化指标。【结果】(1)同正常供水相比,亏缺供水下的幼苗同化枝相对含水量(RWC)、正午同化枝水势(Ψm)、最大气孔导度(gs)、叶绿素含量(Chl)、表观量子效率(Φ)和可溶性糖(SS)含量显著降低;而脯氨酸(Pro)含量显著增加;(2)同未施氮组相比,施氮减缓了亏缺供水和正常供水下头状沙拐枣幼苗同化枝相对含水量的下降,但不显著;同正常供水比,亏缺供水下施氮降低了头状沙拐枣幼苗的同化枝水势;(3)正常供水下,施氮提高了幼苗Pro、SS含量,而丙二醛(MDA)含量显著降低(P<0.05);亏缺供水下,施氮提高了超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)含量、Pro含量和SS含量(P<0.05),而MDA含量显著降低(P<0.05)。【结论】沙拐枣幼苗生理活性受土壤水分有效性的影响,而施氮有助于降低干旱胁迫造成的影响。施氮提高了亏缺供水和正常供水下头状沙拐枣幼苗的抗氧化酶活性和细胞溶质浓度,有助于头状沙拐枣幼苗降低氧化应激反应并减少损伤,增加渗透调节物质。
中图分类号:
李金瑶, 徐贵青, 王立生, 吕平, 石东方, 郑伟华. 氮肥对头状沙拐枣幼苗抗旱性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2330-2340.
LI Jinyao, XU Guiqing, WANG Lisheng, LU Ping, SHI Dongfang, ZHENG Weihua. Study on the effect of N fertilization on drought resistance of Calligonum caput-medusae seedlings[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2330-2340.
| 指标 Indexes | 亏缺供水 Deficient water supply | 正常供水 Adequate water supply | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | N1 | N0 | N1 | |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content(SWC, %) | 1.75±0.25b | 1.85±0.80b | 4.54±1.57a | 5.00±0.67a |
| 同化枝相对含水量 Relative water content(RWC, %) | 83.13±2.89c | 83.76±2.86c | 87.35±2.25ab | 90.16±2.69a |
| 黎明同化枝水势 Predawn shoot water potential(Ψpd, MPa) | -1.06±1.29ab | -1.19±2.03b | -1.03±2.20b | -0.90±2.03a |
| 正午同化枝水势 Midday shoot water potential(Ψmd, MPa) | -2.04±4.32b | -2.38±3.37c | -1.91±2.99b | -1.79±4.69a |
表1 不同水肥处理下土壤和植物的水分状况
Tab.1 Water status of soil and plants under different water and fertilizer treatments
| 指标 Indexes | 亏缺供水 Deficient water supply | 正常供水 Adequate water supply | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | N1 | N0 | N1 | |
| 土壤含水量 Soil moisture content(SWC, %) | 1.75±0.25b | 1.85±0.80b | 4.54±1.57a | 5.00±0.67a |
| 同化枝相对含水量 Relative water content(RWC, %) | 83.13±2.89c | 83.76±2.86c | 87.35±2.25ab | 90.16±2.69a |
| 黎明同化枝水势 Predawn shoot water potential(Ψpd, MPa) | -1.06±1.29ab | -1.19±2.03b | -1.03±2.20b | -0.90±2.03a |
| 正午同化枝水势 Midday shoot water potential(Ψmd, MPa) | -2.04±4.32b | -2.38±3.37c | -1.91±2.99b | -1.79±4.69a |
| 性状 Traits | 亏缺供水 Deficient water supply | 正常供水 Adequate water supply | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | N1 | N0 | N1 | |
| 表观量子效率 The apparent quantum efficiency (Φ)(10-2) | 1.18±0.3b | 1.25±0.21b | 2.28±0.67a | 1.62±0.37ab |
| 最大净光合速率 Max photosynthesis rate (Pmax) (μmol/(m2·s)) | 13.02±5.49a | 13.25±3.52a | 16.59±3.13a | 16.99±7.02a |
| 光补偿点 Light compensation point (LCP) (μmol/(m2 ·s)) | 164±49.43a | 164.69±66.62a | 159.34±37.20a | 127.01±29.10b |
| 暗呼吸速率 Dark respiration rate (Rd) (μmol/(m2· s)) | 1.93±0.93a | 2.09±1.09a | 3.59±1.57a | 2.04±0.65a |
| 最大气孔导度 Max stomatal conductance (gs) (mmol/(m2·s)) | 113.78±28.83b | 127.43±25.88b | 214.78±32a | 240.14±37.66a |
| 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content (SPAD) | 4.26±0.53c | 4.97±1.14b | 5.09±0.81b | 5.66±0.87a |
| 最大光化学量子产量 maximal quantum yield of PSⅡ (Fv/Fm) | 0.66±0.09ab | 0.61±0.11b | 0.72±0.02a | 0.63±0.02ab |
表2 不同水肥处理下植物生理性状的变化
Tab.2 Changes of different water and fertilizer treatments on plant physiological traits
| 性状 Traits | 亏缺供水 Deficient water supply | 正常供水 Adequate water supply | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N0 | N1 | N0 | N1 | |
| 表观量子效率 The apparent quantum efficiency (Φ)(10-2) | 1.18±0.3b | 1.25±0.21b | 2.28±0.67a | 1.62±0.37ab |
| 最大净光合速率 Max photosynthesis rate (Pmax) (μmol/(m2·s)) | 13.02±5.49a | 13.25±3.52a | 16.59±3.13a | 16.99±7.02a |
| 光补偿点 Light compensation point (LCP) (μmol/(m2 ·s)) | 164±49.43a | 164.69±66.62a | 159.34±37.20a | 127.01±29.10b |
| 暗呼吸速率 Dark respiration rate (Rd) (μmol/(m2· s)) | 1.93±0.93a | 2.09±1.09a | 3.59±1.57a | 2.04±0.65a |
| 最大气孔导度 Max stomatal conductance (gs) (mmol/(m2·s)) | 113.78±28.83b | 127.43±25.88b | 214.78±32a | 240.14±37.66a |
| 叶绿素含量 Chlorophyll content (SPAD) | 4.26±0.53c | 4.97±1.14b | 5.09±0.81b | 5.66±0.87a |
| 最大光化学量子产量 maximal quantum yield of PSⅡ (Fv/Fm) | 0.66±0.09ab | 0.61±0.11b | 0.72±0.02a | 0.63±0.02ab |
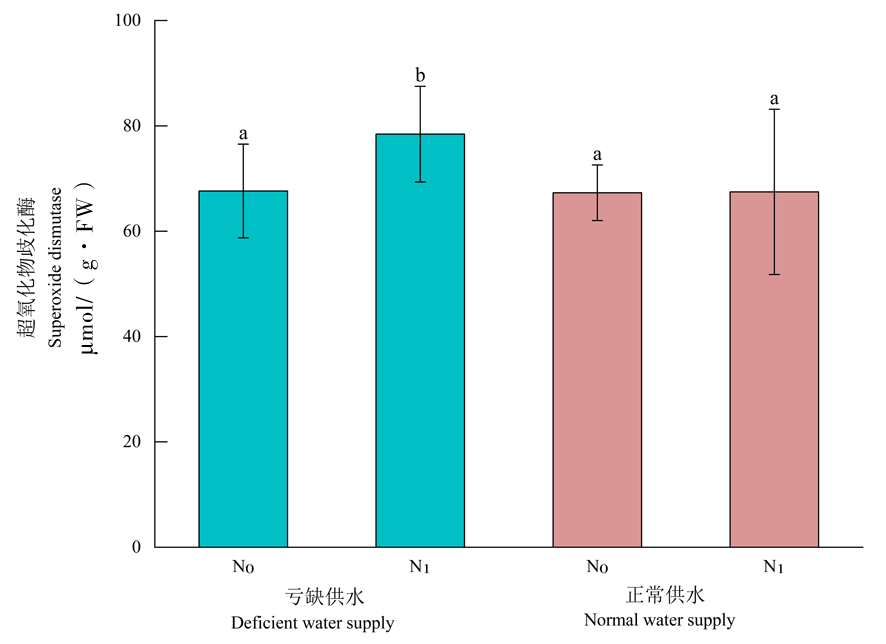
图1 超氧化物歧化酶的变化 注:按Duncan’s检验,不同小写字母表示不同处理间存在显著差异(P< 0.05)。竖线表示±SD,下同
Fig.1 Changes of superoxide dismutase Note:According to Duncan's test, different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among different treatments (P< 0.05). The vertical bar indicates±SD,the same as below
| 性状 Trait | 水 Water | 肥 fertilizer | 水×肥 Water×fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤含水量(SWC)Soil moisture content | 68.291** | 0.71 | 0.305 |
| 同化枝相对含水量(RWC)Relative water content | 28.292** | 2.975 | 1.196 |
| 黎明同化枝水势(Ψpd,)Predawn shoot water potential | 6.144* | 0.003 | 3.851 |
| 正午同化枝水势(Ψmd)Midday shoot water potential | 30.308** | 2.883 | 12.604* |
| 表观量子效率(Φ)The apparent quantum efficiency | 16.966** | 2.795 | 4.261 |
| 最大净光合速率(Pmax)Max photosynthesis rate | 3.697 | 0.028 | 0.002 |
| 光补偿点(LCP)Light compensation point | 0.422 | 0.235 | 0.256 |
| 暗呼吸速率(Rd)Dark respiration rate | 1.832 | 1.37 | 2.048 |
| 最大气孔导度(gs)Max stomatal conductance | 36.701** | 1.221 | 0.11 |
| 叶绿素含量(SPAD)Chlorophyll content | 5.094 | 4.631 | 0.003 |
| 最大光化学量子产量(Fv/Fm)maximal quantum yield of PSⅡ | 1.566 | 6.265* | 0.634 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)Superoxide dismutase | 0.62 | 1.485 | 1.321 |
| 超氧阴离子( | 2.763 | 0.238 | 0.2 |
| 丙二醛(MDA)malonic dialdehyde content | 0.066 | 0.595 | 0.011 |
| 脯氨酸(PRO)Proline content | 26.328 | 7.771* | 5.31 |
| 可溶性糖(SS)Soluble sugar content | 4.943** | 2.747 | 0.798 |
表3 浇水和施肥对沙拐枣幼苗各性状影响的双因素方差
Tab.3 Two-factor variance analysis of the effects of watering and fertilizing on the characteristics of Jujube japonica seedlings
| 性状 Trait | 水 Water | 肥 fertilizer | 水×肥 Water×fertilizer |
|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤含水量(SWC)Soil moisture content | 68.291** | 0.71 | 0.305 |
| 同化枝相对含水量(RWC)Relative water content | 28.292** | 2.975 | 1.196 |
| 黎明同化枝水势(Ψpd,)Predawn shoot water potential | 6.144* | 0.003 | 3.851 |
| 正午同化枝水势(Ψmd)Midday shoot water potential | 30.308** | 2.883 | 12.604* |
| 表观量子效率(Φ)The apparent quantum efficiency | 16.966** | 2.795 | 4.261 |
| 最大净光合速率(Pmax)Max photosynthesis rate | 3.697 | 0.028 | 0.002 |
| 光补偿点(LCP)Light compensation point | 0.422 | 0.235 | 0.256 |
| 暗呼吸速率(Rd)Dark respiration rate | 1.832 | 1.37 | 2.048 |
| 最大气孔导度(gs)Max stomatal conductance | 36.701** | 1.221 | 0.11 |
| 叶绿素含量(SPAD)Chlorophyll content | 5.094 | 4.631 | 0.003 |
| 最大光化学量子产量(Fv/Fm)maximal quantum yield of PSⅡ | 1.566 | 6.265* | 0.634 |
| 超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)Superoxide dismutase | 0.62 | 1.485 | 1.321 |
| 超氧阴离子( | 2.763 | 0.238 | 0.2 |
| 丙二醛(MDA)malonic dialdehyde content | 0.066 | 0.595 | 0.011 |
| 脯氨酸(PRO)Proline content | 26.328 | 7.771* | 5.31 |
| 可溶性糖(SS)Soluble sugar content | 4.943** | 2.747 | 0.798 |
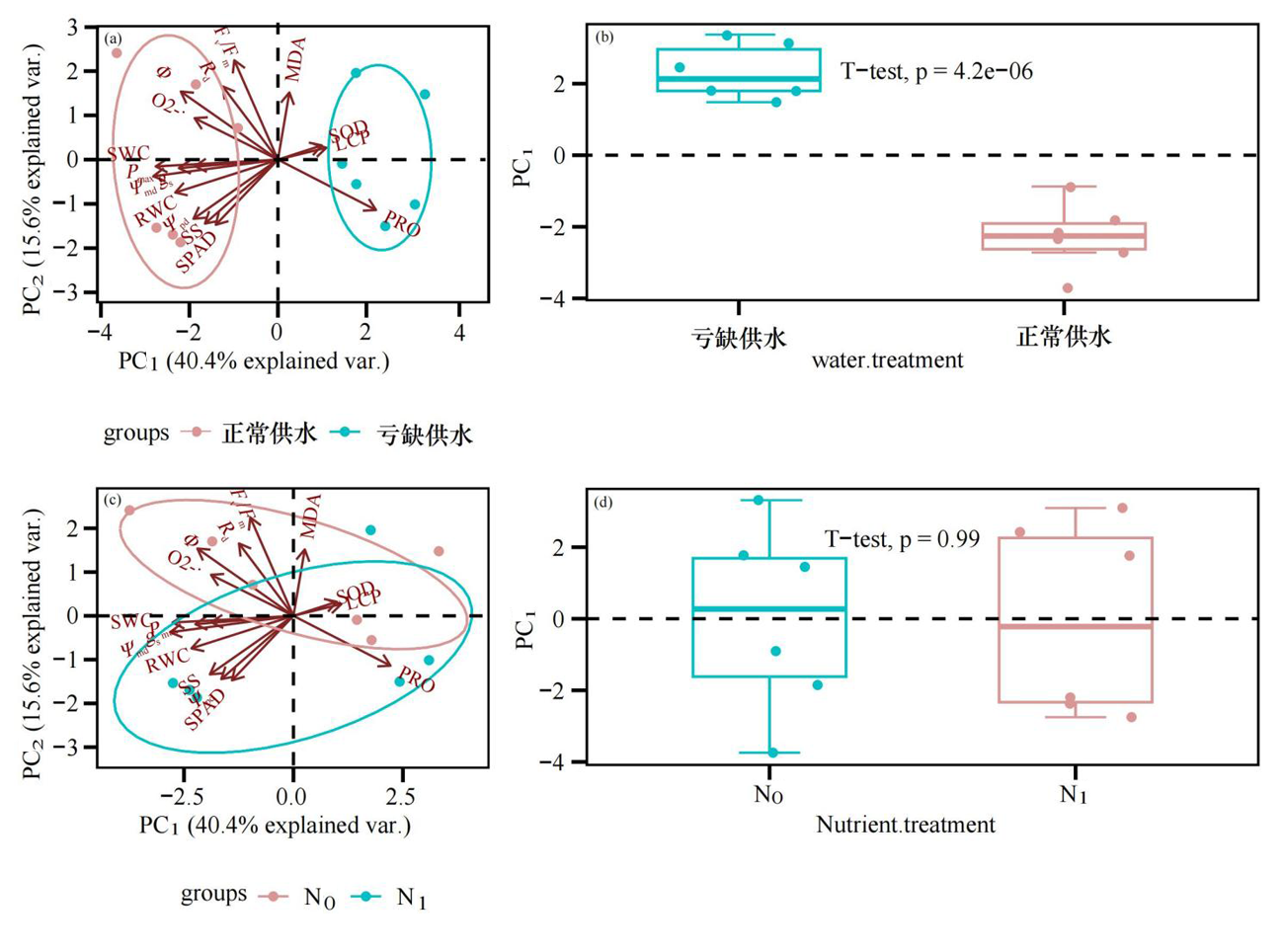
图4 浇水和施肥处理下沙拐枣幼苗各性状的主成分分析 注:a:不同浇水处理下沙拐枣幼苗 16 个性状的主成分分析;b:不同浇水处理下沙拐枣幼苗沿第一轴主成分(PC1)的单因素方差分析;c: 不同施肥处理下沙拐枣幼苗 16 个性状的主成分分析;d:不同施肥处理下沙拐枣幼苗 16 个性状的主成分分析,P<0.05
Fig.4 Principal component analysis of various characters of walnut trees treated with watering and fertilization Note: a: Principal component analysis of 16 characters of walnut tree under different watering treatments; b: One-way ANOVA of principal components (PC1) of walnut trees along the first axis under different watering treatments; c: Principal component analysis of 16 traits of walnut tree under different fertilization treatments; d: Principal component analysis of 16 characters * of walnut tree under different fertilization treatment, P<0.05
| [1] | Cortina J, Amat B, Castillo V, et al. The restoration of vegetation cover in the semi-arid Iberian southeast[J]. Journal of Arid Environments, 2011, 75(12): 1377-1384. |
| [2] | Cortina J, Vilagrosa A, Trubat R. The role of nutrients for improving seedling quality in drylands[J]. New Forests, 2013, 44(5): 719-732. |
| [3] | Piper F I, Fajardo A, Hoch G. Single-provenance mature conifers show higher non-structural carbohydrate storage and reduced growth in a drier location[J]. Tree Physiology, 2017, 37(8): 1001-1010. |
| [4] | Liu X P, Fan Y Y, Long J X, et al. Effects of soil water and nitrogen availability on photosynthesis and water use efficiency of Robinia pseudoacacia seedlings[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2013, 25(3): 585-595. |
| [5] | Huang L L, Li M J, Zhou K, et al. Uptake and metabolism of ammonium and nitrate in response to drought stress in Malus prunifolia[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2018, 127: 185-193. |
| [6] | 张士功, 刘国栋, 刘更另. 植物营养与作物抗旱性[J]. 植物学通报, 2001, 36(1): 64-69, 63. |
| ZHANG Shigong, LIU Guodong, LIU Gengling. Plant nutrition and drought resistance of crops[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2001, 36(1): 64-69, 63. | |
| [7] | 王赟. 植物脂质过氧化研究进展[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(6): 2370-2373. |
| WANG Yun. Research progress on lipid peroxidation of plant[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 41(6): 2370-2373. | |
| [8] | Sevanto S, McDowell N G, Dickman L T, et al. How do trees die? A test of the hydraulic failure and carbon starvation hypotheses[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 2014, 37(1): 153-161. |
| [9] | Fu J M, Huang B R. Involvement of antioxidants and lipid peroxidation in the adaptation of two cool-season grasses to localized drought stress[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2001, 45(2): 105-114. |
| [10] | Luo Z B, Luo J. Uncovering the physiological mechanisms that allow nitrogen availability to affect drought acclimation in Catalpa bungei[J]. Tree Physiology, 2017, 37(11): 1453-1456. |
| [11] | 张杰, 贾斌斌, 张永虎, 等. 我国沙拐枣属植物研究进展[J]. 甘肃科技, 2014, 30(15): 145-148, 144. |
| ZHANG Jie, JIA Binbin, ZHANG Yonghu, et al. Research progress of Calligonum in China[J]. Gansu Science and Technology, 2014, 30(15): 145-148, 144. | |
| [12] | 魏良民, 李康. 沙拐枣幼苗生长规律及与其抗旱性关系研究[J]. 干旱区研究, 1994, 11(3): 47-51. |
| WEI Liangmin, LI Kang. The study on the development of seeding in Calligonum caput-medusae and its relationship with plant drought resistance[J]. Arid Zone Research, 1994, 11(3): 47-51. | |
| [13] | 张佃民, 毛祖美. 新疆的沙拐枣灌木荒漠[J]. 干旱区研究, 1989, 6(2): 13-18. |
| ZHANG Dianmin, MAO Zumei. A study on the calligonum desert in Xinjiang[J]. Arid Zone Research, 1989, 6(2): 13-18. | |
| [14] | 种培芳, 李毅, 苏世平. 干旱胁迫下不同地理种源蒙古沙拐枣(Calligomum mongolicum)光合及荧光特性比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(5): 1301-1306. |
| CHONG Peifang, LI Yi, SU Shiping. The responses of photosynthetic and chlorophyll fluorescence to water stress in three provenances of calligomum mongolicum[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2014, 34(5): 1301-1306. | |
| [15] | 赵小仙, 李毅, 苏世平, 等. 3个地理种群蒙古沙拐枣同化枝解剖结构及抗旱性比较[J]. 中国沙漠, 2014, 34(5): 1293-1300. |
| ZHAO Xiaoxian, LI Yi, SU Shiping, et al. Drought resistance analysis based on anatomical structures of assimilating shoots of Calligonum mongolicum from three geographic populations[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2014, 34(5): 1293-1300. | |
| [16] | 潘航, 冯缨, 王喜勇, 等. 荒漠环境下10种沙拐枣的生理特征比较研究[J]. 草业学报, 2017, 26(6): 68-75. |
| PAN Hang, FENG Ying, WANG Xiyong, et al. Examination and comparison of the physiological characteristics of ten Calligonum species in a desert environment[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2017, 26(6): 68-75. | |
| [17] | 邱真静, 李毅, 种培芳, 等. 基于PEG胁迫响应的不同地理种源沙拐枣抗旱性评价[J]. 中国沙漠, 2011, 31(5): 1231-1237. |
| QIU Zhenjing, LI Yi, CHONG Peifang, et al. Comprehensive evaluation on drought resistance of Calligonum mongolicum turcz.from different geographical provenance based on its response to PEG osmotic stress[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2011, 31(5): 1231-1237. | |
| [18] | 黄彩变, 曾凡江, 雷加强. 极端干旱区头状沙拐枣对水分条件变化的生理生态响应[J]. 植物研究, 2015, 35(2): 225-232. |
| HUANG Caibian, ZENG Fanjiang, LEI Jiaqiang. The ecophysiological response of Calligonum caput-medusae to different water condition in extremely arid region[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research, 2015, 35(2): 225-232. | |
| [19] | 宋聪, 曾凡江, 刘波, 等. 不同水分条件对头状沙拐枣幼苗形态特征及生物量的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2012, 31(9): 2225-2233. |
| SONG Cong, ZENG Fanjiang, LIU Bo, et al. Influence of water condition on morphological characteristics and biomass of Calligonum caput-medusae Schrenk seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2012, 31(9): 2225-2233. | |
| [20] | 苏培玺, 严巧娣. C4荒漠植物梭梭和沙拐枣在不同水分条件下的光合作用特征[J]. 生态学报, 2006, 26(1): 75-82. |
| SU Peixi, YAN Qiaodi. Photosynthetic characteristics of C4 desert species Haloxylon ammodendron and Calligonum mongolicum under different moisture conditions[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2006, 26(1): 75-82. | |
| [21] | Xu G Q, Li Y. Rooting depth and leaf hydraulic conductance in the xeric tree Haloxyolon ammodendron growing at sites of contrasting soil texture[J]. Functional Plant Biology, 2008, 35(12): 1234. |
| [22] | 李从娟, 李彦, 马健, 等. 干旱区植物根际土壤养分状况的对比研究[J]. 干旱区地理, 2011, 34(2): 222-228. |
| LI Congjuan, LI Yan, MA Jian, et al. Nutrition in the rhizosphere of five xerophytic plants[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2011, 34(2): 222-228. | |
| [23] | 冯起. 半湿润地区改良风沙土土壤性质研究[J]. 水土保持通报, 1998, 18(4): 1-6. |
| FENG Qi. Properties of ameliorated sandy land soil in semi-humid area[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 1998, 18(4): 1-6. | |
| [24] | 郑博文, 胡顺军, 周智彬, 等. 古尔班通古特沙漠南缘风沙土土壤水分特征与毛管水最大上升高度[J]. 干旱区地理, 2020, 43(4): 1059-1066. |
| ZHENG Bowen, HU Shunjun, ZHOU Zhibin, et al. Maximum height of capillary rising water and characteristic of soil moisture in the southern edge of Gurbantunggut Desert[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2020, 43(4): 1059-1066. | |
| [25] | Huang G, Li C H, Li Y. Phenological responses to nitrogen and water addition are linked to plant growth patterns in a desert herbaceous community[J]. Ecology and Evolution, 2018, 8(10): 5139-5152. |
| [26] | 张学礼, 胡振琪, 初士立. 土壤含水量测定方法研究进展[J]. 土壤通报, 2005, 36(1): 118-123. |
| ZHANG Xueli, HU Zhenqi, CHU Shili. Methods for measuring soil water content: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2005, 36(1): 118-123. | |
| [27] | Tariq A, Pan K W, Olatunji O A, et al. Phosphorous application improves drought tolerance of Phoebe zhennan[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2017, 8: 1561. |
| [28] | 付培立. 热带喀斯特森林常绿和落叶树木水力结构、水分关系以及光合能力的对比研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2011. |
| FU Peili. Comparative study on hydraulic structure, water relationship and photosynthetic capacity of evergreen and deciduous trees in tropical Karst forest[D]. Beijing: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2011. | |
| [29] | 张喜英. 叶水势反映冬小麦和夏玉米水分亏缺程度的试验(简报)[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1997, 33(4): 249-253. |
| ZHANG Xiying. A report on diagnosis of soil water deficiency of wheat and maize using leaf water potential[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1997, 33(4): 249-253. | |
| [30] | 张中峰, 黄玉清, 莫凌, 等. 岩溶植物光合-光响应曲线的两种拟合模型比较[J]. 武汉植物学研究, 2009, 27(3): 340-344. |
| ZHANG Zhongfeng, HUANG Yuqing, MO Ling, et al. Comparison of two Photosynthesis-light response curve-fitting models of the Karst plant[J]. Journal of Wuhan Botanical Research, 2009, 27(3): 340-344. | |
| [31] | 叶子飘, 李进省. 光合作用对光响应的直角双曲线修正模型和非直角双曲线模型的对比研究[J]. 井冈山大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 31(3): 38-44. |
| YE Zipiao, LI Jinsheng. Comparative investigation light response of photosynthesis on non-rectangular hyperbola model and modified model of rectangular hyperbola[J]. Journal of Jinggangshan University (Natural Science), 2010, 31(3): 38-44. | |
| [32] | Bielinis E Jó? wiak W, Robakowski P. Modelling of the relationship between the SPAD values and photosynthetic pigments content in Quercus petraea and Prunus serotina leaves[J]. Dendrobiology, 2015, 73: 125-134. |
| [33] | Markwell J, Osterman J C, Mitchell J L. Calibration of the Minolta SPAD-502 leaf chlorophyll meter[J]. Photosynthesis Research, 1995, 46(3): 467-472. |
| [34] | Zhou Y H, Lam H M, Zhang J H. Inhibition of photosynthesis and energy dissipation induced by water and high light stresses in rice[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2007, 58(5): 1207-1217. |
| [35] | Panda S K, Chaudhury I, Khan M H. Heavy metals induce lipid peroxidation and affect antioxidants in wheat leaves[J]. Biologia Plantarum, 2003, 46(2): 289-294. |
| [36] | Das K, Samanta L, Chainy G. A modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase using nitrite formation by superoxide radicals[J]. Indian Journal of Biochemistry & Biophysics, 2000, 37(3): 201-204. |
| [37] | Heath R L, Packer L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1968, 125(1): 189-198. |
| [38] | Elstner E F, Heupel A. Formation of hydrogen peroxide by isolated cell walls from horseradish (Armoracia lapathifolia Gilib.)[J]. Planta, 1976, 130(2): 175-180. |
| [39] | Wang Q, Cheng F, Luo X, et al. Effects of growth years on the polysaccharide content in Radix Ophiopogonis[J]. Medicinal Plant, 2013, 4(5): 52-53, 56. |
| [40] | Bates L S, Waldren R P, Teare I D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies[J]. Plant and Soil, 1973, 39(1): 205-207. |
| [41] | Chołuj D, Karwowska R, Ciszewska A, et al. Influence of long-term drought stress on osmolyte accumulation in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) plants[J]. Acta Physiologiae Plantarum, 2008, 30(5): 679-687. |
| [42] | 李吉跃, 张建国. 北方主要造林树种耐旱机理及其分类模型的研究(Ⅰ)——苗木叶水势与土壤含水量的关系及分类[J]. 北京林业大学学报, 1993, 15(3): 1-11. |
| LI Jiyue, ZHANG Jianguo. Studies on classification models and mechanisms of drought tolerance of chief afforestation species in the northern part of China (Ⅰ)—the classification of relationships between seedling leaf water potential and soil water content[J]. Journal of Beijing Forestry University, 1993, 15(3): 1-11. | |
| [43] | 付爱红, 陈亚宁, 李卫红, 等. 干旱、盐胁迫下的植物水势研究与进展[J]. 中国沙漠, 2005, 25(5): 744-749. |
| FU Aihong, CHEN Yaning, LI Weihong, et al. Research advances on plant water potential under drought and salt stress[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2005, 25(5): 744-749. | |
| [44] | 罗杰, 周光良, 胡庭兴, 等. 干旱胁迫对润楠幼苗生长和生理生化指标的影响[J]. 应用与环境生物学报, 2015, 21(3): 563-570. |
| LUO Jie, ZHOU Guangliang, HU Tingxing, et al. Effects of drought stress on growth and physiological parameters of Machilus pingii seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied and Environmental Biology, 2015, 21(3): 563-570. | |
| [45] | 陈少瑜, 郎南军, 李吉跃, 等. 干旱胁迫下3树种苗木叶片相对含水量、质膜相对透性和脯氨酸含量的变化[J]. 西部林业科学, 2004, 33(3): 30-33, 41. |
| CHEN Shaoyu, LANG Nanjun, LI Jiyue, et al. Changes of leaf relative water content, relative plasma membrane permeability and proline content of seedlings of three species under drought stress[J]. Yunnan Forestry Science and Technology, 2004, 33(3): 30-33, 41. | |
| [46] | 付晓玥, 闫建成, 梁存柱, 等. 干旱与半干旱区一年生植物水势对模拟降水变化的响应[J]. 内蒙古大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(2): 160-167. |
| FU Xiaoyue, YAN Jiancheng, LIANG Cunzhu, et al. Water potentials of annual plants response to simulated rainfall in arid and semiarid regions[J]. Journal of Inner Mongolia University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 43(2): 160-167. | |
| [47] | 徐峥静茹. 干旱复水对岷江柏幼苗生理特性影响的初步研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017. |
| XU Zhengjingru. A Preliminary Study on Effects of Drought-rewatering on Physiological Characteristics of Cupressus Chengiana S.Y.Hu[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017. | |
| [48] | 贾荣亮. 超旱生植物红砂和珍珠光合作用生态适应性研究[D]. 兰州: 中国科学院寒区旱区环境与工程研究所, 2006. |
| JIA Rongliang. Study on Ecological Adaptability of Photosynthesis of Super-xerophytes Red Sand and Pearl[D]. Lanzhou: Cold and Arid Regions Environmental and Engineering Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006. | |
| [49] | 雷泽湘, 艾天成, 李方敏, 等. 草莓叶片叶绿素含量、含氮量与SPAD值间的关系[J]. 湖北农学院学报, 2001,(2): 138-140. |
| LEI Zexiang, AI Tiancheng, LI Fangmin, et al. The relationships between SPAD readings and the contents of chlorophyll and nitrogen in strawberry leaves[J]. Journal of Hubei Agricultural College, 2001,(2): 138-140. | |
| [50] | Bowler C, Montagu M V, Inze D. Superoxide dismutase and stress tolerance[J]. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, 1992, 43: 83-116. |
| [51] | 蒋明义, 郭绍川. 水分亏缺诱导的氧化胁迫和植物的抗氧化作用[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 1996, 32(2): 144-150. |
| JIANG Mingyi, GUO Shaochuan. Oxidative stress induced by water deficiency and antioxidant effect of plants[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 1996, 32(2): 144-150. | |
| [52] | 蒋明义, 荆家海, 王韶唐. 渗透胁迫对水稻幼苗膜脂过氧化及体内保护系统的影响[J]. 植物生理学报, 1991, 17(1): 80-84. |
| JIANG Mingyi, JING Jiahai, WANG Shaotang. Effects of osmotic stress on membrane-lipid peroxidation and endogenous protective systems in ricse seedlings[J]. Physiology and Molecular Biology of Plants, 1991, 17(1): 80-84. | |
| [53] | 白娟, 龚春梅, 王刚, 等. 干旱胁迫下荒漠植物红砂叶片抗氧化特性[J]. 西北植物学报, 2010, 30(12): 2444-2450. |
| BAI Juan, GONG Chunmei, WANG Gang, et al. Antioxidative characteristics of Reaumuria soongorica under drought stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2010, 30(12): 2444-2450. | |
| [54] | Placer Z A, Cushman L L, Johnson B C. Estimation of product of lipid peroxidation (malonyl dialdehyde) in biochemical systems[J]. Analytical Biochemistry, 1966, 16(2): 359-364. |
| [55] | Møller I M, Jensen P E, Hansson A. Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants[J]. Annual Review of Plant Biology, 2007, 58: 459-481. |
| [56] | 尹丽, 刘永安, 谢财永, 等. 干旱胁迫与施氮对麻疯树幼苗渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2012, 23(3): 632-638. |
| YIN Li, LIU Yongan, XIE Caiyong, et al. Effects of drought stress and nitrogen fertilization rate on the accumulation of osmolytes in Jatropha curcas seedlings[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2012, 23(3): 632-638. | |
| [57] | Chaves M M, Oliveira M M. Mechanisms underlying plant resilience to water deficits: prospects for water-saving agriculture[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2004, 55(407): 2365-2384. |
| [58] | Ashraf M, Foolad M R. Roles of glycine betaine and proline in improving plant abiotic stress resistance[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2007, 59(2): 206-216. |
| [1] | 曾婉盈, 耿洪伟, 程宇坤, 李思忠, 钱松廷, 高卫时, 张立明. 甜菜品系叶丛快速生长期抗旱性综合评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2140-2151. |
| [2] | 阿热孜姑·吐逊, 高杰. 干旱胁迫和播种密度对洋葱小鳞茎生理特性及产出鳞茎个数的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2211-2222. |
| [3] | 张承洁, 胡浩然, 段松江, 吴一帆, 张巨松. 氮肥与密度互作对海岛棉生长发育及产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [4] | 姚庆, 王杰花, 西尔娜依·阿不都拉, 地力木拉提·吐拉洪, 崔宏亮. 低温胁迫下不同藜麦品种苗期的生理响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1597-1604. |
| [5] | 王一钊, 杨其志, 刘玉秀, 阿拉依·努尔卡马力, Vladimir Shvidchenko, 张正茂. PEG胁迫下评价哈萨克斯坦不同春小麦种质苗期的抗旱性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1352-1360. |
| [6] | 张宏芝, 王立红, 时佳, 孔德鹏, 王重, 高新, 李剑峰, 王春生, 夏建强, 樊哲儒, 张跃强. 土壤水分对不同抗旱性春小麦品种叶片保护性酶活性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1041-1047. |
| [7] | 刘易, 李江涛, 江应红, 杨茹薇, 孙慧, 吴燕. NaCl胁迫下外源亚精胺对马铃薯幼苗生理特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(2): 336-344. |
| [8] | 陈荣, 赖宁, 耿庆龙, 李永福, 信会男, 吕彩霞, 李娜, 陈署晃. 基于遥感数据构建冬小麦孕穗期变量施氮模型[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2705-2712. |
| [9] | 赵康, 程蓉蓉, 庞博, 张梦媛, 张茹, 王勇攀, 杨志宁, 王志, 王红刚, 高文伟. 盐胁迫及复水对棉花叶片生理生化和显微结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2351-2357. |
| [10] | 孙法福, 赖宁, 耿庆龙, 李永福, 吕彩霞, 信会男, 李娜, 陈署晃. 基于SPAD值的滴灌冬小麦氮肥推荐模型分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(10): 2366-2373. |
| [11] | 周小云, 雷斌, 张军高, 梁晶, 龚静云, 周广威, 张少民, 李进. 7.2%萎锈灵和40%拌种灵包衣对棉花幼苗冷胁迫生理生化特征的功效比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 176-183. |
| [12] | 王辉, 郭金成, 宋佳, 张庭军, 何良荣. 高温胁迫下陆地棉GhCIPK6转基因后代生理生化分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2109-2119. |
| [13] | 曲可佳, 时晓磊, 张恒, 王兴州, 耿洪伟, 丁孙磊, 张金波, 严勇亮. PEG处理下引进春小麦品种苗期抗旱性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1363-1371. |
| [14] | 唐茜茜, 木巴热克·阿尤普, 许盼云, 于秋红, 郭春苗, 张萍, 龚鹏. 扁桃不同砧木资源根系解剖结构对干旱胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 897-907. |
| [15] | 王泽鹏, 梁志国, 刘胜尧, 贾宋楠, 范凤翠, 张哲, 杜凤焕, 秦勇. 不同施氮量对设施茄子产量、品质及养分积累的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 951-957. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 34
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 113
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||