

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (8): 2004-2013.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.08.021
姚诗雨1( ), 王杰1, 黄文娟1,2(
), 王杰1, 黄文娟1,2( ), 焦培培1,2, 彭承志1, 熊丹1, 陈月1, 王鑫1
), 焦培培1,2, 彭承志1, 熊丹1, 陈月1, 王鑫1
收稿日期:2023-12-07
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-19
通信作者:
黄文娟(1980-),女,黑龙江富锦人,教授,硕士生导师,研究方向为荒漠区植物生理生态和植物多样性保育,(E-mail)hwjzky@163.com作者简介:姚诗雨(1998-),女,江西上饶人,硕士研究生,研究方向为荒漠区植物保育,(E-mail)1091275698@qq.com
基金资助:
YAO Shiyu1( ), WANG Jie1, HUANG Wenjuan1,2(
), WANG Jie1, HUANG Wenjuan1,2( ), JIAO Peipei1,2, PENG Chengzhi1, XIONG Dan1, CHEN Yue1, WANG Xin1
), JIAO Peipei1,2, PENG Chengzhi1, XIONG Dan1, CHEN Yue1, WANG Xin1
Received:2023-12-07
Published:2024-08-20
Online:2024-09-19
Correspondence author:
HUANG Wenjuan(1980-),female,from Fujin, Heilongjiang, professor, master, master's supervisor, research direction: plant physiological ecology and plant diversity conservation in desert areas,(E-mail)hwjzky@163.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】研究胡杨 (Populus euphratica )对盐渍环境的适应特点,揭示其耐盐生理机制。【方法】以不同盐渍生境中的胡杨叶片为试材,采用沸水水提法与消煮法测定离子含量,采用石蜡切片法在光学显微镜观察叶片的解剖结构,分析叶片各离子含量及比较解剖结构特征。【结果】(1)在低盐生境中,胡杨叶片中栅栏组织较大,叶片厚度、海绵组织、中脉维管束面积最大,且海绵组织厚度与其他环境中相比差异显著;中盐生境中,上、下表皮厚度、栅栏组织及粘液细胞面积均大于其他环境;高盐生境中,胡杨叶片增加下表皮厚度、海绵组织的厚度及叶片厚度;(2)从低盐环境到高盐环境,胡杨叶片中Na+、Mg2+、Ca2+、
中图分类号:
姚诗雨, 王杰, 黄文娟, 焦培培, 彭承志, 熊丹, 陈月, 王鑫. 不同盐渍环境对胡杨叶解剖结构及离子含量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2004-2013.
YAO Shiyu, WANG Jie, HUANG Wenjuan, JIAO Peipei, PENG Chengzhi, XIONG Dan, CHEN Yue, WANG Xin. Effects of different saline environments on anatomical structure and ion content of Populus euphratica leaves[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(8): 2004-2013.
| 样地编号 Sample site number | 地点 Location | 纬度 N (°) | 经度 E (°) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 胡杨胸径 P.euphratica breast diameter (cm) | 距塔里木河距离 Distance from Tarim River (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 沙雅县 | 40.963 11 | 83.340 06 | 881.2 | 20.5 | 南岸:4 305.32 |
| A2 | 沙雅县-克尔克乔勒 | 41.007 75 | 83.321 71 | 891.5 | 21 | 北岸:2 408.88 |
| A3 | 沙雅县-县道×329线 | 41.073 32 | 83.159 26 | 891.8 | 19.833 | 北岸:147 901.4 |
表1 各采样地基本信息
Tab.1 Basic information of each sampling site
| 样地编号 Sample site number | 地点 Location | 纬度 N (°) | 经度 E (°) | 海拔 Altitude (m) | 胡杨胸径 P.euphratica breast diameter (cm) | 距塔里木河距离 Distance from Tarim River (m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 沙雅县 | 40.963 11 | 83.340 06 | 881.2 | 20.5 | 南岸:4 305.32 |
| A2 | 沙雅县-克尔克乔勒 | 41.007 75 | 83.321 71 | 891.5 | 21 | 北岸:2 408.88 |
| A3 | 沙雅县-县道×329线 | 41.073 32 | 83.159 26 | 891.8 | 19.833 | 北岸:147 901.4 |
| 样地 编号 Sample site number | pH值 pH value | 全盐 Total salt (g/kg) | 电导率 Conductivity (μS/cm) | 含水量 Water content (%) | 生境类型 Habitat type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 7.80 | 5.43 | 6.84 | 15.89 | 高盐生境 |
| A2 | 8.03 | 2.42 | 3.37 | 22.45 | 中盐生境 |
| A3 | 8.09 | 1.17 | 1.52 | 11.73 | 低盐生境 |
表2 不同样点土壤基本理化性质和生境类型划分
Tab.2 Analysis and division of soil environmental salinity at different points
| 样地 编号 Sample site number | pH值 pH value | 全盐 Total salt (g/kg) | 电导率 Conductivity (μS/cm) | 含水量 Water content (%) | 生境类型 Habitat type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 7.80 | 5.43 | 6.84 | 15.89 | 高盐生境 |
| A2 | 8.03 | 2.42 | 3.37 | 22.45 | 中盐生境 |
| A3 | 8.09 | 1.17 | 1.52 | 11.73 | 低盐生境 |
| 指标 Indexes | 高盐生境 High-salt habitats | 中盐生境 Medium-salt habitats | 低盐生境 Low-salt habitats |
|---|---|---|---|
| 叶厚度 Leaf thickness(μm) | 152.878±7.432a | 144.562±8.731a | 165.097±11.056a |
| 上表皮厚度 Upper epidermal thickness(μm) | 8.363±0.435a | 8.459±0.281a | 8.02±0.144a |
| 下表皮厚度 Lower epidermal thicknes(μm) | 8.427±0.3a | 8.225±0.305a | 7.672±0.285a |
| 上表皮角质层厚度 Upper stratum corneum thickness(μm) | 1.351±0.168ab | 1.795±0.36a | 1.012±0.094b |
| 栅栏组织厚度 Palisade tissue thickness(μm) | 24.502±1.131a | 26.441±1.836a | 25.606±1.123a |
| 海绵组织厚度 Sponge tissue thickness(μm) | 14.493±0.925ab | 12.608±0.615b | 16.514±1.412a |
| 栅栏组织/海绵组织 Palisade tissue/sponge tissue | 1.832±0.186ab | 2.13±0.128a | 1.664±0.118b |
| 叶片紧密度 Ratio of palisade/leaf thinkness | 0.166±0.011a | 0.189±0.015a | 0.163±0.011a |
| 叶片疏松度 Ratio of spongy/leaf looseness. | 0.097±0.007a | 0.092±0.007a | 0.103±0.008a |
| 粘液细胞面积 Mucus cell area(μm2) | 286.455±14.925b | 414.284±64.407a | 362.685±17.078ab |
| 中脉维管束面积 Midrib vascular bundle area(μm2) | 82 555.936±12 130.119a | 82 821.66±11 027.582a | 119 162.488±18 986.066a |
表3 不同生境胡杨叶片解剖结构特征的比较
Tab.3 Comparisons of basic characteristics of leaf anatomy of P. euphratica in different environments
| 指标 Indexes | 高盐生境 High-salt habitats | 中盐生境 Medium-salt habitats | 低盐生境 Low-salt habitats |
|---|---|---|---|
| 叶厚度 Leaf thickness(μm) | 152.878±7.432a | 144.562±8.731a | 165.097±11.056a |
| 上表皮厚度 Upper epidermal thickness(μm) | 8.363±0.435a | 8.459±0.281a | 8.02±0.144a |
| 下表皮厚度 Lower epidermal thicknes(μm) | 8.427±0.3a | 8.225±0.305a | 7.672±0.285a |
| 上表皮角质层厚度 Upper stratum corneum thickness(μm) | 1.351±0.168ab | 1.795±0.36a | 1.012±0.094b |
| 栅栏组织厚度 Palisade tissue thickness(μm) | 24.502±1.131a | 26.441±1.836a | 25.606±1.123a |
| 海绵组织厚度 Sponge tissue thickness(μm) | 14.493±0.925ab | 12.608±0.615b | 16.514±1.412a |
| 栅栏组织/海绵组织 Palisade tissue/sponge tissue | 1.832±0.186ab | 2.13±0.128a | 1.664±0.118b |
| 叶片紧密度 Ratio of palisade/leaf thinkness | 0.166±0.011a | 0.189±0.015a | 0.163±0.011a |
| 叶片疏松度 Ratio of spongy/leaf looseness. | 0.097±0.007a | 0.092±0.007a | 0.103±0.008a |
| 粘液细胞面积 Mucus cell area(μm2) | 286.455±14.925b | 414.284±64.407a | 362.685±17.078ab |
| 中脉维管束面积 Midrib vascular bundle area(μm2) | 82 555.936±12 130.119a | 82 821.66±11 027.582a | 119 162.488±18 986.066a |
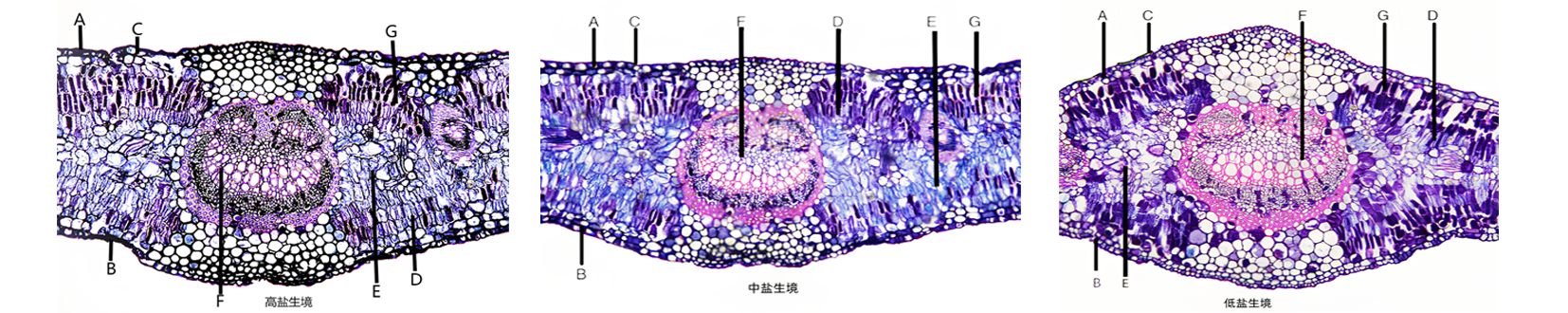
图1 不同生境胡杨叶片解剖结构 注:A.上表皮;B.下表皮;C.上表皮角质层;D.栅栏组织;E.海绵组织;F.中脉维管束;G.粘液细胞
Fig.1 Leaf anatomy of P. euphratica in different habitats Note: A. Upper epidermis; B. Lower epidermis; C. Cuticle of upper epidermis; D. Fence organization; E. Spongy tissue; F. Midvein vascular bundle; G. Mucus cells

图2 不同环境下胡杨叶片各离子含量差异的比较 注:不同小写字母表示不同地点相同结构之间具有显著差异(P<0.05),下同
Fig.2 Comparisons of the content of ions in P. euphratica leaves in different environments Note: The inclusion of different lowercase letters indicates that the difference between different sites under various soil index factors is significant (P<0.05),the same as below
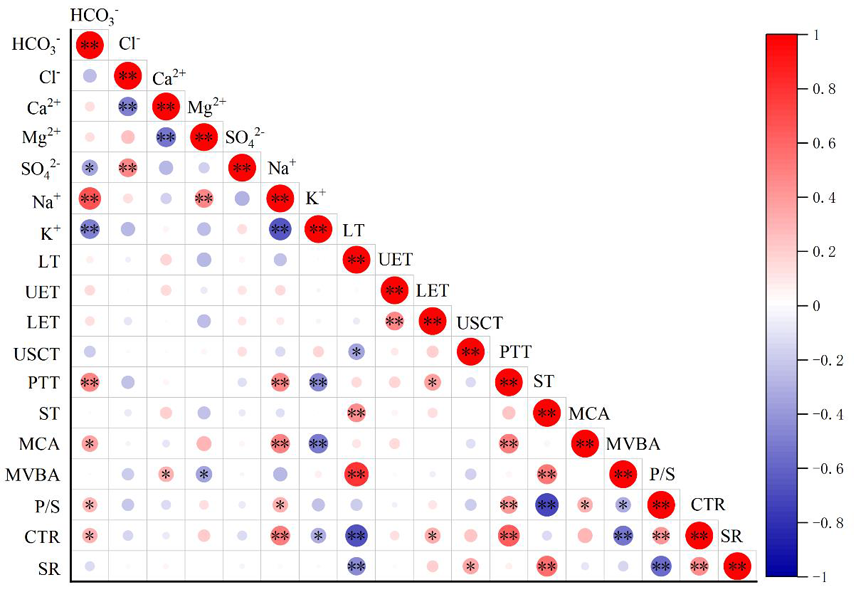
图4 胡杨叶片解剖结构与离子含量相关性的比较 注:** 在 0.01 级别(双尾),相关性显著。* 在 0.05 级别(双尾),相关性显著(下同);LT:叶厚度;UET:上表皮厚度;LET:下表皮厚度;USCT:上角质层厚度 ;PTT:栅栏组织厚度;ST:海绵组织;MCA:粘液细胞面积MVBA:中脉维管束面积 ;P/S:栅/海比 CTR:叶片紧密度 ;SR:叶片疏松度。
Fig.4 Correlations between leaf anatomy and ion content of P. euphratica in different environments Note: ** At level 0.01 (double-tailed), the correlation is significant. * At level 0.05 (double-tailed), the correlation is significant(the same as below); LT: leaf thickness; UET: upper epidermal thickness; LET: lower epidermal thickness; USCT upper stratum corneum thickness ; PTT:palisade tissue thickness ST: sponge tissue; MCA: mucus cell area; MVBA: midrib vascular bundle area; P/S:ratio of palisade tissue/sponge tissue; CTR:ratio of palisade/leaf thinkness; SR: ratio of spongy/leaf looseness
| 指标 Indexes | pH值 pH value | 全盐 Total salt | 含水量 Water content | 电导率 Cond- uctivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.254 | -0.254 | 0.085 | -0.296* | |
| Cl-(g/kg) | 0.263 | 0.017 | -0.185 | -0.002 |
| Ca2+(g/kg) | -0.044 | -0.13 | -0.02 | -0.181 |
| Mg2+(g/kg) | 0.173 | -0.224 | -0.143 | -0.222 |
| -0.164 | 0.323* | 0.008 | 0.375* | |
| Na+(g/kg) | 0.391** | -0.238 | -0.098 | -0.248 |
| K+(g/kg) | -0.498** | 0.508** | -0.274 | 0.603** |
| 叶厚度(LT) | -0.212 | -0.026 | 0.274 | -0.059 |
| 上表皮厚度(UET) | -0.105 | 0.418** | 0.032 | 0.303* |
| 下表皮厚度(LET) | -0.182 | 0.347* | 0.275 | 0.256 |
| 上表皮角质层厚度 (USCT) | -0.031 | 0.016 | 0.101 | 0.074 |
| 栅栏组织厚度(PTT) | 0.088 | -0.104 | 0.414** | -0.128 |
| 海绵组织(ST) | -0.377* | -0.088 | 0.029 | -0.043 |
| 粘液细胞面积(MCA) | -0.017 | -0.183 | 0.473** | -0.098 |
| 中脉维管束面积 (MVBA) | -0.225 | -0.188 | 0.114 | -0.165 |
| 栅/海比(P/S) | 0.382** | -0.032 | 0.334* | -0.055 |
| 叶片紧密度(CTR) | 0.208 | -0.07 | 0.078 | -0.056 |
| 叶片疏松度(SR) | -0.166 | -0.088 | -0.249 | -0.004 |
表4 叶片解剖结构、离子与土壤相关性
Tab.4 Analysis of leaf anatomical structure, ion and soil correlation
| 指标 Indexes | pH值 pH value | 全盐 Total salt | 含水量 Water content | 电导率 Cond- uctivity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.254 | -0.254 | 0.085 | -0.296* | |
| Cl-(g/kg) | 0.263 | 0.017 | -0.185 | -0.002 |
| Ca2+(g/kg) | -0.044 | -0.13 | -0.02 | -0.181 |
| Mg2+(g/kg) | 0.173 | -0.224 | -0.143 | -0.222 |
| -0.164 | 0.323* | 0.008 | 0.375* | |
| Na+(g/kg) | 0.391** | -0.238 | -0.098 | -0.248 |
| K+(g/kg) | -0.498** | 0.508** | -0.274 | 0.603** |
| 叶厚度(LT) | -0.212 | -0.026 | 0.274 | -0.059 |
| 上表皮厚度(UET) | -0.105 | 0.418** | 0.032 | 0.303* |
| 下表皮厚度(LET) | -0.182 | 0.347* | 0.275 | 0.256 |
| 上表皮角质层厚度 (USCT) | -0.031 | 0.016 | 0.101 | 0.074 |
| 栅栏组织厚度(PTT) | 0.088 | -0.104 | 0.414** | -0.128 |
| 海绵组织(ST) | -0.377* | -0.088 | 0.029 | -0.043 |
| 粘液细胞面积(MCA) | -0.017 | -0.183 | 0.473** | -0.098 |
| 中脉维管束面积 (MVBA) | -0.225 | -0.188 | 0.114 | -0.165 |
| 栅/海比(P/S) | 0.382** | -0.032 | 0.334* | -0.055 |
| 叶片紧密度(CTR) | 0.208 | -0.07 | 0.078 | -0.056 |
| 叶片疏松度(SR) | -0.166 | -0.088 | -0.249 | -0.004 |
| [1] | 王遵亲. 中国盐渍土[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1993. |
| WANG Zunqin. Saline soil in China[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1993. | |
| [2] | Meloni D A, Oliva M A, Martinez C A, et al. Photosynthesis and activity of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and glutathione reductase in cotton under salt stress[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2003, 49(1): 69-76. |
| [3] | 乔旭, 黄爱军, 褚贵新. 植物对盐分胁迫的响应及其耐盐机理研究进展[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2011, 48(11): 2089-2094. |
| QIAO Xu, HUANG Aijun, CHU Guixin. Research progress in the effects of salt stress on plant and the mechanism of plant resistance[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 48(11): 2089-2094. | |
| [4] | 赵春彦, 秦洁, 贺晓慧, 等. 荒漠河岸林胡杨对盐胁迫的适应机制[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2022, 36(7): 166-172. |
| ZHAO Chunyan, QIN Jie, HE Xiaohui, et al. Mechanisms underlying adaption of Populus Euphratica to salt stress in desert riparian forests[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2022, 36(7): 166-172. | |
| [5] | Albaladejo I, Meco V, Plasencia F, et al. Unravelling the strategies used by the wild tomato species Solanum pennellii to confront salt stress: From leaf anatomical adaptations to molecular responses[J]. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 2017, (135): 1-12. |
| [6] | 岑湘涛, 沈伟, 牛俊乐, 等. 基于植物叶片解剖结构的抗逆性评价研究进展[J]. 北方园艺, 2021,(18): 140-147. |
| CEN Xiangtao, SHEN Wei, NIU Junle, et al. Research progress of stress resistance evaluation based on the anatomy of plant leaves[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021,(18): 140-147. | |
| [7] | 李芳兰, 包维楷. 植物叶片形态解剖结构对环境变化的响应与适应[J]. 植物学通报, 2005, 40(S1): 118-127. |
| LI Fanglan, BAO Weikai. Response and adaptation of plant leaf morphological and anatomical structure to environmental changes[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany, 2005, 40(S1): 118-127. | |
| [8] | 章英才, 闫天珍. 花花柴叶片解剖结构与生态环境关系的研究[J]. 宁夏农学院学报, 2003, 24(1): 31-33. |
| ZHANG Yingcai, YAN Tianzhen. Study on relationship between anatomical structure of leaves of karelinia capsia (pall) less and ecological environment[J]. Journal of Ningxia Agricultural College, 2003, 24(1): 31-33. | |
| [9] | Parida A K, Das A B, Mittra B. Effects of salt on growth, ion accumulation, photosynthesis and leaf anatomy of the mangrove, Bruguiera parviflora[J]. Trees, 2004, 18(2): 167-174. |
| [10] | 顾骁, 杨文丽, 吴远燕, 等. 植物对盐胁迫的适应机制及其提高耐盐能力的主要途径[J]. 农技服务, 2021, 38(7): 92-96. |
| GU Xiao, YANG Wenli, WU Yuanyan, et al. The adaptive mechanism of plants to salt stress and the main ways to improve salt tolerance[J]. Agricultural Technology Service, 2021, 38(7): 92-96. | |
| [11] | 皇甫文君, 李继武. 塔里木河流域胡杨林退化情况及生态保护建议[J]. 新疆林业, 2021,(2): 4-6. |
| HUANGFU Wenjun, LI Jiwu. Degradation of Populus euphratica forest in Tarim River Basin and suggestions on ecological protection[J]. Forestry of Xinjiang, 2021,(2): 4-6. | |
| [12] | 鲁艳, 雷加强, 曾凡江, 等. NaCl处理对胡杨生长及生理生态特征的影响[J]. 干旱区研究, 2015, 32(2): 279-285. |
| LU Yan, LEI Jiaqiang, ZENG Fanjiang, et al. Effects of NaCl treatments on growth and ecophysiological characteristics of Populus euphratica[J]. Arid Zone Research, 2015, 32(2): 279-285. | |
| [13] | 李菊艳, 赵成义, 闫映宇, 等. 盐分对胡杨(Populus euphratica)幼苗生长和离子平衡的影响[J]. 干旱区地理, 2016, 39(3): 613-620. |
| LI Juyan, ZHAO Chengyi, YAN Yingyu, et al. Effect of salinity on growth, ionic homeostasis in organs of Populus euphratica seedlings[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2016, 39(3): 613-620. | |
| [14] | 张霞, 曾幼玲, 李金耀, 等. 胡杨(Populus euphratica oliv)的耐盐性[J]. 植物生理学通讯, 2006,(6):1190-1194. |
| ZHANG Xia, ZENG Youling, LI Jinyao, et al. Salt tolerance in Populus euphratica oliv[J]. Plant Physiology Communications, 2006,(6):1190-1194. | |
| [15] |
张肖, 王旭, 焦培培, 等. 胡杨(Populus euphratica)种子萌发及胚生长对盐旱胁迫的响应[J]. 中国沙漠, 2016, 36(6): 1597-1605.
DOI |
| ZHANG Xiao, WANG Xu, JIAO Peipei, et al. Response of seed germination and embryo growth to salt stress and drought stress of Populus euphratica[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2016, 36(6): 1597-1605. | |
| [16] | 孙兆军. 银川平原盐碱荒地改良模式研究[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2011. |
| SUN Zhaojun. Amelioration Models for Saline-alkali Wasterland in Yinchuan Plain[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2011. | |
| [17] | 王虹, 齐政, 张富春. 不同浓度盐胁迫下盐穗木叶片结构的比较观察[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(11): 2098-2105. |
| WANG Hong, QI Zheng, ZHANG Fuchun. Leaf anatomical structure of Halostachys caspica under different concentrations of salt stress[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(11): 2098-2105. | |
| [18] | 肖磊, 陈宁美, 陈悦, 等. 内蒙古与北京地区胡杨异形叶表皮蜡质及气孔形态显微结构差异[J]. 中央民族大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 25(3): 85-91. |
| XIAO Lei, CHEN Ningmei, CHEN Yue, et al. The difference of cuticle wax crystallization and Stoma morphology of lanceolate and broad-ovate leaves of Populus euphratica olive between Ejina Area in Inner Mongolia and Beijing Area[J]. Journal of Minzu University of China (Natural Sciences Edition), 2016, 25(3): 85-91. | |
| [19] | 洪文君, 申长青, 庄雪影, 等. 盐胁迫对竹柳幼苗生理响应及结构解剖的研究[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报, 2017, 25(5): 489-496. |
| HONG Wenjun, SHEN Changqing, ZHUANG Xueying, et al. Effect of NaCl stress on physiological responses and anatomical structure of Salix spp. seedlings[J]. Journal of Tropical and Subtropical Botany, 2017, 25(5): 489-496. | |
| [20] | 贾文飞, 魏晓琼, 聂小兰, 等. 盐碱胁迫对越橘生理特性及叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(5): 115-126. |
| JIA Wenfei, WEI Xiaoqiong, NIE Xiaolan, et al. Effects of saline-alkali stress on physiological characteristics and anatomic structure of blueberry leave[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 115-126. | |
| [21] | 章英才. 几种不同盐生植物叶的比较解剖研究[J]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 27(1): 68-71. |
| ZHANG Yingcai. Studies of comparative anatomy structure of several different saline plants leaves[J]. Journal of Ningxia University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 27(1): 68-71. | |
| [22] | 燕玲, 李红, 贺晓, 等. 阿拉善地区9种珍稀濒危植物营养器官生态解剖观察[J]. 内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2000, 21(3): 65-71. |
| YAN Ling, LI Hong, HE Xiao, et al. Ecological anatomy of nine priority species in a la San arwa[J]. Journal of Inner Mongola Institute of Agriculture and Animal Husbandry, 2000, 21(3): 65-71. | |
| [23] | 王斌, 巨波, 赵慧娟, 等. 不同盐梯度处理下沼泽小叶桦的生理特征及叶片结构[J]. 林业科学, 2011, 47(10): 29-36. |
| WANG Bin, JU Bo, ZHAO Huijuan, et al. Photosynthetic performance and variation in leaf anatomic structure of Betula microphylla var. paludosa under different saline conditions[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2011, 47(10): 29-36. | |
| [24] | 李志军, 吕春霞, 段黄金. 胡杨和灰叶胡杨营养器官的解剖学研究[J]. 塔里木农垦大学学报, 1996, 8(2): 21-25, 33. |
| LI Zhijun, LYU Chunxia, DUAN Huangjin. Anatomical studies on the vegetative organs of Populus euphtatica oliv. and Populus pruinosa schrenk[J]. Journal of Tarim University of Agricultural Reclamation, 1996, 8(2): 21-25, 33. | |
| [25] | 戴凌燕, 张立军, 阮燕晔, 等. 苏打盐碱胁迫对甜高粱叶片结构及抗性指标的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2012, 31(3): 468-475. |
| DAI Lingyan, ZHANG Lijun, RUAN Yanye, et al. Effects of saline-sodic stress on the blade structure and resistant indexes in sweet Sorghum(Sorghum bicolor L.Moench)[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2012, 31(3): 468-475. | |
| [26] |
陈旭, 刘洪凯, 赵春周, 等. 山东滨海盐碱地11个造林树种叶解剖特征对土壤条件的响应[J]. 植物生态学报, 2019, 43(8): 697-708.
DOI |
|
CHEN Xu, LIU Hongkai, ZHAO Chunzhou, et al. Responses of foliar anatomical traits to soil conditions in 11 tree species on coastal saline-alkali sites of Shandong, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Ecology, 2019, 43(8): 697-708.
DOI |
|
| [27] |
Ruiz-Lozano J M, Porcel R, Azcón C, et al. Regulation by arbuscular mycorrhizae of the integrated physiological response to salinity in plants: new challenges in physiological and molecular studies[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany, 2012, 63(11): 4033-4044.
DOI PMID |
| [28] | 左照江, 张汝民, 高岩. 盐胁迫下植物细胞离子流变化的研究进展[J]. 浙江农林大学学报, 2014, 31(5): 805-811. |
| ZUO Zhaojiang, ZHANG Rumin, GAO Yan. Advances in plant cell ion flux with salt stress: a review[J]. Journal of Zhejiang A & F University, 2014, 31(5): 805-811. | |
| [29] | 张瑾. 胡杨吸盐能力的研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古大学, 2013. |
| ZHANG Jin. The Research on the Abiliti of Absorbing Salt of Populus Euphratica[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2013. | |
| [30] | 新疆维吾尔自治区农业厅、 新疆维吾尔自治区土壤普查办公室. 新疆土壤[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1996. |
| Department of Agriculture of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Soil Census Office of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region. Xinjiang Soil[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1996. | |
| [31] | Schmidt A. Metabolic background of H2S release from plants[J]. Landbauforschung Volkenrode, 2005, 283(S1):121-129. |
| [32] | Shabala S, Cuin T A. Potassium transport and plant salt tolerance[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2008, 133(4): 651-669. |
| [33] | Sun J, Chen S L, Dai S X, et al. Ion flux profiles and plant ion homeostasis control under salt stress[J]. Plant Signaling & Behavior, 2009, 4(4): 261-264. |
| [34] | 罗青红, 周斌, 李英仑, 等. 盐渍土壤大果沙枣树主要矿质阳离子的吸收和分配特征[J]. 西北植物学报, 2021, 41(8): 1371-1379. |
| LUO Qinghong, ZHOU Bin, LI Yinglun, et al. Absorption and distribution of main mineral cations of Elaeagnus moorcroftii in salinized land[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2021, 41(8): 1371-1379. | |
| [35] |
Brugnoli E, Lauteri M. Effects of salinity on stomatal conductance, photosynthetic capacity, and carbon isotope discrimination of salt-tolerant (Gossypium hirsutum L.) and salt-sensitive (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) C(3) Non-Halophytes[J]. Plant Physiology, 1991, 95(2): 628-635.
DOI PMID |
| [36] | Tang R J, Luan S. Regulation of calcium and magnesium homeostasis in plants: from transporters to signaling network[J]. Current Opinion in Plant Biology, 2017, (39): 97-105. |
| [37] | De Silva D L R, Hetherington A M, Mansfield T A. Where does all the calcium go? Evidence of an important regulatory role for trichomes in two calcicoles[J]. Plant, Cell & Environment, 1996, 19(7): 880-886. |
| [38] | 朱义, 谭贵娥, 何池全, 等. 盐胁迫对高羊茅(Festuca arundinacea)幼苗生长和离子分布的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2007, 27(12): 5447-5454. |
| ZHU Yi, TAN Guie, HE Chiquan, et al. Effect of salinization on growth and ion homeostasis in seedlings of Festuca arundinacea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2007, 27(12): 5447-5454. | |
| [39] | 齐琪, 马书荣, 徐维东. 盐胁迫对植物生长的影响及耐盐生理机制研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2020, 18(8): 2741-2746. |
| QI Qi, MA Shurong, XU Weidong. Advances in the effects of salt stress on plant growth and physiological mechanisms of salt tolerance[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2020, 18(8): 2741-2746. | |
| [40] | Wakeel A, Farooq M, Qadir M, et al. Potassium substitution by sodium in plants[J]. Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2011, 30(4): 401-413. |
| [1] | 杨文莉, 许丽蓉, 刘斌, 凌悦铭, 李寐华, 杨永, 范蓉, 黎玉顺, 张永兵, 张学军. 盐胁迫对薄皮甜瓜‘灰鼠’离子平衡、膜脂过氧化及渗透调节物质积累的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 900-907. |
| [2] | 张优, 刘茂秀, 史军辉, 王新英, 艾吉尔·阿不拉, 张炎. 塔河胡杨林核心区退耕地初始年土壤及植被养分特征数值分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 699-707. |
| [3] | 连雅丽, 孟新涛, 杨永兴, 杨海燕, 张婷, 车凤斌, 马燕. 基于GC-IMS技术分析不同品种沙棘真空冷冻干燥果粉挥发性成分[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1958-1965. |
| [4] | 吕齐, 蒋宇, 赵丰云, 雷叶, 于坤, 姚东东, 李旭娇, 沙日叶, 王芳霞. 施加生物炭对盐胁迫下无花果生物量叶绿素荧光参数及离子分配的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(3): 574-581. |
| [5] | 许昌, 张光弟, 张浩宇, 贾毅男, 张昆明, 王江龙, 侯晓健. 叶面喷施硅素对玫瑰香果实风味物质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 359-367. |
| [6] | 朱珠, 王则玉, 许咏梅, 刘迪, 李杨. 磁化不同水质滴灌对土壤盐分的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(12): 3086-3093. |
| [7] | 王如月, 罗莎莎, 王茹, 虎海防, 孙雅丽. 利用GC-IMS分析3个核桃品种叶片挥发性物质指纹差异[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2764-2778. |
| [8] | 闫淼, 熊韬, 黄全生, 吴婷, 吴海波, 赵准, 胡国智. 外源水杨酸对单盐胁迫下哈密瓜叶片解剖结构的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(9): 2123-2129. |
| [9] | 何宇翔, 武胜利, 韩炜, 管文轲. 不同灌水量对胡杨幼龄林叶水势与土水势的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1110-1118. |
| [10] | 史智欣, 武胜利, 管文轲, 韩玮, 岳永江, 何宇翔. 不同树龄对胡杨叶片水势与光合特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1119-1127. |
| [11] | 孙阳, 韩占江, 师建银, 唐宏宥, 李康. 盐环境对杂交树种密胡杨生长和光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(4): 634-642. |
| [12] | 张炳坤, 李瑜, 周黎, 王萍莉. 温湿度对蔡氏胡杨个木虱越冬成虫存活的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(10): 1893-1899. |
| [13] | 张翠丽, 支金虎, 张桂兵, 姚永生, 卜东升. 塔里木河上游棉区不同类型盐土阳离子交换量分布特征及影响因素[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(6): 1057-1070. |
| [14] | 詹发强, 侯敏, 杨蓉, 王宁, 包慧芳, 侯新强, 崔卫东, 龙宣杞. 1株新疆胡杨林昆虫病原线虫鉴定及生物学特性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(3): 536-544. |
| [15] | 廖欢, 侯振安. 盐碱胁迫对不同棉花品种生长及离子组含量分布的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(2): 219-232. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 27
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 99
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||