

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (6): 1361-1367.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.06.008
• 作物遗传育种•种质资源•分子遗传学•耕作栽培•生理生化 • 上一篇 下一篇
刘跃1( ), 贾永红2, 张金汕1, 于月华1, 王润琪1, 李丹丹1, 石书兵1(
), 贾永红2, 张金汕1, 于月华1, 王润琪1, 李丹丹1, 石书兵1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-10-30
出版日期:2024-06-20
发布日期:2024-08-08
通信作者:
石书兵(1966-),男,山东商河人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为小麦高产栽培,(E-mail)ssb@xjau.edu.cn作者简介:刘跃(1998 - ),女,四川德阳人,硕士研究生,研究方向为作物高产栽培,(E-mail)17690762301@163.com
基金资助:
LIU Yue1( ), JIA Yonghong2, ZHANG Jinshan1, YU Yuehua1, WANG Runqi1, LI Dandan1, SHI Shubing1(
), JIA Yonghong2, ZHANG Jinshan1, YU Yuehua1, WANG Runqi1, LI Dandan1, SHI Shubing1( )
)
Received:2023-10-30
Published:2024-06-20
Online:2024-08-08
Correspondence author:
SHI Shubing (1966-), male, from Shanghe, Shandong, professor, Ph.D., doctoral supervisor, research direction: wheat high yield cultivation, (E-mail)ssb@xjau.edu.cnSupported by:摘要:
【目的】比较不同高油酸花生品种间产量及品质的差异,为筛选出适宜于新疆北疆地区种植的优良高油酸花生品种提供参考依据。【方法】选用5个高油酸花生品种为材料,分析各品种出苗率、农艺性状、单株干物质积累量、产量及品质等指标的差异。【结果】花育655在单株荚果数达21.33个,饱果率为1,籽粒脂肪含量最高为43.35%;花育917主茎高最高为27.80 cm,第一对侧枝长最高22.47 cm,分枝数最多达7.33个,且各时期单株干物质积累最高、百果重172.49 g、百仁重92.41 g、产量达4 644.04 kg/hm2、O/L值为9.30;花育951蛋白质和油酸含量最高,分别为26.71%和80.05%;花育956的出苗率最高为82.75%。花育917的产量最高,花育951的品质最佳。【结论】花育917是新疆北疆地区较为适合种植的高油酸花生品种。
中图分类号:
刘跃, 贾永红, 张金汕, 于月华, 王润琪, 李丹丹, 石书兵. 滴灌条件下不同高油酸花生品种比较[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1361-1367.
LIU Yue, JIA Yonghong, ZHANG Jinshan, YU Yuehua, WANG Runqi, LI Dandan, SHI Shubing. Comparison of peanut varieties with different high oleic acid under drip irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1361-1367.
| 月份 Month | 日照时数 Sunshine hours (h) | 平均气温 Mean temper- ature (℃) | 最低气温 Minimum temper- ature (℃) | 最高气温 Maximum temper- ature (℃) | 降水量 Precipit- ation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5May | 304 | 21.3 | 7.3 | 35.2 | 4.3 |
| 6June | 305.7 | 23.8 | 7.8 | 39.5 | 15.1 |
| 7July | 303 | 24.3 | 11.4 | 36.4 | 11.4 |
| 8August | 304.4 | 22.5 | 6.8 | 38.2 | 9.2 |
| 9September | 276.8 | 18.8 | 3 | 37 | 17.3 |
表1 2022年花生生育期间气象要素
Tab.1 The meteorological elements during the growing period of peanut in 2022
| 月份 Month | 日照时数 Sunshine hours (h) | 平均气温 Mean temper- ature (℃) | 最低气温 Minimum temper- ature (℃) | 最高气温 Maximum temper- ature (℃) | 降水量 Precipit- ation (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5May | 304 | 21.3 | 7.3 | 35.2 | 4.3 |
| 6June | 305.7 | 23.8 | 7.8 | 39.5 | 15.1 |
| 7July | 303 | 24.3 | 11.4 | 36.4 | 11.4 |
| 8August | 304.4 | 22.5 | 6.8 | 38.2 | 9.2 |
| 9September | 276.8 | 18.8 | 3 | 37 | 17.3 |
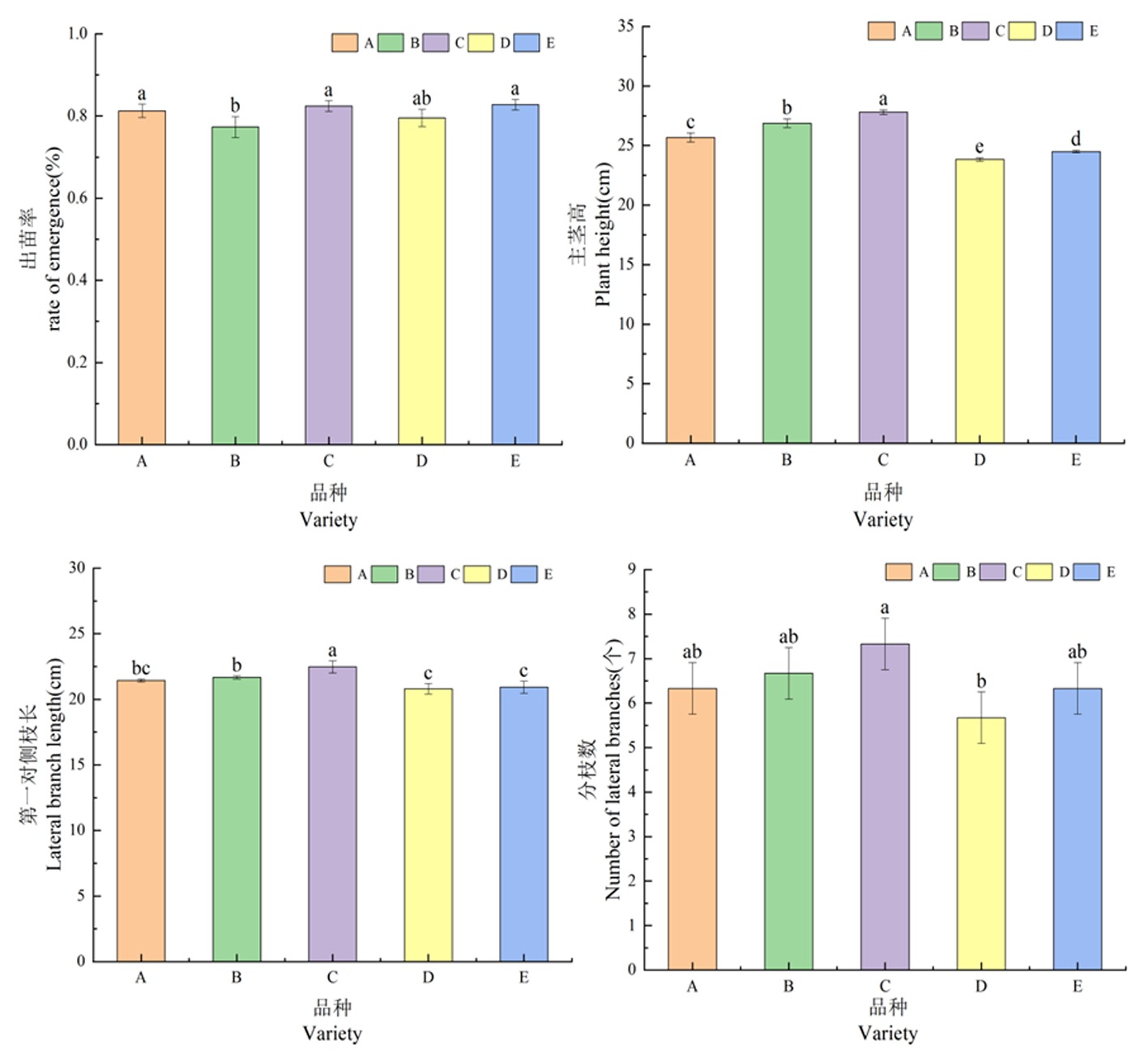
图1 不同高油酸花生品种出苗率、主茎高、第一对侧枝长、分枝数的变化 注:不同字母表示处理间差异显著(P<0.05),下同
Fig.1 Changes of seedling rate,main stem height,height of collatera,branch number of different peanut varieties with high oleic acid Note: Different letters indicate the significance difference at 0.05 level,the same as below
| 品种 Varieties | 单株果数 Number of pods per plant(个) | 饱果率 Full fruit ratio (%) | 百果重 100-pod weight (g) | 百仁重 100-seed weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花育52 Huayu 52 | 17.67±0.58b | 1.00±0.00a | 122.58±0.76c | 56.09±0.20d | 4 196.12±11.24c |
| 花育655 Huayu655 | 21.33±0.58a | 0.97±0.06a | 115.86±0.65e | 69.90±1.53c | 4 342.04±16.10b |
| 花育917 Huayu 917 | 17.67±0.58b | 0.98±0.03a | 172.49±2.83a | 92.41±2.44a | 4 644.04±19.55a |
| 花育951 Huayu 951 | 16.67±1.15b | 0.68±0.07b | 167.48±0.59b | 80.09±1.23b | 3 698.53±30.08d |
| 花育956 Huayu 956 | 11.00±1.00c | 0.76±0.12b | 119.33±1.19d | 58.11±1.71d | 3 395.08±46.69e |
表2 不同高油酸花生品种产量及产量构成因素的变化
Tab.2 Changes of yield and components of different peanut varieties with high oleic acid
| 品种 Varieties | 单株果数 Number of pods per plant(个) | 饱果率 Full fruit ratio (%) | 百果重 100-pod weight (g) | 百仁重 100-seed weight (g) | 产量 Yield (kg/hm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花育52 Huayu 52 | 17.67±0.58b | 1.00±0.00a | 122.58±0.76c | 56.09±0.20d | 4 196.12±11.24c |
| 花育655 Huayu655 | 21.33±0.58a | 0.97±0.06a | 115.86±0.65e | 69.90±1.53c | 4 342.04±16.10b |
| 花育917 Huayu 917 | 17.67±0.58b | 0.98±0.03a | 172.49±2.83a | 92.41±2.44a | 4 644.04±19.55a |
| 花育951 Huayu 951 | 16.67±1.15b | 0.68±0.07b | 167.48±0.59b | 80.09±1.23b | 3 698.53±30.08d |
| 花育956 Huayu 956 | 11.00±1.00c | 0.76±0.12b | 119.33±1.19d | 58.11±1.71d | 3 395.08±46.69e |
| 品种 Varieties | 水分 Moisture (%) | 蛋白质 Protein (%) | 脂肪 Adipose (%) | 油酸 Oleic acid (%) | 亚油酸 Linoleic acid (%) | O/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花育52 Huayu 52 | 6.13±0.06a | 18.72±0.03e | 38.30±0.02d | 75.24±0.4 | 8.96±0.86b | 8.45±0.90a |
| 花育655 Huayu655 | 5.87±0.06b | 23.38±0.02c | 43.35±0.03a | 73.66±0.19d | 8.12±0.49b | 9.10±0.56a |
| 花育917 Huayu 917 | 5.60±0.00c | 22.07±0.02d | 38.23±0.01e | 74.63±0.9 | 8.07±0.84b | 9.30±0.87a |
| 花育951 Huayu 951 | 5.87±0.06b | 26.71±0.02a | 39.57±0.01c | 80.05±0.35a | 10.97±0.49a | 7.31±0.35b |
| 花育956 Huayu 956 | 6.10±0.10a | 24.08±0.01b | 41.03±0.01b | 76.11±1.02b | 9.44±0.78b | 8.10±0.58ab |
表3 不同高油酸花生品种主要品质指标
Tab.3 Main quality traits of different peanut varieties with high oleic acid
| 品种 Varieties | 水分 Moisture (%) | 蛋白质 Protein (%) | 脂肪 Adipose (%) | 油酸 Oleic acid (%) | 亚油酸 Linoleic acid (%) | O/L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 花育52 Huayu 52 | 6.13±0.06a | 18.72±0.03e | 38.30±0.02d | 75.24±0.4 | 8.96±0.86b | 8.45±0.90a |
| 花育655 Huayu655 | 5.87±0.06b | 23.38±0.02c | 43.35±0.03a | 73.66±0.19d | 8.12±0.49b | 9.10±0.56a |
| 花育917 Huayu 917 | 5.60±0.00c | 22.07±0.02d | 38.23±0.01e | 74.63±0.9 | 8.07±0.84b | 9.30±0.87a |
| 花育951 Huayu 951 | 5.87±0.06b | 26.71±0.02a | 39.57±0.01c | 80.05±0.35a | 10.97±0.49a | 7.31±0.35b |
| 花育956 Huayu 956 | 6.10±0.10a | 24.08±0.01b | 41.03±0.01b | 76.11±1.02b | 9.44±0.78b | 8.10±0.58ab |
| [1] | 刘芳, 张哲, 王积军. 推动高油酸花生产业发展助力结构调整质量兴农[J]. 中国农技推广, 2019, 35(11): 14-16. |
| LIU Fang, ZHANG Zhe, WANG Jijun. Promote the development of peanut industry with high oleic acid, help adjust the structure, improve the quality and promote agriculture[J]. China Agricultural Technology Extension, 2019, 35(11): 14-16. | |
| [2] | 王小军. 新疆花生种植面积较上年增加10余万亩[N]. 中国新闻网, 2022-10-09. |
| WANG Xiaojun. The peanut planting area in Xinjiang increased by more than 100,000 mu compared with the previous year[N]. China News Network, 2022-10-09. | |
| [3] | 刘程宏, 杨海棠. 我国高油酸花生研究进展[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报, 2021, 12(16): 6573-6578. |
| LIU Chenghong, YANG Haitang. Research progress of high oleic acid peanuts in China[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality, 2021, 12(16): 6573-6578. | |
| [4] | 迟晓元, 陈明娜, 潘丽娟, 等. 花生高油酸育种研究进展[J]. 花生学报, 2014, 43(4): 32-38. |
| CHI Xiaoyuan, CHEN Mingna, PAN Lijuan, et al. Research progress on high-oleic acid peanut breeding[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2014, 43(4): 32-38. | |
| [5] | 潘丽娟, 王通, 韩鹏, 等. 高油酸新品种花育917在花生主产区的展示试验[J]. 花生学报, 2019, 48(1): 62-65. |
| PAN Lijuan, WANG Tong, HAN Peng, et al. Experiment performance of high-oleic peanut variety Huayu917 in the main producing areas of peanut in China[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2019, 48(1): 62-65. | |
| [6] | 王传堂, 张建成, 唐月异, 等. 中国高油酸花生育种现状与展望[J]. 山东农业科学, 2018, 50(6): 171-176. |
| WANG Chuantang, ZHANG Jiancheng, TANG Yueyi, et al. Current situation and future directions of high oleic peanut breeding in China[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 50(6): 171-176. | |
| [7] | 王纯武, 鲜开梅, 刘芳, 等. 新疆北疆地区高油酸花生新品种引进对比试验[J]. 花生学报, 2019, 48(4): 72-74. |
| WANG Chunwu, XIAN Kaimei, LIU Fang, et al. Comparative experiment on the introduction of new high oleic peanut varieties in northern Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2019, 48(4): 72-74. | |
| [8] | 万书波, 张佳蕾. 新疆花生产业发展战略及对策[J]. 花生学报, 2019, 48(2): 66-68. |
| WAN Shubo, ZHANG Jialei. Development strategy and countermeasure of peanut industry in Xinjiang[J]. Journal of Peanut Science, 2019, 48(2): 66-68. | |
| [9] | 王纯武, 马海新, 李新梅, 等. 北疆高油酸花生新品种对比及播种模式试验初报[J]. 耕作与栽培, 2021, 41(1): 28-31. |
| WANG Chunwu, MA Haixin, LIXinmei, et al. Preliminary report on the comparison of new peanut varieties with high oleic acid in northern Xinjiang[J]. Tillage and Cultivation, 2021, 41(1): 28-31. | |
| [10] | 万书波. 中国花生栽培学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2003. |
| WAN Shubo. Peanut cultivation in China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 2003. | |
| [11] | 王亮, 李艳, 王桥江, 等. 膜下滴灌条件下“花育” 系列花生品种主要农艺性状和产量分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2015, 43(34): 28-30, 58. |
| WANG Liang, LI Yan, WANG Qiaojiang, et al. Analysis of Huayu series of peanut cultivars' agronomic traits and yield under mulched drip irrigation[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 43(34): 28-30, 58. | |
| [12] | 李强, 顾元国, 王娟, 等. 新疆旱区不同种植密度对花生光合生理及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2016, 53(1): 84-90. |
| LI Qiang, GU Yuanguo, WANG Juan, et al. Effects of different density on photosynthetic physiology and yield of peanut in arid regions of Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 53(1): 84-90. | |
| [13] | 肖春燕, 王纯武, 马海新, 等. 新疆北疆单双粒播种模式对不同高油酸花生品种农艺性状及产量的影响[J]. 安徽农学通报, 2021, 27(6): 39-42, 47. |
| XIAO Chunyan, WANG Chunwu, MA Haixin, et al. Effect of single and double seed sowing pattern on agronomic characters and yield of peanut varieties with different high oleic acid in northern Xinjiang[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2021, 27(6): 39-42, 47. | |
| [14] | 王传堂, 唐月异, 王秀贞, 等. 7个高油酸花生新品种的丰产性和脂肪酸成分评价[J]. 山东农业科学, 2016, 48(5): 31-34. |
| WANG Chuantang, TANG Yueyi, WANG Xiuzhen, et al. Appraisal of productivity and fatty acid profiles of seven new high- oleic peanut cultivars[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 48(5): 31-34. | |
| [15] | 叶尚红. 植物生理生化实验教程[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2004. |
| YE Shanghong. Experimental course of plant physiology and biochemistry[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2004. | |
| [16] | 谢向誉, 饶文平, 钟祝秀, 等. 赣南地区不同花生品种比较研究[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2023, 51(2): 44-46. |
| XIE Xiangyu, RAO Wenping, ZHONG Zhuxiu, et al. Comparative study of different peanut varieties in Gannan Region[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 51(2): 44-46. | |
| [17] | Gauch H G. Model selection and validation for yield trials with interaction[J]. Biometrics, 1988, 44(3): 705. |
| [18] | 崔少雄, 王雪, 孙志梅, 等. 不同产量水平花生品种的生长发育特性比较[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016, 44(3): 107-111. |
| CUI Shaoxiong, WANG Xue, SUN Zhimei, et al. Comparison of growth and development characteristics of peanut varieties with different yield levels[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(3): 107-111. | |
| [19] |
郭建斌, 贾朝阳, 荆建国, 等. 花生主要品种出仁率和百果重的生态稳定性分析[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2019, 41(2): 186-191.
DOI |
|
GUO Jianbin, JIA Chaoyang, JING Jianguo, et al. Ecological stability of shelling percentage and hundred pod weight in main peanut cultivars[J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crop Sciences, 2019, 41(2): 186-191.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 于慧佳. 覆膜对高油酸花生光合生理特性和脂肪酸组分的影响[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳农业大学, 2020. |
| YU Huijia. Effects of Film Mulching on Photosynthetic Physiological Characteristics and Fatty Acid Formation of Peanut with High Oleic Acid[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Agricultural University, 2020. | |
| [21] | 严美玲, 李向东, 林英杰, 等. 苗期干旱胁迫对不同抗旱花生品种生理特性、产量和品质的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2007, 33(1): 113-119. |
| YAN Meiling, LI Xiangdong, LIN Yingjie, et al. Effects of drought during seedling stage on physiological traits, yield and quality of different peanut cultivars[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2007, 33(1): 113-119. | |
| [22] | 张翔, 张新友, 毛家伟, 等. 施氮水平对不同花生品种产量与品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(6): 1417-1423. |
| ZHANG Xiang, ZHANG Xinyou, MAO Jiawei, et al. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on yield and quality of different peanut cultivars[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(6): 1417-1423. | |
| [23] | 吴朝昕, 陈庆富, 黄娟, 等. 不同生态区对不同品种甜荞和苦荞农艺性状和品质性状的影响[J]. 安徽农业大学学报, 2020, 47(4): 618-626. |
| WU Chaoxin, CHEN Qingfu, HUANG Juan, et al. Effects of different ecological regions on agronomic and quality characters of different varieties of common buckwheat and Tartary buckwheat[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural University, 2020, 47(4): 618-626. | |
| [24] | 王才斌, 刘云峰, 吴正锋, 等. 山东省不同生态区花生品质差异及稳定性研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2008, 16(5): 1138-1142. |
| WANG Caibin, LIU Yunfeng, WU Zhengfeng, et al. Diversity and stability of peanut kernel quality in different ecological regions of Shandong Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2008, 16(5): 1138-1142. |
| [1] | 张泽华, 叶含春, 王振华, 李文昊, 李海强, 刘健. 等氮配施脲酶抑制剂对滴灌棉花生长发育和产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2103-2111. |
| [2] | 陈瑞杰, 罗林毅, 阮向阳, 冶军. 腐植酸对滴灌棉田土壤养分和棉花产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2112-2121. |
| [3] | 黄铂轩, 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 庞朝友, 徐文修, 董合林. 不同氮素抑制剂对棉花生长发育、氮素利用与产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2122-2131. |
| [4] | 张鸟, 王卉, 冯国郡, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班. 不同粒用高粱品种产量和农艺性状及品质的差异性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2160-2167. |
| [5] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 不同剂量的微生物菌剂对加工番茄产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2285-2289. |
| [6] | 陈勇, 周蕾, 隋春, 蔺彩霞. 32份板蓝根栽培种质在新疆产区的性状表现[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(9): 2307-2314. |
| [7] | 张承洁, 胡浩然, 段松江, 吴一帆, 张巨松. 氮肥与密度互作对海岛棉生长发育及产量和品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1821-1830. |
| [8] | 候丽丽, 王伟, 崔新菊, 周大伟. 有机无机肥配施对冬小麦产量和土壤养分及酶活性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1845-1852. |
| [9] | 陈芳, 李字辉, 王兵跃, 孙孝贵, 张庭军. 微生物菌剂对冬小麦生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1853-1860. |
| [10] | 袁莹莹, 赵经华, 迪力穆拉提·司马义, 杨庭瑞. 基于apriori算法对盆栽春小麦生理指标及产量的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1861-1871. |
| [11] | 苗雨, 陈翠霞, 马艳明, 邢国芳, 董裕生, 陈智军, 王仙, 向莉. 276份中亚大麦种质资源表型性状的遗传多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1888-1895. |
| [12] | 牛婷婷, 马明生, 张军高. 秸秆还田和覆膜对旱作雨养农田土壤理化性质及春玉米产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1896-1906. |
| [13] | 赵敏华, 宋秉曦, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 朱勇勇, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻产量及氮肥偏生产力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915. |
| [14] | 李锁丞, 柳延涛, 董红业, 孙振博, 李紫薇, 张春媛, 王开勇, 李强, 杨明凤. 不同施钾量对滴灌花生光合特性及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1926-1936. |
| [15] | 张彩虹, 王国强, 姜鲁艳, 刘涛, 德贤明. 低能耗组装式深冬生产型日光温室环境因子变化及番茄性状分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 2043-2053. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 36
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 202
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||