

新疆农业科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (4): 1025-1033.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.04.029
• 基因工程·草业·农产品分析检测·畜牧兽医 • 上一篇 下一篇
刘肖利1( ), 程彪1, 刘璐瑶1, 李勤凡2, 佟盼盼1, 张毅1, 刘英玉1, 苏战强1(
), 程彪1, 刘璐瑶1, 李勤凡2, 佟盼盼1, 张毅1, 刘英玉1, 苏战强1( ), 李斌1(
), 李斌1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-13
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-04-24
通信作者:
苏战强(1974-),男,新疆乌鲁木齐人,副教授,博士生导师,研究方向为动物源食品安全,(E-mail) szq00009@163.com;作者简介:刘肖利(1995-),女,河南淮阳人,硕士,研究方向为临床兽医学,(Email) 1316875742@qq.com
基金资助:
LIU Xiaoli1( ), CHENG Biao1, LIU Luyao1, LI Qinfan2, TONG Panpan1, ZHANG Yi1, LIU Yingyu1, SU Zhanqiang1(
), CHENG Biao1, LIU Luyao1, LI Qinfan2, TONG Panpan1, ZHANG Yi1, LIU Yingyu1, SU Zhanqiang1( ), LI Bin1(
), LI Bin1( )
)
Received:2021-05-13
Published:2022-04-20
Online:2022-04-24
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究奶牛乳房炎主要病原微生物及乳汁中微生物群系分布。【方法】对CJ和HZS 2个牛场的奶牛进行乳房炎检查,视觉和触觉等临床检查奶牛乳房及乳汁后,将2个场中确诊为临床乳房炎的奶牛随机采集乳汁样本各3份,并将非临床型奶牛的乳汁样本随机采集各1份,通过对乳房炎奶牛和非临床型奶牛乳样中细菌的16S rRNA基因V3-V4区的PCR扩增和高通量测序,分析临床奶牛乳汁样本和非临床型奶牛乳汁样本中微生物群落的多样性,并比较二者之间的差异性。【结果】6个临床乳房炎样本共获得25个门,47个纲,82个目,174个科,349个属;2个非临床型奶牛乳汁样本共获得23个门,38个纲,61个目,125个科,212个属。在临床乳房炎样本中,优势菌群分别是变形菌门(Proteobacteria)、无壁菌门(Tenericutes)、厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)、放线菌门(Actinobacteria);在非临床型样本中,优势菌群是变形菌门(Proteobacteria),其次是厚壁菌门(Firmicutes)、拟杆菌门(Bacteroidetes)。在属水平上,非临床型样本与乳房炎样本相比,检测到的优势菌群较少,且仅在HZS场乳房炎样本中检测到链球菌,CJ场乳房炎样本中检测到支原体。【结论】奶牛患乳房炎后菌群丰度明显升高,多样性变化显著;奶牛患乳房炎后会引起奶牛乳汁菌群失调,乳汁菌群结构分布和丰度变化与乳房炎的发生具有密切的联系。
中图分类号:
刘肖利, 程彪, 刘璐瑶, 李勤凡, 佟盼盼, 张毅, 刘英玉, 苏战强, 李斌. 基于高通量测序技术分析奶牛乳房炎关联微生物群落结构及多样性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(4): 1025-1033.
LIU Xiaoli, CHENG Biao, LIU Luyao, LI Qinfan, TONG Panpan, ZHANG Yi, LIU Yingyu, SU Zhanqiang, LI Bin. Analysis of the Structure and Diversity of Microbial Communities of Cow Mastitis based on High-throughput Sequencing[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(4): 1025-1033.
| 样品 Sample | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon-index | 均匀度 Pielou_e | 可见物种 Observed- species | 覆盖度 Goods coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CJ.LC1 | 462.288 | 0.121 018 | 0.743 671 | 0.084 275 3 | 453.3 | 99 |
| CJ.LC2 | 1 348.25 | 0.827 401 | 4.431 91 | 0.429 205 | 1 283.5 | 99 |
| CJ.LC3 | 2 622.23 | 0.957 049 | 6.647 99 | 0.586 655 | 2 578 | 99 |
| CJ.ZC | 1 148.38 | 0.650 92 | 3.454 96 | 0.340 844 | 1 125.6 | 99 |
| HZS.LC1 | 2 513.94 | 0.972 411 | 7.153 58 | 0.636 186 | 2 426.2 | 99 |
| HZS.LC2 | 1 779.43 | 0.970 484 | 6.836 3 | 0.636 326 | 1 714.3 | 99 |
| HZS.LC3 | 478.182 | 0.092 715 3 | 0.581 873 | 0.065 990 2 | 451.2 | 99 |
| HZS.ZC | 1 024.69 | 0.956 733 | 5.680 18 | 0.572 007 | 975.7 | 99 |
表1 样本菌群Alpha多样性指数
Table 1 Microflora Alpha Diversity Index of Sample
| 样品 Sample | Chao1指数 Chao1 index | 辛普森指数 Simpson index | 香浓指数 Shannon-index | 均匀度 Pielou_e | 可见物种 Observed- species | 覆盖度 Goods coverage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CJ.LC1 | 462.288 | 0.121 018 | 0.743 671 | 0.084 275 3 | 453.3 | 99 |
| CJ.LC2 | 1 348.25 | 0.827 401 | 4.431 91 | 0.429 205 | 1 283.5 | 99 |
| CJ.LC3 | 2 622.23 | 0.957 049 | 6.647 99 | 0.586 655 | 2 578 | 99 |
| CJ.ZC | 1 148.38 | 0.650 92 | 3.454 96 | 0.340 844 | 1 125.6 | 99 |
| HZS.LC1 | 2 513.94 | 0.972 411 | 7.153 58 | 0.636 186 | 2 426.2 | 99 |
| HZS.LC2 | 1 779.43 | 0.970 484 | 6.836 3 | 0.636 326 | 1 714.3 | 99 |
| HZS.LC3 | 478.182 | 0.092 715 3 | 0.581 873 | 0.065 990 2 | 451.2 | 99 |
| HZS.ZC | 1 024.69 | 0.956 733 | 5.680 18 | 0.572 007 | 975.7 | 99 |
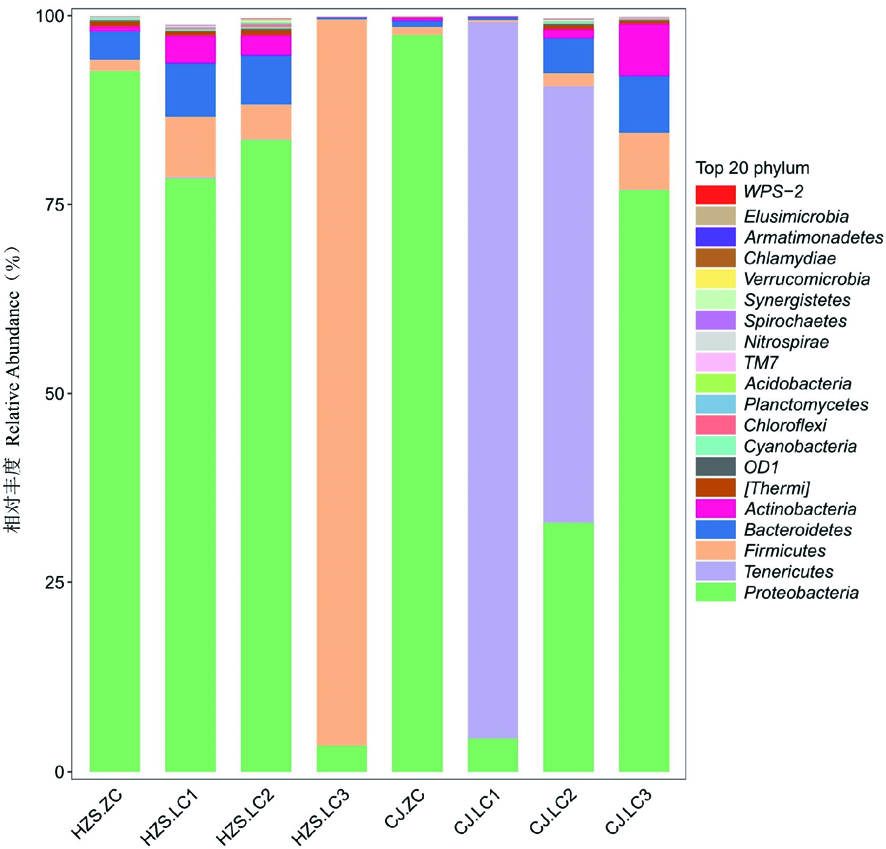
图2 细菌门分类水平的比较 注:HZS.ZC:HZS奶牛场非临床型乳汁样本;HZS.LC1:HZS奶牛场临床型乳房炎乳汁样本;HZS.LC2:HZS奶牛场临床型乳房炎乳汁样本;HZS.LC3:HZS奶牛场临床型乳房炎乳汁样本;CJ.ZC:CJ奶牛场非临床型乳汁样本;CJ.LC1:CJ奶牛场临床型乳房炎乳汁样本;CJ.LC2:CJ奶牛场临床型乳房炎乳汁样本;CJ.LC3:CJ奶牛场临床型乳房炎乳汁样本,下同
Fig.2 Comparison of bacteria groups at phylum level Note:HZS.ZC:Non-clinical milk samples from HZS dairy farm; HZS.LC1:Milk samples of clinical mastitis from HZS dairy farm; HZS.LC2:Milk samples of clinical mastitis from HZS dairy farm; HZS.LC3:Milk samples of clinical mastitis from HZS dairy farm; CJ.ZC:Non-clinical milk samples from CJ dairy farm; CJ.LC1:Milk samples of clinical mastitis from CJ dairy farm; CJ.LC2:Milk samples of clinical mastitis from CJ dairy farm; CJ.LC3:Milk samples of clinical mastitis from CJ dairy farm,the same as below
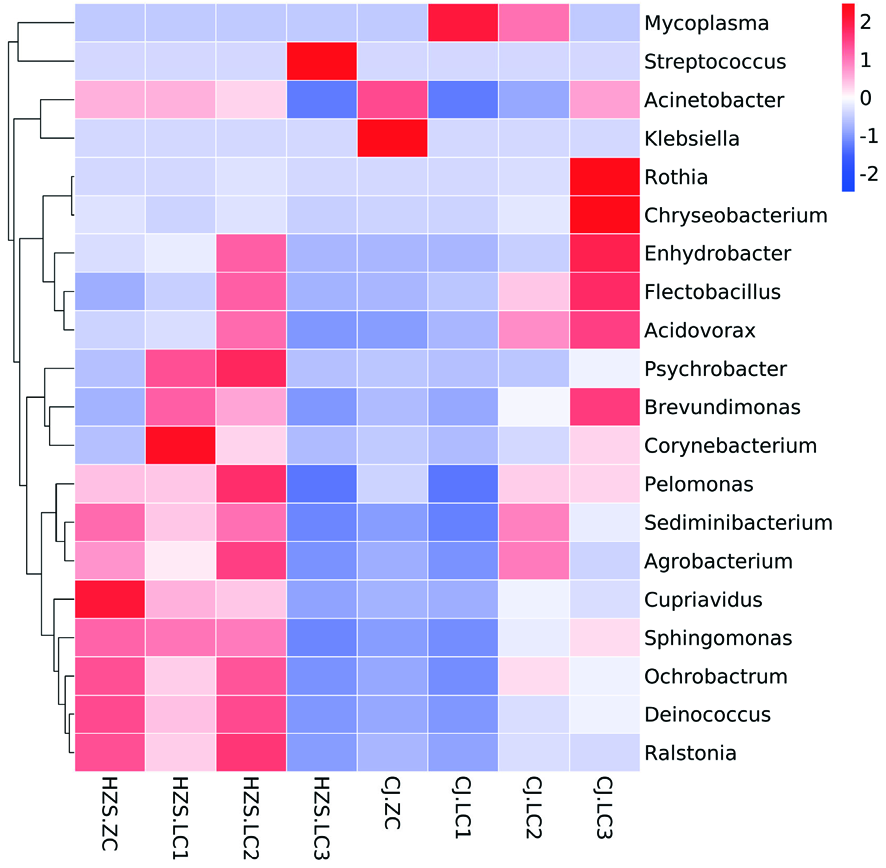
图6 属水平物种组成热图 注:红色色块代表该属在该样本中的丰度较其他样本高,蓝色色块代表该属在该样本中的丰度较其他样本低
Fig.6 Heat map of genus horizontal species composition Note:The red color block indicates that the abundance of this genus in this sample is higher than other samples, the blue color block means that the abundance of this genus in this sample is lower than other samples
| [1] | 缪强, 张绍军, 黄和继, 等. 昆明地区奶牛乳房炎致病菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 动物医学进展, 2011, 32(8):119-123. |
| MIAO Qiang, ZHANG Shaojun, HUANG Heji, et al. Isolation, identification and drug Sensitive test of pathogens causing cow mastitis in kunming, yunnan province[J]. Progress in Veternary Medicine, 2011, 32(8):119-123. | |
| [2] |
Riffon, Sayasith, Khalil, et al. Development of a rapid and sensitive test for identification of major pathogens in bovine mastitis by PCR[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 2001, 39(7):2584-2589.
PMID |
| [3] | 李玉, 敖日格乐, 王纯洁, 等. 临床型奶牛乳房炎致病菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2011, 43(3):78-81. |
| LI Yu, Aorigele, WANG Chunjie, et al. Isolation and identification of pathogenic bacteria for clinical dairy cow mastitis[J]. Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2011, 43(7):78-81. | |
| [4] | 张俊杰. 奶牛乳房炎研究进展[J]. 中国奶牛, 2020,(7):26-30. |
| ZHANG Junjie. Research progress of dairy cow mastitis[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2020(7):26-30. | |
| [5] | 宋亚攀, 杨利国, 宋洛文, 等. 奶牛乳房炎综合防治技术[J]. 中国奶牛, 2008,(4):39-41. |
| SONG Yapan, YANG Liguo, SONG Luowen, et al. Comprehensive prevention and cure technology of dairy cow mastitis[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2008,(4):39-41. | |
| [6] | 郝景锋, 李静姬, 张宇航, 等. 吉林省奶牛乳房炎病原菌分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 动物医学进展, 2016, 37(12):126-129. |
| HAO Jingfeng, LI Jingji, ZHANG Yuhang, et al. Isolation identification and drug sensitivity test of pathogens of dairy cow mastitis in jilin province[J]. Progress in Veternary Medicine, 2016, 37(12):126-129. | |
| [7] | 李春海. 奶牛乳房炎的防治措施探析[J]. 中国畜禽种业, 2020, 16(1):106. |
| LI Chunhai. Analysis on the prevention and treatment of milk cow mastitis[J]. The Chinese Livestock and Poultry Breeding, 2020, 16(1):106. | |
| [8] | 王方正, 田中杰, 田文儒. 噬菌体内溶素对奶牛乳房炎致病菌的溶解作用[J]. 动物医学进展, 2015, 36(4):113-116. |
| WANG Fangzheng, TIAN Zhongjie, TIAN Wenru. Lytic effect of bacteriophage and its endolysin to bovince mastitis pathogens[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2015, 36(4):113-116. | |
| [9] | 叶秀娟, 杜爱芳, 胡松华. 金华地区奶牛乳房炎病原菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2004,(8):41-42. |
| YE Xiujuan, DU Aifang, HU Songhua. Isolation, identification and drug sensitivity test of the pathogen of dairy cow mastitis in jinhua, zhejiang province[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2004,(8):41-42. | |
| [10] | 王军, 陈广宏, 何寿昕, 等. 青海省部分规模化奶牛场乳房炎主要病原菌调查分析[J]. 中国奶牛, 2020,(2):45-48. |
| WANG Jun, CHEN Guanghong, HE Shouxin, et al. Investigation and analysis of the main pathogens of mastitis in some large-scale dairy farms in qinghai province[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2020,(2):45-48. | |
| [11] | 陶娜拉. 高通量测序解析奶牛乳房炎关联菌群[D]. 呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学, 2016. |
| TAO Nala. High throughput sequencing analysis of bovince mastitis associated bacteria.[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| [12] | 王冬梅, 刘磊, 王胜利. 奶牛乳房炎病原菌的分离鉴定及药敏试验[J]. 动物医学进展, 2005,(6):81-83. |
| WANG Dongmei, LIU Lei, WANG Shengli. Isolation and identification of the pathogenic bacteria of cow mastitis and its pharmacosensitive test[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2005,(6):81-83. | |
| [13] | 罗正中, 张保海, 张廷青, 等. 奶牛场金黄色葡萄球菌乳房炎的鉴别诊断及发病特征[J]. 中国奶牛, 2018,(9):27-30. |
| LUO Zhengzhong, ZHANG Baohai, ZHANG Tingqing, et al. Differential diagnosis and incidence characteristics of Staphylococcus aureus mastitis in dairy farms[J]. China Dairy Cattle, 2018,(9):27-30. | |
| [14] |
Taponen S, Salmikivi L, Simojoki H, et al. Real-time polymerase chain reaction-based identification of bacteria in milk samples from bovine clinical mastitis with no growth in conventional culturing[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2009, 92(6):2610-2617.
DOI PMID |
| [15] |
Kuehn J S, Gorden P J, Daniel M, et al. Bacterial community profiling of milk samples as a means to understand culture-negative bovine clinical mastitis[J]. Plos One, 2013, 8(4):e61959.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Li Y, Shi M, Zhang T, et al. Dynamic changes in intestinal microbiota in young forest musk deer during weaning[J]. PeerJ, 2020, 8(3):e8923.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Catozzi C, Bonastre A S, Francino O, et al. The microbiota of water buffalo milk during mastitis[J]. Plos One, 2017, 12(9):e0184710.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Falentin H, Rault L, Nicolas A, et al. Bovine teat microbiome analysis revealed reduced Alpha diversity and significant changes in taxonomic profiles in quarters with a history of Mastitis[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, (7):480. |
| [19] |
Chandel D S, Johnson J A, Chaudhry R, et al. Extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing Gram-negative bacteria causing neonatal sepsis in India in rural and urban settings[J]. Journal of Medical Microbiology, 2011, 60(Pt4):500-507.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
Adler A, Katz D E, Marchaim D. The continuing plague of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing enterobacteriaceae infections[J]. Infect Dis Clin North Am, 2016, 30(2):347-375.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Sabrina M A, Schramm S T J, Traglia G M, et al. The genetic analysis of an acinetobacter johnsonii clinical strain evidenced the presence of horizontal genetic transfer[J]. Plos One, 2016, 11(8):e0161528.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Al Atrouni A, Joly-Guillou M-L, Hamze M, et al. Reservoirs of non-baumannii acinetobacter species[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, (7):49. |
| [23] | Morris F C, Dexter C, Kostoulias X, et al. The mechanisms of disease caused by Acinetobacter baumannii[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, (10):1606. |
| [24] | Kirk J H, Bartlett P C. Nonclinical Pseudomonas aeruginosa mastitis in a dairy herd[J]. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association, 1984, 184(6):671. |
| [25] | Ruffin M, Brochiero E. Repair Process impairment by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in epithelial tissues: major features and potential therapeutic avenues[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 2019,(9):182. |
| [26] | Parkins M D, Ranjani S, Waters V J. Epidemiology, Biology, impact of clonal Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in cystic fibrosis[J]. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 2018, 31(4):e00019-18. |
| [27] |
Podder M P, Laura R, Daler P K, et al. Klebsiella species associated with bovine mastitis in newfoundland[J]. Plos One, 2014, 9(9):e106518.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Elizabeth A M, Bart C W, James D M D O A S, et al. Dissecting the role of milk components on gut microbiota composition[J]. Gut Microbes, 2013, 4(2):136-139.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Ma C, Sun Z, Zeng B, et al. Cow-to-mouse fecal transplantations suggest intestinal microbiome as one cause of mastitis[J]. Microbiome, 2018, 6(1):200.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Gomes F, Saavedra M J, Henriques M. Bovine mastitis disease/pathogenicity: evidence of the potential role of microbial biofilms[J]. Pathogens and Disease, 2016, 74(3): ftw006. |
| [1] | 王丹丹, 李燕, 张庆银, 李世东, 庞永超, 马琨芝, 马龙, 牛瑞生, 钟增明, 齐连芬, 师建华. 不同微生物菌处理对番茄土壤微生物多样性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2248-2257. |
| [2] | 岳丽, 王卉, 山其米克, 再吐尼古丽·库尔班, 涂振东. 基于高通量测序的甜高粱青贮饲料中微生物群落分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2742-2750. |
| [3] | 秦新政, 王玉苗, 王志慧, 谢成娟, 王博. 秸秆还田对棉田土壤养分和微生物多样性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1236-1244. |
| [4] | 艾海白尔·卡斯木, 樊永红, 迪拉热·海米提. 盐碱地白刺不同部位微生物群落高通量分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2562-2573. |
| [5] | 刘建成, 曾军, 丁峰, 许先查, 窦晶晶, 陈开旭, 李凤鸣, 高雁. 再生固体牛粪垫料中细菌多样性分析及评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2334-2341. |
| [6] | 王登峰, 李建军, 刘志强, 翁业斌, 葛建军, 杨学云, 吴建勇. 乳样中金黄色葡萄球菌的靶向分离及其致临床型乳腺炎的风险分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(5): 974-980. |
| [7] | 桑扎根, 张梦华, 董明明, 乔春华, 陈军, 邓晓峰, 姜徽, 魏趁, 王丹, 胥磊, 张晓雪, 赵番番, 种丽伟, 黄锡霞. 新疆昌吉地区荷斯坦万千克奶牛的种公牛系谱追踪分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(10): 1940-1947. |
| [8] | 顾美英, 徐万里, 张志东, 唐光木, 唐琦勇, 雇玉忠, 宋素琴, 古丽尼沙·沙依木, 杨波, 冯雷. 不同腐烂病发病程度核桃根区土壤微生物多样性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(6): 1107-1116. |
| [9] | 陈竞;代金平;杨新平;古丽·艾合买提;买尔哈巴;冯蕾. 新疆北疆地区户用沼气微生物群落多样性分析[J]. , 2016, 53(3): 539-546. |
| [10] | 马梦婷;王珊珊;陈晓莉;依斯拉穆;高庆华;韩春梅. 固相磁珠扣除杂交法筛选奶牛Y-X精子差异表达基因[J]. , 2015, 52(4): 774-778. |
| [11] | 李英;成李静;陈伟. 新疆南疆地区奶牛乳房炎性表皮葡萄球菌生物膜形成依赖型检测[J]. , 2015, 52(4): 754-758. |
| [12] | 王蒴;杨学云;李建军;冉多良;王治才. 奶牛乳房炎无乳链球菌的分离鉴定与特异、快速检测方法[J]. , 2014, 51(7): 1328-1334. |
| [13] | 刘佳佳;易海波;余雄. 外界因素对奶牛产奶性能影响的研究[J]. , 2014, 51(12): 2279-2283. |
| [14] | 王立文;邵伟;赵艳坤;余雄. 奶牛脐带间充质干细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J]. , 2014, 51(11): 2099-2104. |
| [15] | 杨学云;李建军;王蒴;吴建勇;王登峰;王治才. 改良格拉纳达培养基分离奶牛乳房炎奶样中无乳链球菌的效果评价[J]. , 2014, 51(11): 2093-2098. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
全文 63
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
摘要 144
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||