

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (11): 2733-2741.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.11.014
• Crop Genetics and Breeding·Cultivation Physiology • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Yifan1( ), GAO Yan2, LIU Yanan3, HUO Xiangdong2, LOU Kai2, GUAN Bo3, CHEN Kaixu1(
), GAO Yan2, LIU Yanan3, HUO Xiangdong2, LOU Kai2, GUAN Bo3, CHEN Kaixu1( ), ZENG Jun2(
), ZENG Jun2( )
)
Received:2024-03-27
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2025-01-08
Correspondence author:
CHEN Kaixu, ZENG Jun
Supported by:
杨奕凡1( ), 高雁2, 刘亚男3, 霍向东2, 娄恺2, 关波3, 陈开旭1(
), 高雁2, 刘亚男3, 霍向东2, 娄恺2, 关波3, 陈开旭1( ), 曾军2(
), 曾军2( )
)
通讯作者:
陈开旭,曾军
作者简介:杨奕凡(1999-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为动物营养与饲料,(E-mail)623802746@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
YANG Yifan, GAO Yan, LIU Yanan, HUO Xiangdong, LOU Kai, GUAN Bo, CHEN Kaixu, ZENG Jun. Screening of strains producing non-starch polysaccharide enzyme by fermentation of licorice residue and its dynamic changes[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2733-2741.
杨奕凡, 高雁, 刘亚男, 霍向东, 娄恺, 关波, 陈开旭, 曾军. 甘草渣发酵产非淀粉多糖酶菌株筛选及产酶的动态变化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2733-2741.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.11.014
| 菌株 Strains | D(cm) | d(cm) | D/d | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄孢原毛平革 Phanerochaete chrysosporium | 3.0±0.063 | 1.65±0.224 | 1.818 | 0.606 |
| 康宁木霉 Conning wood mold | 3.2±0.141 | 1.4±0.063 | 2.286 | 0.762 |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 3.0±0.327 | 1.67±0.122 | 1.796 | 0.599 |
| 里氏木霉 Trichoderma reeser | 2.52±0.043 | 1.49±0.034 | 1.691 | 0.564 |
Tab.1 Diameter of transparent circle of cellulase produced by four fungi
| 菌株 Strains | D(cm) | d(cm) | D/d | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄孢原毛平革 Phanerochaete chrysosporium | 3.0±0.063 | 1.65±0.224 | 1.818 | 0.606 |
| 康宁木霉 Conning wood mold | 3.2±0.141 | 1.4±0.063 | 2.286 | 0.762 |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 3.0±0.327 | 1.67±0.122 | 1.796 | 0.599 |
| 里氏木霉 Trichoderma reeser | 2.52±0.043 | 1.49±0.034 | 1.691 | 0.564 |
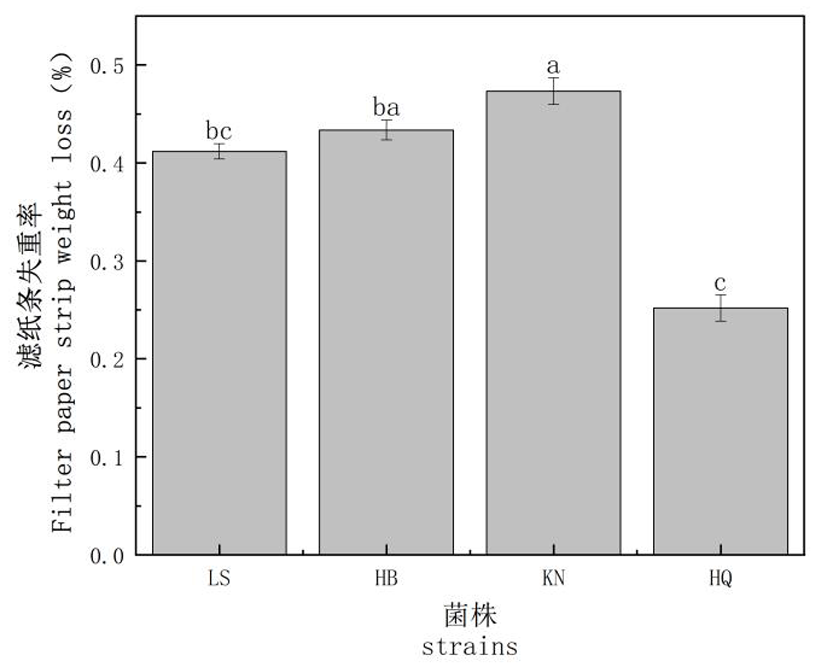
Fig.3 Filter paper strip weight loss results Notes: Different strains containing different letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), and the same letters indicate non-significant differences (P>0.05).
| 菌株 Strains | D(cm) | d(cm) | D/d | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄孢原毛平革 Phanerochaete chrysosporium | 4.37±0.262 | 1.73±0.205 | 2.571 | 0.643 |
| 康宁木霉 Conning wood mold | 6.1±0.572 | 1.63±0.125 | 3.779 | 0.945 |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 5.5±0.082 | 1.47±0.17 | 4.029 | 1.007 |
| 里氏木霉 Trichoderma reeser | 3.97±0.125 | 1.85±0.15 | 2.222 | 0.555 |
Tab.2 Diameter of transparent circle for xylanase production of four fungi
| 菌株 Strains | D(cm) | d(cm) | D/d | A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 黄孢原毛平革 Phanerochaete chrysosporium | 4.37±0.262 | 1.73±0.205 | 2.571 | 0.643 |
| 康宁木霉 Conning wood mold | 6.1±0.572 | 1.63±0.125 | 3.779 | 0.945 |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 5.5±0.082 | 1.47±0.17 | 4.029 | 1.007 |
| 里氏木霉 Trichoderma reeser | 3.97±0.125 | 1.85±0.15 | 2.222 | 0.555 |
| 培养时间 Incubation time | 形态学观察 Morphological observation |
|---|---|
| 第1 d 1st day | 培养基底部有少量的白色菌丝 |
| 第2 d 2nd day | 培养基的表面部分有白色菌丝生成, 黑色孢子逐渐增多 |
| 第3 d 3rd day | 黑色孢子继续增加, 并且孢子子颜色有所加深 |
| 第4 d 4th day | 培养基内容物基本变成纯黑色 |
Tab.3 Morphological observation on enzyme production from solid-state fermentation of licorice residue by Aspergillus Niger
| 培养时间 Incubation time | 形态学观察 Morphological observation |
|---|---|
| 第1 d 1st day | 培养基底部有少量的白色菌丝 |
| 第2 d 2nd day | 培养基的表面部分有白色菌丝生成, 黑色孢子逐渐增多 |
| 第3 d 3rd day | 黑色孢子继续增加, 并且孢子子颜色有所加深 |
| 第4 d 4th day | 培养基内容物基本变成纯黑色 |
| 培养时间 Incubation time | 形态学观察 Morphological observation |
|---|---|
| 第1 d 1st day | 培养基底部有少量的白色菌丝 |
| 第3 d 3rd day | 培养基外壁1/3开始变绿 |
| 第4~5 d 4th day-5th day | 培养基内有部分有白色菌丝生成, 绿色生成物逐渐增多 |
| 第5~6 d 5th day-6th day | 绿色生成物继续增加, 并且颜色有所加深 |
| 第7 d 7th day | 培养基内容物完全变成纯绿色 |
Tab.4 Morphological observation on enzyme production of licorice residue by solid-state fermentation with mixed bacteria
| 培养时间 Incubation time | 形态学观察 Morphological observation |
|---|---|
| 第1 d 1st day | 培养基底部有少量的白色菌丝 |
| 第3 d 3rd day | 培养基外壁1/3开始变绿 |
| 第4~5 d 4th day-5th day | 培养基内有部分有白色菌丝生成, 绿色生成物逐渐增多 |
| 第5~6 d 5th day-6th day | 绿色生成物继续增加, 并且颜色有所加深 |
| 第7 d 7th day | 培养基内容物完全变成纯绿色 |
| 菌种 Strains | 纤维素酶测定结果 Cellulase determination results(U/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 第5 d 5th day | 第8 d 8th day | 第11 d 11th day | |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 50.523±2.095 | 35.617±0.227 | 16.95±1.515 |
| 黄孢原毛平革+ 康宁木霉 Phanerochaete chrysosporium +Conning wood mold | 71.37±2.857 | 56.828±0.593 | 33.46±0.755 |
Tab.5 Results of cellulase production by solid-state fermentation of licorice residue
| 菌种 Strains | 纤维素酶测定结果 Cellulase determination results(U/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 第5 d 5th day | 第8 d 8th day | 第11 d 11th day | |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 50.523±2.095 | 35.617±0.227 | 16.95±1.515 |
| 黄孢原毛平革+ 康宁木霉 Phanerochaete chrysosporium +Conning wood mold | 71.37±2.857 | 56.828±0.593 | 33.46±0.755 |
| 菌种 Strains | 木聚糖酶测定结果 Xylanase determination results(U/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 第5 d 5th day | 第8 d 8th day | 第11 d 11th day | |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 77.056±2.462 | 54.063±1.588 | 13.97±0.609 |
| 黄孢原毛平革+ 康宁木霉 Phanerochaete chrysosporium +Conning wood mold | 74.11±4.547 | 45.188±0.838 | 11.34±0.653 |
Tab.6 Results of xylanase production by solid-state fermentation of licorice residue
| 菌种 Strains | 木聚糖酶测定结果 Xylanase determination results(U/g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 第5 d 5th day | 第8 d 8th day | 第11 d 11th day | |
| 黑曲霉 Aspergillus niger | 77.056±2.462 | 54.063±1.588 | 13.97±0.609 |
| 黄孢原毛平革+ 康宁木霉 Phanerochaete chrysosporium +Conning wood mold | 74.11±4.547 | 45.188±0.838 | 11.34±0.653 |
| [1] | 尹德明, 单玉鑫. 大健康产业背景下中药渣资源化利用路径和技术模式的探讨[J]. 科技创新导报, 2018, 15(13): 96-100, 102. |
| YIN Deming, SHAN Yuxin. Discussion on the resource utilization path and technical model of Chinese medicine residue under the background of big health industry[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2018, 15(13): 96-100, 102. | |
| [2] | 乙凯强. 甘草中活性成分连续提取纯化及多孔炭材料制备工艺研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2021. |
| YI Kaiqiang. Preparation of Porous Carbon Materials and Continuous Extraction and Purification of Active Components in Licorice[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2021. | |
| [3] | 赵爽. 两种不同来源绿色木霉固态发酵及甘草药渣对玉米生长效应研究[D]. 保定: 河北大学, 2020. |
| ZHAO Shuang. Solid State Fermentation by Trichoderma Viride Isolated from Two Different Habitats and Growth Effects of Liquorice Residue on Zea Mays[D]. Baoding: Hebei University, 2020. | |
| [4] | 吴华, 张辉, 康愿. 饲料中添加甘草药渣对肉鸡生产性能的影响[J]. 当代畜牧, 2007,(11): 29-31. |
| WU Hua, ZHANG Hui,KANG Yuan. Effect of adding licorice residue to feed on production performance of broilers[J]. Contemporary Animal Husbandry, 2007,(11): 29-31. | |
| [5] | 吕丽静, 屈青松, 周晴, 等. 甘草药渣发酵工艺优化及成分分析、抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 中南药学, 2022, 20(10): 2312-2317. |
| LYU Lijing, QU Qingsong, ZHOU Qing, et al. Optimization of licorice residue fermentation and analysis of its compositions and antioxidant activity[J]. Central South Pharmacy, 2022, 20(10): 2312-2317. | |
| [6] | 关莹, 薛敏, 王伟. 饲用酶制剂在水产动物中应用的最新研究进展[J]. 中国渔业质量与标准, 2021, 11(1): 61-67. |
| GUAN Ying, XUE Min, WANG Wei. The latest research progress of feed enzyme preparation in aquatic animals[J]. Chinese Fishery Quality and Standards, 2021, 11(1): 61-67. | |
| [7] |
曾飞, 张森, 钱大玮, 等. 甘草药渣降解菌的筛选及其产酶工艺研究[J]. 生物技术通报, 2017, 33(12): 125-131.
DOI |
|
ZENG Fei, ZHANG Sen, QIAN Dawei, et al. Screening the strains degrading glycyrrhiz uralensis residues and its enzyme production[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2017, 33(12): 125-131.
DOI |
|
| [8] | 李曼曼, 姚日生, 李凤和, 等. 中药丹皮残渣固态发酵产酶与糖化工艺的研究[J]. 安徽化工, 2010, 36(S1): 57-60. |
| LI Manman, YAO Risheng, LI Fenghe, et al. Production of cellulase from residues of the peony tree root bark by solid-state fermentation and the saccharification[J]. Anhui Chemical Industry, 2010, 36(S1): 57-60. | |
| [9] | 李鸿梅, 苗琇岩, 魏明, 等. 罗耳阿太菌的鉴定及生长曲线的测定[J]. 食品科技, 2014, 39(6): 35-39. |
| LI Hongmei, MIAO Xiuyan, WEI Ming, et al. Determination of Athelia rolfsii growth curve by glucose consumption[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2014, 39(6): 35-39. | |
| [10] | 郭凯. 黑曲霉HQYX产酶特性及其用作棉花秸秆发酵饲料添加剂的效果研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2019. |
| GUO Kai. Study on Enzyme Production Characteristics of Aspergillus Niger HQYX and Its Application as Feed Additive for Fermentation of Cotton Straw[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang University, 2019. | |
| [11] | 李磊, 王卫国, 郭家瑞, 等. 几株灰树花菌株液态发酵产多糖性能的比较[J]. 河南工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 31(2): 71-75. |
| LI Lei, WANG Weiguo, GUO Jiarui, et al. Comparison of polysaccharide producing capability of several strains of grifola frondosa by liquid fermentation[J]. Journal of Henan University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 31(2): 71-75. | |
| [12] | 张聪聪. 黑曲霉固态发酵产纤维素酶条件优化及秸秆糖化研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2020. |
| ZHANG Congcong. Optimization of Cellulase Production by Solid Fermentation of Aspergillus Niger and Study on Straw Saccharification[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2020. | |
| [13] | 王珂瑶. 黑曲霉Lys2369固体发酵产木聚糖酶条件优化及浅盘放大工艺研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2019. |
| WANG Keyao. Study on Solid-State Fermentation Conditions and Enlargement of Xylanase Production by Aspergillus Niger Lys2369[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2019. | |
| [14] | 岳鹍, 潘志恒, 孙勇民. 中药药渣发酵生产毛云芝菌漆酶培养基的工艺研究[J]. 食品与机械, 2015, 31(5): 47-50. |
| YUE Kun,PAN Zhiheng, SUN Yongmin. Optimization on culture medium for laccase production from Coriolus hirsutus by residues of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Food & Machinery, 2015, 31(5): 47-50. | |
| [15] | 杨冰, 丁斐, 李伟东, 等. 中药渣综合利用研究进展及生态化综合利用模式[J]. 中草药, 2017, 48(2): 377-383. |
| YANG Bing, DING Fei, LI Weidong, et al. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of Chinese medicine residue and ecological comprehensive utilization pattern[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2017, 48(2): 377-383. | |
| [16] | 尹守亮, 杨镒婴, 李秋园, 等. 一株高产纤维素酶真菌的分离与鉴定[J]. 纤维素科学与技术, 2022, 30(2): 9-18. |
| YIN Shouliang, YANG Yiying, LI Qiuyuan, et al. Isolation and identification of a high efficiency cellulose degrading fungus[J]. Journal of Cellulose Science and Technology, 2022, 30(2): 9-18. | |
| [17] | 赵龙妹, 张迎燕, 李旺, 等. 产木聚糖酶微生物的筛选鉴定及特性分析[J]. 家畜生态学报, 2022, 43(4): 14-20. |
| ZHAO Longmei, ZHANG Yingyan, LI Wang, et al. Screening, identification and characterization of xylanase-producing microorganisms[J]. Journal of Domestic Animal Ecology, 2022, 43(4): 14-20. | |
| [18] | Andlar M, Rezi T, Marđetko N, et al. Lignocellulose degradation: an overview of fungi and fungal enzymes involved in lignocellulose degradation[J]. Engineering in Life Sciences, 2018, 18(11): 768-778. |
| [19] |
杨彬, 李小波, 周林, 等. 同步分泌高效纤维素酶和木聚糖酶菌株YB的鉴定及其酶学性质研究[J]. 生物技术通报, 2020, 36(2): 110-118.
DOI |
|
YANG Bin, LI Xiaobo, ZHOU Lin, et al. Identification and enzymatic properties of strain YB simultaneously secreting highly efficient cellulase and xylanase[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2020, 36(2): 110-118.
DOI |
|
| [20] | Shokrkar H, Ebrahimi S, Zamani M. A review of bioreactor technology used for enzymatic hydrolysis of cellulosic materials[J]. Cellulose, 2018, 25(11): 6279-6304. |
| [21] | 单丽君. 以柑橘皮为原料生产饲用复合酶的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2005. |
| SHAN Lijun. Utilization of Orange Peels: Multienzyme Production in Solid-state Fermentation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2005. | |
| [22] | 田杰. 黑曲霉发酵藤茶对其主要活性物质的影响及产酶研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州师范大学, 2021. |
| TIAN Jie. Effects of Aspergillus Niger Fermentation on the Main Active Substances of Ampelopsis Grossedentata and Its Enzyme Production[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou Normal University, 2021. | |
| [23] | 钱静亚, 张正沛, 季蓉蓉, 等. 3株真菌固态发酵产木质素降解酶的研究[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2017, 45(5): 277-280. |
| QIAN Jingya, ZHANG Zhengpei, JI Rongrong, et al. Study on solid-state fermentation of three fungi to produce lignin degrading enzymes[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 45(5): 277-280. | |
| [24] | 邱首哲, 曾飞, 张森, 等. 丹参药渣等不同类型中药固废发酵产纤维素酶研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2020, 45(4): 890-895. |
|
QIU Shouzhe, ZENG Fei, ZHANG Sen, et al. Fermentation of cellulase with multiple types of Salvia miltiorrhiza residues and other solid wastes from Chinese materia medica industrialization[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2020, 45(4): 890-895.
DOI PMID |
|
| [25] | 夏强. 纤维素降解混合菌剂的构建及降解效能[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. |
| XIA Qiang. Construction of Cellulose-degrading Compound Microbial Inoculum and Degradation Efficiency[D]. Harbin:Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. | |
| [26] | 李静, 李明源, 王继莲, 等. 纤维素的微生物降解研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 2022, 43(9): 396-403. |
| LI Jing, LI Mingyuan, WANG Jilian, et al. Research progress on microbial degradation of cellulose[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(9): 396-403. | |
| [27] | 张仲卿, 张爱忠, 姜宁. 混合真菌发酵对玉米秸秆纤维素与木质素降解率的影响[J]. 动物营养学报, 2019, 31(3): 1385-1395. |
| ZHANG Zhongqing, ZHANG Aizhong, JIANG Ning. Effects of mixed fungal fermentation on degradation rate of cellulose and lignin of corn straw[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(3): 1385-1395. | |
| [28] | 王志, 陈雄, 王实玉, 等. 拟康氏木霉和白腐菌混菌发酵处理稻草秸秆的研究[J]. 可再生能源, 2009, 27(2): 36-39. |
| WANG Zhi, CHEN Xiong, WANG Shiyu, et al. Study on degradation of straw stalk by co-fermentation of Trichoderma pseudokoningii and Phanerochaete chrysosporium[J]. Renewable Energy Resources, 2009, 27(2): 36-39. |
| [1] | HE Tingting, WANG Xuzhe, SONG Lei, MA Chunhui. Effects of Different Additives on Quality and Aerobic Stability of Cyperus esculentus Silage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(7): 1767-1775. |
| [2] | LIU Kang-yong, JIAO Yang, ZHAO Fu-xiang, LIU Na, CHEN Quan-jia, GAO Wen-wei, QU Yan-ying. Effects of Spraying TDZ on Leaf Loss Rate and Leaf Enzyme Activity of Cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(6): 981-991. |
| [3] | GUO Kai, HOU Min, BAO Hui-fang, WANG Ning, ZHAN Fa-qiang, YANG Rong, YANG Wen-qi, LONG Xuan-qi, CUI Wei-dong. Study on Optimizing Liquid Fermentation Conditions of Aspergillus niger and Its Degradation Effect on Cotton Stalk with Double Indexes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(11): 2122-2133. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||