

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (3): 669-677.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.03.016
• Horticultural Special Local Products • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Xintong1( ), QIN Lihuan2, Sumirikezi Kaisaer1, ZHANG Dahai2, Gulimire Kasimu3, Waili Kadier3, ZENG Bin1(
), QIN Lihuan2, Sumirikezi Kaisaer1, ZHANG Dahai2, Gulimire Kasimu3, Waili Kadier3, ZENG Bin1( ), XIE Hui2(
), XIE Hui2( )
)
Received:2024-08-12
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-05-14
Correspondence author:
ZENG Bin, XIE Hui
Supported by:
马昕彤1( ), 秦丽欢2, 苏米日克孜·开萨尔1, 张大海2, 古丽米热·喀斯木3, 外力·喀迪尔3, 曾斌1(
), 秦丽欢2, 苏米日克孜·开萨尔1, 张大海2, 古丽米热·喀斯木3, 外力·喀迪尔3, 曾斌1( ), 谢辉2(
), 谢辉2( )
)
通讯作者:
曾斌,谢辉
作者简介:马昕彤(1999-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为杏树栽培与生理,(E-mail) asherr0227@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
MA Xintong, QIN Lihuan, Sumirikezi Kaisaer, ZHANG Dahai, Gulimire Kasimu, Waili Kadier, ZENG Bin, XIE Hui. Analysis of sugar and acid components and contents in different varieties of apricot fruits[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(3): 669-677.
马昕彤, 秦丽欢, 苏米日克孜·开萨尔, 张大海, 古丽米热·喀斯木, 外力·喀迪尔, 曾斌, 谢辉. 不同品种杏果实的糖酸组分及含量分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(3): 669-677.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.xjnykx.com/EN/10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.03.016
| 品种名称 Cultivars | 采样时间(开花后天数) Sampling time(d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |
| 长赛买提 Chang saimaiti | 23 | 37 | 76 | 85 | 92 |
| 依朗吐木休克 Yilangtumuxiuke | 23 | 37 | 76 | 85 | 92 |
Tab.1 Sampling time of different apricot varieties
| 品种名称 Cultivars | 采样时间(开花后天数) Sampling time(d) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | |
| 长赛买提 Chang saimaiti | 23 | 37 | 76 | 85 | 92 |
| 依朗吐木休克 Yilangtumuxiuke | 23 | 37 | 76 | 85 | 92 |
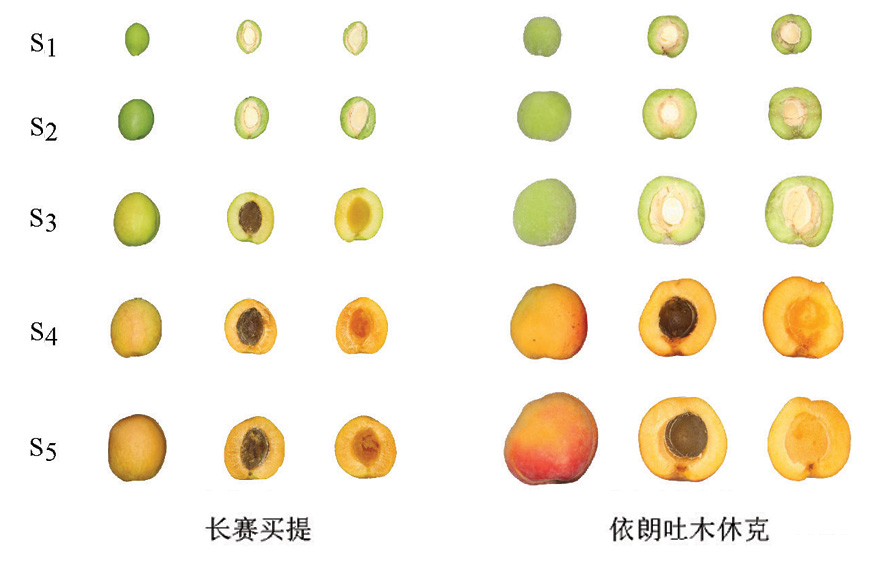
Fig.1 Fruit development of two apricot varieties at different developmental stages Notes:S1:Fruit setting period;S2:Hardcore period;S3:Color change peried;S4:Green maturity period;S5:Full maturity
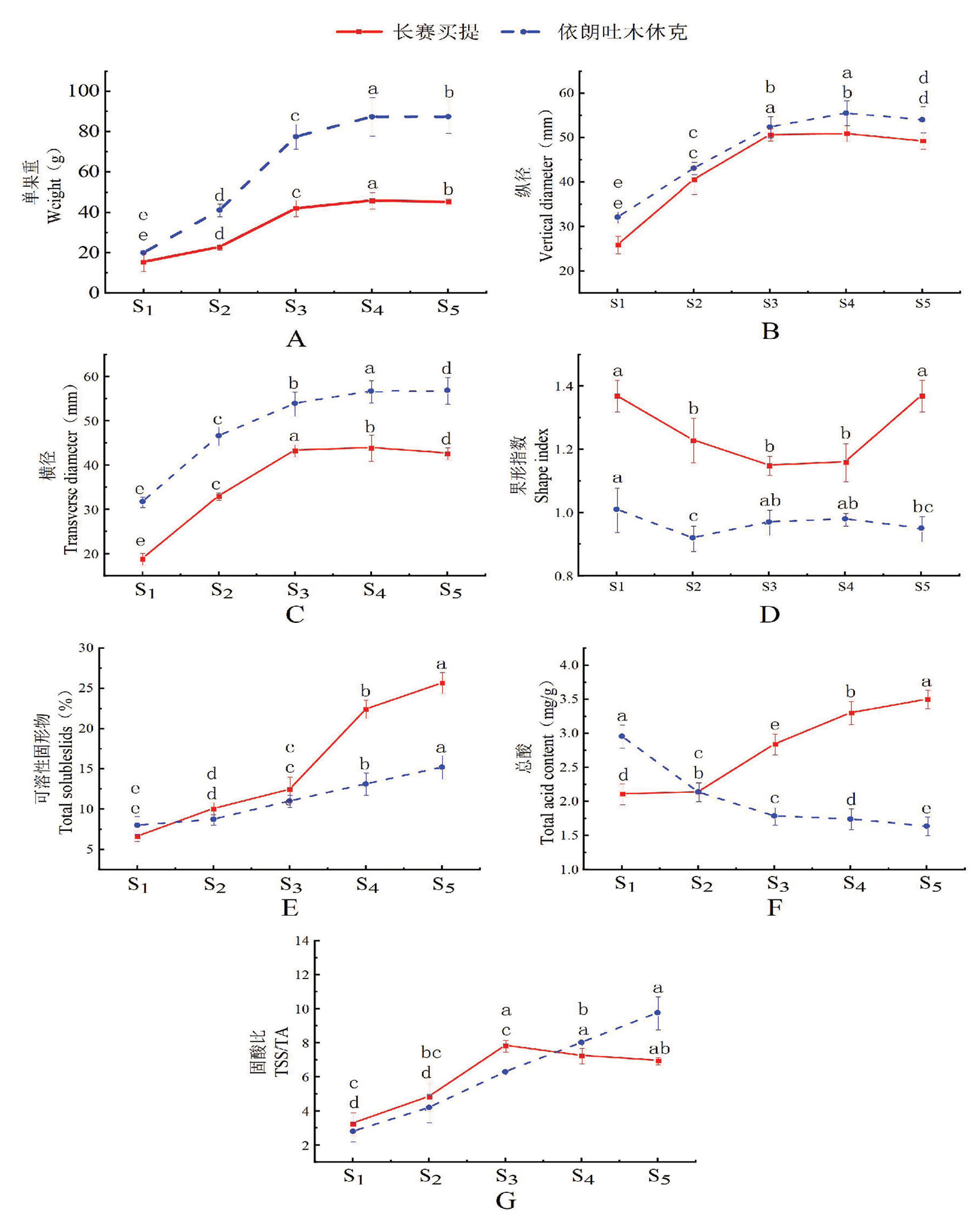
Fig.2 Changes of basic physiological indexes of apricot fruits at different developmental stages Notes:Different lowercase letters marked in the figure indicate significant differences (P < 0.05), the same as below
| [1] | Alajil O, Sagar V R, Kaur C, et al. Nutritional and phytochemical traits of apricots (Prunus armeniaca L.) for application in nutraceutical and health industry[J]. Foods, 2021, 10(6): 1344. |
| [2] | Erdogan-Orhan I, Kartal M. Insights into research on phytochemistry and biological activities of Prunus armeniaca L. (apricot)[J]. Food Research International, 2011, 44(5): 1238-1243. |
| [3] |
Hegedus A, Engel R, Abrankó L, et al. Antioxidant and antiradical capacities in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) fruits: variations from genotypes, years, and analytical methods[J]. Journal of Food Science, 2010, 75(9): 722-730.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Ruiz D, Egea J, Tomás-Barberán F A, et al. Carotenoids from new apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) varieties and their relationship with flesh and skin color[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2005, 53(16): 6368-6374. |
| [5] | Bureau S, Renard C M G C, Reich M, et al. Change in anthocyanin concentrations in red apricot fruits during ripening[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology, 2009, 42(1): 372-377. |
| [6] |
Turan S, Topcu A, Karabulut I, et al. Fatty acid, triacylglycerol, phytosterol, and tocopherol variations in kernel oil of Malatya apricots from Turkey[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2007, 55(26): 10787-10794.
PMID |
| [7] | 王超, 韩刚. 枣果实风味研究进展[J]. 果树学报, 2020, 37(6): 920-928. |
| WANG Chao, HAN Gang. Advances in research on jujube flavor[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2020, 37(6): 920-928. | |
| [8] | Kader A A. Flavor quality of fruits and vegetables[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2008, 88(11): 1863-1868. |
| [9] | 张永平, 乔永旭, 喻景权, 等. 园艺植物果实糖积累的研究进展[J]. 中国农业科学, 2008, 41(4): 1151-1157. |
| ZHANG Yongping, QIAO Yongxu, YU Jingquan, et al. Progress of researches of sugar accumulation mechanism of horticultural plant fruits[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(4): 1151-1157. | |
| [10] | 李金龙. 果实内糖的积累与糖代谢相关酶[J]. 中国林副特产, 2015,(3): 92-93. |
| LI Jinlong. Sugar accumulation in fruits and enzymes related to sugar metabolism[J]. Forest By-Product and Speciality in China, 2015,(3): 92-93. | |
| [11] | 焦晋华, 薛晓芳, 任海燕, 等. 影响枣果实风味品质的指标分析[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(3): 205-208. |
| JIAO Jinhua, XUE Xiaofang, REN Haiyan, et al. Analysis on the indices affecting the jujube fruit flavor quality[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(3): 205-208. | |
| [12] | Bureau S, Ruiz D, Reich M, et al. Application of ATR-FTIR for a rapid and simultaneous determination of sugars and organic acids in apricot fruit[J]. Food Chemistry, 2009, 115(3): 1133-1140. |
| [13] | 陈美霞, 陈学森, 慈志娟, 等. 杏果实糖酸组成及其不同发育阶段的变化[J]. 园艺学报, 2006, 33(4): 805-808. |
| CHEN Meixia, CHEN Xuesen, CI Zhijuan, et al. Changes of sugar and acid constituents in apricot during fruit development[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2006, 33(4): 805-808. | |
| [14] |
郑惠文, 张秋云, 李文慧, 等. 新疆杏果实发育过程中可溶性糖和有机酸的变化[J]. 中国农业科学, 2016, 49(20): 3981-3992.
DOI |
|
ZHENG Huiwen, ZHANG Qiuyun, LI Wenhui, et al. Changes in soluble sugars and organic acids of Xinjiang apricot during fruit development and ripening[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2016, 49(20): 3981-3992.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 石岩, 贺苗, 谢辉, 等. 我国消费者对鲜杏的消费行为与偏好研究[J]. 中国果树, 2022,(7): 84-90. |
| SHI Yan, HE Miao, XIE Hui, et al. Chinese consumers' behavior and preference to fresh apricot[J]. China Fruits, 2022,(7): 84-90. | |
| [16] | 梁俊, 郭燕, 刘玉莲, 等. 不同品种苹果果实中糖酸组成与含量分析[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 39(10): 163-170. |
| LIANG Jun, GUO Yan, LIU Yulian, et al. Analysis of contents and constituents of sugar and organic acid in different apple cultivars[J]. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(10): 163-170. | |
| [17] | 高阳, 杨滢滢, 郑嘉鹏, 等. 靖安椪柑果实发育阶段糖、酸组分含量变化[J]. 江西农业大学学报, 2016, 38(4): 631-636. |
| GAO Yang, YANG Yingying, ZHENG Jiapeng, et al. Changes in sugar and organic acid components during fruit development in Jing’an ponkan(Citrus reticulata) fruit[J]. Acta Agriculturae Universitatis Jiangxiensis, 2016, 38(4): 631-636. | |
| [18] | 张丽丽, 刘威生, 刘有春, 等. 不同原产地杏种质果实糖酸组分含量特点的研究[J]. 北方果树, 2009,(5): 4-8. |
| ZHANG Lili, LIU Weisheng, LIU Youchun, et al. Sugar and acid contents in apricot derived from different countries and places of production[J]. Northern Fruits, 2009,(5): 4-8. | |
| [19] | 安娇, 刘铭, 贾佳林, 等. 软枣猕猴桃果实发育过程中糖酸组分及含量的变化[J]. 东北农业科学, 2020, 45(5): 88-91. |
| AN Jiao, LIU Ming, JIA Jialin, et al. Changes of sugar and acid components and contents during fruit development of Actinidia arguta[J]. Journal of Northeast Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 45(5): 88-91. | |
| [20] | Moing A, Svanella L, Rolin D, et al. Compositional changes during the fruit development of two peach cultivars differing in juice acidity[J]. Journal of the American Society for Horticultural Science, 123(5): 770-775. |
| [21] | Wu B H, Quilot B, Génard M, et al. Changes in sugar and organic acid concentrations during fruit maturation in peaches, P. davidiana and hybrids as analyzed by principal component analysis[J]. Scientia Horticulturae, 2005, 103(4): 429-439. |
| [22] | 陈发兴, 刘星辉, 陈立松. 果实有机酸代谢研究进展[J]. 果树学报, 2005, 22(5): 526-531. |
| CHEN Faxing, LIU Xinghui, CHEN Lisong. Advances in research on organic acid metabolism in fruits[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2005, 22(5): 526-531. | |
| [23]. | 赵淼, 吴延军, 蒋桂华, 等. 柑橘果实有机酸代谢研究进展[J]. 果树学报, 2008, 25(2): 225-230. |
| ZHAO Miao, WU Yanjun, JIANG Guihua, et al. Research progress of organic acid metabolism in citrus fruits[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2008, 25(2): 225-230. | |
| [24] | Yamaki Y T. Organic acids in the juice of Citrus fruits[J]. Journal of the Japanese Society for Horticultural Science, 1989, 58(3): 587-594. |
| [25] | Cámara M M, Díez C, Torija M E, et al. HPLC determination of organic acids in pineapple juices and nectars[J]. Zeitschrift Für Lebensmittel-Untersuchung und Forschung, 1994, 198(1): 52-56. |
| [26] | 吴林, 张强, 臧慧明, 等. 云南丽江和吉林靖宇蓝莓糖酸组分差异化分析[J]. 中国果树, 2019,(6): 54-58, 64. |
| WU Lin, ZHANG Qiang, ZANG Huiming, et al. Determination of sugar and acid components in blueberries from Lijiang, Yunnan and Jingyu, Jilin[J]. China Fruits, 2019,(6): 54-58, 64. | |
| [27] | 龚荣高, 吕秀兰, 张光伦, 等. 罗伯逊脐橙在不同生境下果实有机酸代谢相关酶的研究[J]. 果树学报, 2006, 23(6): 805-808. |
| GONG Ronggao, LYU Xiulan, ZHANG Guanglun, et al. Study on the organic acid-metabolizing enzymes in Robertson Navel orange fruit collected from different habitats[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2006, 23(6): 805-808. |
| [1] | JIA Binxin, YANG Shiying, WANG Yan, YANG Pengpeng, HE Weizhong, WANG Cheng, LIU Fengjuan, FAN Yingying. Comparison of postharvest sugar content and sugar metabolizing enzyme activities of different varieties of thick-skinned melons [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(6): 1476-1484. |
| [2] | MA Chao, ZHANG Kai, YUAN Fang, ZHANG Nan, SHENG Jiandong, ZHANG Wentai. Effects of Organic acid Addition on Field Phosphorus Status and Yield in Cotton Field with Different Phosphorus Fertilization Rates in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(9): 2247-2257. |
| [3] | LI Junru, QIN Ning, LI Wenlong, DU Hui, LI Xihuan, ZHANG Caiying. Identification of Seed Oligosaccharide and Its Components and Screening for Elite Germplasms in Soybean [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(2): 353-360. |
| [4] | GUO Hang, ZHANG Rui, WANG Zhi, QIAO Kunyun, YAN Nana, ZHAO Duoyong. Study on the Regularity of the Quality Change of Korla Fragrant Pear during the Growth Period [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(2): 377-384. |
| [5] | DAI Xiaohua, GU Hongfei, JIN Kexu, SHU Jiamin, YANG Ruolan, WU Menglan, PAN Hui, ZHAO Hongqiong. Determination of Flavonoids in Wild Apricot Flesh by RP-HPLC [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(8): 1476-1485. |
| [6] | Alinuer Abudureyimu, ZHANG Zhenzhen, HUANG Yadong, Abuduwarisi Tuerxunjiang, CHEN Kai, LI Huanrong. Construction of Dynamic Model of Soluble Sugar Content in Dried Jujube [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(7): 1342-1354. |
| [7] | FENG Beibei, MEI Chuang, ZHANG Zhengjun, LIU Hairong, Aishajiang Maimaiti, WANG Jixun, YAN Peng. Correlation Analysis of Mineral Elements and Soluble Sugar in Different Maturity Stages of Fuji Apple [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(3): 502-510. |
| [8] | Mei KE, Yurong HOU, Yigong ZHANG. Study on the Relationship between pH and Organic Acid in the Root of Agropyron cristatum Tawukumu under Alkaline Stress [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(10): 1929-1937. |
| [9] | YANG Yong, ZHAI Wenqiang, ZHANG Xuejun, LI Meihua, ZHANG Yongbing, MA Xinli, YI Hongping. A Comparative Analysis of the Difference and Soluble Sugar Accumulation Rule of Xinjiang Muskmelon Fruit [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(1): 1-8. |
| [10] | WANG Yanan, LI Wenwen, ZHOU Weiquan, FAN Guoquan, ZHANG Shikui, WANG Yatong, LIAO Kang. Analysis Xinjiang Apricot Varieties Relationship Based on Floral Organ Characteristics [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(1): 9-22. |
| [11] | ZHOU Wenjing, LI Wensheng, WANG Anli, WU Zezhen, HU Anhong. Quality Changes of Sugar Core Red FujiApple under Two Storage Conditions [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(8): 1431-1442. |
| [12] | ZHU Jiahang, LI Yan, ZHU Jinfang, LIANG Jiapei, Baejiang Nuhuyifu. Comparative Determination of Vitamin B1 in Mosquitoes Repellent Cream by HPLC and UV [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(10): 1892-1900. |
| [13] | MENG Xin-tao, WEI Jian, XU Ming-qiang, LI De-hua, TAN Gui, ZHU Li-na, SHAO Wen-zhi, PAN Yan. Determination of Five Flavonoids in Pomegranate Peel of Different Cultivars by High Performance Liquid Chromatography [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(9): 1659-1667. |
| [14] | HU Jiang-lan, ZHU Jin-fang, Parhat Dolkun. Study on HPLC Fingerprint of Hymenoleana nana [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(2): 308-316. |
| [15] | ZHONG Hai-xia, PAN Ming-qi, ZHANG Fu-chun, ZHANG Wen, XIE Hui, HAN Shou-an, Ermek·Chaikasimu, WU Xin-yu. Effects of Different Rootstocks on Soluble Sugar Content of Crimson Grape Fruit [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(9): 1633-1638. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||