

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2023, Vol. 60 ›› Issue (3): 742-749.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2023.03.026
• Prataculture·Agricultural Eeconomy • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Xingyu( ), SUN Hairong, YANG Hanjun, ZHANG Fanfan(
), SUN Hairong, YANG Hanjun, ZHANG Fanfan( ),
),  )
)
Received:2022-07-09
Online:2023-03-20
Published:2023-04-18
Correspondence author:
Supported by:通讯作者:
作者简介:黄星宇(1997- ),男,硕士研究生,研究方向为牧草生产与加工,(E-mail)huangshzu@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
HUANG Xingyu, SUN Hairong, YANG Hanjun, ZHANG Fanfan,
黄星宇, 孙海荣, 杨寒珺, 张凡凡,
| 原料 Material | 干物质 DM % | 粗蛋白 CP% DM | 可溶性碳水化合物 WSC % DM | 中性洗涤纤维 NDF % DM | 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF % DM | 粗灰分 Ash% DM | 粗脂肪 EE % DM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绢蒿 Seriphidium | 58.69 | 11.81 | 8.77 | 59.20 | 34.88 | 9.54 | 8.37 |
| 甜叶菊渣 Residue of stevia rebaudiana | 65.34 | 7.25 | 13.46 | 50.42 | 37.28 | 8.23 | 2.25 |
Tab.1 Material nutrition parameters Seriphidium of Stevia straw
| 原料 Material | 干物质 DM % | 粗蛋白 CP% DM | 可溶性碳水化合物 WSC % DM | 中性洗涤纤维 NDF % DM | 酸性洗涤纤维 ADF % DM | 粗灰分 Ash% DM | 粗脂肪 EE % DM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 绢蒿 Seriphidium | 58.69 | 11.81 | 8.77 | 59.20 | 34.88 | 9.54 | 8.37 |
| 甜叶菊渣 Residue of stevia rebaudiana | 65.34 | 7.25 | 13.46 | 50.42 | 37.28 | 8.23 | 2.25 |
| 处理 Treatment | 颜色 Colour | 气味 Odour | 酸味 Sour | 质地 Texure | 感官综合评定 Comprehensive sensory evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 黄褐色 | 乳酸气味 | 轻微 | 松散不黏手,无霉变 | 差 |
| T1 | 黄褐色 | 乳酸气味 | 中等 | 松散不黏手,无霉变 | 良好 |
| T2 | 黄绿色 | 乳酸气味 | 浓 | 微黏手,无霉变 | 优秀 |
| T3 | 黄绿色 | 乳酸气味 | 浓 | 微黏手,无霉变 | 优秀 |
Tab.2 Sensory evaluation of mixed storage of Seriphidium and Stevia straws in bags during the dry season
| 处理 Treatment | 颜色 Colour | 气味 Odour | 酸味 Sour | 质地 Texure | 感官综合评定 Comprehensive sensory evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 黄褐色 | 乳酸气味 | 轻微 | 松散不黏手,无霉变 | 差 |
| T1 | 黄褐色 | 乳酸气味 | 中等 | 松散不黏手,无霉变 | 良好 |
| T2 | 黄绿色 | 乳酸气味 | 浓 | 微黏手,无霉变 | 优秀 |
| T3 | 黄绿色 | 乳酸气味 | 浓 | 微黏手,无霉变 | 优秀 |
| 项目 Item | CK处理 CK treatment | T1处理 T1 treatment | T2处理 T2 treatment | T3处理 T3 treatment | 标准误 SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质Dry matter(%) | 35.17±0.32a | 35.02±0.4a | 35.37±0.24a | 35.05±0.14a | 0.08 |
| 粗蛋白 Crude protein(% DM) | 7.90±0.13b | 7.85±0.05b | 8.14±0.08a | 7.73±0.11b | 0.18 |
| 粗脂肪Crude fat(% DM) | 8.10±0.04a | 7.67±0.04b | 7.08±0.03c | 6.49±0.02d | 0.18 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber(% DM) | 56.53±1.55a | 53.08±0.53b | 51.40±0.14c | 49.60±0.31d | 0.80 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber(% DM) | 34.37±0.25b | 35.02±0.12a | 35.12±0.23a | 35.20±0.44a | 0.12 |
| 粗灰分Coarse ash(% DM) | 9.36±0.89b | 10.73±0.4a | 11.02±0.25a | 11.09±1.03a | 0.40 |
| 可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrates(% DM) | 4.87±0.24d | 5.25±0.06c | 5.55±0.14b | 6.04±0.12a | 0.47 |
| pH | 4.23±0.03a | 4.13±0.05b | 4.16±0.06ab | 4.11±0.04b | 0.03 |
| 氨态氮Ammonia nitrogen(% FM) | 1.63±0.05a | 1.59±0.04a | 1.52±0.01b | 1.46±0.01b | 0.21 |
| 氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia nitrogen/total nitrogen | 1.32±0.04a | 1.21±0.01b | 1.16±0.01b | 1.18±0.02b | 0.02 |
| 乳酸Lactic acid(% FM) | 3.07±0.45d | 3.57±0.05c | 4.62±0.04b | 4.90±0.08a | 0.39 |
| 乙酸Acetic acid(% FM) | 1.61±0.04a | 1.34±0.05c | 1.42±0.04bc | 1.47±0.05b | 0.06 |
| 丙酸Propionic acid(% FM) | 0.86±0.09a | 0.37±0.06b | 0.22±0.08c | 0.30±0.02bc | 0.14 |
| 丁酸Butyric acid(% FM) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
Tab.3 Analysis of fermentation quality of Artemisia sericata and Stevia straws in bags during the dry yellow period
| 项目 Item | CK处理 CK treatment | T1处理 T1 treatment | T2处理 T2 treatment | T3处理 T3 treatment | 标准误 SEM |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质Dry matter(%) | 35.17±0.32a | 35.02±0.4a | 35.37±0.24a | 35.05±0.14a | 0.08 |
| 粗蛋白 Crude protein(% DM) | 7.90±0.13b | 7.85±0.05b | 8.14±0.08a | 7.73±0.11b | 0.18 |
| 粗脂肪Crude fat(% DM) | 8.10±0.04a | 7.67±0.04b | 7.08±0.03c | 6.49±0.02d | 0.18 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber(% DM) | 56.53±1.55a | 53.08±0.53b | 51.40±0.14c | 49.60±0.31d | 0.80 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber(% DM) | 34.37±0.25b | 35.02±0.12a | 35.12±0.23a | 35.20±0.44a | 0.12 |
| 粗灰分Coarse ash(% DM) | 9.36±0.89b | 10.73±0.4a | 11.02±0.25a | 11.09±1.03a | 0.40 |
| 可溶性碳水化合物 Water soluble carbohydrates(% DM) | 4.87±0.24d | 5.25±0.06c | 5.55±0.14b | 6.04±0.12a | 0.47 |
| pH | 4.23±0.03a | 4.13±0.05b | 4.16±0.06ab | 4.11±0.04b | 0.03 |
| 氨态氮Ammonia nitrogen(% FM) | 1.63±0.05a | 1.59±0.04a | 1.52±0.01b | 1.46±0.01b | 0.21 |
| 氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia nitrogen/total nitrogen | 1.32±0.04a | 1.21±0.01b | 1.16±0.01b | 1.18±0.02b | 0.02 |
| 乳酸Lactic acid(% FM) | 3.07±0.45d | 3.57±0.05c | 4.62±0.04b | 4.90±0.08a | 0.39 |
| 乙酸Acetic acid(% FM) | 1.61±0.04a | 1.34±0.05c | 1.42±0.04bc | 1.47±0.05b | 0.06 |
| 丙酸Propionic acid(% FM) | 0.86±0.09a | 0.37±0.06b | 0.22±0.08c | 0.30±0.02bc | 0.14 |
| 丁酸Butyric acid(% FM) | ND | ND | ND | ND |
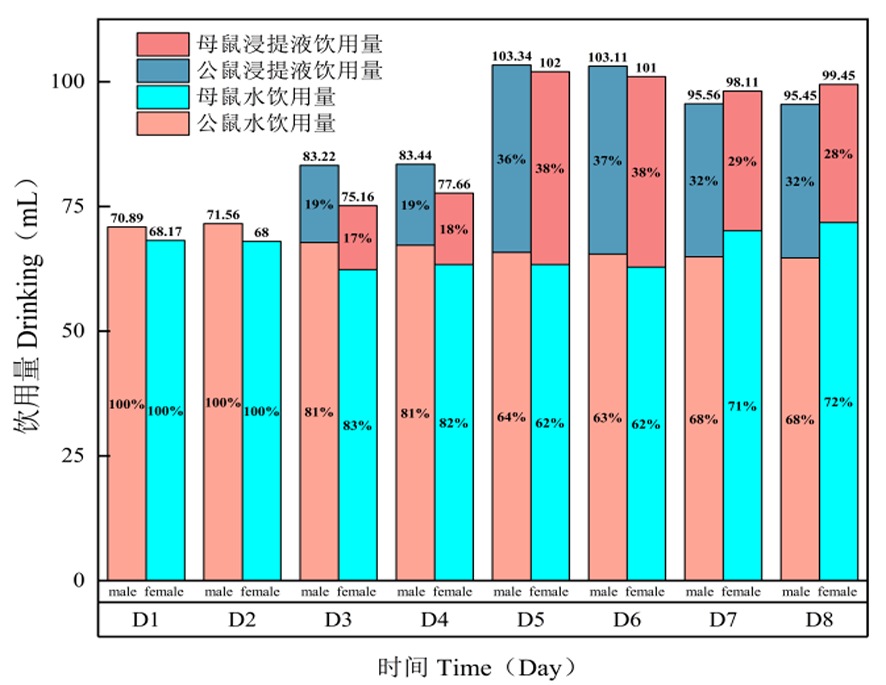
Fig.1 Analysis of TBP test results in mice Note:The experimental data were expressed by mean ± SD, and there were 15 mice in each group;T1 treatment (D1, D2), T2 treatment (D3, D4), T3 treatment (D5, D6), T4 treatment (D7, D8)
| 项目 Item | CK处理 CK treatment | T1处理 T1 treatment | T2处理 T2 treatment | T3处理 T3 treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质 Dry matter(%) | 0.43 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.09 |
| 粗蛋白 Crude protein(% DM) | 0.41 | 0.29 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 粗脂肪Crude fat(% DM) | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.37 | 0.00 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber(% DM) | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.74 | 1.00 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber(% DM) | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| 粗灰分Coarse ash(% DM) | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 1.00 |
| pH | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.00 |
| 氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia nitrogen/total nitrogen | 0.00 | 0.27 | 1.00 | 0.91 |
| 乳酸 Lactic acid(% FM) | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.85 | 1.00 |
| 乙酸 Acetic acid(% FM) | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.48 |
| 丙酸 Propionic acid(% FM) | 1.00 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.13 |
| 平均值 Average | 5.84 | 3.01 | 6.34 | 4.60 |
| 排序Rank | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
Tab.4 Membership function analysis and nutritional value ranking for each treatment
| 项目 Item | CK处理 CK treatment | T1处理 T1 treatment | T2处理 T2 treatment | T3处理 T3 treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 干物质 Dry matter(%) | 0.43 | 0.00 | 1.00 | 0.09 |
| 粗蛋白 Crude protein(% DM) | 0.41 | 0.29 | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| 粗脂肪Crude fat(% DM) | 1.00 | 0.73 | 0.37 | 0.00 |
| 中性洗涤纤维 Neutral detergent fiber(% DM) | 0.00 | 0.50 | 0.74 | 1.00 |
| 酸性洗涤纤维 Acid detergent fiber(% DM) | 1.00 | 0.22 | 0.10 | 0.00 |
| 粗灰分Coarse ash(% DM) | 0.00 | 0.32 | 0.58 | 1.00 |
| pH | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.42 | 0.00 |
| 氨态氮/总氮 Ammonia nitrogen/total nitrogen | 0.00 | 0.27 | 1.00 | 0.91 |
| 乳酸 Lactic acid(% FM) | 0.00 | 0.27 | 0.85 | 1.00 |
| 乙酸 Acetic acid(% FM) | 1.00 | 0.00 | 0.30 | 0.48 |
| 丙酸 Propionic acid(% FM) | 1.00 | 0.23 | 0.00 | 0.13 |
| 平均值 Average | 5.84 | 3.01 | 6.34 | 4.60 |
| 排序Rank | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3 |
| [1] | 冯缨. 新疆蒿类半灌木植被中牧草资源、分布及其饲用价值[J]. 中国科学院新疆生态与地理研究所, 2010. |
| FENG Ying. Forage resources, distribution and feeding value of artemisia annua subshrub vegetation in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Institute of Ecology and Geography, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2010. | |
| [2] | 范燕敏. 天山北坡中段伊犁绢蒿荒漠退化草地土壤质量的演变与评价及预警系统的研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2009. |
| FAN Yanmin. Evolution, Evaluation and Early Warning System of Soil quality in desert Degraded Grassland of Artemisia serratus Yili in the middle part of north Slope of Tianshan Mountain[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2009. | |
| [3] | 鲁为华, 朱进忠, 王东江. 等. 天山北坡围栏封育条件下绢蒿幼苗分布格局及数量动态变化规律研究[J]. 草业学报, 2009, 18(4): 17-26. |
| LU Weihua, ZHU Jinzhong, WANG Dongjiang, et al. Study on the distribution pattern and dynamic change of seedling quantity of Artemisia serrata under enclosure enclosure on the north slope of Tianshan Mountain[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2009, 18(4): 17-26. | |
| [4] | 陶梦. 蒿类荒漠春秋牧场始牧期、终牧期的确定[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2007. |
| TAO Meng. Determination of the initial and final grazing stages of Artemisia annua Desert Pastures in Spring and Autumn[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2007. | |
| [5] | 何雪青, 徐光青, 于非. 等. 沙漠绢蒿和冷蒿挥发油成分的气相色谱-质谱分析[J]. 质谱学报, 2009, 30(5):314-320. |
| HE Xueqing, XU guangqing, YU fei, et al. Analysis of volatile oil components in Artemisia serrata and Artemisia frigaria[J]. Journal of Chinese Mass Spectrometry Society, 2009, 30(5):314-320. | |
| [6] | Park H J, Cho J G, Baek Y S, et al. Identification of bitter components from Artemisia princeps, Pamp[J]. Food Science & Biotechnology, 2016, 25(1):27-32. |
| [7] | 刘晶晶. 苦味机理及苦味物质的研究概况[J]. 食品科技, 2006, 31(8):21-24. |
| LIU Jingjing. Research overview of bitter mechanism and bitter substances[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2006, 31(8): 21-24. | |
| [8] | 王晨. 2018年中国甜菊栽培总面积约27万亩[J]. 精细与专用化学品, 2019, 27(8):14. |
| WANG Chen. The total cultivated area of Stevia in China in 2018 is about 270000 Mu[J]. Fine and Special Chemicals, 2019, 27 (8): 14. | |
| [9] | 张雪颖, 徐仲伟, 战宇. 等. 酶法浸提甜菊糖甙的研究[J]. 食品工业科技, 2007(5):190-192. |
| ZHANG Xueying, XU Zhongwei, ZHAN Yu, et al. Study on enzymatic extraction of stevioside[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2007(5): 190-192. | |
| [10] | 张正鹏. 浅谈甜叶菊副产品的开发利用[J]. 中国糖料, 2015, 37(6):79-80. |
| ZHANG Zhengpeng. Development and utilization of Stevia by-products[J]. Sugar Crops of China, 2015, 37(6): 79-80. | |
| [11] | 孙艳宾, 林英庭, 王利华. 等. 甜叶菊渣对肉兔生产性能和养分消化率的影响[J]. 饲料研究, 2011(1):52-53. |
| SUN Yanbin, LIN Yingting, WANG Lihua, et al. effects of Stevia rebaudiana residue on production performance and nutrient digestibility of meat rabbits[J]. Feed Research, 2011(1): 52-53. | |
| [12] | 尚宏芹. 甜叶菊综合利用研究进展[J]. 生物学教学, 2011, 36(8):4-6. |
| SHANG Hongqin. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of Stevia rebaudiana[J]. Biology Teaching, 2011, 36(8): 4-6. | |
| [13] | 谢凤岩, 王桂杰. 奶牛日粮中添加甜叶菊秆粉对奶牛泌乳性能的影响[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2010,(12):106. |
| XIE Fengyan, WANG Guijie. Effect of Stevia stalk powder on lactation performance of dairy cows[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2010, (12): 106. | |
| [14] | 何力, 计少石, 张志红. 等. 穿心莲药渣和甜叶菊渣对羊瘤胃体外发酵的影响[J]. 中国畜牧杂志, 2017, 53(7):86-89. |
| HE Li, JI Shaoshi, ZHANG Zhihong, et al. The effect of Andrographis paniculata residue and sweet leaf chrysanthemum residue on in vitro rumen fermentation of sheep[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2017, 53 (7): 86-89. | |
| [15] | 朱原, 李欣泽, 郝贺. 等. 甜叶菊绿原酸发酵液对雏鸡肠道菌群的影响[J]. 饲料工业, 2020, 41(13):27-33. |
| ZHU Yuan, LI Xinze, HAO he, et al. Effects of Stevia chlorogenic acid fermentation broth on intestinal microflora of chicks[J]. Feed Industry, 2020, 41 (13): 27-33. | |
| [16] | 中华人民共和国国务院. 《实验动物管理条例》节选[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2020, 19(5):488. |
| The State Council of the People's Republic of China. Regulations on the Control of Experimental Animals (excerpts)[J]. Chinese Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 2020, 19(5):488. | |
| [17] |
Alexander A,. Bachmanov, Xia Li, Danielle R. Reed, et al. Positional Cloning of the Mouse Saccharin Preference (Sac) Locus.[J]. Chemical Senses, 2001,(7):925-933.
PMID |
| [18] | 刘建新, 杨振海, 叶均安. 等. 青贮饲料的合理调制与质量评定标准(续)[J]. 饲料工业, 1999,(4): 3-5. |
| LIU Jianxin, YANG Zhenhai, YE Junan, et al. Criteria for rational modulation and quality assessment of silage (continued)[J]. Feed Industry, 1999,(4): 3-5. | |
| [19] | GB/T 14924. 9. 实验动物配合饲料常规营养成分的测定[S]. |
| GB/T 14924. 9. Determination of conventional nutritional components in compound feed of labora-toryanimals[S]. | |
| [20] | Fang Miao, Fanfan Zhang, Xuzhe Wang, et al. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum, Pediococcus acidilactici and Lactobacillus buchneri at low doses on the fermentation, aerobic stability and ruminal digestibility of corn silage[J]. International Journal of Agriculture and Biology, 2019, 22(4): 655-664. |
| [21] | 郭金桂, 宋灵峰, 玉柱. 等. 混合比例对紫花苜蓿与燕麦混贮品质的动态影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2018, 40(1): 73-79. |
| GUO Jingui, SONG Lingfeng, YU Zhu, et al. Dynamic effect of mixing ratio on the quality of alfalfa and oat mixed storage[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2018, 40 (1): 73-79. | |
| [22] |
Q. Zhang, Q X Li M, Zhao Z. Yu. Lactic acid bacteria strains for enhancing the fermentation quality and aerobic stability of L eymus chinensis silage[J]. Grass and Forage Science, 2016, 71(3):472-481.
DOI URL |
| [23] | 刘晶晶, 高丽娟, 师建芳. 等. 乳酸菌复合系和植物乳杆菌提高柳枝稷青贮效果[J]. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(9):295-302. |
| LIU Jingjing, GAO Lijuan, SHI Jianfang, et al. Improvement of switchgrass silage effect by Lactobacillus plantarum complex system and Lactobacillus plantarum[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2015, 31(9): 295-302. | |
| [24] | Dogi Cecilia A, Pellegrino Matías, Poloni Valeria, Poloni Luis, Pereyra Carina M, Sanabria Analía, Pianzzola María Julia, Dalcero Ana, Cavaglieri Lilia. Efficacy of corn silage inoculants on the fermentation quality under farm conditions and their influence on Aspergillus parasitucus, A. flavus and A. fumigatus determined by q-PCR.[J]. Food additives & contaminants. Part A, Chemistry, Analysis, Control, Exposure & Risk Assessment, 2015, 32(2):229-235. |
| [25] | 玉柱, 孙启忠. 饲草青贮技术[M]. 北京: 中国农业大学出版社, 2011. |
| YU Zhu, SUN Qizhong. Forage silage technology[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural University Press, 2011. | |
| [26] | 庄益芬, 张文昌, 陈鑫珠. 等. 绿汁发酵液、纤维素酶及其混合物对水葫芦青贮品质的影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2008,(5):35-38. |
| ZHUANG Yifen, ZHANG Wenchang, CHEN Xinzhu, et al. Effects of green juice fermentation broth, cellulase and their mixture on the quality of Water Hyacinth Silage[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2008,(5): 35-38. | |
| [27] | 赵庆杰, 原现军, 郭刚. 等. 添加糖蜜和乳酸菌制剂对西藏青稞秸秆和多年生黑麦草混合青贮发酵品质的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2014, 23(4):100-106. |
| ZHAO Qingjie, YUAN Xianjun, GUO Gang, et al. Effect of molasses and lactic acid bacteria on fermentation quality of Tibetan highland barley straw and perennial ryegrass Mixed Silage[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2014, 23(4): 100-106. | |
| [28] |
Queiroz O C M, Arriola K G, Daniel J L P, et al. Effects of 8 chemical and bacterial additives on the quality of corn silage[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2013, 96(9): 5836-5843.
DOI PMID |
| [29] |
Tabacco E, Righi F, Quarantelli A, et al. Dry matter and nutritional losses during aerobic deterioration of corn and sorghum silages as influenced by different lactic acid bacteria inocula[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2011, 94(3): 1409-1419.
DOI PMID |
| [30] | 冯涛, 唐海洋, 杨文祥. 等. 甜高粱凋萎青贮和混合青贮对发酵品质及营养成分保存效果的影响[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2019, 42(2):352-357. |
| FENG Tao, TANG Haiyang, YANG Wenxiang, et al. Effects of wilting and mixing straws on fermentation quality and nutrients preservation of sweet sorghum silage[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2019, 42(2): 352-357. | |
| [31] |
Iwasaki K, Sato M. Neural and behavioral responses to taste stimuli in the mouse[J]. Physiology & Behavior, 1984, 32(5): 803-807.
DOI URL |
| [32] | 刘斯斯. 咖啡因苦味适应小鼠模型的建立及其外周机制初步研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2012. |
| LIU Sisi. Establishment of caffeine bitter adaptation mouse model and preliminary study on its peripheral mechanism[D]. Suzhou: Suzhou University, 2012. |
| [1] | XIAN Ouyang, LI Xiao, CHEN Yongcheng, WANG Xuze, ZHANG Fanfan, HOU Guoqing. Effects of Lactiplantibacillus plantarumand molasses on the silage of Silphium perfoliatum [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(6): 1505-1511. |
| [2] | XIAN Ouyang, LI Xiao, CHEN Yongcheng, WANG Ting, WANG Xuze, ZHANG Fanfan, MA Chunhui. Effects of molasses and Lactobacillus plantarum on silage quality,microbial quantity and rumen degradation rate of hop branches and leaves [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(3): 719-726. |
| [3] |
XU Pengfei, WANG Xuzhe, YANG Hanjun, HUANG Xingyu, FU Dongqing, |
| [4] | WANG Ting, ZHANG Fanfan, HUANG Hua, YANG Guangwei, CHENG Weiguo, ZHANG Li, MA Chunhui. Evaluation of the Whole-Plant Corn Silage Quality of Large-Scale Pastures Based on Fuzzy Similarity Priority Ratio Method [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(1): 215-225. |
| [5] | Lei SONG, Yanchao WANG, Fanfan ZHANG, Xuzhe WANG, Jian ZHANG, Chunhui MA. Study on the Quality of Oat Silage in Different Harvest Periods [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(10): 1938-1946. |
| [6] | Zaoreguli Reheman, Yeerlan Duishanbieke, WAN Jiang-chun, Aibibula Yimamu. Effects of Defect Fragrant Pear Juice Residue on Fermentation Quality of Alfalfa Silage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(6): 1136-1141. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 40
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 212
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||