

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (5): 1203-1215.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.05.020
• Plant Protection·Microbes·Storage and Preservation Processing • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Yujie1( ), ZHAN Faqiang1,2(
), ZHAN Faqiang1,2( ), CHEN Cheng1, BAO Huifang2, YANG Rong2, WANG Ning2, HOU Xinqiang2, HOU Min2, SHI Yingwu2, LONG Xuanqi1,2(
), CHEN Cheng1, BAO Huifang2, YANG Rong2, WANG Ning2, HOU Xinqiang2, HOU Min2, SHI Yingwu2, LONG Xuanqi1,2( )
)
Received:2021-11-30
Online:2022-05-20
Published:2022-06-09
Correspondence author:
ZHAN Faqiang, LONG Xuanqi
Supported by:
高宇洁1( ), 詹发强1,2(
), 詹发强1,2( ), 陈澄1, 包慧芳2, 杨蓉2, 王宁2, 侯新强2, 侯敏2, 史应武2, 龙宣杞1,2(
), 陈澄1, 包慧芳2, 杨蓉2, 王宁2, 侯新强2, 侯敏2, 史应武2, 龙宣杞1,2( )
)
通讯作者:
詹发强,龙宣杞
作者简介:高宇洁(1997-),女,河北石家庄人,硕士研究生,研究方向为食品工程(E-mail) 631353539@qq.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
GAO Yujie, ZHAN Faqiang, CHEN Cheng, BAO Huifang, YANG Rong, WANG Ning, HOU Xinqiang, HOU Min, SHI Yingwu, LONG Xuanqi. Screening, identification and optimization of fermentation conditions of antagonistic Xenorhabdus bovienii 445 against Aspergillus niger[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(5): 1203-1215.
高宇洁, 詹发强, 陈澄, 包慧芳, 杨蓉, 王宁, 侯新强, 侯敏, 史应武, 龙宣杞. 黑曲霉拮抗菌Xenorhabdus bovienii445筛选、鉴定及发酵优化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1203-1215.
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 种 Species |
|---|---|
| B5 | Photorhabdus luminescens B5 |
| 445 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 445 |
| NLKSD 3-1 | Photorhabdus temperata NLKSD 3-1 |
| YC | Xenorhabdus bovienii YC |
| ALL | Xenorhabdus nematophila ALL |
| sf-scp | Xenorhabdus bovienii SCP |
| sf-ZMCH | Xenorhabdus bovienii sf-ZMCH |
| Turkey 40-4 | Xenorhabdus bovienii Turkey40-4 |
| B4-3 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B4-3 |
| 482 | Photorhabdus laumondii 482 |
| B4-2 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B4-2 |
| sf-ZMBHW | Xenorhabdus bovienii ZMBHW |
| B30 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B30 |
| B13 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B13 |
| 422 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 422 |
| B24 | Xenorhabdusbovienii B24 |
| 421 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 421 |
| B4-1 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B4-1 |
| 757 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 757 |
| sf-ZMHYL | Xenorhabdu bovienii ZMHYL |
Table 1 Test strains of Entomopathogenic nematode symbiotic bacteria
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 种 Species |
|---|---|
| B5 | Photorhabdus luminescens B5 |
| 445 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 445 |
| NLKSD 3-1 | Photorhabdus temperata NLKSD 3-1 |
| YC | Xenorhabdus bovienii YC |
| ALL | Xenorhabdus nematophila ALL |
| sf-scp | Xenorhabdus bovienii SCP |
| sf-ZMCH | Xenorhabdus bovienii sf-ZMCH |
| Turkey 40-4 | Xenorhabdus bovienii Turkey40-4 |
| B4-3 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B4-3 |
| 482 | Photorhabdus laumondii 482 |
| B4-2 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B4-2 |
| sf-ZMBHW | Xenorhabdus bovienii ZMBHW |
| B30 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B30 |
| B13 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B13 |
| 422 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 422 |
| B24 | Xenorhabdusbovienii B24 |
| 421 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 421 |
| B4-1 | Xenorhabdus bovienii B4-1 |
| 757 | Xenorhabdus bovienii 757 |
| sf-ZMHYL | Xenorhabdu bovienii ZMHYL |
| 因素 Design | 水平Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 接种量A Lnoculation Amocont (%) | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 |
| pH B | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.5 |
| 装液量C Liquid loading (mL) | 90 | 100 | 110 |
Table 2 Factors and levels of Box-Behnken design
| 因素 Design | 水平Levels | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | |
| 接种量A Lnoculation Amocont (%) | 2.5 | 3 | 3.5 |
| pH B | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.5 |
| 装液量C Liquid loading (mL) | 90 | 100 | 110 |
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 抑制率 Inhibition rate(%) |
|---|---|
| B5 | 65.00±1.47a |
| 445 | 64.92±2.05a |
| NLKSD 3-1 | 64.30±1.95ab |
| YC | 63.58±0.50abc |
| ALL | 62.86±2.98abcd |
| sf-scp | 62.25±1.67abcd |
| sf-ZMCH | 61.86±1.58bcd |
| Turkey 40-4 | 61.75±1.36bcd |
| B4-3 | 61.50±3.53bcde |
| 482 | 61.44±0.55bcde |
| B4-2 | 61.35±3.20bcde |
| sf-ZMBHW | 61.12±1.20cde |
| B30 | 61.02±0.94cde |
| B13 | 60.96±1.74cde |
| 422 | 60.95±1.80cde |
| B24 | 60.68±1.67cde |
| 421 | 60.20±1.02de |
| B4-1 | 60.00±1.38de |
| 757 | 59.84±1.26de |
| sf-ZMHYL | 58.49±1.55e |
Table 3 Inhibition rate of Aspergillus niger by different symbiotic strains
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 抑制率 Inhibition rate(%) |
|---|---|
| B5 | 65.00±1.47a |
| 445 | 64.92±2.05a |
| NLKSD 3-1 | 64.30±1.95ab |
| YC | 63.58±0.50abc |
| ALL | 62.86±2.98abcd |
| sf-scp | 62.25±1.67abcd |
| sf-ZMCH | 61.86±1.58bcd |
| Turkey 40-4 | 61.75±1.36bcd |
| B4-3 | 61.50±3.53bcde |
| 482 | 61.44±0.55bcde |
| B4-2 | 61.35±3.20bcde |
| sf-ZMBHW | 61.12±1.20cde |
| B30 | 61.02±0.94cde |
| B13 | 60.96±1.74cde |
| 422 | 60.95±1.80cde |
| B24 | 60.68±1.67cde |
| 421 | 60.20±1.02de |
| B4-1 | 60.00±1.38de |
| 757 | 59.84±1.26de |
| sf-ZMHYL | 58.49±1.55e |
| 菌株 Strain No. | 抑菌圈直径 Inhibition zone diameter (mm) | 抑菌效价 Anti-bacterial potency(cm/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 445 | 23.72±0.61a | 7.61 |
| YC | 23.33±0.50b | 7.41 |
| B5 | 20.42±0.46c | 5.96 |
| NLKSD3-1 | 13.96±0.59d | 2.73 |
| sf-scp | 13.20±0.51e | 2.35 |
| ALL | 0 | - |
Table 4 The inhibitory effect of different symbiotic strains on Aspergillus niger
| 菌株 Strain No. | 抑菌圈直径 Inhibition zone diameter (mm) | 抑菌效价 Anti-bacterial potency(cm/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 445 | 23.72±0.61a | 7.61 |
| YC | 23.33±0.50b | 7.41 |
| B5 | 20.42±0.46c | 5.96 |
| NLKSD3-1 | 13.96±0.59d | 2.73 |
| sf-scp | 13.20±0.51e | 2.35 |
| ALL | 0 | - |
| 生理生化试验 Physiological and biochemical test | 结果 Results |
|---|---|
| 革兰氏染色 | - |
| 葡萄糖氧化发酵试验 | 发酵型 |
| V-P 试验 | - |
| 甲基红试验 | - |
| 耐盐性试验 | 2% |
| 油脂水解试验 | + |
| 淀粉水解试验 | - |
| 硫化氢产生试验 | - |
| 接触酶试验 | - |
| 明胶液化试验 | - |
| 葡萄糖酸盐氧化试验 | + |
| 脲酶试验 | - |
| 蔗糖发酵试验 | - |
| 脂酶试验 | - |
| 乳糖发酵试验 | + |
| 甘露醇发酵试验 | - |
Table 5 Main physiological and biochemical test of Xenorhabdus bovienii 445
| 生理生化试验 Physiological and biochemical test | 结果 Results |
|---|---|
| 革兰氏染色 | - |
| 葡萄糖氧化发酵试验 | 发酵型 |
| V-P 试验 | - |
| 甲基红试验 | - |
| 耐盐性试验 | 2% |
| 油脂水解试验 | + |
| 淀粉水解试验 | - |
| 硫化氢产生试验 | - |
| 接触酶试验 | - |
| 明胶液化试验 | - |
| 葡萄糖酸盐氧化试验 | + |
| 脲酶试验 | - |
| 蔗糖发酵试验 | - |
| 脂酶试验 | - |
| 乳糖发酵试验 | + |
| 甘露醇发酵试验 | - |
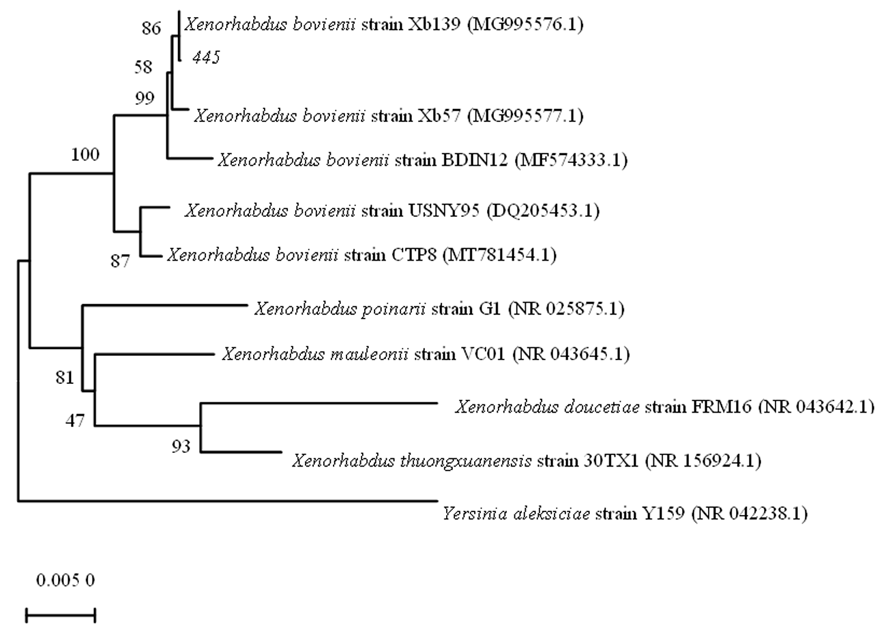
Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree of strain 445 based on 16S rRNA genesequence Note: Numbers at branch nodes present bootstrap value; The GeneBank accession number of aligned sequences are shown in the brackets; Bar: Nucleotide divergence
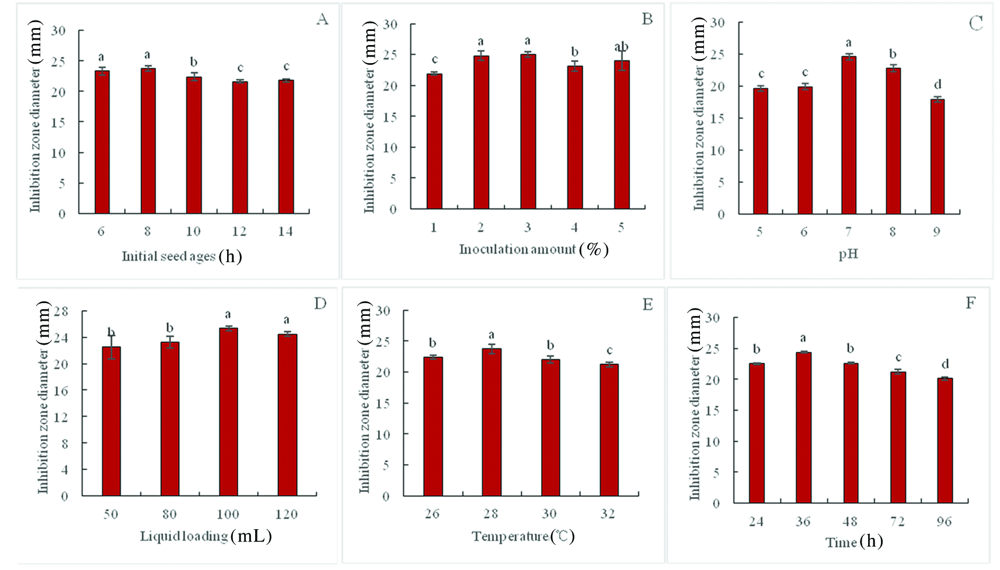
Fig.6 Effects of different initial seed ages (A),inoculum concentration (B), pH (C), liquid loading (D), time (E), and temperature (F) on the inhibitory activity of Xenorhabdus bovienii 445
| 试验编码 Experi mental coding | 编码水平 Encoding level | 抑菌圈直径 Bacteriostatic sphere diameter (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| 1 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 24.46 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 25.44 |
| 3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 25.06 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 25.78 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.79 |
| 6 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 24.30 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 26.23 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.23 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.46 |
| 10 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 23.12 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.31 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.44 |
| 13 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 25.31 |
| 14 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 23.65 |
| 15 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 24.44 |
| 16 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 24.57 |
| 17 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 25.38 |
Table 6 Effect of different test sites on the antibacterial activity of strain 445
| 试验编码 Experi mental coding | 编码水平 Encoding level | 抑菌圈直径 Bacteriostatic sphere diameter (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | C | ||
| 1 | -1 | 1 | 0 | 24.46 |
| 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 25.44 |
| 3 | -1 | 0 | 1 | 25.06 |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 25.78 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.79 |
| 6 | 1 | -1 | 0 | 24.30 |
| 7 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 26.23 |
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 28.23 |
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.46 |
| 10 | 0 | -1 | 1 | 23.12 |
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.31 |
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27.44 |
| 13 | 0 | -1 | -1 | 25.31 |
| 14 | -1 | 0 | -1 | 23.65 |
| 15 | -1 | -1 | 0 | 24.44 |
| 16 | 1 | 0 | -1 | 24.57 |
| 17 | 0 | 1 | -1 | 25.38 |
| 方差来源 Source of variance | 平方和 Quadratic sum | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | P值 P value | 显著性 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 34.96 | 9 | 3.88 | 10.03 | 0.003 | ** |
| A-接种量 | 1.07 | 1 | 1.07 | 2.77 | 0.14 | |
| B- PH | 2.74 | 1 | 2.74 | 7.07 | 0.032 5 | * |
| C-装液量 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.077 | 0.788 8 | |
| AB | 0.91 | 1 | 0.91 | 2.35 | 0.168 8 | |
| AC | 0.07 | 1 | 0.073 | 0.19 | 0.677 5 | |
| BC | 1.68 | 1 | 1.68 | 4.33 | 0.076 | |
| A2 | 9.51 | 1 | 9.51 | 24.55 | 0.001 6 | ** |
| B2 | 6.96 | 1 | 6.96 | 17.96 | 0.003 9 | ** |
| C2 | 9.01 | 1 | 9.01 | 23.26 | 0.001 9 | ** |
| 剩余 | 2.71 | 7 | 0.39 | |||
| 失拟项 | 2.16 | 3 | 0.72 | 5.22 | 0.072 1 | |
| 纯误差 | 0.55 | 4 | 0.14 | |||
| 总离差 | 37.68 | 16 | ||||
| R2=0.928 0 | ||||||
Table 7 Significance of the variance in the quadratic regression model
| 方差来源 Source of variance | 平方和 Quadratic sum | 自由度 Degree of freedom | 均方 Mean square | F值 F value | P值 P value | 显著性 Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 模型 | 34.96 | 9 | 3.88 | 10.03 | 0.003 | ** |
| A-接种量 | 1.07 | 1 | 1.07 | 2.77 | 0.14 | |
| B- PH | 2.74 | 1 | 2.74 | 7.07 | 0.032 5 | * |
| C-装液量 | 0.03 | 1 | 0.03 | 0.077 | 0.788 8 | |
| AB | 0.91 | 1 | 0.91 | 2.35 | 0.168 8 | |
| AC | 0.07 | 1 | 0.073 | 0.19 | 0.677 5 | |
| BC | 1.68 | 1 | 1.68 | 4.33 | 0.076 | |
| A2 | 9.51 | 1 | 9.51 | 24.55 | 0.001 6 | ** |
| B2 | 6.96 | 1 | 6.96 | 17.96 | 0.003 9 | ** |
| C2 | 9.01 | 1 | 9.01 | 23.26 | 0.001 9 | ** |
| 剩余 | 2.71 | 7 | 0.39 | |||
| 失拟项 | 2.16 | 3 | 0.72 | 5.22 | 0.072 1 | |
| 纯误差 | 0.55 | 4 | 0.14 | |||
| 总离差 | 37.68 | 16 | ||||
| R2=0.928 0 | ||||||

Fig.8 Comparison of the antibacterial activity before and after the optimization Note: A and B are the optimized antibacterial effect; C and D are the antibacterial effect before optimization
| 时间 Time (d) | Incidence(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 处理组 | CK | |
| 3 | 0.00 | 6.00 |
| 4 | 32.00 | 54.00 |
| 5 | 42.00 | 62.00 |
| 6 | 75.00 | 76.00 |
| 7 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
Table 8 Incidence rate of treatment group and control group within 3-7 days
| 时间 Time (d) | Incidence(%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 处理组 | CK | |
| 3 | 0.00 | 6.00 |
| 4 | 32.00 | 54.00 |
| 5 | 42.00 | 62.00 |
| 6 | 75.00 | 76.00 |
| 7 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| Time (d) | CK | 处理组 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion diameter (mm) | Lesion diameter (mm) | Control effect (%) | |
| 3 | 7.19±0.10a | 0.00 | - |
| 4 | 7.61±0.32a | 6.01±0.40a | 61.30 |
| 5 | 8.80±0.03a | 6.93±0.45b | 49.21 |
| 6 | 10.89±0.99a | 8.65±0.48b | 38.03 |
| 7 | 12.57±0.29a | 10.47±0.0 | 27.74 |
Table 9 The inhibitory effect of Xenorhabdus bovienii 445 on Aspergillus niger within 3-7 days
| Time (d) | CK | 处理组 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lesion diameter (mm) | Lesion diameter (mm) | Control effect (%) | |
| 3 | 7.19±0.10a | 0.00 | - |
| 4 | 7.61±0.32a | 6.01±0.40a | 61.30 |
| 5 | 8.80±0.03a | 6.93±0.45b | 49.21 |
| 6 | 10.89±0.99a | 8.65±0.48b | 38.03 |
| 7 | 12.57±0.29a | 10.47±0.0 | 27.74 |
| [1] | 李小红, 李运景, 马晓青, 等. 我国葡萄产业发展现状与展望[J]. 中国南方果树, 2021,(5):161-166. |
| Li X H, Li Y J, Ma X Q, et al. Current situation and prospect of grape industry development in China[J]. Southern China Fruit Tree, 2021, (5): 161-166. | |
| [2] | 李丽梅, 刘霞, 李喜宏, 等. 常温下黑曲霉对刺伤红提葡萄的致病规律研究及拮抗菌筛选[J]. 食品研究与开发, 2020,(15):35-39. |
| Li L M, Liu X, Li X H, et al. Study on the wound pathogenicity of aspergillus niger and its antagonistic bacteria screening of postharvest red globe grapes at room temperature[J]. Food Research and Development, 2020, (15): 35-39. | |
| [3] | 李宁. 葡萄采后致腐菌检测及真菌源激发子诱导抗病研究[D]. 杨陵: 西北农林科技大学, 2005. |
| Li N. Study on detection of rot pathogen on post-harvest grapes and induced resistance by elicitor from fungal[D]. Yang Ling: Northwest A & Forestry University, 2005 | |
| [4] | 宋开艳, 阿米尼古丽·再那吉, 冯宏祖, 等. 南疆葡萄采后致病菌分离鉴定及拮抗菌的筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2011(5): 871-876. |
| Song K Y, Amigiguli then Naji, Feng H Z, et al. Separation and identification of pathogens and screening of antagonistic microorganisms against postharvest grapes[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Science, 2011 (5): 871-876. | |
| [5] | 王立霞, 杨秀芬, 简恒, 等. 昆虫病原线虫共生细菌的代谢产物[J]. 微生物学报, 2001, (6): 753-756. |
| Wang L X, Yang X F, Jian H, et al. Metabolites of symbiotic bacteria of the entomogenic insect pathogen nematodes[J]. Microbiology Journal, 2001, (6): 753-756. | |
| [6] | 米亚辉, 张晓蕾, 仲鑫, 等. 葡萄保鲜技术理论及其应用研究进展[J]. 现代园艺, 2015(24):42-43. |
| Mi Y H, Zhang X L, Zhong X, et al. Progress in grape preservation technology[J]. Modern gardening, 2015 (24): 42-43. | |
| [7] | 马丽丽, 许艳丽, 台莲梅. 昆虫病原线虫共生细菌对植物病原菌的抑制作用[J]. 植物保护, 2007, 33(4):7-10. |
| Ma L L, Xu Y L, Tai L M. Antimirobial activity of the symbiotic bactria of entomopathgenic nematode against plant pathogens[J]. Plant Protection, 2007, 33 (4): 7-10. | |
| [8] | 刘霞, 李骞, 许贤, 等. 昆虫病原线虫共生菌YL001细胞内代谢产物抑菌作用研究初报[J]. 农药学学报, 2006, 8(1):95-98. |
| Liu X, Li Q, Xu X, et al. Study on the Antifungal Activity of Intracllular Secondary Metabolic Products from Xenorhabdus nematophilus[J]. Pesticide Journal, 2006, 8 (1): 95-98. | |
| [9] | 张园, 南宫自艳, 王勤英, 等. 嗜线虫致病杆菌HB310对五种苹果病原菌抑菌活性的影响[J]. 北方园艺, 2012(20):123-126. |
| Zhang Y, Nangong Z Y, Wang Q Y, et al. Study on Antimicrobial Activity of Symbiotic Bacteria of Xenorhabdus nematophila HB310 Against Five Apple Pathogens[J]. Northern gardening, 2012 (20): 123-126. | |
| [10] | Fang X, Zhang M, Tang Q, et al. Inhibitory effect of Xenorhabdus nematophila TB on plant pathogens Phytophthora capsici and Botrytis cinerea in vitro and in planta[J]. 2014, 4(4): 324-330 |
| [11] | 俞晗. 致病杆菌Xenorhabdus bovienii SN84次生代谢产物对三种植物病原真菌抑菌作用的研究[D]. 沈阳农业大学, 2017. |
| Yu H. The bacteriostasis of secondary metabolites of pathogenic Xenorhabdus bovienii SN84 on three kinds of plant pathogenic fungus[D]. Shenyang Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [12] |
PARAFATI L, VITALE A, RESTUCCIA C, et al. Biocontrol ability and action mechanism of food-isolated yeast strains against Botrytis cinerea causing postharvest bunch rot of table grape[J]Food Microbiology, 2015, 47:85-92.
DOI URL |
| [13] | 蒋凯丽, 周新丽, 高海燕. 一株具有拮抗作用的解淀粉芽孢杆菌的筛选、鉴定及生物学特性研究[J]. 工业微生物, 2020, 50(1):8-13. |
| Jiang K L, Zhou X L, Gao H Y. Screening, identification and biological characteristics of an antagonistic Bacillus Amyloliquefaciens[J]. Industrial Microbiology, 2020, 50 (1): 8-13. | |
| [14] | 魏雪, 江孟遥, 钟涛, 等. 荧光假单胞菌ZX对葡萄采后灰霉病的防治[J]. 食品工业科技, 2021, 42(22):125-132. |
| Wei X, Jiang M Y, Zhong T, et al. Control of Gray Mold in Postharvest Grapes with Pseudomonas fluorescens ZX[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(22): 125-132. | |
| [15] | 方响. 高原乳酸菌对采后水果生物保鲜效果研究及其微生物学机制初探[D]. 兰州大学, 2020. |
| Fang X. Study on the effect of lactic acid bacteria from Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau on the biopreservation of postharvest fruits and preliminary exploration of its microbiological mechanism[D]. Lanzhou University, 2020. | |
| [16] | 东秀珠, 蔡妙英. 常见细菌系统鉴定手册[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001: 349-387. |
| Dong X Z, Cai M Y. Manual for systematic identifica-tion of common bacteria[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001: 349-387. | |
| [17] |
Ullah I, Khan A L, Ali L, Khan A R, Waqas M, Lee I J, Shin J H.2014. An insecticidal compound produced by an insect-pathogenic bacterium suppresses host defenses through phenoloxidase inhibition. Molecules, 19(12): 20913-20928.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Kumar S N, Nambisan B.2014. Antifungal activity of diketopiperazines and stilbenes against plant pathogenic fungi in vitro. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology, 172(2): 741-754.
DOI URL |
| [19] | 张潘杰, 窦振国, 王浩, 等. 9株昆虫病原线虫共生菌菌株的分离、鉴定及其抗菌谱的筛选[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2021, 44(3): 487-496. |
| Zhang P J, Dou Z G, Wang H, et al. Isolation, identification and screening of antifungal spectrum of nine entomopathogenic nematode symbiotic bacterial strains[J], Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021, 44 (3): 487-496. | |
| [20] | 窦振国, 邵子腾, 张潘杰, 等. 伯氏致病杆菌NN6胞外总蛋白抑制植物病原真菌的生防潜力[J/OL]. 中国生物防治学报. |
| Dou Z G, Shao Z T, Zhang P J, et al. The extracellular total protein of B. NN6 suppresses the biodefense potential of plant pathogenic fungi [J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Biological Control:1-11 | |
| [21] |
Julie G,. Chacón Orozco, César Jr.Bueno, David I,. Shapiro Ilan, et al. Antifungal activity of Xenorhabdus spp. and Photorhabdus spp. against the soybean pathogenic Sclerotinia sclerotiorum[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1):20649.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | Li Bo, Kong Lingxiao, Qiu Dewen, et al. Biocontrol potential and mode of action of entomopathogenic bacteria Xenorhabdus budapestensis C72 against Bipolaris maydis[J]. Biological Control, 2021,158,104605. |
| [23] | 曹林青, 詹发强, 高宇洁, 等. 嗜线虫致病杆菌抑制灰葡萄孢的效应[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(11):4123-4133. |
| Cao L Q, Zhan F Q, Gao Y J, et al. The inhibitory effect of Xenorhabdus nematophilus on Botrytis cinerea[J]. Microbiology Bulletin, 2021, 48 (11): 4123-4133. | |
| [24] | 张梦君, 黎继烈, 申爱荣, 等. 亚麻立枯病拮抗菌的筛选、生防效果及发酵条件优化[J]. 微生物学通报, 2017, 44(5):1099-1107. |
| Zhang M J, Li J L, Shen A R, et al. Screening, biocontrol effect and optimization of fermentation conditions of an antagonistic bacteria against Flax[J]. Microbiology China, 2017, 44(5):1099-1107. | |
| [25] |
Marcosa B, Ricardo E, Eliane P, et al. Response surface methodology(RSM) as a tool for optimization in analytical chemistry[J]. Talanta, 2008, 76(5):965-977.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Wang Yonghong, Fang Xiangling, An Fengqiu, et al. Improvement of antibiotic activity of Xenorhabdus bovienii by medium optimization using response surface methodology[J]. Microbial Cell Factories, 2011, 10(1):98.
DOI URL |
| [27] | 王永娟, 张杰, 孔繁芳, 等. 嗜线虫致病杆菌HB310培养基筛选和培养条件优化[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2014, 36(6):997-1003. |
| Wang Y J, Zhang J, Kong F F, et al. Screening of original medium and optimizing fermentation conditions of Xenorhabdus nematophila HB310[J]. Environmental Entomology, 2014, 36 (6): 997-1003. | |
| [28] | 张磊, 魏佳, 张政, 等. 硫化氢(H2S)熏蒸对葡萄损伤接种黑曲霉的抑制及其采后品质的影响[J]. 现代食品科技, 2018, 34(7): 89-96. |
| Zhang L, Wei J, Zhang Z, et al. HEffect of Gaseous H2S Fumigation on Aspergillusnige Inhibition and Postharvest Quality of Table Grape[J]Modern Food Technology, 2018, 34 (7): 89-96. |
| [1] | AN Zhe, NIU Ruichang, ZHU Xiangzhen, WANG Li, ZHANG Kaixin, LI Dongyang, JI Jichao, NIU Lin, GAO Xueke, LUO Junyu, CUI Jinjie, MA Deying. Analyze the microbial diversity of cotton aphids with different bacterial types in cotton fields [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(9): 2277-2284. |
| [2] | CHEN Cheng, HOU Xinqiang, ZHAN Faqiang, YANG Rong, BAO Huifang, WANG Ning, SHI Yingwu, LONG Xuanqi. Study on abiotic stress tolerance of three entomopathogenic nematodes and its bacteriostasis of symbiotic bacteria [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(12): 3072-3079. |
| [3] | LI Hui, LIU Baojun, WU Qiong, GUO Qingyuan. Effect Evaluation of Control Red Rot and Damping off with Three Bio-control Agents on Cotton [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(4): 694-704. |
| [4] | DU Pengcheng , LIU Haiyang, ZHANG Jungao, LI Jin, ZHOU Xiaoyun, LIU Mengli, LEI Bin, GUO Qingyuan. Screening and Identification of Biocontrol Bacteria against Cotton Root Rot Diseases at Seedling Stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(4): 686-693. |
| [5] | ZHAN Faqiang, HOU Min, YANG Rong, WANG Ning, BAO Huifang, HOU Xinqiang, CUI Weidong, LONG Xuanqi. Research on Steinernema litorale from Populus euphratica Forest in Xinjiang by Identification and Biological Characteristics [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(3): 536-544. |
| [6] | DING Jian-peng, FAN Ying-ge, YAO Yong-sheng. Identification and Control Effect on Cotton Fusarium wilt of Biocontrol Bacteria HFW217 [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(3): 498-508. |
| [7] | CHU Min, GU Mei-Ying, TANG Qi-yong, ZHU Jing, HAO Xiu-ying, ZHANG Zhi-dong. Identification of Pathogenic Fungi Causing the Root Rot Disease of Dabancheng Faba Bean and Analysis of Antagonistic Effect by the Biocontrol Bacteria [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(10): 1904-1911. |
| [8] | LUO Yan-liang, LI Xue-ling, LI Hui, XIE Xin, LIU Yong-jian, WANG Pei-ling, LU Yan-hui. Effects of Sophora Strips on the Population Occurrence of Predators in Cotton Fields [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(1): 74-83. |
| [9] | GUO Kai, HOU Min, BAO Hui-fang, WANG Ning, ZHAN Fa-qiang, YANG Rong, YANG Wen-qi, LONG Xuan-qi, CUI Wei-dong. Study on Optimizing Liquid Fermentation Conditions of Aspergillus niger and Its Degradation Effect on Cotton Stalk with Double Indexes [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(11): 2122-2133. |
| [10] | LIN Si-yu;CAO Wen-qiu;WANG Yu-qing;HU Hong-ying. Primary Investigation and Study of Chalcidoid Wasps Resources in Xinjiang Manas National Wetland Park Where Cicadella viridis Breaks Out [J]. , 2016, 53(10): 1850-1857. |
| [11] | Buka·Ouerna;ZHAN Fa-qiang;LONG Xuan-qi;LUO Ming;HOU Min;YANG Rong. Mass Production Technology for Heterorhabditis NLK-1 [J]. , 2015, 52(9): 1693-1699. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 70
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 236
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||