

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2021, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (12): 2265-2273.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2021.12.014
• Plant Protection· Horticultural Special Local Products· Soil Fertilizer· Water Saving Irrigation Agroecological Environment· Agricultural Equipment Engineering and Mechanization • Previous Articles Next Articles
LING Yueming, LI Meihua, YANG Yong, YANG Wenli, FAN Rong, YI Hongping, ZHANG Hong, ZHANG Xuejun
Received:2021-01-30
Online:2021-12-20
Published:2021-12-31
Supported by:凌悦铭, 李寐华, 杨永, 杨文莉, 范蓉, 伊鸿平, 张红, 张学军
基金资助:CLC Number:
LING Yueming, LI Meihua, YANG Yong, YANG Wenli, FAN Rong, YI Hongping, ZHANG Hong, ZHANG Xuejun. Development of InDel Marker for Melon Resistance to Downy Mildew Based on BSA Resequencing[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(12): 2265-2273.
凌悦铭, 李寐华, 杨永, 杨文莉, 范蓉, 伊鸿平, 张红, 张学军. 基于BSA-Seq技术的甜瓜抗霜霉病InDel标记开发[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2265-2273.
| 样本名 Sample | 原始数据量 Raw Base (bp) | 有效数据量 Clean Base (bp) | 碱基错误率 Error Rate(%) | Q20(%) | Q30(%) | GC含量 GC Content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM-4 | 5 230 484 100 | 5 205 287 100 | 0.01 | 97.74 | 94.94 | 37.39 |
| DM-2 | 5 954 570 100 | 5 926 054 500 | 0.01 | 97.83 | 95.10 | 37.23 |
| DM-R | 9 302 519 100 | 9 266 289 000 | 0.01 | 97.93 | 95.27 | 37.17 |
| DM-S | 9 931 454 700 | 9 878 084 400 | 0.01 | 97.81 | 95.08 | 37.12 |
Table 1 The quality of sequencing data
| 样本名 Sample | 原始数据量 Raw Base (bp) | 有效数据量 Clean Base (bp) | 碱基错误率 Error Rate(%) | Q20(%) | Q30(%) | GC含量 GC Content(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM-4 | 5 230 484 100 | 5 205 287 100 | 0.01 | 97.74 | 94.94 | 37.39 |
| DM-2 | 5 954 570 100 | 5 926 054 500 | 0.01 | 97.83 | 95.10 | 37.23 |
| DM-R | 9 302 519 100 | 9 266 289 000 | 0.01 | 97.93 | 95.27 | 37.17 |
| DM-S | 9 931 454 700 | 9 878 084 400 | 0.01 | 97.81 | 95.08 | 37.12 |
| 样本名 Sample | 比对序列数 Mapped reads | 有效序列数 Total reads | 比对率 Mapping rate(%) | 平均测序深度 Average depth(X) | 1X覆盖度 Coverage at least 1X(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM-2 | 36 714 906 | 39 507 030 | 92.93 | 13.11 | 96.38 |
| DM-4 | 32 024 597 | 34 701 914 | 92.28 | 11.57 | 96.37 |
| DM-S | 61 510 228 | 65 853 896 | 93.40 | 21.29 | 97.75 |
| DM-R | 57 254 273 | 61 775 260 | 92.68 | 19.85 | 97.70 |
Table 2 Sequencing depth and coverage
| 样本名 Sample | 比对序列数 Mapped reads | 有效序列数 Total reads | 比对率 Mapping rate(%) | 平均测序深度 Average depth(X) | 1X覆盖度 Coverage at least 1X(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM-2 | 36 714 906 | 39 507 030 | 92.93 | 13.11 | 96.38 |
| DM-4 | 32 024 597 | 34 701 914 | 92.28 | 11.57 | 96.37 |
| DM-S | 61 510 228 | 65 853 896 | 93.40 | 21.29 | 97.75 |
| DM-R | 57 254 273 | 61 775 260 | 92.68 | 19.85 | 97.70 |
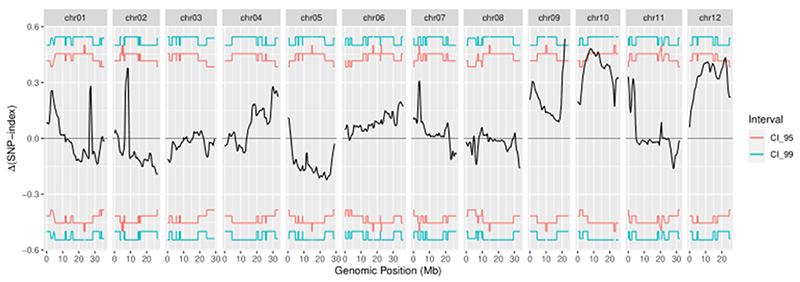
Fig. 2 Distribution curve of Δ( SNP-Index ) Note: Orange curve represents the confidence threshold line of 0.95, and green curve represents the confidence threshold line of 0.99
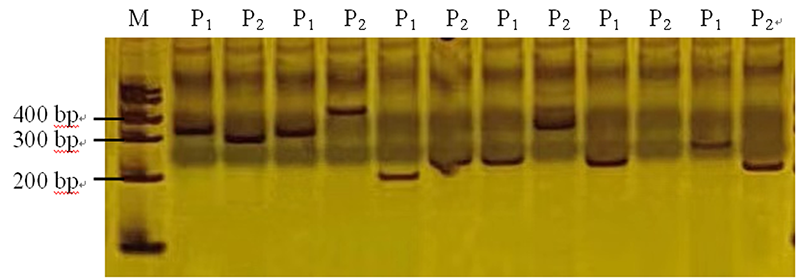
Fig. 3 Polymorphism detected by InDel primers among F2 individual plants Note: M:Marker I; P1: PCR amplification in DM-4; P2: PCR amplification in DM-2
| 名称 Name | 正向引物序列5’- 3’ Forward primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 反向引物5’- 3’ Reverse primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 是否具有多态性 Polymorphism or not |
|---|---|---|---|
| InDel 1 | AGGTAAAGCCCCAGAGAGGA | CCTCCCGTGAAGTTTGGAGT | 否 |
| InDel 2 | AGTGAATGTGGTCATTGTGCT | CCTCCCGTGAAGTTTGGAGT | 是 |
| InDel 3 | ACACAGCACAACCCAGACAA | CTACGACCAACCCCCACATG | 是 |
| InDel 4 | GCACTCTCCAGCCTTGAACT | GAGCAAAGGTACCGCTGTCT | 是 |
| InDel 5 | TTTTCATTCGGATTCCTTGTTGT | AAGCTATGAGACCTACGCGC | 否 |
| InDel 6 | TCAAAGTGACCCCATCCAGTG | TGTTTTGAGTTCAACGGGGGA | 否 |
| InDel 7 | GTGACCCACGATAGGTACACC | TCAAGTTTGGGAGATTGGATCA | 否 |
| InDel 8 | AGCATTCTCCCAGTTTCCCC | TGGGAACAAGAAAGTCAGGCA | 否 |
| InDel 9 | ACACAATGAACCAAGATATTTGCCA | TGTTTGTAAGCCACTCGACT | 是 |
| InDel 10 | ACGACACTAAATGACAGTCCGT | CCAAAATGGAAACCCATGCCC | 否 |
| InDel 11 | GCAAAGTTGACCCTCTGTTCG | CAGCGTTCTAGGGGTTGGTT | 否 |
| InDel 12 | TGTGAGAATGACAGCCCACA | CACATCTCTCAAGAGGCGGA | 否 |
| InDel 13 | CCTCGCTCTATTTGCATTCACA | TTTATACGCGTACTAGTTCTCTCA | 否 |
| InDel 14 | AAAGTCAGGATGGCCGAGTG | TCTCTTTCATCAGCGGCGTT | 是 |
| InDel 15 | TCACAGCTCACAATCACAGGT | AGGGGAAGCTGGAGAAGACA | 是 |
| InDel 16 | ACCTGCCGTCTATCGTGTTT | TGAGGTCGGTCCAAACAAGT | 否 |
| InDel 17 | GCTGCCGTTTCGTTTTCAGT | ACGACCAAGAAACCCAGGAA | 否 |
| InDel 18 | CCGTTGATTGCGCTAACACA | TGCCGCACGAGTATTCACTT | 是 |
| InDel 19 | AGGAGTTTGGGTATGACACGAC | TTCTCCCTTTACCCGTTGCC | 是 |
| InDel 20 | TGGGGTTGCTTGTGGATAGT | AGGCGAACACCTTTTGATTCA | 是 |
| InDel 21 | GGAAGAGGAAGAGGCAGAGG | ACGAATCATTTCCTCCTCCGA | 否 |
| InDel 22 | TGCTCTTGAGGCTAGGGCTA | TAGAGAGGTCCGAGCCCATC | 否 |
| InDel 23 | TCATTGGCTAGAACTTCGACCA | CGAAAGTGATGGCCATGGGA | 否 |
| InDel 24 | AGTGGTTGGTGGTGCATAGG | GCAACACTTTGATCCCCACA | 否 |
| InDel 25 | ACCTCCAAGAAATGAATTCAGGA | TGAACGACGACGACCAATCT | 否 |
| InDel 26 | CTTGCAAGGGCTAATGGTGC | ACGAATCAAAGGTGTAGCCA | 否 |
| InDel 27 | ACAGTTTAGCTTCCATCCCTACA | TCGTTTAGGTCATTGTCCTCCA | 否 |
Table 3 The information of InDel primers
| 名称 Name | 正向引物序列5’- 3’ Forward primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 反向引物5’- 3’ Reverse primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 是否具有多态性 Polymorphism or not |
|---|---|---|---|
| InDel 1 | AGGTAAAGCCCCAGAGAGGA | CCTCCCGTGAAGTTTGGAGT | 否 |
| InDel 2 | AGTGAATGTGGTCATTGTGCT | CCTCCCGTGAAGTTTGGAGT | 是 |
| InDel 3 | ACACAGCACAACCCAGACAA | CTACGACCAACCCCCACATG | 是 |
| InDel 4 | GCACTCTCCAGCCTTGAACT | GAGCAAAGGTACCGCTGTCT | 是 |
| InDel 5 | TTTTCATTCGGATTCCTTGTTGT | AAGCTATGAGACCTACGCGC | 否 |
| InDel 6 | TCAAAGTGACCCCATCCAGTG | TGTTTTGAGTTCAACGGGGGA | 否 |
| InDel 7 | GTGACCCACGATAGGTACACC | TCAAGTTTGGGAGATTGGATCA | 否 |
| InDel 8 | AGCATTCTCCCAGTTTCCCC | TGGGAACAAGAAAGTCAGGCA | 否 |
| InDel 9 | ACACAATGAACCAAGATATTTGCCA | TGTTTGTAAGCCACTCGACT | 是 |
| InDel 10 | ACGACACTAAATGACAGTCCGT | CCAAAATGGAAACCCATGCCC | 否 |
| InDel 11 | GCAAAGTTGACCCTCTGTTCG | CAGCGTTCTAGGGGTTGGTT | 否 |
| InDel 12 | TGTGAGAATGACAGCCCACA | CACATCTCTCAAGAGGCGGA | 否 |
| InDel 13 | CCTCGCTCTATTTGCATTCACA | TTTATACGCGTACTAGTTCTCTCA | 否 |
| InDel 14 | AAAGTCAGGATGGCCGAGTG | TCTCTTTCATCAGCGGCGTT | 是 |
| InDel 15 | TCACAGCTCACAATCACAGGT | AGGGGAAGCTGGAGAAGACA | 是 |
| InDel 16 | ACCTGCCGTCTATCGTGTTT | TGAGGTCGGTCCAAACAAGT | 否 |
| InDel 17 | GCTGCCGTTTCGTTTTCAGT | ACGACCAAGAAACCCAGGAA | 否 |
| InDel 18 | CCGTTGATTGCGCTAACACA | TGCCGCACGAGTATTCACTT | 是 |
| InDel 19 | AGGAGTTTGGGTATGACACGAC | TTCTCCCTTTACCCGTTGCC | 是 |
| InDel 20 | TGGGGTTGCTTGTGGATAGT | AGGCGAACACCTTTTGATTCA | 是 |
| InDel 21 | GGAAGAGGAAGAGGCAGAGG | ACGAATCATTTCCTCCTCCGA | 否 |
| InDel 22 | TGCTCTTGAGGCTAGGGCTA | TAGAGAGGTCCGAGCCCATC | 否 |
| InDel 23 | TCATTGGCTAGAACTTCGACCA | CGAAAGTGATGGCCATGGGA | 否 |
| InDel 24 | AGTGGTTGGTGGTGCATAGG | GCAACACTTTGATCCCCACA | 否 |
| InDel 25 | ACCTCCAAGAAATGAATTCAGGA | TGAACGACGACGACCAATCT | 否 |
| InDel 26 | CTTGCAAGGGCTAATGGTGC | ACGAATCAAAGGTGTAGCCA | 否 |
| InDel 27 | ACAGTTTAGCTTCCATCCCTACA | TCGTTTAGGTCATTGTCCTCCA | 否 |
| 名称 Name | 正向引物序列5’- 3’ Forward primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 反向引物5’- 3’ Reverse primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 是否具有多态性 Polymorphism or not |
|---|---|---|---|
| InDel 28 | TCATTGGCCGACACATGTCA | ACTCCAAAACTCCAAACCCCA | 否 |
| InDel 29 | TGGTCCCTAACTAAATTACCCTCA | TCCCATAGCCGCCAACATTT | 否 |
| InDel 30 | CTCAACTGGGTGTCGCTTCT | ATCGCAATGCCCCCAGTTAA | 否 |
| InDel 31 | AACAGAGCTAACTTTGGCGC | TGTGAGAGTTTGGGCTTCCA | 否 |
| InDel 32 | TCGAGCTAAAATGATTGTTGGCA | TCCTTCAAACATAAGGACACTCT | 否 |
| InDel 33 | ACGAAACTCAATACTCGAGTGGA | TCACCACCTCCAATTCTTTGT | 否 |
| InDel 34 | AAAAGCACCCCTCCCTTAGC | CGTACTCTAGACGTGTGCGG | 否 |
| InDel 35 | TCTTTCACCCGTCAACTTAACT | TGTCCCACTTGAGTTGCATT | 否 |
| InDel 36 | TGGTTGGGGAGCAAAATACA | AAACGTCCGTCGAAAATGCC | 否 |
| InDel 37 | CGGCCGAATGGATGCTTTTT | TGCATTCGTTTTGGTTGGCA | 否 |
Table 3 The information of InDel primers
| 名称 Name | 正向引物序列5’- 3’ Forward primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 反向引物5’- 3’ Reverse primers sequence 5’ - 3’ | 是否具有多态性 Polymorphism or not |
|---|---|---|---|
| InDel 28 | TCATTGGCCGACACATGTCA | ACTCCAAAACTCCAAACCCCA | 否 |
| InDel 29 | TGGTCCCTAACTAAATTACCCTCA | TCCCATAGCCGCCAACATTT | 否 |
| InDel 30 | CTCAACTGGGTGTCGCTTCT | ATCGCAATGCCCCCAGTTAA | 否 |
| InDel 31 | AACAGAGCTAACTTTGGCGC | TGTGAGAGTTTGGGCTTCCA | 否 |
| InDel 32 | TCGAGCTAAAATGATTGTTGGCA | TCCTTCAAACATAAGGACACTCT | 否 |
| InDel 33 | ACGAAACTCAATACTCGAGTGGA | TCACCACCTCCAATTCTTTGT | 否 |
| InDel 34 | AAAAGCACCCCTCCCTTAGC | CGTACTCTAGACGTGTGCGG | 否 |
| InDel 35 | TCTTTCACCCGTCAACTTAACT | TGTCCCACTTGAGTTGCATT | 否 |
| InDel 36 | TGGTTGGGGAGCAAAATACA | AAACGTCCGTCGAAAATGCC | 否 |
| InDel 37 | CGGCCGAATGGATGCTTTTT | TGCATTCGTTTTGGTTGGCA | 否 |
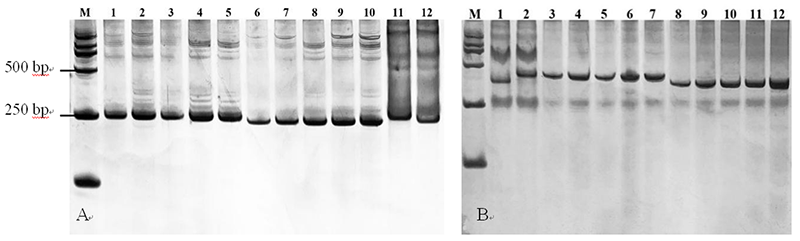
Fig.4 Result of amplification by primers InDel 15, InDel 20 among parents and F2 individual plants Note: Fig.2A: Result of amplification by primers InDel 15. 11: DM-4, 12: DM-2, 1~5: resistant individual, 6~10: susceptible individual. Fig.2B: Result of amplification by primers InDel 20. 2: DM-4, 1: DM-2, 3~7: resistant individual, 8~12: susceptible individual. M: DL2000 DNA Marker
| [1] | 王志丹. 中国甜瓜产业经济发展研究[D]. 中国农业科学院, 2014. |
| WANG Zhidan. Study on the Development of Muskmelon Industry Economy in China[D]. Chinese Beijing: Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2014. | |
| [2] | Wallace E C, D'Arcangelo K N, Quesada-Ocampo L M. Population Analyses Reveal Two Host-Adapted Clades of Pseudoperonospora cubensis, the Causal Agent of Cucurbit Downy Mildew, on Commercial and Wild Cucurbits[J]. Phytopathology, 2020,110(9):1-10. |
| [3] | Ulrich Gisi, Helge Sierotzki. Fungicide modes of action and resistance in downy mildews[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2008,122(1):157-167. |
| [4] | Yigal Cohen, Kyle M,. Van den Langenberg, Todd C. Wehner, et al. Resurgence of Pseudoperonospora cubensis: The Causal Agent of Cucurbit Downy Mildew[J]. Phytopathology, 2015,105(7):998-1012. |
| [5] | 贺玉花, 徐永阳, 徐志红, 等. 甜瓜霜霉病抗性研究进展[J]. 果树学报, 2014,31(2):324-334. |
| HE Yuhua, XU Yongyang, XU Zhihong, et al. Research progress of resistance to downy mildew in melon[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2014,31(2):324-334. | |
| [6] | Takagi H, Tamiru M, Abe A, et al. MutMap accelerates breeding of a salt-tolerant rice cultivar[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2015,33:445-449. |
| [7] | Takagi H, Abe A, Yoshide K, et al. QTL-seq: rapid mapping of quantitative trait loci in rice by whole genome resequencing of DNA from two bulked populations[J]. The Plant Journal, 2013,74:174-183. |
| [8] | Lu H F, Liu T, Jo?l K, et al. QTL-seq identifies an early flowering QTL located near flowering Locus T in cucumber[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2014,127:1491-1499. |
| [9] | Illa-Berenguer E, Houten J V, Huang Z J, et al. Rapid and reliable identification of tomato fruit weight and locule number loci by QTL-seq[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2015,128:1329-1342. |
| [10] | Zhong C, Sun S, Li Y, et al. Next-generation sequencing to identify candidate genes and develop diagnostic markers for a novel Phytophthora resistance gene, RpsHC18, in soybean[J]. Theor Appl Genet, 2018,131:525-538. |
| [11] | 张学军, 郭丽霞, 马新力, 等. 甜瓜种质资源抗霜霉病和蔓枯病苗期筛选与评价[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2014,27(S1):38-40. |
| ZHANG Xuejun, GUO Lixia, MA Xinli, et al. Screening and evaluation of melon germplasm resources against downy mildew and vine blight at seedling stage[J]. China Cucurbits and Vegetables, 2014,27(S1):38-40. | |
| [12] | Criswell A D, Wehner T C, Klosinska U, et al. Use of sporulation and other leaf and vine traits for evaluation of resistance to downy mildew in cucumber. In: Pitrat M (ed)[C]. Proceedings of the IXth EUCARPIA meeting on genetics and breeding of Cucurbitaceae, INRA, Avignon, France, 2008, 433-440. |
| [13] | Épinat C,. and Pitrat M. Inheritance of resistance to downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora cubensis) in muskmelon (Cucumis melo). I. Analysis of a 8 x 8 diallel table[J]. Agronomie, 1994,14(4):239-248. |
| [14] | Épinat C,. and Pitrat M. Inheritance of resistance to downy mildew (Pseudoperonospora cubensis) in muskmelon (Cucumis melo). II. Generation means analysis of 5 genitors[J]. Agronomie, 1994,14(4):249-257. |
| [15] | Heng Li, and Richard Durbin. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009,25(14):1754-1760. |
| [16] | Lebeda A, Stepankova J, Krskova M, et al. Resistance in Cucumis melo germplasm to Pseudoperonospora cubensis pathotypes. In: Advances in Downy Mildew Research[C]. Proceedings of the 2nd International Downy Mildews Symposium, 2nd International Downy Mildews Symposium, Olomouc, Czech Republic, 2007: 157-167. |
| [17] | Ivanoff S S, Resistance of cantaloupes to downy mildew and the melon aphid[J]. Journal of Heredity, 1944,35(2):35-39. |
| [18] | 李靖, 利容千, 袁文静. 黄瓜感染霜霉病菌叶片中一些酶活性的变化[J]. 植物病理学报, 1991,(4):39-45. |
| LI Jing, LI Rongqian, YUAN Wenjing. ON the Change of Enzyme Activites of Cucumber Leaf Infected By Pseudoperonospora Cubensis(Berk. Et Ctrt) Rosws[J]. Acta Phytopathologica Sinica, 1991,(4):39-45. | |
| [19] | 杨柳燕, 徐永阳, 徐志红, 等. 甜瓜霜霉病抗性遗传及SRAP分子标记[J]. 江苏农业学报, 2012,28(5):1200-1202. |
| YANG Liuyan, XU Yongyang, XU Zhihong, et al. Inheritance of downy mildew resistance in melon and SRAP marker linked to resistant genes[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2012,28(5):1200-1202. | |
| [20] | 贺玉花, 徐永阳, 徐志红, 等. 甜瓜霜霉病抗性基因的SSR标记[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2014,42(7):54-55. |
| HE Yuhua, XU Yongyang, XU Zhihong, et al. SSR markers of downy mildew resistance genes in melon[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2014,42(7):54-55. | |
| [21] | 张学军, 宁雪飞, 杨永, 等. 甜瓜PI390452霜霉病抗性基因的QTL定位[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2016,53(12):2157-2165. |
| ZHANG Xuejun, NING Xuefei, YANG Yong, et al. QTL Mapping of Resistance Genes to Downy Mildew in Cucumis melo ssp. melo PI390452[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016,53(12):2157-2165. | |
| [22] | 张学军, 杨俊涛, 李寐华, 等. 甜瓜PI414723抗霜霉病基因SSR分子标记[J]. 华北农学报, 2016,31(S1):86-91. |
| ZHANG Xuejun, YANG Juntao, LI Meihua, et al. SSR Markers Linked of the Resistance Gene for Downy Mildew in Cucumis melo ssp. melo PI414723[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Sinica, 2016,31(S1):86-91. | |
| [23] | 徐婷婷, 汪巧玲, 邹淑琼, 等. 基于高通量测序的大麦InDel标记开发及应用[J]. 作物学报, 2020,46(9):1340-1355. |
| XU Tingting, WANG Qiaoling, ZOU Shuqiong, et al. Development and application of InDel markers based on high throughput sequencing in barley[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2020,46(9):1340-1355. | |
| [24] | Islam M R, Hossain M R, Jesse M I, et al. Development of Molecular Marker Linked with Bacterial Fruit Blotch Resistance in Melon (Cucumis melo L.)[J].Genes, 2020, 11(2):220-. |
| [25] | Hassan M Z, Robin A, Rahim M A, et al. Gummy Stem Blight Resistance in Melon: Inheritance Pattern and Development of Molecular Markers[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2018. 19(10):2914. |
| [26] | Sathishkumar N, Hoy-Taek K, Kumar T S, et al. Whole Genome Re-Sequencing and Characterization of Powdery Mildew Disease-Associated Allelic Variation in Melon[J]. Plos One, 2016,11(6):e0157524. |
| [1] | SHEN Yue, LING Yueming, DUAN Xiaoyu, YANG Wenli, LI Meihua, WANG Yirou, WANG Huilin, ZHANG Xuejun. Development and verification of KASP marker for resistance to downy mildew in muskmelon [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2626-2634. |
| [2] | SUN Fenglei, REN Jiaojiao, LEI Bin, GAO Wenwei, QU Yanying. QTL mapping and genomic selection of maize leaf width [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(10): 2341-2351. |
| [3] | LU Yi, NuerziyaYalimaimaiti, FU Wenjun, CHEN Rong, Wenqiemu Abulizi, CHEN Haoyu, HAO Jingzhe, WANG Huiqin. Research the Relationship between the Epidemic of Grape Downy Mildew and Climatic Conditions in Ili Valley of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(10): 1855-1862. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xue-jun, GUO LI-xia, ZHANG Jian, YANG Yong, LI Mei-hua, YI Hong-ping. Establishment of Identification Methods and Germplasm Resource Evaluation of Cucumis melo ssp.melo Downy Mildew at Seedling Stage [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(5): 899-909. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xue-jun,YANG Wen-li,Zhang Yong-bing,Zhang Jian,Guo Li-xia,YANG Yong,LI Mei-hua,YI Hong-ping. Construction of High Density Genetic Map and QTL Mapping for Downy Mildew Traits in Cucumis melo ssp.melo [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 56(10): 1828-1838. |
| [6] | LI Jing;ZHANG Xiang-lin;WANG Chong;LI Ya-wei;ZHANG Xiao-ju. Molecular Detecting Technology of Sugar Beet Downy Mildew Baswd on Mitochondrial DNA Gene cox2 [J]. , 2016, 53(5): 857-865. |
| [7] | LI Jing;ZHANG Xiang-lin;WANG Chong;LI Ya-wei;ZHANG Xiao-ju. Rapid Detection Spinach Downy Mildew Pathogen by Molecular Method [J]. , 2016, 53(2): 346-351. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xue-jun;NING Xue-fei;YANG Yong;LI Mei-hua;WANG Xian-lei;YI Hong-ping. QTL Mapping of Resistance Genes to Downy Mildew in Cucumis melo ssp.melo PI390452 [J]. , 2016, 53(12): 2157-2165. |
| [9] | LI Zhuo;JIN Gong-xi;LANG Ning;SUN Qi;REN Yu-zhong;ZHAO Bao-long;ZHANG Li;LI Guo-ying. Effects of Temperature,Humidity and Illumination on the Germination and Survival of Sporangia of Downy Mildew of Grapes [J]. , 2016, 53(11): 2090-2097. |
| [10] | JIN Gong-xi;YUE Yong-liang;SONG Yu-ping;WEI Xin-zheng;REN Yu-zhong;ZHANG Li;LI Guo-ying. The First Time Infection Source of Grape Downy Mildew and Its Characteristics and Some Control Approaches [J]. , 2015, 52(6): 1105-1111. |
| [11] | ZHOU Ting-ting;JING Gong-xi;YUE Yong-liang;ZHANG Li;LI Guo-ying. Resistance Identification of Wine Grape Germplasm to Downy Mildew [J]. , 2014, 51(10): 1845-1850. |
| [12] | DAI Pei-hong;LA Ping;GUO Chang-kui;GAO Wen-wei;ZhANG Jian-xin;LUO Shu-ping. Study on Optimization for SSR Reaction System and Molecular Marker of Important Agronomy Traits in Beta vulgaris [J]. , 2013, 50(7): 1199-1205. |
| [13] | LIU Xin-xiu;JIN Gong-xi;LI Hu;ZHANG Li;ZHAO Bao-long;REN Yu-zhong;LI Guo-ying. Identification of Disease-resistant Property of the Grape Germplasm Resource to Plasmopara viticola [J]. , 2013, 50(5): 857-863. |
| [14] | LUO Yan-ping;WANG Qiang;LIU Lin;LU Yi;YANG De-song;ZHANG Dong-hai;LI Guo-ying. Study on the Sensitivity of Plasmopara viticola to Four Fungicides in Xinjiang [J]. , 2013, 50(5): 851-856. |
| [15] | LIU Yan;CHEN Quan-jia;QU Yan-ying;LIANG Ya-jun;LI Pei-yu;ZHU Biao;L(U) Yu-qiang. Molecular Markers of Screening of the Disease-resistance Gene of Cotton Using SRAP-BSA Technique [J]. , 2009, 46(6): 1158-1163. |
| Viewed | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Full text 131
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Abstract 237
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||