

新疆农业科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (6): 1328-1336.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.06.004
丁银灯( ), 范贵强, 高永红, 黄天荣, 周安定, 吴新元, 方辉(
), 范贵强, 高永红, 黄天荣, 周安定, 吴新元, 方辉( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-05
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-07-29
通信作者:
方辉(1988-),男,河南信阳人,副研究员,硕士,研究方向为小麦遗传育种与栽培,(E-mail)13179911060@163.com作者简介:丁银灯(1992-),男,河南周口人,助理研究员,硕士,研究方向为小麦遗传育种与栽培,(E-mail)1457676749@qq.com
基金资助:
DING Yingdeng( ), FAN Guiqiang, GAO Yonghong, HUANG Tianrong, ZHOU Anding, WU Xinyuan, FANG Hui(
), FAN Guiqiang, GAO Yonghong, HUANG Tianrong, ZHOU Anding, WU Xinyuan, FANG Hui( )
)
Received:2024-11-05
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-07-29
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】探明干旱胁迫下植物生长调节剂对冬小麦的影响作用机制,为提高水分利用效率提供依据。【方法】采用双因素裂区试验设计,设2个水分处理:苗期干旱胁迫(正常灌水量的25%,记为I1)和拔节期干旱胁迫(正常灌水量的25%,记为I2),设置1.67、2.22和3.33 g/L三个矮壮素浓度梯度(分别以C1、C2和C3表示),以清水(CK)为对照,分析不同灌水干旱胁迫下叶面喷施矮壮素对冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累和转运及产量的影响。【结果】两种灌水处理下,拔节期干旱胁迫使得孕穗期冬小麦旗叶叶面积、单株叶面积显著降低87.73%和65.40%,花后冬小麦旗叶的Pn值、Tr值降低,Ci浓度上升,同时生殖生长时间缩短,光合产物积累和转运量下降,冬小麦穗数、穗粒数和千粒重降低,最终导致产量下降达40.28%。叶面喷施矮壮素后可削弱干旱胁迫对冬小麦产量减少的负面影响,C2、C3浓度下,冬小麦的旗叶叶面积、单株叶面积上升;叶面喷施矮壮素溶液能够增强冬小麦光合作用,延缓植株衰老,两种处理下花后旗叶光合速率峰值在C1、C2和C3浓度下分别比CK高出28.62%、36.23%、34.19%和21.62%、21.27%、45.87%,光合速率产生的峰值至生育末期下降幅度减小;矮壮素处理下成熟期营养器官干重、干物质转运量和转运率均上升,且均以C2浓度下各指标达到最高;两种灌水处理下C1、C2和C3浓度矮壮素处理的小麦产量分别比CK增加了0.32%、16.08%、11.75%和4.52%、23.60%、6.42%。【结论】综合灌水处理和矮壮素浓度,干旱胁迫对小麦穗数、穗粒数和千粒质量降低,进而导致产量下降,在冬小麦花前干旱胁迫下,以拔节期干旱胁迫对产量的影响更大;外源施加矮壮素均可以不同程度改善干旱胁迫条件对小麦造成的不利影响,其中2.22 g/L浓度效果最佳。
中图分类号:
丁银灯, 范贵强, 高永红, 黄天荣, 周安定, 吴新元, 方辉. 花前干旱和矮壮素浓度对冬小麦光合特性及产量形成的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(6): 1328-1336.
DING Yingdeng, FAN Guiqiang, GAO Yonghong, HUANG Tianrong, ZHOU Anding, WU Xinyuan, FANG Hui. Effects of pre-flowering drought and gibberellin concentration on photosynthetic characteristics and yield formation in winter wheat[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(6): 1328-1336.
| 灌水处理 Water injection treatment | 灌水量Irrigation volume(m3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling stage | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 扬花期 Flowering period | 灌浆期 Grouting period | 灌水总量 Total Water Volume | |
| I1 | 300 | 1 200 | 1 200 | 1 200 | 3 900 |
| I2 | 1 200 | 300 | 1 200 | 1 200 | 325 |
表1 冬小麦各生育时期灌水量
Tab.1 Irrigation amount of spring wheat at different growth stages
| 灌水处理 Water injection treatment | 灌水量Irrigation volume(m3) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling stage | 拔节期 Jointing stage | 扬花期 Flowering period | 灌浆期 Grouting period | 灌水总量 Total Water Volume | |
| I1 | 300 | 1 200 | 1 200 | 1 200 | 3 900 |
| I2 | 1 200 | 300 | 1 200 | 1 200 | 325 |
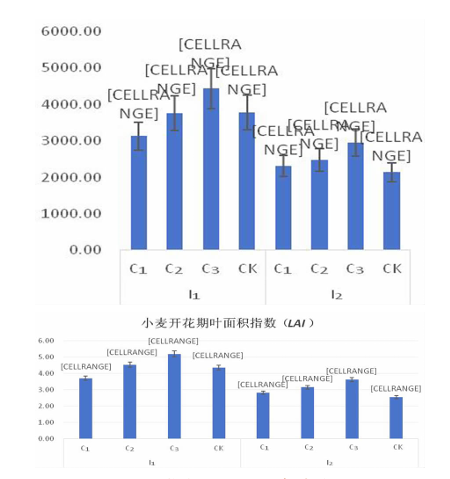
图2 不同灌水量及矮壮素浓度处理下冬小麦单株叶面积的变化
Fig.2 Changes in leaf area per plant of winter wheat under different irrigation amount treatments and dwarfing concentration
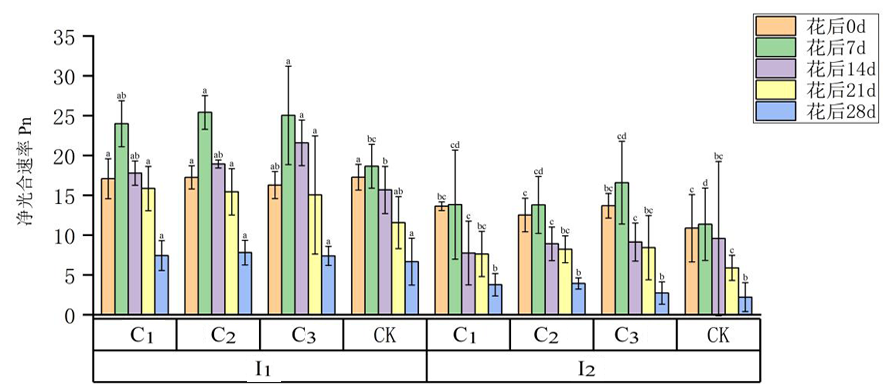
图3 不同灌水量及矮壮素处理下冬小麦旗叶光合速率的变化
Fig.3 Changes of different irrigation amount treatments and paclobutrazol concentrations on the photosynthetic rate of winter wheat flag leaves
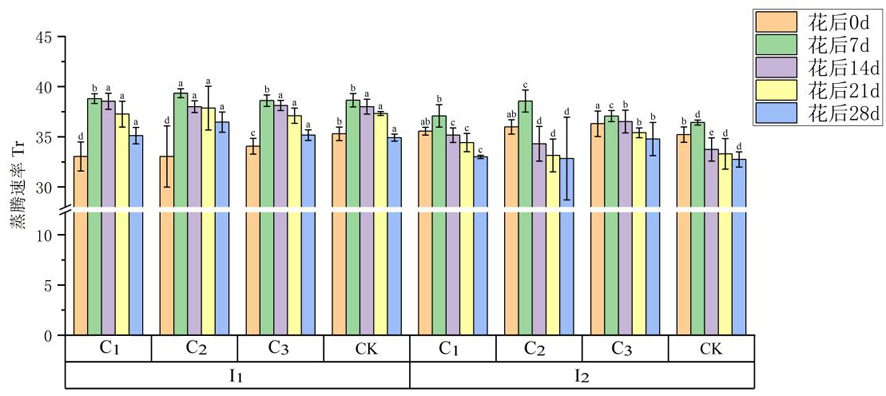
图4 不同灌水量及矮壮素处理下冬小麦旗叶蒸腾速率的变化
Fig.4 Changes of different irrigation amount treatments and concentrations of Gibberellic Acid on the transpiration rate of flag leaves in winter wheat
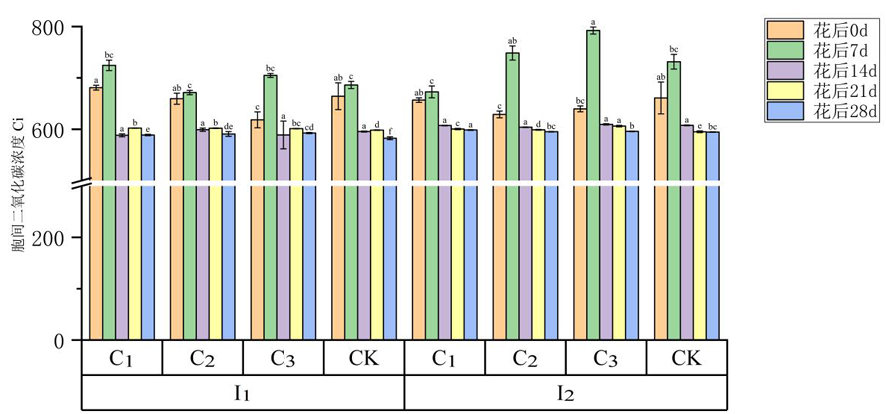
图5 不同灌水量及矮壮素处理下冬小麦旗叶胞间二氧化碳浓度的变化
Fig.5 Changes of different irrigation amount treatments and gibberellin concentrations on intercellular carbon dioxide concentration in winter wheat's flag leaves
| 干旱处理 Drought management | 矮壮素浓度 Gibberellin concentration | 开花期营养 器官干重 Biomass before anthesis (g/株) | 成熟期营养 器官干重 Biomass at maturity (g/株) | 籽粒重 Grain weight (g/株) | 干物质转运量 Dry matter transport amount (g/株) | 干物质转运率 Dry matter transport rate (%) | 干物质转运对 籽粒贡献率 Dry matter transport contribution rate of wheat seed (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | C1 | 1.452b | 0.964a | 1.046bc | 0.488 1 | 33.60 | 34.57 |
| C2 | 1.565a | 1.039a | 1.188a | 0.526 6 | 33.65 | 32.82 | |
| C3 | 1.501a | 0.996a | 1.176ab | 0.504 6 | 33.62 | 31.79 | |
| CK | 1.397b | 0.928ab | 1.067bc | 0.4693 | 33.59 | 32.59 | |
| I2 | C1 | 0.989cd | 0.699d | 0.830d | 0.289 5 | 29.27 | 25.83 |
| C2 | 1.252c | 0.885c | 0.938cd | 0.366 8 | 29.30 | 28.97 | |
| C3 | 1.095c | 0.775d | 0.800d | 0.320 3 | 29.25 | 29.66 | |
| CK | 0.974d | 0.689d | 0.812d | 0.284 7 | 29.23 | 25.98 |
表2 不同灌水量和矮壮素处理下冬小麦成熟期干物质积累、转运的变化
Tab.2 Changes of different irrigation amount treatments and chlormequat concentrations on dry matter accumulation and translocation during the maturity phase of winter wheat
| 干旱处理 Drought management | 矮壮素浓度 Gibberellin concentration | 开花期营养 器官干重 Biomass before anthesis (g/株) | 成熟期营养 器官干重 Biomass at maturity (g/株) | 籽粒重 Grain weight (g/株) | 干物质转运量 Dry matter transport amount (g/株) | 干物质转运率 Dry matter transport rate (%) | 干物质转运对 籽粒贡献率 Dry matter transport contribution rate of wheat seed (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I1 | C1 | 1.452b | 0.964a | 1.046bc | 0.488 1 | 33.60 | 34.57 |
| C2 | 1.565a | 1.039a | 1.188a | 0.526 6 | 33.65 | 32.82 | |
| C3 | 1.501a | 0.996a | 1.176ab | 0.504 6 | 33.62 | 31.79 | |
| CK | 1.397b | 0.928ab | 1.067bc | 0.4693 | 33.59 | 32.59 | |
| I2 | C1 | 0.989cd | 0.699d | 0.830d | 0.289 5 | 29.27 | 25.83 |
| C2 | 1.252c | 0.885c | 0.938cd | 0.366 8 | 29.30 | 28.97 | |
| C3 | 1.095c | 0.775d | 0.800d | 0.320 3 | 29.25 | 29.66 | |
| CK | 0.974d | 0.689d | 0.812d | 0.284 7 | 29.23 | 25.98 |
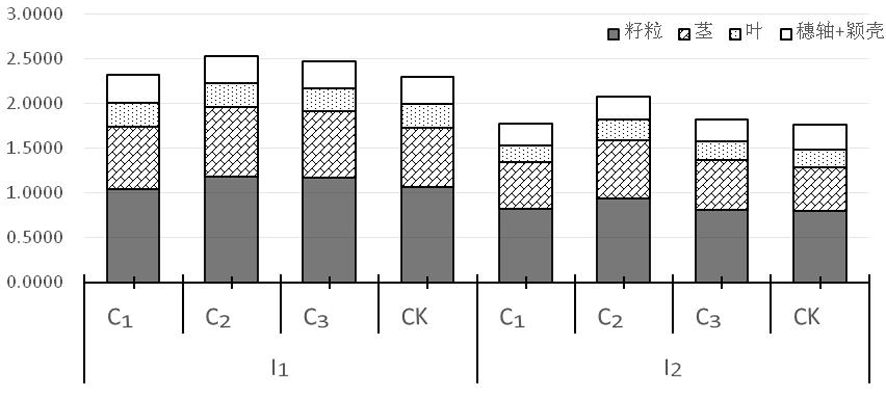
图6 不同灌水量和矮壮素处理下冬小麦成熟期干物质积累、分配的变化
Fig.6 Changes of different irrigation amount treatment and gibberellin concentration on the accumulation and distribution of dry matter at the maturity stage of winter wheat
| 项目 Items | 干旱处理 Drought management | 矮壮素浓度 Gibberellin concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | CK | ||
| 穗数 Spike | I1 | 583.52a | 594.36a | 578.15a | 570.09a |
| I2 | 538.08b | 562.99b | 541.09b | 526.36b | |
| 平均 | 560.8ab | 578.68a | 559.62ab | 548.23b | |
| 穗粒数 Grain per spike/(个) | I1 | 25.18a | 26.98a | 28.14a | 27.12a |
| I2 | 21.31b | 23.78b | 21.25b | 20.94b | |
| 平均 | 23.25a | 25.38a | 24.7a | 24.03a | |
| 千粒重 Thousand seed Ieight/(g) | I1 | 41.54ab | 44.04a | 41.79a | 39.35c |
| I2 | 38.95d | 39.45c | 39.55c | 38.77d | |
| 平均 | 40.25b | 41.75a | 40.67b | 39.06d | |
| 产量 Yield/(kg/hm2) | I1 | 5 401.35ab | 6 249.68a | 6 016.66a | 5 383.92ab |
| I2 | 3 952.37d | 4 673.95c | 4 024.38cd | 3 781.62d | |
| 平均 | 4 676.86c | 5 461.82ab | 5 020.52ab | 4 582.77c | |
表3 不同灌水量和矮壮素处理下冬小麦产量的变化
Tab.3 Changes of different irrigation amount treatment and gibberellin concentration on winter wheat yield
| 项目 Items | 干旱处理 Drought management | 矮壮素浓度 Gibberellin concentration | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | C2 | C3 | CK | ||
| 穗数 Spike | I1 | 583.52a | 594.36a | 578.15a | 570.09a |
| I2 | 538.08b | 562.99b | 541.09b | 526.36b | |
| 平均 | 560.8ab | 578.68a | 559.62ab | 548.23b | |
| 穗粒数 Grain per spike/(个) | I1 | 25.18a | 26.98a | 28.14a | 27.12a |
| I2 | 21.31b | 23.78b | 21.25b | 20.94b | |
| 平均 | 23.25a | 25.38a | 24.7a | 24.03a | |
| 千粒重 Thousand seed Ieight/(g) | I1 | 41.54ab | 44.04a | 41.79a | 39.35c |
| I2 | 38.95d | 39.45c | 39.55c | 38.77d | |
| 平均 | 40.25b | 41.75a | 40.67b | 39.06d | |
| 产量 Yield/(kg/hm2) | I1 | 5 401.35ab | 6 249.68a | 6 016.66a | 5 383.92ab |
| I2 | 3 952.37d | 4 673.95c | 4 024.38cd | 3 781.62d | |
| 平均 | 4 676.86c | 5 461.82ab | 5 020.52ab | 4 582.77c | |
| [1] | 郝卫平. 干旱复水对玉米水分利用效率及补偿效应影响研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2013. |
| HAO Weiping. Study on the influence of drought and rehydration on water use efficiency and compensation effect of maize[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2013. | |
| [2] | 山仑. 我国旱地农业发展中的几个问题[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2023, 41(3): 2-4. |
| SHAN Lun. Issues in dryland agricultural research in China[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2023, 41(3): 2-4. | |
| [3] | 文廷刚, 陈昱利, 杜小凤, 等. 不同植物生长调节剂对小麦籽粒灌浆特性及粒重的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2014, 34(1): 84-90. |
| WEN Tinggang, CHEN Yuli, DU Xiaofeng, et al. Effects of different plant growth regulators on the grain filling characteristics and grain weight in wheat[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2014, 34(1): 84-90. | |
| [4] | 陈蔚燕. 新型植物生长调节剂(PGRs)的研制及其应用技术研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2015. |
| CHEN Weiyan. Development and application of new plant growth regulators (PGRs)[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science & Technology, 2015. | |
| [5] | 王慧, 张明伟, 雷晓伟, 等. 植物生长调节剂拌种对扬麦13茎秆生长及籽粒产量的影响[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2016, 36(2): 206-214. |
| WANG Hui, ZHANG Mingwei, LEI Xiaowei, et al. Effect of plant growth regulators on stem growth and grain yield of Yangmai 13[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2016, 36(2): 206-214. | |
| [6] | 陈晓娜, 高永, 宋晓敏, 等. 植物延缓剂对杨柴抗旱性的调控作用[J]. 北方园艺, 2017,(10): 65-69. |
| CHEN Xiaona, GAO Yong, SONG Xiaomin, et al. Effects of paclobutrazol on Hedysarum mongolicum under drought condition[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2017,(10): 65-69. | |
| [7] | 康靓, 张娜, 张永强, 等. 矮壮素滴施量对滴灌冬小麦茎秆特征及其抗倒伏性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 63-69. |
| KANG Liang, ZHANG Na, ZHANG Yongqiang, et al. Effects of CCC irrigation amount on stem characteristics and lodging resistance of winter wheat under drip irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 63-69. | |
| [8] | 郭建文, 田新会, 张舒芸, 等. 不同浓度矮壮素对黑麦抗倒伏性和种子产量的影响[J]. 草业科学, 2018, 35(5): 1128-1137. |
| GUO Jianwen, TIAN Xinhui, ZHANG Shuyun, et al. Effect of different chlorocholine chlorid(CCC)concentrations on lodging resistance and seed yield of rye[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2018, 35(5): 1128-1137. | |
| [9] | 黄洁, 李天, 魏云霞, 等. 矮壮素浸种对木薯生长与产量的影响[J]. 中国热带农业, 2024,(4): 32-39. |
| HUANG Jie, LI Tian, WEI Yunxia, et al. Effect on the growth and yield by soaking cassava cutting in the solution of chlorocholine chloride[J]. China Tropical Agriculture, 2024,(4): 32-39. | |
| [10] | 马亚男, 曹依林, 苏璐璐, 等. 喷施矮壮素对番茄植株及果实品质的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2023, 55(12): 71-78. |
| MA Yanan, CAO Yilin, SU Lulu, et al. Effects of spraying chlormequat chloride on tomato plant and fruit quality[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 55(12): 71-78. | |
| [11] | 闫艳. 矮壮素提高糯玉米抗旱性的转录组学分析[D]. 广州: 仲恺农业工程学院, 2023. |
| YAN Yan. Transcriptome analysis of chlormequat chloride improving drought resistance of waxy corn[D]. Guangzhou: Zhongkai University of Agriculture and Engineering, 2023. | |
| [12] | 宁淑香, 陈静, 张慧清. PP333处理对小麦植株抗旱能力的影响[J]. 大连教育学院学报, 1999, 15(4):67-71. |
| NING Shuxiang, CHEN Jing, ZHANG Huiqing. Effect of PP333 treatment on drought resistance of wheat plants[J]. Journal of Dalian Education Institute, 1999, 15(4):67-71. | |
| [13] | 杨鲤糠, 蒋桂英, 祁静玉. 减量施氮对滴灌春小麦光合特性和荧光参数的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(12): 2164-2175. |
| YANG Likang, JIANG Guiying, QI Jingyu. Effects of reduced nitrogen application on photosynthetic characteristics and fluorescence parameters of spring wheat under drip irrigation[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(12): 2164-2175. | |
| [14] | 梁银丽, 曹导叶, 由海霞, 等. 西北半湿润渠灌区作物节水高效种植制度[J]. 西北农业学报, 2006, 15(3): 50-53. |
| LIANG Yinli, CAO Daoye, YOU Haixia, et al. Water-saving and efficient cropping system in northwest semi-humidity irrigation area[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2006, 15(3): 50-53. | |
| [15] | 郑婧, 佘维维, 白宇轩, 等. 氮素和水分添加对毛乌素沙地油蒿群落优势植物叶片性状的影响[J]. 林业科学, 2018, 54(10): 164-171. |
| ZHENG Jing, SHE Weiwei, BAI Yuxuan, et al. Effects of nitrogen and water addition on leaf traits of dominant plant species in Artemisia ordosica community of the mu us desert[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae, 2018, 54(10): 164-171. | |
| [16] | 许丽娟, 吴鞠, 刘海轩, 等. 生长抑制剂对大叶黄杨形态观赏性的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2018, 46(11): 16-21. |
| XU Lijuan, WU Ju, LIU Haixuan, et al. Effect of growth inhibitors on the morphological ornamentality characteristic of Euonymus japonicus[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2018, 46(11): 16-21. | |
| [17] | Panyam N S, Lakshmi V T R, Krishnan R K, et al. Modeling of palm leaf character recognition system using transform based techniques[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2016, 84(DEC.1):29-34. |
| [18] | 高翠民, 杨永辉, 何方, 等. 不同灌溉技术下水氮耦合对小麦光合特性、灌水利用特性及产量的影响[J]. 华北农报, 2020, 35(5):72-80. |
| GAO Cuimin, YANG Yonghui, HE Fang, et al. Effects of water and nitrogen coupling under different irrigation techniques on photosynthetic characteristics, water use efficiency, and yield of wheat[J]. 2020, 35(5):72-80. | |
| [19] | 黄明, 吴金芝, 李友军, 等. 干旱对不同抗旱性小麦旗叶光响应特征和产量的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究, 2020, 38(3): 64-73. |
| HUANG Ming, WU Jinzhi, LI Youjun, et al. Effects of drought on flag-leaf photosynthetic characteristics to light and yield of wheat with different drought resistance[J]. Agricultural Research in the Arid Areas, 2020, 38(3): 64-73. | |
| [20] | Monsi M, Saeki T. On the factor light in plant communities and its importance for matter production[J]. Annals of Botany, 2005, 95(3):549-567. |
| [21] | 秦娜, 许为钢, 齐学礼, 等. 干旱胁迫下郑麦7698的抗旱性能及光合特性分析[J]. 河南农业科学, 2018, 47(2): 7-11. |
| QIN Na, XU Weigang, QI Xueli, et al. Drought tolerance and photosynthetic characteristics of Zhengmai 7698 under drought stress condition[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 47(2): 7-11. | |
| [22] | 田媛, 李丰, 王东勇, 等. 矮壮素对改善芝麻机收农艺性状的作用及其对光合生理的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2024, 52(5): 128-133. |
| TIAN Yuan, LI Feng, WANG Dongyong, et al. The effect of gibberellic acid on improving the agronomic traits for mechanical harvesting of sesame and its influence on photosynthetic physiology[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 52(5): 128-133. | |
| [23] | 张春宇, 金喜军, 张明聪, 等. 烯效唑与矮壮素复配微量元素拌种对大豆光合生理及产量的影响[J]. 大豆科学, 2020, 39(4): 587-594. |
| ZHANG Chunyu, JIN Xijun, ZHANG Mingcong, et al. Effects of S3307 and CCC mixed trace element dressing on the photosynthetic physiology and yield of soybean[J]. Soybean Science, 2020, 39(4): 587-594. | |
| [24] | 许锋, 张威威, 孙楠楠, 等. 矮壮素对银杏叶片光合代谢与萜内酯生物合成的影响[J]. 园艺学报, 2011, 38(12): 2253-2260. |
| XU Feng, ZHANG Weiwei, SUN Nannan, et al. Effects of chlorocholine chloride on photosynthesis metabolism and terpene trilactones biosynthesis in the leaf of Ginkgo biloba[J]. Acta Horticulturae Sinica, 2011, 38(12): 2253-2260. | |
| [25] | Ercoli L, Lulli L, Mariotti M, et al. Post-anthesis dry matter and nitrogen dynamics in durum wheat as affected by nitrogen supply and soil water availability[J]. European Journal of Agronomy, 2008, 28(2):138-147. |
| [26] | 卢小兰, 于振文, 张永丽, 等. 测墒补灌条件下不同穗型小麦耗水特性和同化物积累与分配研究[J]. 麦类作物学报, 2019, 39(12):1486-1493. |
| LU Xiaolan, YU Zhenwen, ZHANG Yongli, et al. Research on Water Consumption Characteristics and Accumulation and Distribution of Assimilates in Different Spike Types of Wheat under Moisture Monitoring Irrigation Conditions[J]. Journal of Triticeae Crops, 2019, 39(12):1486-1493. | |
| [27] | 杨磊, 孙敏, 林文, 等. 群体结构对旱地小麦土壤耗水与物质生产形成的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2021, 40(5): 1356-1365. |
| YANG Lei, SUN Min, LIN Wen, et al. Effects of population structure on soil water consumption and dry matter production of dryland wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2021, 40(5): 1356-1365. | |
| [28] | 张振, 张永丽, 石玉, 等. 灌溉量对冬小麦耗水量、旗叶衰老及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(3): 393-402. |
| ZHANG Zhen, ZHANG Yongli, SHI Yu, et al. Effects of irrigation amount on water-use efficiency, flag leaf senescence, and grain yield of winter wheat[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(3): 393-402. | |
| [29] | 孙培杰, 王媛媛, 陈涛, 等. 喷施矮壮素与延缓施氮对冬小麦抗倒伏能力及产量形成的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2024, 35(8): 2141-2149. |
| SUN Peijie, WANG Yuanyuan, CHEN Tao, et al. Effects of spraying cycocel and delaying nitrogen application on lodging resistance and yield formation of winter wheat[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2024, 35(8): 2141-2149. | |
| [30] | 韩守威, 司纪升, 余维宝, 等. 山东省冬小麦产量差与氮肥利用效率差形成机理解析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2022, 55(16): 3110-3122. |
| HAN Shouwei, SI Jisheng, YU Weibao, et al. Mechanisms analysis on yield gap and nitrogen use efficiency gap of winter wheat in Shandong Province[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(16): 3110-3122. | |
| [31] | Khannachopra R, Rao P, Maheswari M, et al. Effect of water-deficit on accum -ulation of dry-matter, carbon and nitrogen in the kernel of wheat genotypes differing in yield stability[J]. Annals of Botany, 1994, 74(5):503-511. |
| [32] | 梁振兴, 马兴林. 冬小麦分蘖发生过程中内源激素作用的研究[J]. 作物学报, 1998, 24(6): 788-792. |
| LIANG Zhenxing, MA Xinglin. Studies on the effects of endogenous hormones on tiller development process of winter wheat[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 1998, 24(6): 788-792. | |
| [33] | 李春喜, 尚玉磊, 姜丽娜, 等. 不同植物生长调节剂对小麦衰老及产量构成的调节效应[J]. 西北植物学报, 2001, 21(5): 931-936. |
| LI Chunxi, SHANG Yulei, JIANG Lina, et al. Regulation of plant growth regulator on leaves senescence and yield constitutions of wheat[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2001, 21(5): 931-936. |
| [1] | 景彦强, 洪明, 于秋月, 衡通, 肖键, 张新乐. 新疆北疆膜下滴灌春油葵适宜土壤水分的下限分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(6): 1344-1353. |
| [2] | 任世恒, 王爱凡, 毛李平, 朱麒任, 苏秀娟. 不同繁殖方式对薰衣草农艺性状、精油产量及品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(6): 1371-1379. |
| [3] | 郝洪龙, 张翠芳, 王世伟, 杨先安, 郭桐, 耿召坤, 赵龙, 李振瑜. 整株尺度上核桃初果期光合同化物向果实的分配特性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(6): 1461-1468. |
| [4] | 廖兴洋, 王方永, 傅积海, 陈伟明, 韩焕勇. 不同用量滴灌水与缩节胺协同打顶对新疆机采棉群体结构产量品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1051-1063. |
| [5] | 张梦珂, 林丽, 林豪, 惠瑞晗, 杨可攀. 不同灌溉频次对陆地棉生长指标和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1064-1074. |
| [6] | 穆光荣, 李杰, 古丽娜孜·居来提, 娄善伟, 帕尔哈提·买买提, 马腾飞, 张鹏忠, 吴湘林, 张立祯, 巴特尔·巴克. 钾肥配施及用量对膜下滴灌棉花生长发育及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1075-1083. |
| [7] | 陈创洲, 张炎, 哈丽哈什·依巴提, 佘玲艺, 樊林鑫, 张优. 施氮对棉花生长发育、产量及棉田土壤养分的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1092-1101. |
| [8] | 吴斌, 吴海波, 刘翔宇, 赵龙. 苦豆子生物碱对西瓜品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1151-1158. |
| [9] | 陈兵权, 陈虹, 赵善超, 郭来珍, 赵鑫, 陈俊杰, 韩珏. 光照对天山花楸幼苗生长和光合特征的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1208-1218. |
| [10] | 乔迪, 林涛, 崔建平, 张鹏忠, 张昊, 鲍龙龙, 汤秋香. 基于RZWQM2的氮肥运筹方式对棉花生长及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(4): 807-819. |
| [11] | 郝曦煜, 张仲鹃, 郑成栋, 张斯文, 张瑾, 郑春秀, 吴世凯, 王雪. 不同鲜食玉米品种(系)农艺性状与产量的比较分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(4): 837-849. |
| [12] | 马如海, 黄春燕, 崔辉梅, 郑越辉, 方圆, 王登伟. 黄沙基质不同栽培方式对设施番茄产量与品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(4): 903-910. |
| [13] | 焦润兴, 卜东升, 邵延慧, 张涛, 陈玲, 张冬冬. “干播湿出”对不同盐碱化土壤水盐分布、养分及棉花产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(3): 572-583. |
| [14] | 聂凌帆, 张金汕, 田文强, 孙刚刚, 王泓懿, 张君, 张强斌, 郭飞, 吴利, 石书兵. 不同水氮处理对超晚播冬麦生长、水氮利用及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(3): 584-592. |
| [15] | 孙刚刚, 郭飞, 聂凌帆, 田文强, 王泓懿, 史永清, 吴利, 艾红玉, 张金汕, 石书兵. 种肥分离对冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累和产量形成的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(3): 593-599. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||