

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (12): 2861-2871.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.12.001
• 种质资源·分子遗传学·耕作栽培·生理生化·微生物 • 上一篇 下一篇
孟卓1,2,3( ), 唐小雯1,3, 张广杰1,2,3, 徐安东1,3, 颜宇1,3, 付娆1,3, 羌松1,2,3, 蒋平安2(
), 唐小雯1,3, 张广杰1,2,3, 徐安东1,3, 颜宇1,3, 付娆1,3, 羌松1,2,3, 蒋平安2( ), 马德英1,2,3(
), 马德英1,2,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-21
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2025-01-16
通信作者:
马德英(1968-),女,新疆乌鲁木齐人,教授,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为有害生物绿色防控,(E-mail)mdynd@163.com;作者简介:孟卓(1998-),女,新疆博乐人,硕士研究生,研究方向为棉花黄萎病绿色防控,(E-mail)1349641389@qq.com
基金资助:
MENG Zhuo1,2,3( ), TANG Xiaowen1,3, ZHANG Guangjie1,2,3, XU Andong1,3, YAN Yu1,3, FU Rao1,3, QIANG Song1,2,3, JIANG Pingan2(
), TANG Xiaowen1,3, ZHANG Guangjie1,2,3, XU Andong1,3, YAN Yu1,3, FU Rao1,3, QIANG Song1,2,3, JIANG Pingan2( ), MA Deying1,2,3(
), MA Deying1,2,3( )
)
Received:2024-04-21
Published:2024-12-20
Online:2025-01-16
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 通过白星花金龟虫砂与黄萎病生防菌相结合,研究棉花黄萎病绿色防控技术,分析两者协同作用下不同施用方式对棉花生长发育及防控黄萎病的影响,为棉花黄萎病的绿色防控和棉花产业可持续发展提供参考。【方法】 设置虫砂复合枯草芽孢杆菌(LD-KC)、解淀粉芽孢杆菌(LD-JDF)、哈茨木霉(LD-HC)、中棉菌乐土(LD-ZM)4种组合,分别以虫砂复合生防菌全量基施(TBF)和虫砂基施+生防菌追施(BF+DBM)2种方式施入田间,在棉花全生育期测量生长发育和产量指标,在黄萎病发病期调查棉花黄萎病病情指数。【结果】 BF+DBM组的棉花生长发育指标(株高、茎粗、果枝始节高等)优于TBF组,以LD-JDF和LD-ZM表现较好;BF+DBM组籽棉增产效果明显,显著高于TBF组和对照组(CK),BF+DBM籽棉增产在24.37%~33.40%,LD-JDF组增产最高,增产率达33.40%,其次为LD-HC,增产率为31.10%。黄萎病发生初期,TBF组的病情指数在3.80~5.85,LD-JDF处理对棉花黄萎病的防效较高,达到44.36%,BF+DBM组病情指数在2.50~5.33,LD-HC处理下的病情指数最低,防效为63.40%,黄萎病发生后期,TBF组和BF+DBM组病情指数分别在27.00~31.67、21.67~30.83,均为JDF防效最高,分别达到19.00%、34.98%。【结论】 在棉花整个生育期内,虫砂基施+生防菌追施能有效促进棉花的生长发育,对棉花黄萎病的防治效果较佳,且增产效果较为显著,以LD-JDF增产效果最佳,虫砂基施和生防追施相结合的施用方式。
中图分类号:
孟卓, 唐小雯, 张广杰, 徐安东, 颜宇, 付娆, 羌松, 蒋平安, 马德英. 虫砂复合微生物菌剂2种施用方式对棉花生长发育及防控黄萎病的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(12): 2861-2871.
MENG Zhuo, TANG Xiaowen, ZHANG Guangjie, XU Andong, YAN Yu, FU Rao, QIANG Song, JIANG Pingan, MA Deying. Effects of two application methods of insect-sand compound microbial agent on cotton growth and control of Verticillium wilt[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(12): 2861-2871.

图3 虫砂复合生防菌2种施用方式下棉花茎粗的变化
Fig.3 Changes of two application methods of larvae dung-sand combined with biocontrol microorganisms on cotton stem thickness

图5 虫砂复合生防菌2种施用方式下棉花果枝始节高的变化
Fig.5 Changes of two application methods of larvae dung-sand combined with biocontrol microorganisms on cotton fruit branch start height
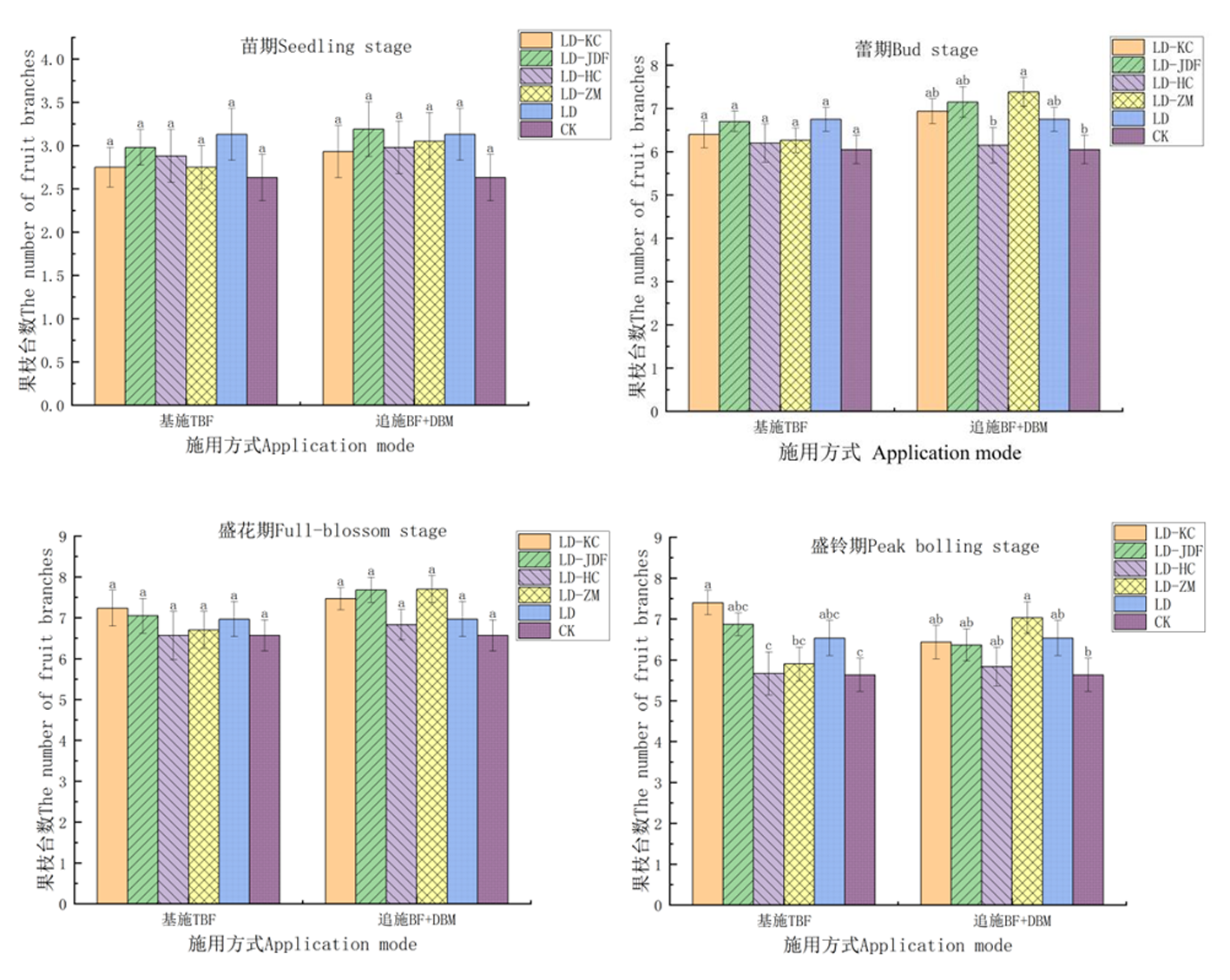
图6 虫砂复合生防菌2种施用方式下棉花果枝台数的变化
Fig.6 Changes of two application methods of larvae dung-sand combined with biocontrol microorganisms on cotton the number of fruit branches

图7 虫砂复合生防菌2种施用方式下叶绿素含量SPAD值的变化
Fig.7 Changes of two application methods of larvae dung-sand combined with biocontrol microorganisms on cotton chlorophyll content SPAD
| 处理 Treatments | 7月1日 July 1st | 7月28日 July 28th | 8月11日 August 11th | 8月30日 The 30th of August | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | ||
| 基施 TBF | LD-KC | 5.85±0.83a | 14.35 | 10.50±1.44a | 25.90 | 13.87±1.44a | 24.35 | 31.67±3.33a | 5.00 |
| LD-JDF | 3.80±1.44a | 44.36 | 6.67±2.20a | 52.93 | 13.50±3.82a | 26.36 | 27.00±0.00a | 19.00 | |
| LD-HC | 5.00±3.82a | 26.79 | 11.33±0.83a | 20.04 | 15.00±1.44a | 18.18 | 29.17±2.20a | 12.50 | |
| LD-ZM | 5.83±0.83a | 14.59 | 10.83±3.33a | 23.57 | 15.00±2.50a | 18.18 | 30.83±3.33a | 7.50 | |
| 追施 BF+ DBM | LD-KC | 5.33±0.83a | 21.96 | 9.17±0.83a | 35.29 | 12.83±1.74a | 30.01 | 30.83±2.64a | 7.50 |
| LD-JDF | 3.17±0.83a | 53.59 | 10.33±2.20a | 23.53 | 10.83±1.67a | 40.92 | 21.67±3.00a | 34.98 | |
| LD-HC | 2.50±0.00a | 63.40 | 8.33±0.83a | 41.18 | 10.83±2.20a | 40.92 | 25±2.33a | 24.99 | |
| LD-ZM | 3.33±2.20a | 51.24 | 10.00±2.5a | 29.41 | 11.50±3.81a | 37.26 | 25±2.33a | 24.99 | |
| LD | 3.17±1.67a | 38.99 | 11.44±0.83a | 19.22 | 13.67±4.17a | 25.45 | 29.67±0.83a | 11.00 | |
| CK | 6.83±0.00a | - | 14.17±3.46a | - | 18.33±2.20a | - | 33.33±2.20a | - | |
表1 虫砂复合生防菌2种施用方式下棉花黄萎病发生的变化
Tab.1 Changes of two application methods of larvae dung-sand combined with biocontrol microorganisms on the occurrence of cotton wilt disease
| 处理 Treatments | 7月1日 July 1st | 7月28日 July 28th | 8月11日 August 11th | 8月30日 The 30th of August | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | 病情指数 Disease index | 防效 Anti- efficiency (%) | ||
| 基施 TBF | LD-KC | 5.85±0.83a | 14.35 | 10.50±1.44a | 25.90 | 13.87±1.44a | 24.35 | 31.67±3.33a | 5.00 |
| LD-JDF | 3.80±1.44a | 44.36 | 6.67±2.20a | 52.93 | 13.50±3.82a | 26.36 | 27.00±0.00a | 19.00 | |
| LD-HC | 5.00±3.82a | 26.79 | 11.33±0.83a | 20.04 | 15.00±1.44a | 18.18 | 29.17±2.20a | 12.50 | |
| LD-ZM | 5.83±0.83a | 14.59 | 10.83±3.33a | 23.57 | 15.00±2.50a | 18.18 | 30.83±3.33a | 7.50 | |
| 追施 BF+ DBM | LD-KC | 5.33±0.83a | 21.96 | 9.17±0.83a | 35.29 | 12.83±1.74a | 30.01 | 30.83±2.64a | 7.50 |
| LD-JDF | 3.17±0.83a | 53.59 | 10.33±2.20a | 23.53 | 10.83±1.67a | 40.92 | 21.67±3.00a | 34.98 | |
| LD-HC | 2.50±0.00a | 63.40 | 8.33±0.83a | 41.18 | 10.83±2.20a | 40.92 | 25±2.33a | 24.99 | |
| LD-ZM | 3.33±2.20a | 51.24 | 10.00±2.5a | 29.41 | 11.50±3.81a | 37.26 | 25±2.33a | 24.99 | |
| LD | 3.17±1.67a | 38.99 | 11.44±0.83a | 19.22 | 13.67±4.17a | 25.45 | 29.67±0.83a | 11.00 | |
| CK | 6.83±0.00a | - | 14.17±3.46a | - | 18.33±2.20a | - | 33.33±2.20a | - | |
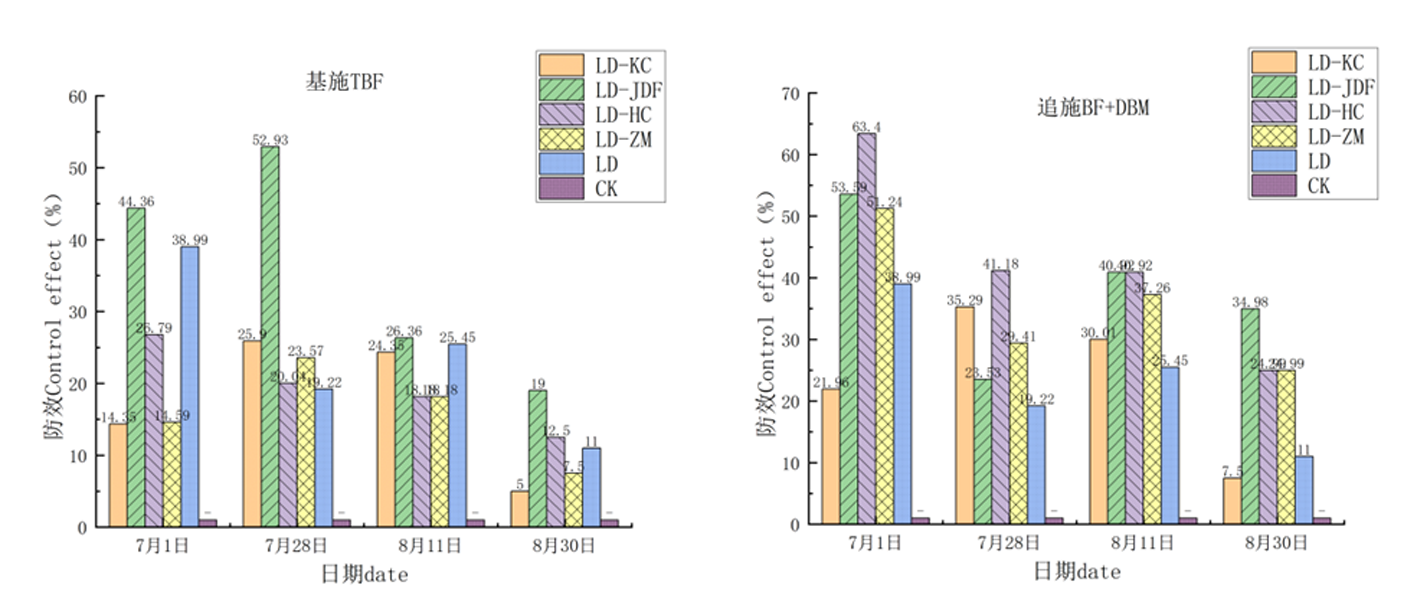
图8 虫砂复合生防菌2种施用方式对棉花黄萎病防效的变化
Fig.8 Changes on the control effect of two kinds of larvae dung-sand combined with biocontrol microorganisms on cotton verticillium wilt
| 处理 Treatments | 出苗率 Seedling emergence rate(%) | 单株铃数 Number of cotton bells per plant | 单铃重 Single boll weight(g) | 单产 Yield per (kg/667m2) | 增产率 Rate of growth(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基施 TBF | LD-KC | 81.94±6.06a | 5.10±0.40ab | 6.34±0.67a | 372.97±4.76a | 4.82 |
| LD-JDF | 83.33±4.81a | 5.37±0.51ab | 5.67±0.19a | 386.25±1.25a | 8.56 | |
| LD-HC | 76.39±5.01a | 4.70±0.63b | 5.67±0.19a | 376.35±15.95a | 5.77 | |
| LD-ZM | 83.33±4.17a | 5.07±0.63ab | 5.67±0.00a | 365.29±22.24a | 2.66 | |
| 追施 BF+DBM | LD-KC | 86.11±6.05a | 6.10±0.35ab | 5.67±0.19a | 454.13±11.34a | 27.63 |
| LD-JDF | 83.33±4.17a | 6.13±0.47ab | 5.78±0.40a | 474.66±8.36a | 33.40 | |
| LD-HC | 76.39±9.11a | 5.07±0.50ab | 5.55±0.22a | 466.45±7.47a | 31.10 | |
| LD-ZM | 78.05±2.11a | 6.57±0.40a | 5.44±0.11a | 442.53±7.50a | 24.37 | |
| LD | 86.33±1.39a | 5.90±0.49ab | 5.64±0.11a | 390.84±8.64a | 9.85 | |
| CK | 71.73±3.93a | 4.83±0.38ab | 5.78±0.22a | 355.81±24.67 | - | |
表2 病田小区虫砂复合生防菌2种施用方式下棉花产量的变化
Tab.2 Changes of two kinds of application methods of larvae dung-sand combined with biocontrol microorganisms on cotton yield in diseased field
| 处理 Treatments | 出苗率 Seedling emergence rate(%) | 单株铃数 Number of cotton bells per plant | 单铃重 Single boll weight(g) | 单产 Yield per (kg/667m2) | 增产率 Rate of growth(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 基施 TBF | LD-KC | 81.94±6.06a | 5.10±0.40ab | 6.34±0.67a | 372.97±4.76a | 4.82 |
| LD-JDF | 83.33±4.81a | 5.37±0.51ab | 5.67±0.19a | 386.25±1.25a | 8.56 | |
| LD-HC | 76.39±5.01a | 4.70±0.63b | 5.67±0.19a | 376.35±15.95a | 5.77 | |
| LD-ZM | 83.33±4.17a | 5.07±0.63ab | 5.67±0.00a | 365.29±22.24a | 2.66 | |
| 追施 BF+DBM | LD-KC | 86.11±6.05a | 6.10±0.35ab | 5.67±0.19a | 454.13±11.34a | 27.63 |
| LD-JDF | 83.33±4.17a | 6.13±0.47ab | 5.78±0.40a | 474.66±8.36a | 33.40 | |
| LD-HC | 76.39±9.11a | 5.07±0.50ab | 5.55±0.22a | 466.45±7.47a | 31.10 | |
| LD-ZM | 78.05±2.11a | 6.57±0.40a | 5.44±0.11a | 442.53±7.50a | 24.37 | |
| LD | 86.33±1.39a | 5.90±0.49ab | 5.64±0.11a | 390.84±8.64a | 9.85 | |
| CK | 71.73±3.93a | 4.83±0.38ab | 5.78±0.22a | 355.81±24.67 | - | |
| [1] |
Wei F, Fan R, Dong H T, et al. Threshold microsclerotial inoculum for cotton Verticillium wilt determined through wet-sieving and real-time quantitative PCR[J]. Phytopathology, 2015, 105(2): 220-229.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | 蔡利华, 练文明, 邰红忠, 等. 新疆地区棉花生育期揭膜与否对黄萎病发生的影响[J]. 棉花科学, 2021, 43(4): 58-62, 72. |
| CAI Lihua, LIAN Wenming, TAI Hongzhong, et al. Effect of film-uncovering or not during cotton growth period on the Verticillium wilt in Xinjiang[J]. Cotton Sciences, 2021, 43(4): 58-62, 72. | |
| [3] | 王珏. 棉花黄萎病发病成因与预防治理策略的经济效益[J]. 中国纤检, 2022,(7): 47-50. |
| WANG Jue. Occurrence characteristics and control strategies of cotton blight and Verticillium wilt in northern Xinjiang[J]. China Fiber Inspection, 2022,(7): 47-50. | |
| [4] |
蒲丹丹, 张亚林, 白红燕, 等. 内生真菌简青霉CEF-818对棉花黄萎病的防治效果及机理[J]. 棉花学报, 2022, 34(4): 313-324.
DOI |
| PU Dandan, ZHANG Yalin, BAI Hongyan, et al. Control effect and mechanism of endophytic fungus Penicillium simplicissimum CEF-818 on cotton Verticillium wilt[J]. Cotton Science, 2022, 34(4): 313-324. | |
| [5] | 白红燕. 枯草芽孢杆菌EBS03防治棉花黄萎病效果评测及培养条件优化[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2022. |
| BAI Hongyan. Evaluation on the effect of Bacillus subtilis EBS03 in controlling cotton Verticillium wilt and optimization of culture conditions[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| [6] |
白红燕, 冯自力, 冯鸿杰, 等. 48株枯草芽孢杆菌对棉花黄萎病防治效果评测[J]. 中国棉花, 2021, 48(12): 13-19.
DOI |
|
BAI Hongyan, FENG Zili, FENG Hongjie, et al. Evaluation of the control effect of 48 strains of Bacillus subtilis on cotton Verticillium wilt[J]. China Cotton, 2021, 48(12): 13-19.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 刘璐. 对节白蜡内生细菌YZU-SG146对棉花黄萎病生防作用机制的研究[D]. 荆州: 长江大学, 2021. |
| LIU Lu. Study on the biological control mechanism of endophytic bacteria YZU-SG146 against cotton Verticillium wilt[D]. Jingzhou: Yangtze University, 2021. | |
| [8] |
Zabihullah Sherzad, 杨娜, 张静, 等. 棉花内生解淀粉芽孢杆菌489-2-2对棉花黄萎病的防效研究[J]. 核农学报, 2021, 35(1): 41-48.
DOI |
| SHERZAD Z, YANG Na, ZHANG Jing, et al. Study on the control effect of endophytic Bacillus amyloliquefaciens 489-2-2 on Verticillium wilt of cotton[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 35(1): 41-48. | |
| [9] | 邱媛媛. 两株芽孢杆菌提高棉花黄萎病抗性与促生作用的机制的研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2021. |
| QIU Yuanyuan. Study on the mechanism of two Bacillus strains improving cotton Verticillium wilt resistance and promoting growth[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [10] |
Berg G, Fritze A, Roskot N, et al. Evaluation of potential biocontrol rhizobacteria from different host plants of Verticillium dahliae Kleb[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 2001, 91(6): 963-971.
PMID |
| [11] | Bubici G, Marsico A D, D’Amico M, et al. Evaluation of Streptomyces spp. for the biological control of corky root of tomato and Verticillium wilt of eggplant[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2013, 72: 128-134. |
| [12] |
Han Q, Wu F L, Wang X N, et al. The bacterial lipopeptide iturins induce Verticillium dahliae cell death by affecting fungal signalling pathways and mediate plant defence responses involved in pathogen-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity[J]. Environmental Microbiology, 2015, 17(4): 1166-1188.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Li Z F, Wang L F, Feng Z L, et al. Diversity of endophytic fungi from different Verticillium-wilt-resistant Gossypium hirsutum and evaluation of antifungal activity against Verticillium dahliae in vitro[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2014, 24(9): 1149-1161. |
| [14] |
王静怡, 佐长赓, 牛新湘, 等. 生防菌在棉田土壤中定殖数量与防病作用相关性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(1): 178-184.
DOI |
|
WANG Jingyi, ZUO Changgeng, NIU Xinxiang, et al. The quantity and activity of biocontrol bacteria in cotton field soil and the correlation of disease prevention[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(1): 178-184.
DOI |
|
| [15] | 张国漪, 丁传雨, 任丽轩, 等. 菌根真菌和死谷芽孢杆菌生物有机肥对连作棉花黄萎病的协同抑制[J]. 南京农业大学学报, 2012, 35(6): 68-74. |
| ZHANG Guoyi, DING Chuanyu, REN Lixuan, et al. The synergetic inhibition effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi cooperated Bacillus vallismortis organic fertilizer on cotton Verticillium wilt[J]. Journal of Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012, 35(6): 68-74. | |
| [16] | 朱荷琴, 李志芳, 冯自力, 等. 我国棉花黄萎病研究十年回顾及展望[J]. 棉花学报, 2017, 29(S1): 37-50. |
| ZHU Heqin, LI Zhifang, FENG Zili, et al. Overview of cotton Verticillium wilt research over the past decade in China and its prospect in future[J]. Cotton Science, 2017, 29(S1): 37-50. | |
| [17] |
刘海洋, 王伟, 张仁福, 等. 利用生防菌防治棉花黄萎病效果的制约因素[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 155-161.
DOI |
|
LIU Haiyang, WANG Wei, ZHANG Renfu, et al. A brief analysis of the factors restricting the effectiveness of controlling cotton Verticillium wilt by using biocontrol bacteria in the field[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 155-161.
DOI |
|
| [18] | 张广杰. 虫菌复合技术转化棉秆还田对棉花生长发育及黄萎病发生的影响[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆农业大学, 2022. |
| ZHANG Guangjie. Effect of insect-fungus compound technology on cotton growth and Verticillium wilt[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2022. | |
| [19] | 张广杰, 王倩, 刘玉升. 白星花金龟人为条件生物学与应用潜力[J]. 环境昆虫学报, 2020, 42(2): 257-266. |
| ZHANG Guangjie, WANG Qian, LIU Yusheng. Biology under artificial condition and utilization potential of Potosia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Cetoniidea)[J]. Journal of Environmental Entomology, 2020, 42(2): 257-266. | |
| [20] | Zhang G J, Meng Z, Ge H, et al. Investigating Verticillium wilt occurrence in cotton and its risk management by the direct return of cotton plants infected with Verticillium dahliae to the field[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2023, 14: 1220921. |
| [21] | Zhang G J, Xu Y S, Zhang S, et al. Transformation capability optimization and product application potential of proteatia brevitarsis (Coleoptera: Cetoniidae) larvae on cotton stalks[J]. Insects, 2022, 13(12): 1083. |
| [22] | 李俊, 徐艳琪, 刘肖肖. 枯草芽孢杆菌FXX-3对棉花的促生作用[J]. 农业开发与装备, 2017,(8): 100-101. |
| LI Jun, XU Yanqi, LIU Xiaoxiao. Effect of Bacillus subtilis FXX-3 on cotton growth promotion[J]. Agricultural Development & Equipments, 2017,(8): 100-101. | |
| [23] | 史长旭, 张广杰, 徐业山, 等. 白星花金龟虫粪砂混配基质对黄瓜和辣椒育苗效果的影响[J]. 新疆农业大学学报, 2021, 44(6): 443-447. |
| SHI Changxu, ZHANG Guangjie, XU Yeshan, et al. Effects of Protaetia brevitarsis lewis larvae dung-sand mixture matrix on cucumber and pepper seedling[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Agricultural University, 2021, 44(6): 443-447. | |
| [24] |
李红丽, 李清飞, 郭夏丽, 等. 调节土壤微生态防治烟草青枯病[J]. 河南农业科学, 2006, 35(2): 57-60.
DOI |
| LI Hongli, LI Qingfei, GUO Xiali, et al. A report of investigating and studying tobacco infectious diseases of 16 main tobacco producing provinces(regions)in China[J]. Journal of Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2006, 35(2): 57-60. | |
| [25] | 陈英化, 李爱霞, 冯丽娜, 等. 棉花黄萎病内生拮抗细菌L-4-2的鉴定及定殖[J]. 西北农业学报, 2012, 21(2): 68-71. |
| CHEN Yinghua, LI Aixia, FENG Lina, et al. Identification and colonization of an antagonistic endophytic bacterium L-4-2 against cotton Verticillium wilt[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica, 2012, 21(2): 68-71. | |
| [26] | 匡志豪, 王典, 云菲, 等. 哈茨木霉施用方式对烟草生长、黑胫病防治及诱导抗性的影响[J]. 山东农业科学, 2023, 55(2): 119-126. |
| KUANG Zhihao, WANG Dian, YUN Fei, et al. Effect of Trichoderma harzianum application method on tobacco growth, black shank control and inducing resistance[J]. Shandong Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 55(2): 119-126. |
| [1] | 袁梓涵, 赵雯慧, 王小武, 吐尔逊·阿合买提, 丁新华, 张帅, 付开赟, 贾尊尊, 郭文超. 玉米茎腐病生防菌的筛选及生防效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(S1): 35-48. |
| [2] | 耿松毅, 孙洪涛, 赵伟琦, 王梅, 芦屹, 马荣. 苹果树腐烂病发生及新型防治药剂筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1461-1467. |
| [3] | 曹竹君, 张振宇, 康宁, 赵倩, 胡红英. 新疆西天山野果林杏鬃球蚧寄生蜂资源调查[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 971-983. |
| [4] | 文霞, 田立超, 高桂珍. 四斑月瓢虫对紫薇长斑蚜的捕食功能反应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2266-2272. |
| [5] | 杨海涛, 席欧彦, 赵倩, 曹竹君, 胡红英. 朝鲜球坚蚧成虫寄生蜂资源调查[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2273-2280. |
| [6] | 阳妮, 玛依拉·玉素音, 杨延龙, 李春平, 张大伟, 徐海江, 赖成霞. 黄萎病枯斑型与黄化型病症棉花叶片的植物挥发物对比[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1975-1986. |
| [7] | 李艳兵, 郭小虎, 努尔什瓦克·阿达力别克, 帕提玛·乌木尔汗, 马德英. 人工助迁多异瓢虫和化防2种模式对棉蚜的防效及天敌种群动态影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1173-1179. |
| [8] | 高宇洁, 詹发强, 陈澄, 包慧芳, 杨蓉, 王宁, 侯新强, 侯敏, 史应武, 龙宣杞. 黑曲霉拮抗菌Xenorhabdus bovienii445筛选、鉴定及发酵优化[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1203-1215. |
| [9] | 赵莹莹, 张军高, 李进, 梁晶, 高翔宇, 顾爱星, 雷斌. 枯草芽孢杆菌KXZ-33与化学药剂协同防控棉花枯萎病的效果评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(5): 1216-1222. |
| [10] | 刘海洋, 王伟, 张仁福, 温切木·阿布列孜, 姚举. 利用生防菌防治棉花黄萎病效果的制约因素[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 155-161. |
| [11] | 刘海洋, 王伟, 张仁福, 温切木·阿布列孜, 姚举. 不同因素影响下棉田土壤中大丽轮枝菌微菌核的数量特征[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(3): 522-531. |
| [12] | 赖成霞, 玛依拉·玉素音, 石必显, 李春平, 姜梦竹, 郑子漂, 杨栋. 助剂激健在防治棉花黄萎病中的效果[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2220-2227. |
| [13] | 石志钰, 裴雅琨, 朱玉涛, 贾玉姣, 胡晓倩, 侯士聪, 侯玉霞. 基于数字图像棉花黄萎病诊断与防治的管理远程监测[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(6): 1166-1174. |
| [14] | 杜鹏程, 刘海洋, 张军高, 李进, 周小云, 刘梦丽, 雷斌, 郭庆元. 棉花苗期根腐类病害生防细菌的筛选与鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(4): 686-693. |
| [15] | 朱丹, 鲁佳雄, 钟问, 李勤, 郭文超, 胡红英. 新疆马铃薯叶甲寄生蜂天敌资源调查研究[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(12): 2248-2254. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||