

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (4): 1011-1020.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.04.026
• 植物保护·微生物·农业装备工程与机械化 • 上一篇 下一篇
柏晓玉1,2( ), 朱丽英3, 包慧芳2, 江凌4, 朱静2, 顾美英2, 朱艳蕾1, 张志东1,2(
), 朱丽英3, 包慧芳2, 江凌4, 朱静2, 顾美英2, 朱艳蕾1, 张志东1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2023-08-22
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-05-31
通信作者:
张志东(1977-),男,新疆乌鲁木齐人,研究员,博士,硕士生/博士生导师,研究方向为特殊环境微生物及益生菌资源挖掘与应用,(E-mail)zhangzheedong@qq.com作者简介:柏晓玉(1997-),女,山东益都人,硕士研究生,研究方向为微生物生态(E-mail)1306439822@qq.com
基金资助:
BAI Xiaoyu1,2( ), ZHU Liying3, BAO Huifang2, JIANG Ling4, ZHU Jing2, GU Meiying2, Zhu Yanlei1, ZHANG Zhidong1,2(
), ZHU Liying3, BAO Huifang2, JIANG Ling4, ZHU Jing2, GU Meiying2, Zhu Yanlei1, ZHANG Zhidong1,2( )
)
Received:2023-08-22
Published:2024-04-20
Online:2024-05-31
Correspondence author:
ZHANG Zhidong(1977-),male, from Urumqi,Xinjiang,master, researcher, research direction: Special environmental microorganisms and food Microbiology,(E-mail)zhangzheedong@qq.comSupported by:摘要:
【目的】挖掘干旱区放线菌天然产物代谢潜力,筛选群体感应抑制活性的产物,研究其对梨火疫病原菌毒力因子代谢能力的影响。【方法】利用紫色杆菌(Chromobacterium violaceum 026, CV026)群体感应抑制活性筛选模型,对新疆库木塔格沙漠周边干旱地区土壤中分离的放线菌进行发酵,采用牛津杯法对其发酵液进行活性筛选;鉴定群体感应抑制活性菌株及验证其发酵液提取和活性,分析粗提液对欧文氏菌毒力因子代谢影响,并采用液质联用(liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry, LC-MS)方法检测菌株代谢产物活性物质,挑选相似结构化合物验证群体感应抑制活性。【结果】获得一株具有明显群体感应抑制活性菌株K-9,其与Streptomyces rubradiris strain NBRC 14000T相似性达到99.72%。该菌发酵粗提液具有明显的群体感应抑制活性,可有效降低紫色杆菌CV026产紫色素和梨火疫病原菌的游动能力,并对梨火疫病原菌生物膜、胞外多糖和胞外酶等毒力因子产生具有显著抑制活性,呈明显的浓度依赖性;从链霉菌K-9粗提液中得到635种化合物,苯基丙烯酸、4-羟基-3甲氧基苯甲酸等5种明显群体感应抑制化合物。【结论】干旱区放线菌K-9为Streptomyces rubradiris,其发酵代谢产物具有明显群体感应抑制活性,能显著抑制欧文氏菌毒力因子的产生,并发现了多种新型的群体感应抑制活性化合物。
中图分类号:
柏晓玉, 朱丽英, 包慧芳, 江凌, 朱静, 顾美英, 朱艳蕾, 张志东. 一株群体感应抑制活性链霉菌的筛选鉴定及其毒力因子代谢能力分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 1011-1020.
BAI Xiaoyu, ZHU Liying, BAO Huifang, JIANG Ling, ZHU Jing, GU Meiying, Zhu Yanlei, ZHANG Zhidong. Screening and identification of a Streptomyces strain with quorum sensing inhibitory activity and effect of the crude extracts on virulence factors of Erwinia amylovora[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(4): 1011-1020.
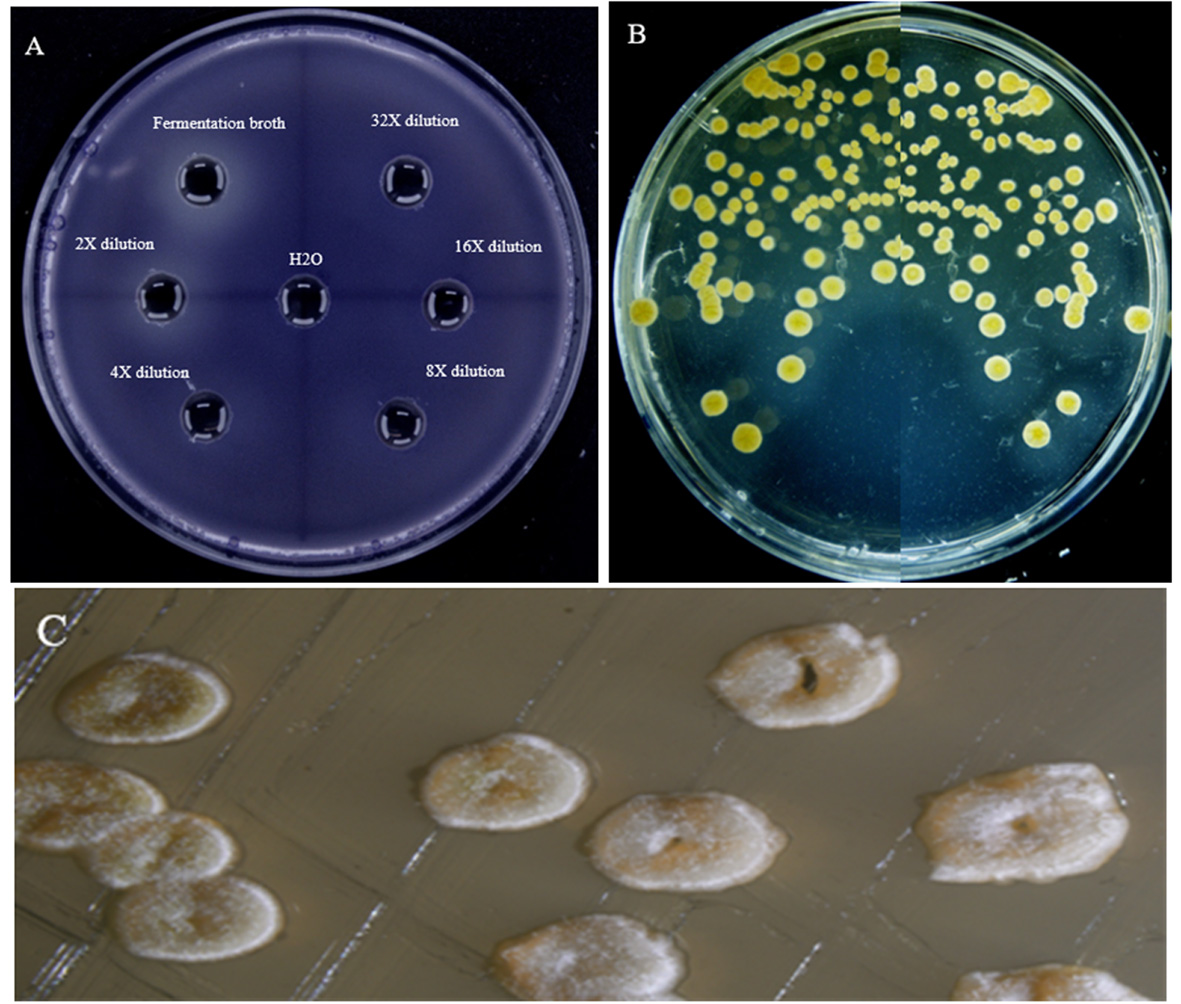
图1 菌株K-9的筛选及菌落形态 注:A: 菌株K-9不同稀释梯度的发酵液对紫色杆菌CV026紫色色素的抑制作用; B: 菌株K-9菌落形态;C: 菌株K-9菌落显微形态
Fig.1 Screening and morphological characteristics of strain K-9 Note:A: Inhibition of violacein of Chromobacterium violaceum CV026 by fermentation broth of strain K-9 with different dilution gradients; B: Colony morphology of strain K-9; C: Morphological characteristics of the colony under stereomicroscope
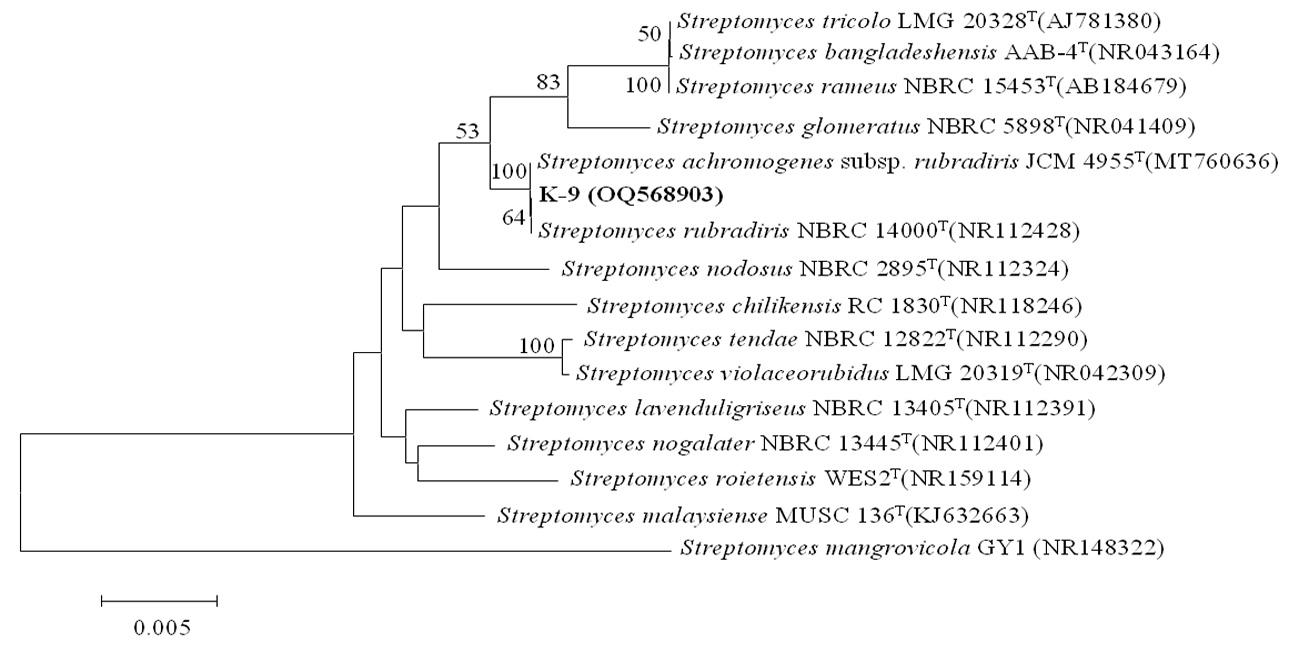
图2 基于菌株 K-9及相关近源菌株16S rRNA 基因序列的NJ系统进化树 注:Bootstrap检验次数为1 000次;分支结点上的数字为自举值(显示≥50%的数值);标尺为0.01
Fig.2 Neighbor-Joining tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the phylogenetic relationships among K-9 strain and other related strains Note:Bootstrap values (≥50%) based on 1,000 replications are shown at branch nodes. Bar 0.01 sequence variation
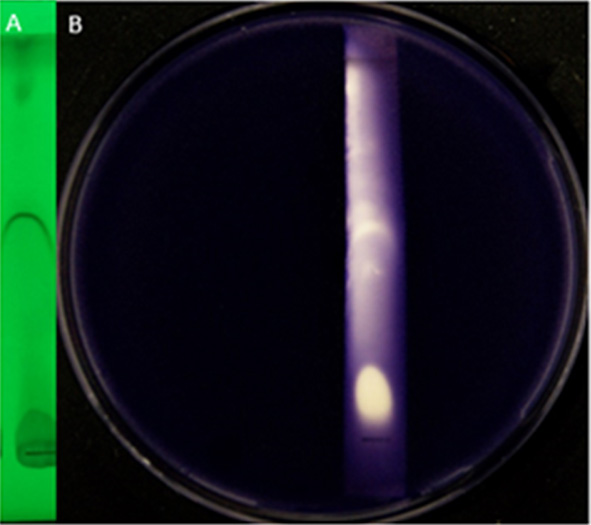
图3 粗提液TLC图及活性成分生物显影 注:A:粗提物层析在254 nm波长下显影结果;B:粗提物中活性成分的生物自显影
Fig.3 Analysis of crude extracts of strain K-9 by bioautography of active ingredients and TLC Note:A: TLC of crude extract on 254 nm; B: Bioautography of active components in crude extract
| 粗提液浓度 Concentration of crude extracts (mg/mL) | 紫色杆菌026 Chromobacterium violaceum 026 | 梨火疫病原菌 Erwinia amylovora |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | - | - |
| 5 | - | W |
| 2.5 | W | + |
| 1.25 | + | + |
| 0.6 | + | + |
| 0.3 | + | + |
| 0.15 | + | + |
表1 不同浓度粗提液下菌株生长变化
Tab.1 Effect of crude extracts with different concentrations on the growth of strains
| 粗提液浓度 Concentration of crude extracts (mg/mL) | 紫色杆菌026 Chromobacterium violaceum 026 | 梨火疫病原菌 Erwinia amylovora |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | - | - |
| 5 | - | W |
| 2.5 | W | + |
| 1.25 | + | + |
| 0.6 | + | + |
| 0.3 | + | + |
| 0.15 | + | + |
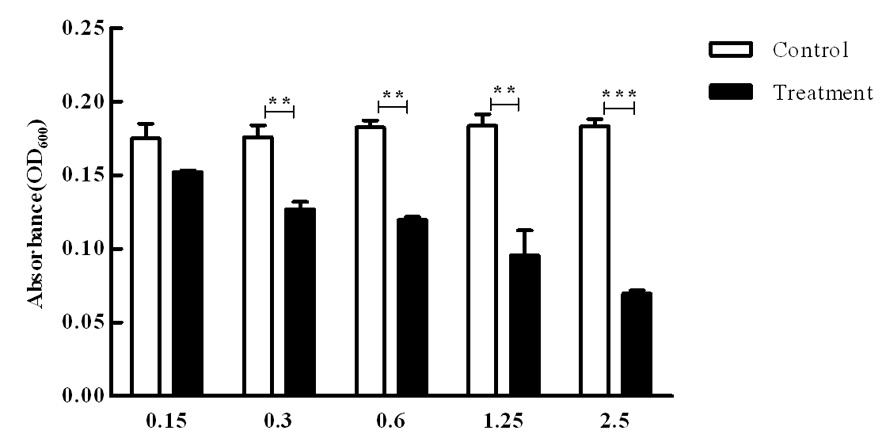
图4 不同浓度粗提液下紫色杆菌CV026紫色素产量变化 注:***:对照组和处理组差异极其显著(P<0.001);**对照组和处理组差异极显著(P<0.01),下同
Fig.4 Changes of crude extracts with different concentrations on violacein production of CV026 Note:***: means extremely significant difference between control and treatment (P<0.001); **:means highly significant difference between control and treatment (P<0. 01),the same as below
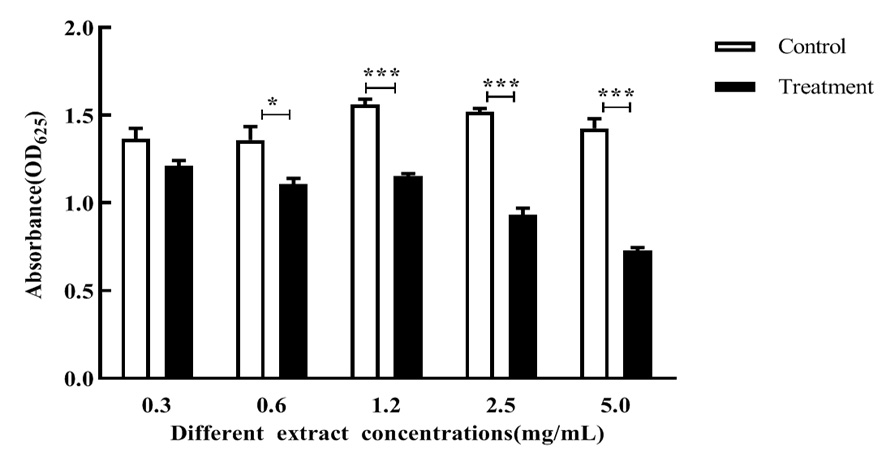
图6 不同浓度粗提液下胞外多糖产量的变化 注:*:对照组和处理组显著差异(P<0. 05);无*指两组无显著差异,下同
Fig.6 Changes of crude extracts with different concentrations on rhamnolipid production by Erwinia amylovora Note:* :means significant difference between control and treatment(P<0. 05); No * :means significant difference between two groups,the same as below
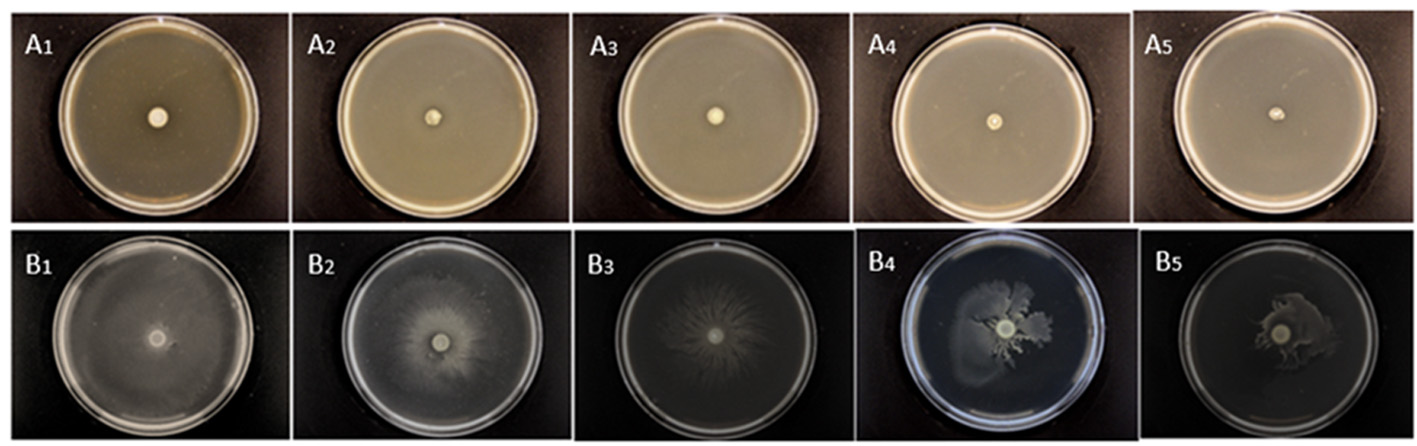
图8 不同浓度粗提液下梨火疫病原菌群集和泳动性变化 注:A: 梨火疫病原菌群集;B:梨火疫病原菌泳动。下标1~5分别为阳性对照,0.6、1.2、2.5、5 mg/mL 粗提液
Fig.8 Changes of different crude extracts on swarming and swimming of Erwinia amylovora Note:A: Erwinia amylovora swarming; B: Erwinia amylovora swimming. Subscripts 1-5 were positive controls, 0.6, 1.2, 2.5, and 5.0 mg/mL crude extract
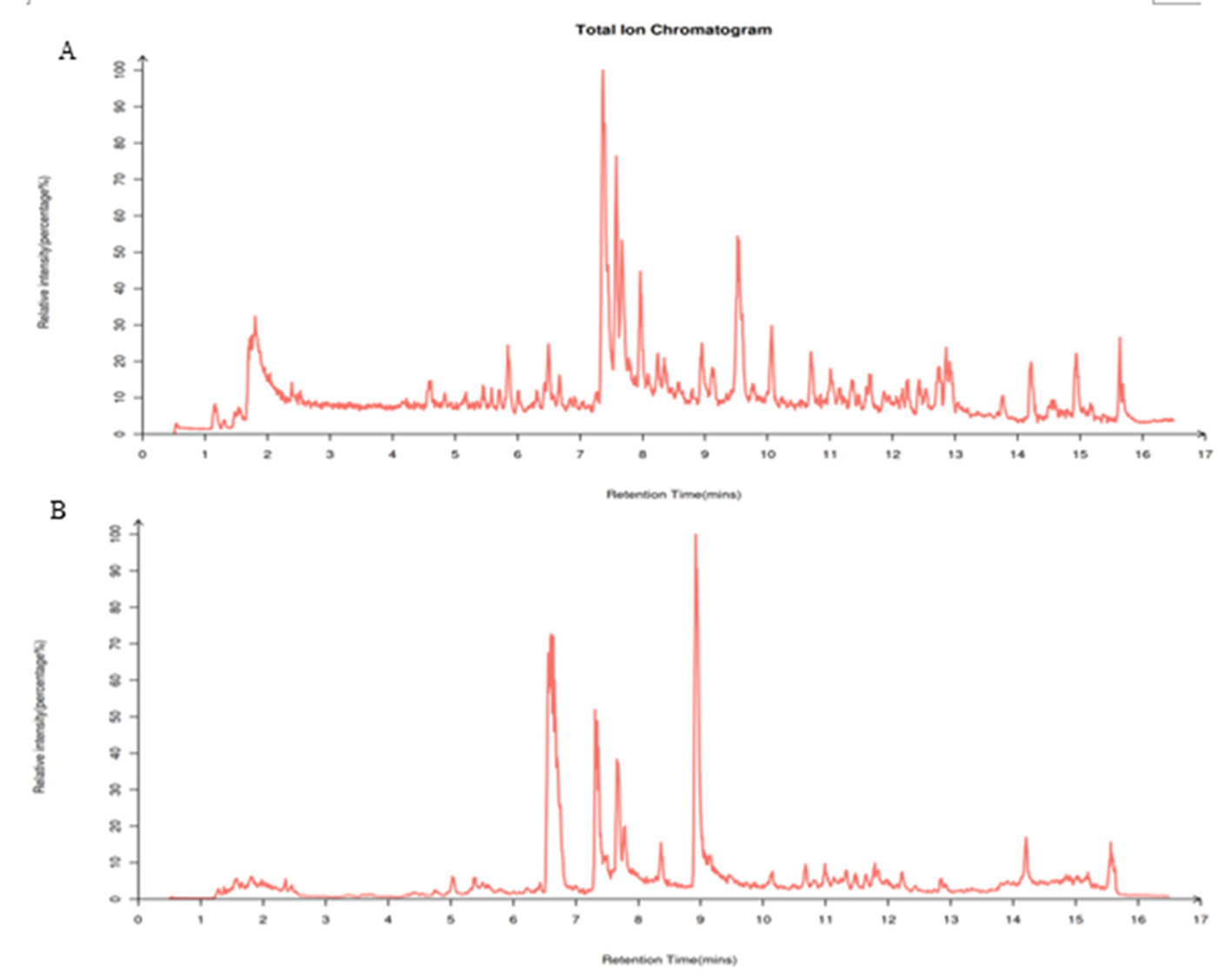
图9 菌株K-9粗提液总离子流 注:A:粗提液正离子流;B:粗提液负离子流
Fig.9 Total ionic chromatographic fingerprints of crude extract of strain K-9 Note:A: positive ionic chromatographic fingerprints of crude extract; B: negative ionic chromatographic fingerprints of crude extract
| 化合物 Compounds | 抑菌面积 Inhibition area (cm2) | 紫色素透明圈 Violacein inhibition area (cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| 苯基丙烯酸 Trans-Cinnamic acid | - | 4.15 |
| 4-羟基-3甲氧基苯甲酸 Vanillic acid | - | 3.14 |
| 吡咯-2-羧酸 Pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid | 0.2 | 1.57 |
| 3,4-二羟苯基丙酸 3,4-Dihydroxyhydro cinnamic acid | 0.2 | 1.54 |
| DL-4-羟基苯乳酸 DL-4-Hydroxyphenyllactic acid | - | 0.79 |
| 哌啶酸 Pipecolic acid | - | - |
| 甘氨酸三甲胺内盐 Betaine | - | - |
| 4-羟基-3,5-二甲 氧基苯甲酸 Syringic acid | - | - |
表2 8种化合物的抑菌和群体感应抑制活性检测
Tab.2 Detection of Inhibition and Quorum sensing inhibitory activity of 8 compounds
| 化合物 Compounds | 抑菌面积 Inhibition area (cm2) | 紫色素透明圈 Violacein inhibition area (cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| 苯基丙烯酸 Trans-Cinnamic acid | - | 4.15 |
| 4-羟基-3甲氧基苯甲酸 Vanillic acid | - | 3.14 |
| 吡咯-2-羧酸 Pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid | 0.2 | 1.57 |
| 3,4-二羟苯基丙酸 3,4-Dihydroxyhydro cinnamic acid | 0.2 | 1.54 |
| DL-4-羟基苯乳酸 DL-4-Hydroxyphenyllactic acid | - | 0.79 |
| 哌啶酸 Pipecolic acid | - | - |
| 甘氨酸三甲胺内盐 Betaine | - | - |
| 4-羟基-3,5-二甲 氧基苯甲酸 Syringic acid | - | - |
| [1] |
Kalia V C. Quorum sensing inhibitors: an overview[J]. Biotechnology Advances, 2013, 31(2): 224-245.
DOI PMID |
| [2] |
Papenfort K, Bassler B L. Quorum sensing signal-response systems in Gram-negative bacteria[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2016, 14(9): 576-588.
DOI PMID |
| [3] |
Liu L, Yan Y, Feng L, et al. Quorum sensing asaI mutants affect spoilage phenotypes, motility, and biofilm formation in a marine fish isolate of Aeromonas salmonicida[J]. Food Microbiology, 2018, 76: 40-51.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | 周静煌, 严准, 高春生, 等. 群体感应抑制及其植物病害防控应用研究进展[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(12): 2197-2203. |
| ZHOU Jinghuang, YAN Zhun, GAO Chunsheng, et al. Quorum sensing inhibition and its application in plant disease control: a review[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2017, 48(12): 2197-2203. | |
| [5] |
Defoirdt T. Quorum-sensing systems as targets for antivirulence therapy[J]. Trends in Microbiology, 2018, 26(4): 313-328.
DOI PMID |
| [6] | 鲁晏宏, 郝金辉, 罗明, 等. 梨火疫病拮抗菌筛选及温室防效测定[J]. 微生物学通报, 2021, 48(10): 3690-3699. |
| LU Yanhong, HAO Jinhui, LUO Ming, et al. Screening of antagonistic bacteria against Erwinia amylovora and its control effect in greenhouse[J]. Microbiology China, 2021, 48(10): 3690-3699. | |
| [7] | 李雅华, 咸洪泉, 李树文, 等. 拮抗胡萝卜软腐欧文氏杆菌的放线菌的分离和筛选[J]. 青岛农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 26(2): 143-146. |
| LI Yahua, XIAN Hongquan, LI Shuwen, et al. Isolating and screening of antagonistic Actinomyces to erwonia carotovora var. carotovora[J]. Journal of Qingdao Agricultural University (Natural Science), 2009, 26(2): 143-146. | |
| [8] |
Barnard A M L, Salmond G P C. Quorum sensing in Erwinia species[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2007, 387(2): 415-423.
PMID |
| [9] | 高岩. 梨火疫病菌群体感应系统的初步研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2006. |
| GAO Yan. A Primary Study of Quorum Sensing in Erwinia Amylovora[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2006. | |
| [10] |
Kang J E, Han J W, Jeon B J, et al. Efficacies of quorum sensing inhibitors, piericidin A and glucopiericidin A, produced by Streptomyces xanthocidicus KPP01532 for the control of potato soft rot caused by Erwinia carotovora subsp. atroseptica[J]. Microbiological Research, 2016, 184: 32-41.
DOI PMID |
| [11] | Dong Y H, Wang L H, Xu J L, et al. Quenching quorum-sensing-dependent bacterial infection by an N-acyl homoserine lactonase[J]. Nature, 2001, 411(6839): 813-817. |
| [12] | Abdulla Y, Al-Mahdi, Saeed M, et al. Isolation and Identification of Bioactive Actinomycete Isolates from Yemen Soils[J]. Thamar University Journal of Natural & Applied Sciences, 2020, 4(2073-0764): 113-123. |
| [13] |
Rehman Z U, Leiknes T. Quorum-quenching bacteria isolated from red sea sediments reduce biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1354.
DOI PMID |
| [14] |
Martinelli D, Grossmann G, Séquin U, et al. Effects of natural and chemically synthesized furanones on quorum sensing in Chromobacterium violaceum[J]. BMC Microbiology, 2004, 4: 25.
PMID |
| [15] | 丁晓艳, 赵英博, 王伟杰, 等. 薄层色谱-生物自显影技术在活性物质筛选中的应用[J]. 实用药物与临床, 2017, 20(10): 1220-1224. |
| DING Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yingbo, WANG Weijie, et al. Application of TLC-bioautography in active components screening[J]. Practical Pharmacy and Clinical Remedies, 2017, 20(10): 1220-1224. | |
| [16] |
Choo J H, Rukayadi Y, Hwang J K. Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing by vanilla extract[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2006, 42(6): 637-641.
DOI PMID |
| [17] | Zhang J, Rui X, Wang L, et al. Polyphenolic extract from Rosa rugosa tea inhibits bacterial quorum sensing and biofilm formation[J]. Food Control, 2014, 42: 125-131. |
| [18] | 于福浩, 娄在祥, 王洪新, 等. 咖啡酸对铜绿假单胞菌群体感应的抑制及毒力因子降低的研究[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2019, 38(6): 56-63. |
| YU Fuhao, LOU Zaixiang, WANG Hongxin, et al. Effect of caffeic acid on quorum sensing and virulence factors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2019, 38(6): 56-63. | |
| [19] | 刘佳宜, 李婷婷, 励建荣, 等. 乙基麦芽酚对杀鲑气单胞菌群体感应及腐败活性的抑制作用[J]. 食品科学, 2021, 42(17): 27-33. |
| LIU Jiayi, LI Tingting, LI Jianrong, et al. Inhibitory effect of ethyl maltol on quorum sensing and spoilage capacity of Aeromonas salmonicida[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(17): 27-33. | |
| [20] |
Zelena E, Dunn W B, Broadhurst D, et al. Development of a robust and repeatable UPLC-MS method for the long-term metabolomic study of human serum[J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2009, 81(4): 1357-1364.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Want E J, Masson P, Michopoulos F, et al. Global metabolic profiling of animal and human tissues via UPLC-MS[J]. Nature Protocols, 2013, 8(1): 17-32.
DOI PMID |
| [22] |
Nouioui I, Carro L, García-López M, et al. Genome-based taxonomic classification of the Phylum Actinobacteria[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 2007.
DOI PMID |
| [23] |
Sun Y, Shi Y L, Wang H, et al. Diversity of bacteria and the characteristics of Actinobacteria community structure in badain jaran desert and tengger desert of China[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2018, 9: 1068.
DOI PMID |
| [24] |
周恒, 姜芸, 许叶祥, 等. 一株海洋微小链霉菌群体感应抑制活性及培养条件的研究[J]. 生物技术通报, 2019, 35(10): 137-143.
DOI |
|
ZHOU Heng, JIANG Yun, XU Yexiang, et al. Research on quorum sensing inhibitory activity and culture condition of a marine Streptomyces parvulus[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2019, 35(10): 137-143.
DOI |
|
| [25] | Hassan R, Shaaban M I, Abdel Bar F M, et al. Quorum sensing inhibiting activity of Streptomyces coelicoflavus isolated from soil[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2016, 7: 659. |
| [26] | Ooka K, Fukumoto A, Yamanaka T, et al. Piericidins, novel quorum-sensing inhibitors against Chromobacterium violaceum CV026, from Streptomyces sp. TOHO-Y209 and TOHO-O348[J]. Open Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2013, 3(4): 93-99. |
| [27] | Ishaque N M, Burgsdorf I, Limlingan Malit J J, et al. Isolation, genomic and metabolomic characterization of Streptomyces tendae VITAKN with quorum sensing inhibitory activity from southern India[J]. Microorganisms, 2020, 8(1): 121. |
| [28] | Velasco-Bucheli R, Hormigo D, Fernández-Lucas J, et al. Penicillin acylase from Streptomyces lavendulae and aculeacin A acylase from Actinoplanes utahensis: two versatile enzymes as useful tools for quorum quenching processes[J]. Catalysts, 2020, 10(7): 730. |
| [29] |
Kamarudheen N, Rao K V B. Fatty acyl compounds from marine Streptomyces griseoincarnatus strain HK12 against two major bio-film forming nosocomial pathogens; an in vitro and in silico approach[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2019, 127: 121-130.
DOI PMID |
| [30] |
Molina L, Constantinescu F, Michel L, et al. Degradation of pathogen quorum-sensing molecules by soil bacteria: a preventive and curative biological control mechanism[J]. FEMS Microbiology Ecology, 2003, 45(1): 71-81.
DOI PMID |
| [31] | Wang W Z, Morohoshi T, Ikenoya M, et al. AiiM, a novel class of N-acylhomoserine lactonase from the leaf-associated bacterium Microbacterium testaceum[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2010, 76(8): 2524-2530. |
| [32] | 曾芝瑞. 从中药中虚拟筛选和鉴定细菌群体感应抑制剂[D]. 广州: 中山大学, 2009. |
| ZENG Zhirui. Virtual screening and identification of bacterial quorum sensing inhibitors from traditional Chinese medicine[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University, 2009. | |
| [33] | 曾利, 蔡杨, 凌保东. 中药单体对细菌群体感应系统的影响[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志, 2021, 35(10): 754. |
| ZENG Li, CAI Yang, LING Baodong. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine monomer on bacterial quorum sensing system[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology, 2021, 35(10): 754. |
| [1] | 史应武, 牛新湘, 杨红梅, 楚敏, 包慧芳, 王宁, 詹发强, 林青, 杨蓉, 龙宣杞, 娄恺. 4种药剂对梨火疫病防病效果及库尔勒香梨产量与品质的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(6): 1432-1440. |
| [2] | 陈伟, 段红雁, 李紫英, 郝海婷, 王兰. 不同类型杀菌剂对解淀粉欧文氏菌室内毒力测定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(9): 1723-1728. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||