

新疆农业科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (6): 1496-1506.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.06.022
李馨妍1( ), 黄天宇2,3, 王志强2, 周洪旭1, 王冰2(
), 黄天宇2,3, 王志强2, 周洪旭1, 王冰2( ), 王桂荣2,4(
), 王桂荣2,4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-30
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-07-29
通信作者:
王桂荣(1972-),男,安徽宿松人,研究员,研究方向为化学生态学,(E-mail)wangguirong@caas.cn;作者简介:李馨妍(1999-),女,河北唐山人,硕士研究生,研究方向为化学生态学,(E-mail)lixinyan@stu.qau.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Xinyan1( ), HUANG Tianyu2,3, WANG Zhiqiang2, ZHOU Hongxu1, WANG Bing2(
), HUANG Tianyu2,3, WANG Zhiqiang2, ZHOU Hongxu1, WANG Bing2( ), WANG Guirong2,4(
), WANG Guirong2,4( )
)
Received:2024-10-30
Published:2025-06-20
Online:2025-07-29
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】蚜虫腹管是分泌防御性化学物质的重要组织器官,测序与分析腹管转录组,为蚜虫报警信息素合成与释放相关基因的鉴定提供分子基础。【方法】利用Illumina NoveSeq 6000测序平台对豌豆修尾蚜Megoura crassicauda腹管和残体进行转录组测序与比较分析,利用差异基因分析(Differential Expression Analysis,DEG)鉴定参与报警信息素合成与释放相关的候选基因,通过实时荧光定量PCR(Real-time Quantitative PCR,RT-qPCR)技术验证这些基因的表达模式。【结果】共鉴定出2 156个在腹管和残体之间存在显著差异表达的基因(表达差异≥2倍)。分析报警信息素合成相关的细胞色素P450(cytochrome P450 monooxygenase,CYP450)和萜烯合成酶(terpene synthase,TPS)基因家族。其中,3个CYP450s(McraCYP380C、McraCYP4CK1和McraCYP315A1)在腹管中的表达水平显著高于残体。而鉴定到的2个异戊烯基二磷酸合成酶(isoprenyl diphosphate synthase,IDS)基因,即法尼基焦磷酸合酶(farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase,FPPS)和香叶基焦磷酸合酶(geranyl pyrophosphate synthase,GPPS),在组织间的表达水平无显著差异。此外,分析报警信息素释放运输相关的潜在基因,鉴定到2个化学感觉蛋白(chemosensory proteins,CSP)基因在腹管高表达。McraCYP380C、McraCYP4CK1、McraCYP315A1以及McraCSP7基因在腹管中的表达水平显著上调。【结论】鉴定并分析了豌豆修尾蚜M. crassicauda腹管和残体转录组中的差异表达基因。
中图分类号:
李馨妍, 黄天宇, 王志强, 周洪旭, 王冰, 王桂荣. 豌豆修尾蚜报警信息素合成与释放相关基因的鉴定与分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(6): 1496-1506.
LI Xinyan, HUANG Tianyu, WANG Zhiqiang, ZHOU Hongxu, WANG Bing, WANG Guirong. Identification and analysis of genes related to the synthesis and release of alarm pheromone of Megoura crassicauda[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(6): 1496-1506.
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene Name | FPKM-平均值 FPKM-Mean | 对数2倍数变化 log2FoldChange | P-值 P-value | 调整后P-值 P-adj | 上/下调 Up/Down- Regulation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 残体 Residues | 腹管 Cornicles | ||||||
| MSTRG.2087.1 | McraCYP380C | 147.453 254 9 | 2902.503 026 | 4.299 216 63 | 3.22E-05 | 0.000 605 208 | Up |
| MSTRG.6860.1 | McraCYP4CK1 | 5 487.062 689 | 11 026.344 26 | 1.007 029 351 | 1.04E-17 | 2.15E-15 | Up |
| MSTRG.8070.6 | McraCYP315A1 | 5.033 902 502 | 518.314 676 4 | 6.685 247 751 | 2.80E-06 | 7.50E-05 | Up |
| MSTRG.11084.1 | McraCSP7 | 2 779.474 791 | 9 640.821 777 | 1.794 432 213 | 2.84E-156 | 6.04E-152 | Up |
| MSTRG.465.1 | McraCSP8 | 4 680.169 046 | 18 727.825 01 | 2.000 517 384 | 1.69E-34 | 1.57E-31 | Up |
| MSTRG.11160.2 | McraGPPS | 5 219 | 2 429 | -0.449 135 111 | 0.066 290 039 | 0.066 290 039 | - |
| MSTRG.7985.1 | McraFPPS | 8 660.666 667 | 3 161.666 667 | -0.597964673 | 1.48E-07 | 5.42E-06 | - |
表1 候选基因在豌豆修尾蚜M. crassicauda腹管和残体中的表达水平
Tab.1 Expression levels of candidate genes in the cornicles and residues of M. crassicauda
| 基因ID Gene ID | 基因名称 Gene Name | FPKM-平均值 FPKM-Mean | 对数2倍数变化 log2FoldChange | P-值 P-value | 调整后P-值 P-adj | 上/下调 Up/Down- Regulation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 残体 Residues | 腹管 Cornicles | ||||||
| MSTRG.2087.1 | McraCYP380C | 147.453 254 9 | 2902.503 026 | 4.299 216 63 | 3.22E-05 | 0.000 605 208 | Up |
| MSTRG.6860.1 | McraCYP4CK1 | 5 487.062 689 | 11 026.344 26 | 1.007 029 351 | 1.04E-17 | 2.15E-15 | Up |
| MSTRG.8070.6 | McraCYP315A1 | 5.033 902 502 | 518.314 676 4 | 6.685 247 751 | 2.80E-06 | 7.50E-05 | Up |
| MSTRG.11084.1 | McraCSP7 | 2 779.474 791 | 9 640.821 777 | 1.794 432 213 | 2.84E-156 | 6.04E-152 | Up |
| MSTRG.465.1 | McraCSP8 | 4 680.169 046 | 18 727.825 01 | 2.000 517 384 | 1.69E-34 | 1.57E-31 | Up |
| MSTRG.11160.2 | McraGPPS | 5 219 | 2 429 | -0.449 135 111 | 0.066 290 039 | 0.066 290 039 | - |
| MSTRG.7985.1 | McraFPPS | 8 660.666 667 | 3 161.666 667 | -0.597964673 | 1.48E-07 | 5.42E-06 | - |
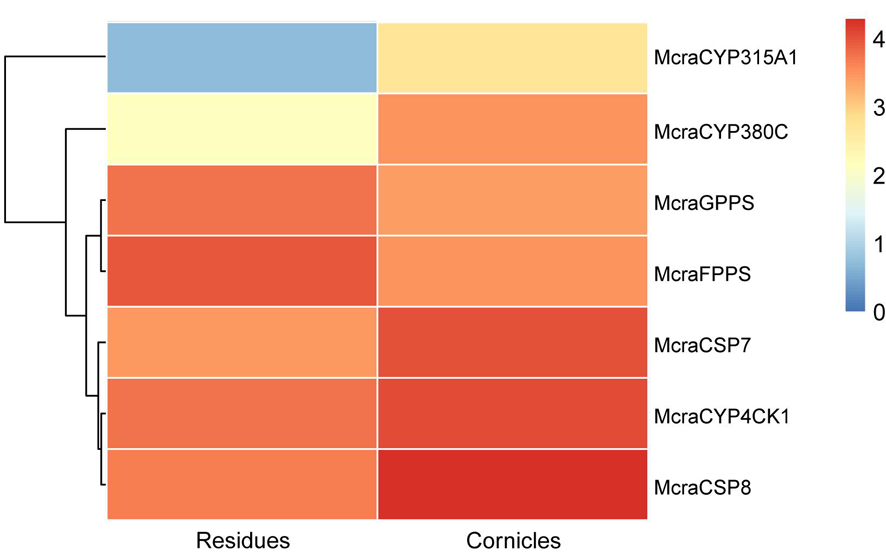
图3 豌豆修尾蚜M. crassicauda候选基因的表达谱 注: Mcra:豌豆修尾蚜;Agos:棉蚜;Apis:豌豆蚜;Pbam:竹茎扁蚜;CYP4CK1分支用红色背景突出显示,CYP315A1分支用橙色背景突出显示,CYP380C分支用蓝紫色背景突出显示
Fig.3 Expression profiles of candidate genes from M. crassicauda Notes: Mcra: M. crassicauda; Agos: A. gossypii; Apis: A. pisum; Pbam: P. bambucicola; The CYP4CK1 clade is highlighted with a red background, the CYP315A1 clade is marked with an orange background, and the CYP380C clade is indicated by a bluish purple background
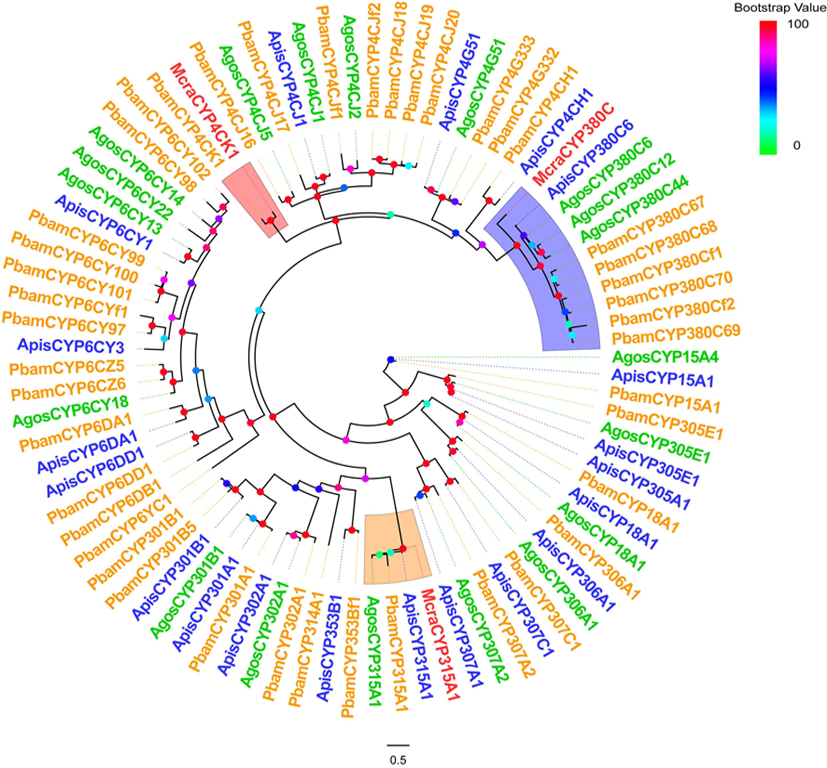
图4 4种蚜虫的CYP450s基因家族系统发育树 注:A. McraCYP380C与ApisCYP380C的氨基酸序列比对;B. McraCYP4CK1与PbamCYP4CK1的氨基酸序列比对;C. McraCYP315A与ApisCYP315A1的氨基酸序列比对;Mcra:豌豆修尾蚜;Apis:豌豆蚜;Pbam:竹茎扁蚜
Fig.4 Phylogenetic tree of the CYP450s gene family of the four aphid species Notes: A. Amino acid sequence alignment between McraCYP380C and ApisCYP380C; B. Amino acid sequence alignment between McraCYP4CK1 and PbamCYP4CK1; C. Amino acid sequence alignment between McraCYP315A and ApisCYP315A1; Mcra: M. crassicauda; Apis: A. pisum; Pbam: P. bambucicola
| 参考基因 Unigene reference | 基因名 Gene name | 长度 Length (nt) | 开放 阅读框 ORF (aa) | E值 E- value | 相似度 Identity (%) | 最佳BLASTx匹配 Blastx best hit (Reference/Name/Species) | 信号肽 SP (No.) | 跨膜 结构域 TMD (No.) | 全长 Full length | 组织 Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSTRG.2087.1 | McraCYP380C | 1548 | 515 | 0.0 | 74.37 | >XP_060860450.1 PREDICTED: cytochrome P450 4C1-like isoform X1 [Metopolophium dirhodum] | 0 | 1 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.6860.1 | McraCYP4CK1 | 1547 | 515 | 0.0 | 89.57 | >XP_060860450.1 PREDICTED: cytochrome P450 4C1-like [Metopolophium dirhodum] | 0 | 1 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.8070.6 | McraCYP315A1 | 1434 | 477 | 0.0 | 90.78 | >XP_001944183.2 PREDICTED: cytochrome P450 315a1, mitochondrial [Acyrthosiphon pisum] | 0 | 0 | YES | C |
| MSTRG.11084.1 | McraCSP7 | 468 | 155 | 1e-109 | 100.00 | >ULF48248.1 PREDICTED: chemosensory protein 7 (CSP7) mRNA [Acyrthosiphon pisum] | 0 | 0 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.465.1 | McraCSP8 | 219 | 72 | 4e-27 | 100.00 | >ULF48249.1 PREDICTED: chemosensory protein 8 (CSP8) mRNA [Acyrthosiphon pisum] | - | - | 3’ | C&R |
| MSTRG.11160.2 | McraGPPS | 930 | 309 | 0.0 | 100.00 | >QUH22249.1 PREDICTED: geranyl pyrophosphate synthase mRNA [Megoura viciae] | 0 | 0 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.7985.1 | McraFPPS | 1185 | 394 | 0.0 | 98.98 | >AAY33489.2 PREDICTED: putative mitochondrial isoprenyl diphosphate synthase precursor, mRNA [Megoura viciae] | 0 | 0 | YES | C&R |
表2 候选基因的注释信息
Tab.2 Annotated information of candidate genes
| 参考基因 Unigene reference | 基因名 Gene name | 长度 Length (nt) | 开放 阅读框 ORF (aa) | E值 E- value | 相似度 Identity (%) | 最佳BLASTx匹配 Blastx best hit (Reference/Name/Species) | 信号肽 SP (No.) | 跨膜 结构域 TMD (No.) | 全长 Full length | 组织 Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSTRG.2087.1 | McraCYP380C | 1548 | 515 | 0.0 | 74.37 | >XP_060860450.1 PREDICTED: cytochrome P450 4C1-like isoform X1 [Metopolophium dirhodum] | 0 | 1 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.6860.1 | McraCYP4CK1 | 1547 | 515 | 0.0 | 89.57 | >XP_060860450.1 PREDICTED: cytochrome P450 4C1-like [Metopolophium dirhodum] | 0 | 1 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.8070.6 | McraCYP315A1 | 1434 | 477 | 0.0 | 90.78 | >XP_001944183.2 PREDICTED: cytochrome P450 315a1, mitochondrial [Acyrthosiphon pisum] | 0 | 0 | YES | C |
| MSTRG.11084.1 | McraCSP7 | 468 | 155 | 1e-109 | 100.00 | >ULF48248.1 PREDICTED: chemosensory protein 7 (CSP7) mRNA [Acyrthosiphon pisum] | 0 | 0 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.465.1 | McraCSP8 | 219 | 72 | 4e-27 | 100.00 | >ULF48249.1 PREDICTED: chemosensory protein 8 (CSP8) mRNA [Acyrthosiphon pisum] | - | - | 3’ | C&R |
| MSTRG.11160.2 | McraGPPS | 930 | 309 | 0.0 | 100.00 | >QUH22249.1 PREDICTED: geranyl pyrophosphate synthase mRNA [Megoura viciae] | 0 | 0 | YES | C&R |
| MSTRG.7985.1 | McraFPPS | 1185 | 394 | 0.0 | 98.98 | >AAY33489.2 PREDICTED: putative mitochondrial isoprenyl diphosphate synthase precursor, mRNA [Megoura viciae] | 0 | 0 | YES | C&R |

图5 豌豆修尾蚜McraCYP450s基因与其他蚜虫同源基因的氨基酸序列比对 注: Mcra:豌豆修尾蚜;Agos:棉蚜;Apis:豌豆蚜;Agly:大豆蚜;Mper:桃蚜;Save:麦长管蚜;黑框显示了从豌豆修尾蚜M. crassicauda的腹管中鉴定出的候选CSPs基因。CSP7分支以浅红色背景突出显示,而CSP8分支以紫色背景突出显示
Fig.5 Amino acid sequence alignment of McraCYP450s genes from M. crassicauda with homologous genes of other aphid species Notes: Mcra: M. crassicauda; Agos: A. gossypii; Apis: A. pisum; Agly: A. glycines; Mper: M. persicae; Save: S. avenae; The candidate CSP genes identified from the cornicles of M. crassicauda are indicated by black boxes. The CSP7 clade is highlighted with a light red background, while the CSP8 clade is high-lighted with a purple background
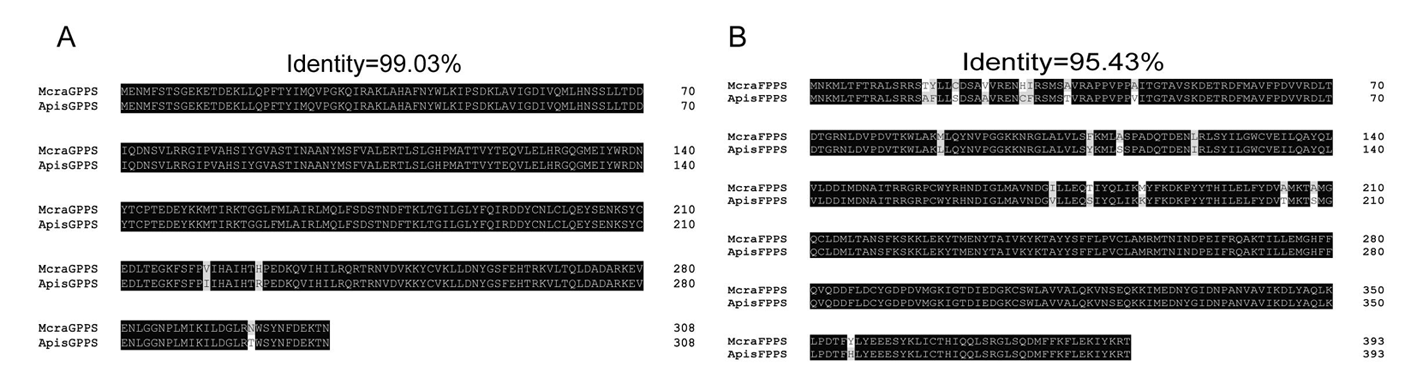
图7 豌豆修尾蚜McraIDSs基因与豌豆蚜ApisIDSs同源基因的氨基酸序列比对 注:A. McraGPPS与ApisGPPS的序列比对;B. McraFPPS与ApisFPPS的序列比对;Mcra:豌豆修尾蚜;Apis:豌豆蚜
Fig.7 Amino acid sequence alignment of McraIDS genes from M. crassicauda with homologous genes of A. pisum Notes: A. Sequence alignment between McraGPPS and ApisGPPS; B. Sequence alignment between McraFPPS and ApisFPPS; Mcra: M. crassicauda; Apis: A. pisum
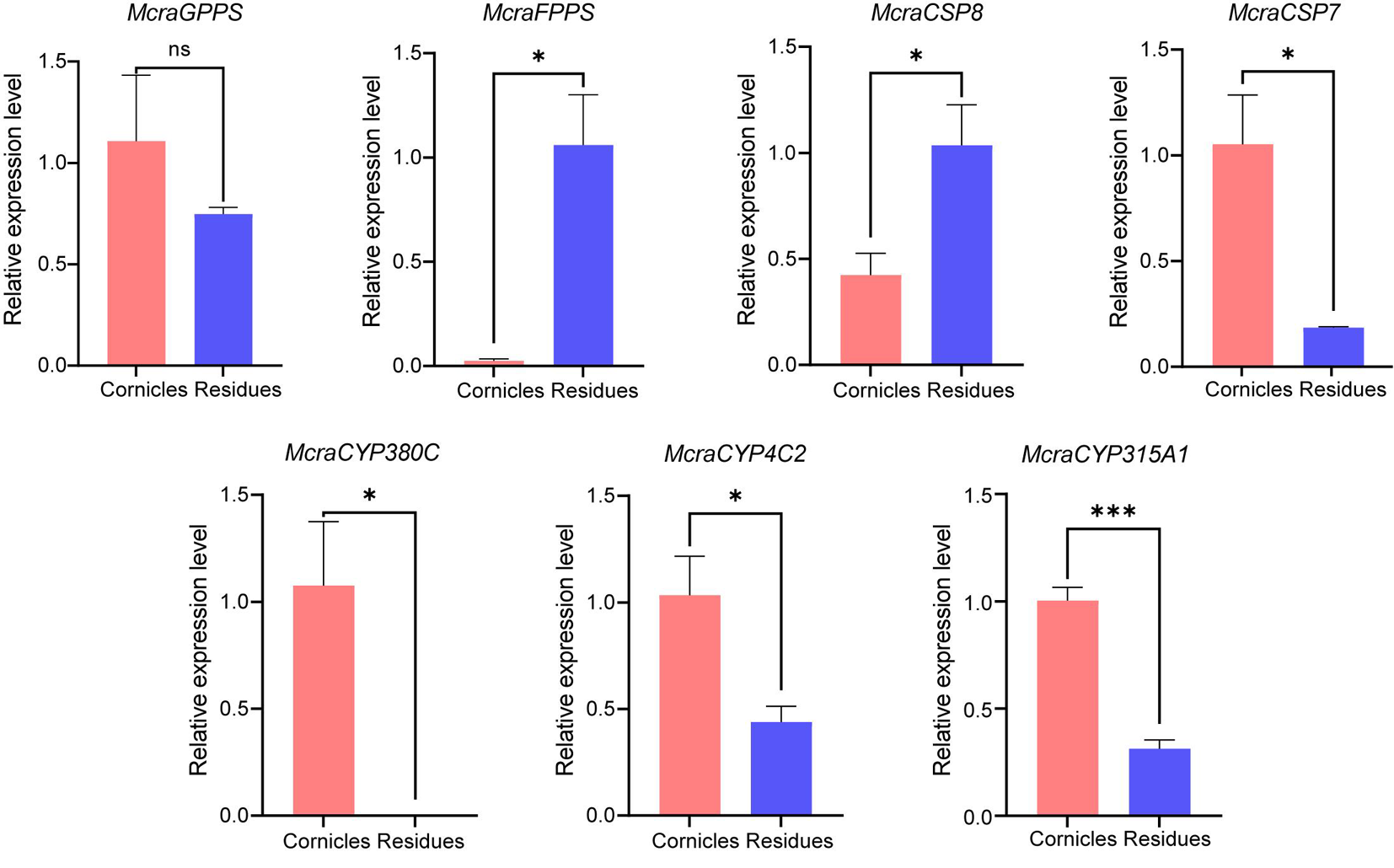
图8 豌豆修尾蚜M. crassicauda 7个候选基因的组织特异性表达水平 注:数据以Mean±SE表示(n=3)。通过独立样本T检验分析,星号表示在α=0.05水平存在显著性差异,n.s.表示在α=0.05水平无显著性差异
Fig.8 T Tissue-specific expression levels of seven candidate genes from M. crassicauda Notes: Data are presented as Mean±SE (n=3). The relative expression between cornicles and residues was analyzed by t-test, asterisks indicate a significant difference at the α=0.05 level, while n.s. indicates no significant difference at the α=0.05 level
| [1] | Weisser W W, Braendle C, Minoretti N. Predator-induced morphological shift in the pea aphid[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series B: Biological Sciences, 1999, 266(1424): 1175-1181. |
| [2] | Badji C A, Sol-Mochkovitch Z, Fallais C, et al. Alarm pheromone responses depend on genotype, but not on the presence of facultative endosymbionts in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum[J]. Insects, 2021, 12(1): 43. |
| [3] | Chen S W, Edwards J S. Observations on the structure of secretory cells associated with aphid cornicles[J]. Zeitschrift Fur Zellforschung und Mikroskopische Anatomie, 1972, 130(3): 312-317. |
| [4] | Vandermoten S, Mescher M C, Francis F, et al. Aphid alarm pheromone: an overview of current knowledge on biosynthesis and functions[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2012, 42(3): 155-163. |
| [5] | Micha S G, Wyss U. Aphid alarm pheromone (E)-β-farnesene: a host finding kairomone for the aphid primary parasitoidAphidius uzbekistanicus (Hymenoptera: Aphidiinae)[J]. CHEMOECOLOGY, 1996, 7(3): 132-139. |
| [6] | Bowers W S, Nault L R, Webb R E, et al. Aphid alarm pheromone: isolation, identification, synthesis[J]. Science, 1972, 177(4054): 1121-1122. |
| [7] | Pickett J A, Wadhams L J, Woodcock C M, et al. The chemical ecology of aphids[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 1992, 37: 67-90. |
| [8] | Edwards L J, Siddall J B, Dunham L L, et al. Trans-β-farnesene, alarm pheromone of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae (Sulzer)[J]. Nature, 1973, 241(5385): 126-127. |
| [9] | Pickett J A, Griffiths D C. Composition of aphid alarm pheromones[J]. Journal of Chemical Ecology, 1980, 6(2): 349-360. |
| [10] | Wang B, Dong W Y, Li H M, et al. Molecular basis of (E)-β-farnesene-mediated aphid location in the predator Eupeodes corollae[J]. Current Biology, 2022, 32(5): 951-962.e7. |
| [11] | Lewis M J, Prosser I M, Mohib A, et al. Cloning and characterisation of a prenyltransferase from the aphid Myzus persicae with potential involvement in alarm pheromone biosynthesis[J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2008, 17(4): 437-443. |
| [12] | Sun Z J, Li Z X. The terpenoid backbone biosynthesis pathway directly affects the biosynthesis of alarm pheromone in the aphid[J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2018, 27(6): 824-834. |
| [13] | Ma G Y, Sun X F, Zhang Y L, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of a prenyltransferase from the cotton aphid, Aphis gossypii[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2010, 40(7): 552-561. |
| [14] | Sun X F, Li Z X. In silico and in vitro analyses identified three amino acid residues critical to the catalysis of two aphid farnesyl diphosphate synthase[J]. The Protein Journal, 2012, 31(5): 417-424. |
| [15] | Song X, Qin Y G, Zhang Y H, et al. Farnesyl/geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthases regulate the biosynthesis of alarm pheromone in a unique manner in the vetch aphid Megoura viciae[J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2023, 32(3): 229-239. |
| [16] | Beran F, Rahfeld P, Luck K, et al. Novel family of terpene synthases evolved from trans-isoprenyl diphosphate synthases in a flea beetle[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2016, 113(11): 2922-2927. |
| [17] | Lancaster J, Khrimian A, Young S, et al. De novo formation of an aggregation pheromone precursor by an isoprenyl diphosphate synthase-related terpene synthase in the harlequin bug[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2018, 115(37): E8634-E8641. |
| [18] | Lu K, Song Y Y, Zeng R S. The role of cytochrome P450-mediated detoxification in insect adaptation to xenobiotics[J]. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 2021, 43: 103-107. |
| [19] | Sezutsu H, Le Goff G, Feyereisen R. Origins of P450 diversity[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 2013, 368(1612): 20120428. |
| [20] | Song M M, Kim A C, Gorzalski A J, et al. Functional characterization of myrcene hydroxylases from two geographically distinct Ips pini populations[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2013, 43(4): 336-343. |
| [21] | Fu N X, Yang Z L, Pauchet Y, et al. A cytochrome P450 from the mustard leaf beetles hydroxylates geraniol, a key step in iridoid biosynthesis[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2019, 113: 103212. |
| [22] | Wang Q, Zhou J J, Liu J T, et al. Integrative transcriptomic and genomic analysis of odorant binding proteins and chemosensory proteins in aphids[J]. Insect Molecular Biology, 2019, 28(1): 1-22. |
| [23] | Wenger J A, Cassone B J, Legeai F, et al. Whole genome sequence of the soybean aphid, Aphis glycines[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2020, 123: 102917. |
| [24] | Lu J J, Zhang H, Wang Q, et al. Genome-wide identification and expression pattern of cytochrome P450 genes in the social aphid Pseudoregma bambucicola[J]. Insects, 2023, 14(2): 212. |
| [25] | Gauthier J P, Legeai F, Zasadzinski A, et al. AphidBase: a database for aphid genomic resources[J]. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(6): 783-784. |
| [26] | Kislow C J, Edwards L J. Repellent Odour in Aphids[J]. Nature, Nature Publishing Group, 1972, 235(5333): 108-109. |
| [27] | Gut J, van Oosten A M. Functional significance of the alarm pheromone composition in various morphs of the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae[J]. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 1985, 37(2): 199-204. |
| [28] | Grabherr M G, Haas B J, Yassour M, et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2011, 29(7): 644-652. |
| [29] | Pertea G, Huang X Q, Liang F, et al. TIGR Gene Indices clustering tools (TGICL): a softwaresystem for fast clustering of large EST datasets[J]. Bioinformatics, 2003, 19(5): 651-652. |
| [30] | Wang B, Liu Y, Wang G R. Chemosensory genes in the antennal transcriptome of two syrphid species, Episyrphus balteatus and Eupeodes corollae (Diptera: Syrphidae)[J]. BMC Genomics, 2017, 18(1): 586. |
| [31] | Liu Y P, Cui Z Y, Si P F, et al. Characterization of a specific odorant receptor for linalool in the Chinese Citrus fly Bactrocera minax (Diptera: Tephritidae)[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2020, 122: 103389. |
| [32] | Conesa A, Götz S, García-Gómez J M, et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research[J]. Bioinformatics, 2005, 21(18): 3674-3676. |
| [33] | Gasteiger E, Gattiker A, Hoogland C, et al. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2003, 31(13): 3784-3788. |
| [34] | Petersen T N, Brunak S, von Heijne G, et al. SignalP 4.0: discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions[J]. Nature Methods, 2011, 8(10): 785-786. |
| [35] | Krogh A, Larsson B, von Heijne G, et al. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 2001, 305(3): 567-580. |
| [36] | Katoh K, Standley D M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 2013, 30(4): 772-780. |
| [37] | Stamatakis A. RAxML version 8: a tool for phylogenetic analysis and post-analysis of large phylogenies[J]. Bioinformatics, 2014, 30(9): 1312-1313. |
| [38] | Wang B, Huang T Y, Yao Y, et al. A conserved odorant receptor identified from antennal transcriptome of Megoura crassicauda that specifically responds to Cis-jasmone[J]. Journal of Integrative Agriculture, 2022, 21(7): 2042-2054. |
| [39] | Li B, Dewey C N. RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome[J]. BMC Bioinformatics, 2011, 12: 323. |
| [40] | Wickham H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis[M]. Springer Publishing Company, Incorporated, 2009. |
| [41] | Ishikawa A, Ishikawa Y, Okada Y, et al. Screening of upregulated genes induced by high density in the vetch aphid Megoura crassicauda[J]. Journal of Experimental Zoology Part A, Ecological Genetics and Physiology, 2012, 317(3): 194-203. |
| [42] | Pfaffl M W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR[J]. Nucleic Acids Research, 2001, 29(9): e45. |
| [43] | Livak K J, Schmittgen T D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 (-Delta Delta C(T)) Method[J]. Methods, 2001, 25(4): 402-408. |
| [44] | Angeli S, Ceron F, Scaloni A, et al. Purification, structural characterization, cloning and immunocytochemical localization of chemoreception proteins from Schistocerca gregaria[J]. European Journal of Biochemistry, 1999, 262(3): 745-754. |
| [45] | Butler P J, Harris J I, Hartley B S, et al. Reversible blocking of peptide amino groups by maleic anhydride[J]. The Biochemical Journal, 1967, 103(3): 78P-79P. |
| [46] | Waschkuhn A. Robert A. Dahl, Polyarchy: Participation and Opposition, New Haven 1971[A]. In: S. Kailitz. Schlüsselwerke der Politikwissenschaft[M]. Wiesbaden: VS Verlag für Sozialwissenschaften, 2007: 86-88. |
| [47] | Rane R V, Ghodke A B, Hoffmann A A, et al. Detoxifying enzyme complements and host use phenotypes in 160 insect species[J]. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 2019, 31: 131-138. |
| [48] | Sun C X, Li Z X. Biosynthesis of aphid alarm pheromone is modulated in response to starvation stress under regulation by the insulin, glycolysis and isoprenoid pathways[J]. Journal of Insect Physiology, 2021, 128: 104174. |
| [49] | Zhang H, Li Z X. A type-III insect geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase with a novel catalytic property[J]. Protein and Peptide Letters, 2014, 21(7): 615-623. |
| [50] | Cheng Y J, Li Z X. Spatiotemporal expression profiling of the farnesyl diphosphate synthase genes in aphids and analysis of their associations with the biosynthesis of alarm pheromone[J]. Bulletin of Entomological Research, 2019, 109(3): 398-407. |
| [51] | Truman J W, Riddiford L M. Endocrine insights into the evolution of metamorphosis in insects[J]. Annual Review of Entomology, 2002, 47: 467-500. |
| [52] | Picimbon J F, Dietrich K, Krieger J, et al. Identity and expression pattern of chemosensory proteins in Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae)[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2001, 31(12): 1173-1181. |
| [53] | Pelosi P, Iovinella I, Zhu J, et al. Beyond chemoreception: diverse tasks of soluble olfactory proteins in insects[J]. Biological Reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society, 2018, 93(1): 184-200. |
| [54] | Nomura Kitabayashi A, Arai T, Kubo T, et al. Molecular cloning of cDNA for p10, a novel protein that increases in the regenerating legs of Periplaneta americana (American cockroach)[J]. Insect Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 1998, 28(10): 785-790. |
| [1] | 王亚玲, 江应红, 孙慧, 刘易. 不同马铃薯耐盐性转录组比较及耐盐基因的挖掘[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(5): 1121-1130. |
| [2] | 鞠乐, 齐军仓, 牛银亭, 石培春, 宋瑞娇, 宋凌宇, 阴志刚, 陈培育, 强学兰. 基于RNA-seq的大麦苗期抗旱相关基因的挖掘与分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(5): 1077-1084. |
| [3] | 何婉洁, 孟涵颖, 支梦婷, 陈静. 双斑长跗萤叶甲雌虫、雄虫触角转录组及差异表达基因分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 984-995. |
| [4] | 户金鸽, 白世践, 陈光, 蔡军社. 不同地面覆盖方式下新郁葡萄果皮黄酮转录组和代谢组联合分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 63-78. |
| [5] | 韦伟, 单守明, 徐文娣, 李光宗. 山葡萄‘双优’组织培养生根期愈伤组织的转录组分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1451-1459. |
| [6] | 宋金迪, 刘君, 孙玉芳, 优丽图孜·乃比, 陈宝强, 颉兵兵. 铜胁迫下的西瓜食酸菌转录组分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 389-398. |
| [7] | 杨永, 范蓉, 张学军, 李寐华, 凌悦铭, 张红, 杨文莉, 姜雪, 张永兵, 伊鸿平. 厚皮甜瓜心部果肉蔗糖含量QTL定位及候选基因分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(10): 2446-2455. |
| [8] | 王业建, 杨杰, 梁晓玲, 阿布来提·阿布拉, 韩登旭, 郗浩江, 刘俊, 李铭东. 干旱胁迫下两个玉米自交系雄穗花器官分化期的转录组分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2020, 57(9): 1578-1585. |
| [9] | 王振东, 鲁晓燕, 涂文文, 王晓丽, 何晨晨. 外源CaCl2缓解NaCl胁迫下酸枣幼苗叶和根转录组测序分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2019, 56(6): 1052-1062. |
| [10] | 张译元, 郭延华, 王聪慧, 唐红, 南海艳, 王立民, 周平. 绵羊iPS细胞诱导及转录组学分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(11): 2142-2149. |
| [11] | 包秋娟, 张丽丽, 海那尔·乌拉孜巴依, 张富春. 干旱胁迫棉花转录组DNA损伤修复相关基因的分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 54(11): 1999-2005. |
| [12] | 沈春修. 水稻LOC_Os10g05490位点冷胁迫条件下表达分析及CRISPR/Cas9定向编辑[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2017, 1(1): 1-10. |
| [13] | 潘贻武;刘宁;刘小宁. 昆虫细胞色素P450的研究进展及其介导的抗药性[J]. , 2007, 44(4): 470-475. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||