

新疆农业科学 ›› 2025, Vol. 62 ›› Issue (1): 103-109.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2025.01.013
• 耕作栽培·生理生化·种质资源·分子遗传学·土壤肥料 • 上一篇 下一篇
凌沥1( ), 翟辉1(
), 翟辉1( ), 张云舒2(
), 张云舒2( ), 邵华伟2, 唐光木2, 葛春辉2, 徐万里2, 杨建军1,3
), 邵华伟2, 唐光木2, 葛春辉2, 徐万里2, 杨建军1,3
收稿日期:2024-05-10
出版日期:2025-01-20
发布日期:2025-03-11
通信作者:
翟辉(1992-),女,内蒙古人,副教授,博士,研究方向为土壤金属的迁移转化,(E-mail)zhaihui@xju.edu.cn;作者简介:凌沥(1998-),男,四川大竹人,硕士研究生,研究方向为生态工程,(E-mail)2467419517@qq.com
基金资助:
LING Li1( ), ZHAI Hui1(
), ZHAI Hui1( ), ZHANG Yunshu2(
), ZHANG Yunshu2( ), SHAO Huawei2, TANG Guangmu2, GE Chunhui2, XU Wanli2, YANG Jianjun1,3
), SHAO Huawei2, TANG Guangmu2, GE Chunhui2, XU Wanli2, YANG Jianjun1,3
Received:2024-05-10
Published:2025-01-20
Online:2025-03-11
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 研究新疆南疆气候条件下水稻主栽品种喷硒肥的吸收转移特征,分析硒肥种类与浓度交互作用对水稻籽粒硒含量的影响,为新疆南疆富硒水稻的种植生产提供理论依据。【方法】 以新疆南疆阿克苏地区主栽水稻品种新稻11号为材料,采用纳米硒、亚硒酸钠和有机硒类的硒肥,设置2.5、5、10和20 mg/L 4个喷施浓度的组合试验,研究叶面喷施硒肥对水稻植株硒吸收和转运的影响。【结果】 硒肥处理均可显著提高稻米中的硒含量。籽粒、精米、叶片和茎部中的硒含量均随硒肥浓度的增加而提高;3种硒肥对稻米的富硒效果为有机硒>亚硒酸钠>纳米硒。喷施纳米硒肥时大部分硒积累在谷壳和米糠中,精米中的硒含量提高较少,而喷施有机硒和亚硒酸钠则使籽粒或精米的硒含量均显著提高。【结论】 20 mg/L的有机硒和亚硒酸钠对水稻硒生物强化的效果最佳,使精米硒含量分别提高到0.88和0.72 mg/kg。
中图分类号:
凌沥, 翟辉, 张云舒, 邵华伟, 唐光木, 葛春辉, 徐万里, 杨建军. 外源硒对水稻硒吸收和转运的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 103-109.
LING Li, ZHAI Hui, ZHANG Yunshu, SHAO Huawei, TANG Guangmu, GE Chunhui, XU Wanli, YANG Jianjun. Effects of exogenous selenium on its uptake and translocation in rice[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2025, 62(1): 103-109.

图1 不同硒肥处理下水稻各部位硒含量的变化 注:a.纳米硒;b.亚硒酸钠;c.有机硒;不同小写字母表示不同浓度处理间差异在P<0.05水平具有显著性
Fig.1 Changes of Se content in different parts of rice under different Se fertilizer treatments Notes: a.nano-Se, b.sodium selenite, c.organic Se ; different lowercase letters indicated that the difference between different concentration treatments was significant at the P < 0.05 level
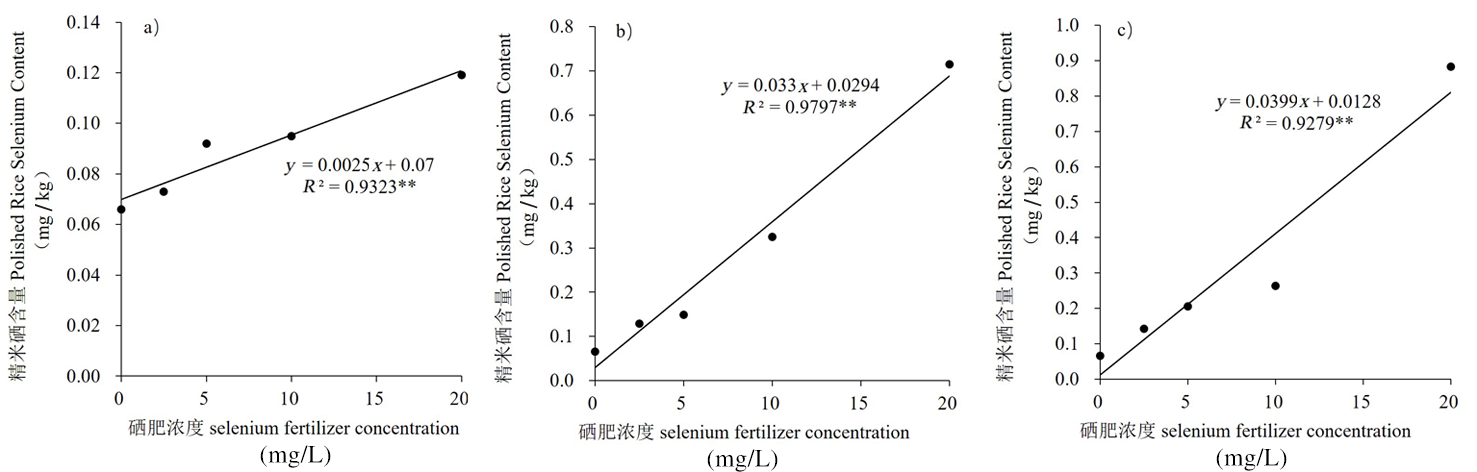
图2 精米硒含量与硒肥浓度之间的相关性 注:a.纳米硒;b.亚硒酸钠;c.有机硒;**表示相关性达极显著水平(P<0.01)
Fig.2 Correlation between polished rice Se content and Se fertilizer concentration Notes: a.Nano-Se ; b.sodium selenite ; c.organic Se ; ** indicated that the correlation was extremely significant (P<0.01)
| 硒种类 Types of Se | 硒浓度 Concentration of Se(mg/L) | TF根/茎 TFRoot/Stem | TF根/叶 TFRoot/Leaf | TF茎/叶 TFStem/Leaf | TF籽粒/茎 TFGrains/Stem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 3.31±0.05 | 2.68±0.02 | 0.81±0.02 | 0.89±0.00 |
| 纳米硒 Nano-Se | 2.5 | 5.38±0.31aɑ | 2.01±0.11aβ | 0.37±0.00aγ | 1.35±0.12cβ |
| 5 | 5.12±0.06abɑ | 1.29±0.01bγ | 0.25±0.00cγ | 2.20±0.01aɑ | |
| 10 | 4.84±0.02bɑ | 1.35±0.06bɑ | 0.28±0.01bβ | 2.25±0.05aɑ | |
| 20 | 2.43±0.03cɑ | 0.73±0.01cɑ | 0.30±0.00bβ | 1.79±0.01bγ | |
| 亚硒酸钠 Sodium selenite | 2.5 | 5.28±0.15aɑ | 2.92±0.05aɑ | 0.55±0.02bɑ | 1.60±0.04cɑβ |
| 5 | 3.38±0.18bβ | 2.11±0.07bɑ | 0.62±0.01aɑ | 1.42±0.00cγ | |
| 10 | 1.97±0.09cγ | 0.86±0.00cβ | 0.44±0.02cɑ | 1.88±0.12bβ | |
| 20 | 1.67±0.03cβ | 0.41±0.01dγ | 0.24±0.01dγ | 3.49±0.11aɑ | |
| 有机硒 Organic Se | 2.5 | 3.39±0.13aβ | 1.61±0.01aγ | 0.48±0.02aβ | 1.75±0.08bɑ |
| 5 | 3.22±0.09aβ | 1.49±0.03bβ | 0.46±0.00abβ | 1.89±0.03bβ | |
| 10 | 2.33±0.12bβ | 0.96±0.05cβ | 0.41±0.00cɑ | 1.86±0.00bβ | |
| 20 | 1.07±0.06cγ | 0.46±0.01dβ | 0.43±0.01bcɑ | 2.91±0.14aβ | |
| Two-way ANOVA(F value) | |||||
| 种类Types | 489.4*** | 201.8*** | 333.2*** | 20.1*** | |
| 浓度Concentration | 594.1*** | 1 575.8*** | 135.3*** | 263.2*** | |
| 种类×浓度Types×Concentration | 53.2*** | 182.8*** | 94.1*** | 110.2*** | |
表1 水稻不同部位的转运系数
Tab.1 Transport coefficient of different parts of rice
| 硒种类 Types of Se | 硒浓度 Concentration of Se(mg/L) | TF根/茎 TFRoot/Stem | TF根/叶 TFRoot/Leaf | TF茎/叶 TFStem/Leaf | TF籽粒/茎 TFGrains/Stem |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 0 | 3.31±0.05 | 2.68±0.02 | 0.81±0.02 | 0.89±0.00 |
| 纳米硒 Nano-Se | 2.5 | 5.38±0.31aɑ | 2.01±0.11aβ | 0.37±0.00aγ | 1.35±0.12cβ |
| 5 | 5.12±0.06abɑ | 1.29±0.01bγ | 0.25±0.00cγ | 2.20±0.01aɑ | |
| 10 | 4.84±0.02bɑ | 1.35±0.06bɑ | 0.28±0.01bβ | 2.25±0.05aɑ | |
| 20 | 2.43±0.03cɑ | 0.73±0.01cɑ | 0.30±0.00bβ | 1.79±0.01bγ | |
| 亚硒酸钠 Sodium selenite | 2.5 | 5.28±0.15aɑ | 2.92±0.05aɑ | 0.55±0.02bɑ | 1.60±0.04cɑβ |
| 5 | 3.38±0.18bβ | 2.11±0.07bɑ | 0.62±0.01aɑ | 1.42±0.00cγ | |
| 10 | 1.97±0.09cγ | 0.86±0.00cβ | 0.44±0.02cɑ | 1.88±0.12bβ | |
| 20 | 1.67±0.03cβ | 0.41±0.01dγ | 0.24±0.01dγ | 3.49±0.11aɑ | |
| 有机硒 Organic Se | 2.5 | 3.39±0.13aβ | 1.61±0.01aγ | 0.48±0.02aβ | 1.75±0.08bɑ |
| 5 | 3.22±0.09aβ | 1.49±0.03bβ | 0.46±0.00abβ | 1.89±0.03bβ | |
| 10 | 2.33±0.12bβ | 0.96±0.05cβ | 0.41±0.00cɑ | 1.86±0.00bβ | |
| 20 | 1.07±0.06cγ | 0.46±0.01dβ | 0.43±0.01bcɑ | 2.91±0.14aβ | |
| Two-way ANOVA(F value) | |||||
| 种类Types | 489.4*** | 201.8*** | 333.2*** | 20.1*** | |
| 浓度Concentration | 594.1*** | 1 575.8*** | 135.3*** | 263.2*** | |
| 种类×浓度Types×Concentration | 53.2*** | 182.8*** | 94.1*** | 110.2*** | |
| 硒肥 Se fertilizers | 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 籽粒 Grains | 精米 Polished rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纳米硒Nano-Se | 0.841** | 0.884** | 0.960** | 0.983** | 1 |
| 亚硒酸钠Sodium selenite | -0.459 | 0.929** | 0.995** | 0.992** | 1 |
| 有机硒Organic Se | 0.443 | 0.997** | 0.994** | 0.999** | 1 |
表2 喷施不同硒肥时,精米与根、茎、叶、籽粒间的皮尔逊相关系数
Tab.2 Pearson’s correlation coefficients of polished rice with root, stem, leaf and grain when spraying different Se fertilizer
| 硒肥 Se fertilizers | 根 Root | 茎 Stem | 叶 Leaf | 籽粒 Grains | 精米 Polished rice |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 纳米硒Nano-Se | 0.841** | 0.884** | 0.960** | 0.983** | 1 |
| 亚硒酸钠Sodium selenite | -0.459 | 0.929** | 0.995** | 0.992** | 1 |
| 有机硒Organic Se | 0.443 | 0.997** | 0.994** | 0.999** | 1 |
| [1] | Winkel L H E, Johnson C A, Lenz M, et al. Environmental selenium research: from microscopic processes to global understanding[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2012, 46(2): 571-579. |
| [2] |
Wu Z L, Banuelos G S, Lin Z Q, et al. Biofortification and phytoremediation of selenium in China[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science, 2015, 6: 136.
DOI PMID |
| [3] | 李以暖, 薛立文. 富硒保健食品硒含量标准的探讨[J]. 广东微量元素科学, 2000, 7(5): 18-21. |
| LI Yinuan, XUE Liwen. Discussion on content standards of rich-Se healthy food[J]. Trace Elements Science, 2000, 7(5): 18-21. | |
| [4] | Ramkissoon C, Degryse F, da Silva R C, et al. Improving the efficacy of selenium fertilizers for wheat biofortification[J]. Scientific Reports, 2019, 9(1): 19520. |
| [5] | 陈雪, 沈方科, 梁欢婷, 等. 外源施硒措施对水稻产量品质及植株硒分布的影响[J]. 南方农业学报, 2017, 48(1): 46-50. |
| CHEN Xue, SHEN Fangke, LIANG Huanting, et al. Effects of exogenous selenium application on rice yield, quality, distribution of selenium in seedling[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture, 2017, 48(1): 46-50. | |
| [6] | Li Z, Liang D L, Peng Q, et al. Interaction between selenium and soil organic matter and its impact on soil selenium bioavailability: a review[J]. Geoderma, 2017, 295: 69-79. |
| [7] | Yuan Z Q, Long W X, Liang T, et al. Effect of foliar spraying of organic and inorganic selenium fertilizers during different growth stages on selenium accumulation and speciation in rice[J]. Plant and Soil, 2023, 486(1): 87-101. |
| [8] |
Farooq M U, Tang Z C, Zeng R, et al. Accumulation, mobilization, and transformation of selenium in rice grain provided with foliar sodium selenite[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture, 2019, 99(6): 2892-2900.
DOI PMID |
| [9] |
Premarathna L, McLaughlin M J, Kirby J K, et al. Selenate-enriched urea granules are a highly effective fertilizer for selenium biofortification of paddy rice grain[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2012, 60(23): 6037-6044.
DOI PMID |
| [10] | Gali L, Vinkovi T, Ravnjak B, et al. Agronomic biofortification of significant cereal crops with selenium—a review[J]. Agronomy, 2021, 11(5): 1015. |
| [11] | Lidon F C, Oliveira K, Ribeiro M M, et al. Selenium biofortification of rice grains and implications on macronutrients quality[J]. Journal of Cereal Science, 2018, 81: 22-29. |
| [12] | 郭天宇. 叶面喷施不同硒肥对水稻含硒量、产量及品质的影响[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2016. |
| GUO Tianyu. Effects of foliar application of different selenium fertilizers on selenium content, yield and quality of rice[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2016. | |
| [13] | 池忠志, 杨洋, 杨福明, 等. 生产富硒稻谷的硒肥施用技术研究[J]. 西南农业学报, 2011, 24(6): 2289-2292. |
| CHI Zhongzhi, YANG Yang, YANG Fuming, et al. Se fertilizer application technique for producing selenium-rich rice[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2011, 24(6): 2289-2292. | |
| [14] | 管恩相, 姜守全, 谭旭生, 等. 喷施硒肥对水稻产量及稻米含硒量的影响[J]. 中国种业, 2012,(5): 43-45. |
| GUAN Enxiang, JIANG Shouquan, TAN Xusheng, et al. Effects of spraying selenium fertilizer on rice yield and selenium content in rice[J]. China Seed Industry, 2012,(5): 43-45. | |
| [15] | 王亚萍. 外源硒施用方式对水稻富硒及稻米硒形态的影响[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2020. |
| WANG Yaping. Effects of exogenous selenium application methods on selenium enrichment and selenium speciation in rice[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2020. | |
| [16] | Wang K, Wang Y Q, Li K, et al. Uptake, translocation and biotransformation of selenium nanoparticles in rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.)[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology, 2020, 18(1): 103. |
| [17] | Kapoor P, Dhaka R K, Sihag P, et al. Nanotechnology-enabled biofortification strategies for micronutrients enrichment of food crops: current understanding and future scope[J]. NanoImpact, 2022, 26: 100407. |
| [18] | 石吕, 薛亚光, 石晓旭, 等. 喷施硒肥对富硒土壤水稻产量、品质及硒分配的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022,(10): 174-183. |
| SHI Lyu, XUE Yaguang, SHI Xiaoxu, et al. Effects of spraying selenium fertilizer on rice yield, quality and selenium distribution in selenium-rich soil[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022,(10): 174-183. | |
| [19] |
戴志华, 高菲, 赵敏, 等. 作物对硒的吸收利用及合理施用硒肥[J]. 生物技术进展, 2017, 7(5): 415-420.
DOI |
|
DAI Zhihua, GAO Fei, ZHAO Min, et al. The absorption and utilization of selenium in crops and rational application of selenium fertilizer[J]. Current Biotechnology, 2017, 7(5): 415-420.
DOI |
|
| [20] | 沈方科, 王亚萍, 赵雪梅, 等. 叶面喷施硒对水稻籽粒中硒含量及形态的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2022,(6): 144-150. |
| SHEN Fangke, WANG Yaping, ZHAO Xuemei, et al. Effects of foliar application of selenium on selenium content and speciation in rice grain[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2022,(6): 144-150. | |
| [21] | 高梦瑶. 中国地质学会公布第二批天然富硒土地认定结果[J]. 地质论评, 2022, 68(6): 2409-2411. |
| GAO Mengyao. The second batch of natural seleniumriched land identified by Geological Society of China[J]. Geological Review, 2022, 68(6): 2409-2411. | |
| [22] | 高梦瑶, 张丽华. 中国地质学会认定首批天然富硒土地[J]. 地质论评, 2021, 67(5): 1296, 1356. |
| GAO Mengyao, ZHANG Lihua. The first batch of natural selenium-riched land identified by Geological Society of China[J]. Geological Review, 2021, 67(5): 1296, 1356. | |
| [23] | 张栋, 翟勇, 张妮, 等. 新疆水稻主产区土壤硒含量与水稻籽粒硒含量的相关性[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017,(1): 139-143. |
| ZHANG Dong, ZHAI Yong, ZHANG Ni, et al. Correlation between soil selenium content and rice grain selenium content in Xinjiang rice production areas[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017,(1): 139-143. | |
| [24] | 魏丹, 杨谦, 迟凤琴, 等. 叶面喷施硒肥对水稻含硒量及产量的影响[J]. 土壤肥料, 2005,(1): 39-41. |
| WEI Dan, YANG Qian, CHI Fengqin, et al. Effect of foliage dressing Se fertilizer on the rice in the field[J]. Soils and Fertilizers, 2005,(1): 39-41. | |
| [25] | 王琪. 水稻和小麦对有机硒的吸收、转运及形态转化机制[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017. |
| WANG Qi. Mechanisms of absorption, translocation and speciation transformation of organic selenium in rice and wheat[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [26] |
Wang C R, Cheng T T, Liu H T, et al. Nano-selenium controlled cadmium accumulation and improved photosynthesis in indica rice cultivated in lead and cadmium combined paddy soils[J]. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 2021, 103: 336-346.
DOI PMID |
| [27] | 周鑫斌, 施卫明, 杨林章. 叶面喷硒对水稻籽粒硒富集及分布的影响[J]. 土壤学报, 2007, 44(1): 73-78. |
| ZHOU Xinbin, SHI Weiming, YANG Linzhang. Effect of foliar application of selenite on selenium accumulation and distribution in rice[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2007, 44(1): 73-78. | |
| [28] | 管文文. 水稻吸收累积硒元素的特点及稻米富硒技术途径的初步研究[D]. 扬州: 扬州大学, 2011. |
| GUAN Wenwen. A preliminary study on the characteristics of selenium absorption and accumulation in rice and the technical ways of selenium enrichment in rice[D]. Yangzhou: Yangzhou University, 2011. | |
| [29] | 晏娟, 张忠平, 朱同贵. 不同硒肥对水稻产量及硒累积效应的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2021, 49(19): 142-143, 156. |
| YAN Juan, ZHANG Zhongping, ZHU Tonggui. The effect of different selenium fertilizers on yield and selenium accumulation of rice[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 49(19): 142-143, 156. |
| [1] | 杜孝敬, 侯天钰, 李冬, 吕玉平, 袁杰, 张燕红, 赵志强, 布哈丽且木·阿不力孜, 王奉斌. 水稻种子萌发期耐旱性鉴定及优异品种筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2025, 62(1): 95-102. |
| [2] | 赵敏华, 宋秉曦, 张宇鹏, 高志红, 朱勇勇, 陈晓远. 旱作条件下氮肥减施对水稻产量及氮肥偏生产力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(8): 1907-1915. |
| [3] | 叶扬, 侯振安, 闵伟, 郭慧娟. 添加脲酶/硝化抑制剂对棉花养分吸收和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(4): 814-822. |
| [4] | 康民泰, 杜孝敬, 张燕红, 陈玉环, 文孝荣, 唐福森, 赵志强, 袁杰, 王奉斌. 新疆盐渍区水稻品种生育表现与耐盐性筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(3): 591-598. |
| [5] | 邓永辉, 郑强卿, 兖攀, 王文军, 陈奇凌, 王晶晶, 张锦强, 王振东. 干旱区骏枣根系分布和土壤养分关系分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 156-164. |
| [6] | 成志慧, 李红梅, 赵红梅, 涂永峰, 宋海英, 盛建东. 15N同位素标记氮肥减施棉田养分利用效率分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(1): 34-41. |
| [7] | 李怀胜, 艾洪玉, 孟玲, 王贺亚, 张磊, 艾海峰. 减氮下运筹养分吸收高峰期追施比例对春小麦的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1866-1872. |
| [8] | 赖宁, 耿庆龙, 李永福, 李娜, 信会男, 步生兵, 陈署晃. 有机无机配施对超晚播冬小麦产量、氮磷养分吸收利用及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1335-1343. |
| [9] | 张燕红, 侯天钰, 巴音花, 赵彩月, 吕玉平, 布哈丽且木·阿不力孜, 赵志强, 李冬, 杜孝敬, 袁杰, 王奉斌. 水稻重组自交系群体芽期和苗期耐盐性鉴定与评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1041-1049. |
| [10] | 布哈丽且木·阿不力孜, 张燕红, 袁杰, 赵志强, 文孝荣, 杜孝敬, 王奉斌, 吕玉平, 阿曼古丽·艾孜子. 新疆优质丰产香型水稻品种筛选与评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(11): 2694-2703. |
| [11] | 陈丽, 马静, 朱志明, 刘炜, 孙建昌. 基于水稻RIL群体的加工品质性状QTL分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(10): 2419-2425. |
| [12] | 蒲胜海, 王则玉, 丁峰, 王彩风, 刘小利, 马晓鹏, 王涛, 彭银双, 李韵同. 膜下滴灌水稻生理生化特性对灌浆期控水的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(9): 2091-2103. |
| [13] | 杜孝敬, 张燕红, 吕玉平, 袁杰, 李冬, 赵志强, 布哈丽且木·阿不力孜, 王奉斌. 不同香稻品种种子萌发和苗期对NaCl胁迫的响应[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(4): 827-838. |
| [14] | 孟阿静, 齐莹莹, 付彦博, 王治国, 王新勇, 冯耀祖. 增温水滴灌对棉花生物量、养分吸收及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(3): 558-566. |
| [15] | 马庆华, 王兴红, 蔡京艳, 汤志敏, 杨德付, 郑广顺. 氮磷供应水平对野蔷薇生长和养分吸收的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(3): 609-616. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||