

新疆农业科学 ›› 2022, Vol. 59 ›› Issue (6): 1491-1501.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2022.06.021
伊力夏提·艾热提1( ), 李伟2, 徐杨林1, 严宏孟1, 戴志伟1, 周建中1(
), 李伟2, 徐杨林1, 严宏孟1, 戴志伟1, 周建中1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-08-18
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-07-07
通信作者:
周建中
作者简介:伊力夏提·艾热提(1994-),男,新疆人,硕士研究生,研究方向为食品科学与工程,(E-mail) 763161355@qq.com
基金资助:
YilixiatiAireti 1( ), LI Wei2, XU Yanglin1, YAN Hongmeng1, DAI Zhiwei1, ZHOU Jianzhong1(
), LI Wei2, XU Yanglin1, YAN Hongmeng1, DAI Zhiwei1, ZHOU Jianzhong1( )
)
Received:2021-08-18
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-07-07
Correspondence author:
ZHOU Jianzhong
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】 研究传统发酵酸凝硬质奶酪中乳酸菌的分离鉴定及其体外益生特性,得到产酸性能较高的菌株,测试体外益生特性,筛选出优良益生菌。【方法】 采用传统分离纯化方法,以新疆伊犁地区昭苏县农家自制自然发酵酸凝硬质奶酪为原材料,运用稀释涂布、平板划线以及复筛纯化的方法,从自然发酵奶酪中分离得36株菌株,观察其菌落与菌株形态特征并检测生理生化,选取符合条件的菌株运用16S rDNA同源序列分析方法鉴定其分子生物学。【结果】 鉴定6株为乳酸菌,5株是瑞士乳杆菌(Lactobacillus helveticus),另外1株为植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum)。这些菌株的耐胆盐、耐酸、耐模拟胃液以及表面特性得知植物乳杆菌E11在这些方面的性能最佳。【结论】 该菌株在浓度为0.5%的胆盐培养基中存活率达到46.42%,pH 2的条件下存活率仍然保持在20%以上,静置5 h后其自凝集率达到63.6%,对二甲苯的疏水率为44.26%。
中图分类号:
伊力夏提·艾热提, 李伟, 徐杨林, 严宏孟, 戴志伟, 周建中. 传统发酵酸凝硬质奶酪中乳酸菌的分离鉴定及其体外益生特性[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(6): 1491-1501.
YilixiatiAireti , LI Wei, XU Yanglin, YAN Hongmeng, DAI Zhiwei, ZHOU Jianzhong. Screening and Identification of Lactic Acid bacteria in Traditionally Fermented and Acid Coagulated Hard Cheese and Analysis of Its in Vitro Probiotic Properties[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(6): 1491-1501.
| 编号 Number | 菌落特点 Characteristics of the colonies | 菌体形态 Mycelia morphology |
|---|---|---|
| A4 | 奶白色,扁圆形,周围整齐且不透明,中间凸起 | 细长杆状,单个或成连 |
| A75 | 奶白色,直径偏小,周围基本整齐及带有透明圈,中间凸起 | 细长杆状,单个或成连 |
| B25 | 奶白色,直径偏大,呈圆形,周围整齐及带有透明圈,中间凸起 | 细长杆菌,单个、成连或成团 |
| B34 | 奶白色,呈圆形,周边整齐,不透明,中间凸起 | 细长杆菌,单个 |
| B8 | 奶白色,呈圆形,周围整齐,不透明,微扁平 | 细长杆菌,单个 |
| E11 | 奶白色,直径偏小,周边整齐,不透明 | 短杆状,单独或成对 |
表1 菌株菌落特征及菌体形态
Table 1 Colonialand morphological characteristics of the strains
| 编号 Number | 菌落特点 Characteristics of the colonies | 菌体形态 Mycelia morphology |
|---|---|---|
| A4 | 奶白色,扁圆形,周围整齐且不透明,中间凸起 | 细长杆状,单个或成连 |
| A75 | 奶白色,直径偏小,周围基本整齐及带有透明圈,中间凸起 | 细长杆状,单个或成连 |
| B25 | 奶白色,直径偏大,呈圆形,周围整齐及带有透明圈,中间凸起 | 细长杆菌,单个、成连或成团 |
| B34 | 奶白色,呈圆形,周边整齐,不透明,中间凸起 | 细长杆菌,单个 |
| B8 | 奶白色,呈圆形,周围整齐,不透明,微扁平 | 细长杆菌,单个 |
| E11 | 奶白色,直径偏小,周边整齐,不透明 | 短杆状,单独或成对 |
| 编号 Number | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | H2S实验 H2S test | 葡萄糖 Glucose | 革兰氏染色 Gram stain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | - | - | + | + |
| A75 | - | - | + | + |
| B25 | - | - | + | + |
| B34 | - | - | + | + |
| B8 | - | - | + | + |
| E11 | - | - | + | + |
表2 菌株生理生化鉴定
Table 2 Physiological and biochemical identification test results of the strains
| 编号 Number | 过氧化氢酶 Catalase | H2S实验 H2S test | 葡萄糖 Glucose | 革兰氏染色 Gram stain |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | - | - | + | + |
| A75 | - | - | + | + |
| B25 | - | - | + | + |
| B34 | - | - | + | + |
| B8 | - | - | + | + |
| E11 | - | - | + | + |
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 亲缘相似菌株 Related strains | Accession | 相似度 Similarity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | Lactobacillus helveticusstrain 4538 | MT459351.1 | 100 |
| A75 | Lactobacillus helveticusstrainNWAFU1447 | MG551111.1 | 99.93 |
| B8 | Lactobacillus helveticusMG585 | MN055698.1 | 100 |
| B25 | Lactobacillus helveticusNWAFU1331 | MG550993.1 | 100 |
| B34 | Lactobacillus helveticusMGB67-2 | HM058202.2 | 100 |
| E11 | Lactobacillus plantarum strain 3334 | MT613627.1 | 100 |
表3 菌株相似鉴定
Table 3 Analysis on the results of similar identification of strains
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 亲缘相似菌株 Related strains | Accession | 相似度 Similarity(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A4 | Lactobacillus helveticusstrain 4538 | MT459351.1 | 100 |
| A75 | Lactobacillus helveticusstrainNWAFU1447 | MG551111.1 | 99.93 |
| B8 | Lactobacillus helveticusMG585 | MN055698.1 | 100 |
| B25 | Lactobacillus helveticusNWAFU1331 | MG550993.1 | 100 |
| B34 | Lactobacillus helveticusMGB67-2 | HM058202.2 | 100 |
| E11 | Lactobacillus plantarum strain 3334 | MT613627.1 | 100 |
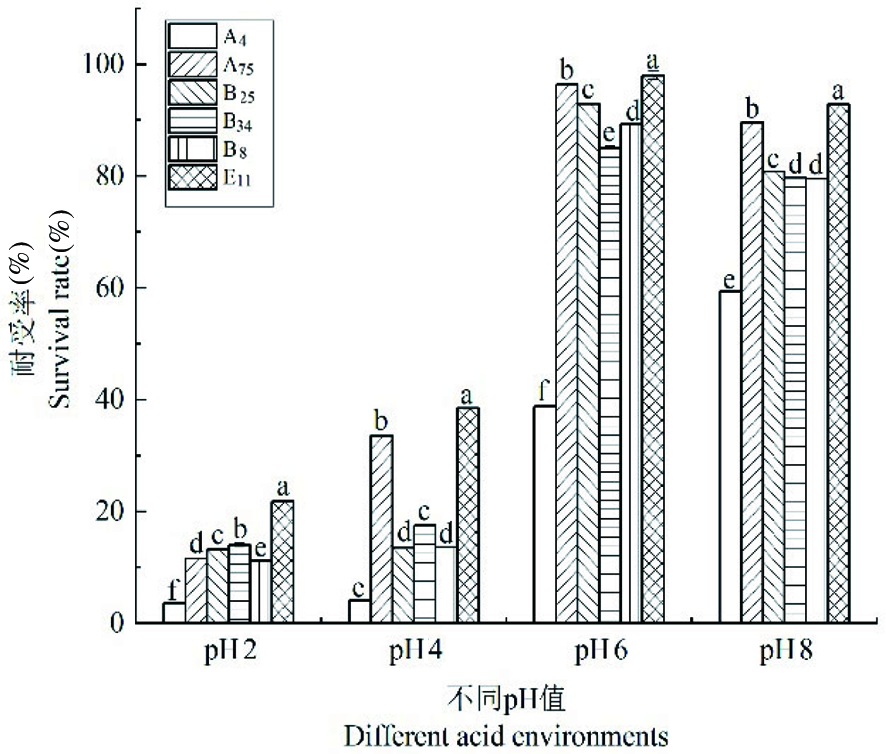
图7 菌株耐酸能力 注:在图中不同的字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),同一个字母表示差异不显著(P>0.05),下同
Fig.7 Acid tolerance of the strains Note: Different letters in the figure indicate significant differences (P<0.05), the same letter means no significant difference (P>0.05)
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 不同时间活菌数(Lg(CFU/mL)) Number of viable bacteria at different times | 2 h存活率 2 h survival (%) | 4 h存活率 4 h survival (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 2 h | 4 h | |||
| A4 | 10.71±0.01 | 9.71±0.01 | 6.28±0.04 | 90.7±0.14 d | 58.64±0.41 c |
| A75 | 10.79±0.01 | 10.68±0.01 | 6.68±0.01 | 99.04±0.12 b | 61.91±0.14 b |
| B25 | 9.65±0.01 | 8.75±0.01 | 6.02±0.02 | 90.71±0.09 d | 62.38±0.21 ab |
| B34 | 9.48±0.04 | 8.72±0.01 | 5.93±0.02 | 91.97±0.27c | 62.55±0.18 a |
| B8 | 9.70±0.01 | 8.72±0.01 | 6.05±0.02 | 89.93±0.04 e | 62.37±0.13 ab |
| E11 | 10.80±0.01 | 10.75±0.01 | 6.78±0.01 | 99.52±0.14 a | 62.78±0.12 a |
表4 各菌株在模拟人工胃液的耐受能力
Table 4 Resistance tosimulated gastric solution of the strains
| 菌株编号 Strain No. | 不同时间活菌数(Lg(CFU/mL)) Number of viable bacteria at different times | 2 h存活率 2 h survival (%) | 4 h存活率 4 h survival (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 h | 2 h | 4 h | |||
| A4 | 10.71±0.01 | 9.71±0.01 | 6.28±0.04 | 90.7±0.14 d | 58.64±0.41 c |
| A75 | 10.79±0.01 | 10.68±0.01 | 6.68±0.01 | 99.04±0.12 b | 61.91±0.14 b |
| B25 | 9.65±0.01 | 8.75±0.01 | 6.02±0.02 | 90.71±0.09 d | 62.38±0.21 ab |
| B34 | 9.48±0.04 | 8.72±0.01 | 5.93±0.02 | 91.97±0.27c | 62.55±0.18 a |
| B8 | 9.70±0.01 | 8.72±0.01 | 6.05±0.02 | 89.93±0.04 e | 62.37±0.13 ab |
| E11 | 10.80±0.01 | 10.75±0.01 | 6.78±0.01 | 99.52±0.14 a | 62.78±0.12 a |
| [1] | 李宇辉, 王俊钢, 刘成江, 等. 新疆伊犁牧区发酵乳制品中酵母菌的分离和多样性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2013, 39(7):98-103. |
| LI Yuhui, WANG Jungang, LIU Chengjiang, et al. Analysis on separation and diversity of yeast from traditional fermented milk product in Xinjiang Yili of China[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2013, 39(7):98-103. | |
| [2] | 张亚川, 蔡静静, 剡文莉, 等. 新疆伊犁地区乳品中发酵菌种的筛选及产酸性能研究[J]. 中国乳品工业, 2019, 47(7):4-7,18. |
| ZHANG Yachuan, CAI Jingjing, YAN Wenli, et al. Study on screening and acid-production performance of yogurt starter strains from Yili dairy products in Xinjiang[J]. China Dairy Industry, 2019, 47(7):4-7,18. | |
| [3] | 马燕, 倪永清, 卢士玲, 等. 新疆特色干酪中乳酸菌的分离鉴定[J]. 中国酿造, 2011, 30(8):38-40. |
| MA Yan, NI Yongqing, LU Shiling, et al. Isolation and identification of lactic acid bacteria from a traditional cheese in Xinjiang[J]. China Brewing, 2011, 30(8):38-40. | |
| [4] | 杜紫萱, 卢士玲, 王晓雯, 等. 新疆哈族奶酪中产蛋白酶非发酵剂乳酸菌的筛选及其系统发育分析[J]. 中国酿造, 2016, 35(5):20-24. |
| DU Zixuan, LU Shiling, WANG Xiaowen, et al. Screening of protease-producing non-starter lactic acid bacteria from Xinjiang Kazak cheese and its phylogenetic analysis[J]. China Brewing, 2016, 35(5):20-24. | |
| [5] | 拉米拉·阿萨特, 刘艳, 李伟, 等. 新疆传统发酵奶酪中乳酸菌的益生特性研究(英文)[J]. 浙江大学学报B辑(生物医学与生物技术)(英文版), 2016, 17(8):597-609. |
|
Ramila Azat, LIU Yan, LI Wei, et al. Probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditionally fermented Xinjiang cheese[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University - Science B (Biomedicine & Biotechnology), 2016, 17(8):597-609.
DOI URL |
|
| [6] | 马杨. 新疆酸凝奶酪菌种动态变化与风味物质相关性研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2013. |
| MA Yang. Study on the Relevance between Strains Dynamic Changes and Flavor Compounds of Xinjiang Characteristics Cheese[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2013. | |
| [7] |
Berlec A, Tompa G, Slapar N, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions for the expression of sweet‐tasting protein brazzein in Lactococcus lactis[J]. Letters in Applied Microbiology, 2010, 46(2):227-231.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
Liu W J, Sun Z H, Zhang Y B, et al. A survey of the bacterial composition of kurut from Tibet using a culture-independent approach[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2012, 95(3):1064-1072.
DOI PMID |
| [9] | 陈欢. 新疆哈萨克族传统奶酪中乳酸菌发酵剂的筛选及对奶酪风味影响的研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2019. |
| CHEN Huan. Screening of Lactic Acid Bacteria Starter in Xinjiang Kazakh Traditional Cheese and Its Effect on Cheese Flavor[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2019. | |
| [10] | 王晓雯. 新疆塔城地区哈萨克族传统奶酪中非发酵剂乳酸菌多样性研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2016. |
| WANG Xiaowen. Diversity of Non Starter Lactic Acid Bacteria for Xinjiang Kazak Traditional Cheese in Tacheng Area[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2016. | |
| [11] | 郑晓吉. 新疆哈萨克族奶酪微生物菌群结构及特征风味解析[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2018. |
| ZHENG Xiaoji. Microbial Community Flora in Kazak Artisanal Cheese and Analysis on the Formation of Flavor Compounds[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2018. | |
| [12] | 张俊, 王炳文, 赵保堂, 等. 甘南传统牦牛酸奶来源抗氧化性乳酸发酵菌株的筛选[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2019, 45(15):74-80. |
| ZHANG Jun, WANG Bingwen, ZHAO Baotang, et al. Antioxidative lactic acid fermenting strains screening from traditional yak yogurt in Gannan[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(15):74-80. | |
| [13] | 黄澄, 陈睿, 朱春燕, 等. 一株产酸性菊粉酶乳酸菌的筛选及其酶学性质研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(19):43-47. |
| HUANG Cheng, CHEN Rui, ZHU Chunyan, et al. Screening and characterization of an acidic inulinase produced by Leuconostoccitreum strain[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(19):43-47. | |
| [14] | GB 4789.35—2016食品微生物学检验:乳酸菌检验[S]. |
| GB 4789.35-2016. Food microbiological examination: Lactic acid bacteria[S]. | |
| [15] | 李美伦, 姜萌艺, 龚川杰, 等. 乳酸菌、酵母菌的筛选鉴定及其在米发糕中的应用[J]. 食品与机械, 2019, 35(5):14-20. |
| LI Meilun, JIANG Mengyi, GONG Chuanjie, et al. Screening and identification of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts and its application in fermented rice cake[J]. Food & Machinery, 2019, 35(5):14-20. | |
| [16] | 杨行, 王莉, 郭丽君, 等. 新疆喀什地区传统酸奶中乳酸菌的分离鉴定及产酸能力评价[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(2):102-107. |
| YANG Hang, WANG Li, GUO Lijun, et al. Screening and identification of lactic acid bacteria from traditional yoghurt in Kashi region and its acid-producing characteristics[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(2):102-107. | |
| [17] | 罗强, 李幸洋, 陈炼红, 等. 传统发酵泡菜中乳酸菌种群组成及优良菌株产酸耐酸特性分析[J/OL]. 食品科学. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.ts.20200108.1307.008.html |
| LUO Qiang, LI Xingyang, CHEN Lianhong, et al. Study on the Composition of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Traditional Fermented Pickled Vegetables and Analysis of Acid-Producing and Acid-Resistant Characteristics of Excellent Strains[J/OL]. Food Science, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.ts.20200108.1307.008.html | |
| [18] | GB/T 5413.34-2010 食品安全国家标准:乳和乳制品酸度的测定[S]. |
| GB/T 5413.34-2010. National food safety standard Determination of acidity in milk and milk products[S]. | |
| [19] | 缑敬轩, 吕嘉枥, 张智维, 等. 泡菜中益生性乳酸菌的筛选和鉴定[J]. 中国酿造, 2008, 27(6):22-24. |
| GOU Jingxuan, LÜ Jiali, ZAHNG Zhiwei, et al. Isolation and identification of probiotic lactic acid bacteria starter from pickles[J]. China Brewing, 2008, 27(6):22-24. | |
| [20] | 龚加路, 赵兴秀, 邹伟, 等. 高产酸乳酸菌的分离鉴定及其益生特性的研究[J]. 中国调味品, 2016, 41(3):17-20,31. |
| GONG Jialu, ZHAO Xingxiu, ZOU Wei, et al. Isolation and Identification of a High-yield Lactic Acid Bacterium and Its Probiotic Property[J]. China Condiment, 2016, 41(3):17-20,31. | |
| [21] | 唐璎, 孟宪刚, 邓展瑞, 等. 西北酸菜中吸附黄曲霉毒素B_1乳酸菌株的筛选鉴定及稳定性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(15):60-65. |
| TANG Ying, MENG Xiangang, DENG Zhanrui, et al. Screening and stability of an aflatoxin B1-adsorbing lactic acid bacterium isolated from pickled vegetable in northwest China[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(15):60-65. | |
| [22] | Domingos-Lopes M, Stanton C, Ross P R, et al. Genetic diversity, safety and technological characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from artisanal Pico cheese[J]. Food Microbiology, 2017, 63(MAY):178-190. |
| [23] |
Han Q, Kong B, Chen Q, et al. In vitro comparison of probiotic properties of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Harbin dry sausages and selected probiotics[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2017, 32:391-400.
DOI URL |
| [24] | 于迪, 乔羽, 范振宇, 等. 山西老陈醋发酵过程中高产酸乳酸菌的鉴定[J]. 中国调味品, 2018, 43(4):4-8. |
| YU Di, QIAO Yu, FAN Zhenyu, et al. Screening and Identification of High Acid-producing Lactic Acid Bacteria in the Fementation of Shanxi Mature Vinegar[J]. China Condiment, 2018, 43(4):4-8. | |
| [25] | 林丽, 邓倩, 罗琳, 等. 代谢多种低聚糖乳酸菌的筛选鉴定及其部分益生特性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2020, 46(17):80-86. |
| LIN Li, DENG Qian, LUO Lin, et al. Screening and identification of lactic acid bacteria utilizing various oligosaccharides and their partial prebiotic properties[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(17):80-86. | |
| [26] | 武怡荷, 胡会玲, 陈书明, 等. 四株儿茶酚类铁载体高产菌株产消化酶活性及其益生特性[J]. 微生物学通报, 2020, 47(6):1807-1816. |
| WU Yihe, HU Huiling, CHEN Shuming, et al. Digestive enzymes and probiotic properties of four bacteria with high yield catechol siderophore[J]. Microbiology China, 2020, 47(6):1807-1816. | |
| [27] |
Ding W, Shi C, Chen M, et al. Screening for lactic acid bacteria in traditional fermented Tibetan yak milk and evaluating their probiotic and cholesterol-lowering potentials in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2017, 32:324-332.
DOI URL |
| [28] | 夏海燕, 周思多, 张明喆, 等. 酢辣椒中益生乳酸菌的筛选及其功能特性[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(6):93-99. |
| XIA Haiyan, ZHOU Siduo, ZHANG Mingzhe, et al. Screening and Functional Characteristics of Probiotics from Zuolajiao, a Traditional Fermented Hot Pepper Product[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(6):93-99. | |
| [29] | 赵圣明, 赵岩岩, 马汉军, 等. 发酵酸菜来源乳酸菌的益生特性及其在发酵乳中的应用[J]. 食品科学, 2019, 40(6):187-194. |
| ZHAO Shengming, ZHAO Yanyan, MA Hanjun, et al. Probiotic Properties of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Pickled Chinese Cabbage and Its Application in Fermented Milk[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(6):187-194. | |
| [30] | Santiago Ruiz-Moyano, María Teresa P,. Gonçalves dos Santos, Ana I.Galván, et al. Screening of autochthonous lactic acid bacteria strains from artisanal soft cheese:probiotic characteristics and prebiotic metabolism[J]. Elsevier Ltd, 2019:114. |
| [31] |
LÜ Xin, Pan H U, Ying D, et al. Purification and partial characterization of a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus casei TN-2 isolated from fermented camel milk (Shubat) of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous region, China[J]. Food Control, 2014, 43(5):276-283.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Zheng X, Fei L, Li K, et al. Evaluating the microbial ecology and metabolite profile in Kazak artisanal cheeses from Xinjiang, China[J]. Food Research International, 2018, 111(SEP.):130-136. |
| [33] | 陈欢, 王斌, 史学伟, 等. 新疆哈萨克族传统奶酪中潜在益生乳酸菌的筛选[J]. 中国调味品, 2019, 44(12):50-54. |
| CHEN Huan, WANG Bin, SHI Xuewei, et al. Screening of Potential Probiotic Lactic Acid Bacteria in Xinjiang Kazak Traditional Cheese[J]. China Condiment, 2019, 44(12):50-54. | |
| [34] | Saez G D, Hebert E M, Saavedra L, et al. Molecular identification and technological characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from fermented kidney beans flours (Phaseolus vulgaris L. and P. coccineus) in northwestern Argentina[J]. Food Research International, 2017, 102(dec.):605. |
| [35] | Hernán E, Verón, et al. Isolation and selection of potential probiotic lactic acid bacteria from Opuntia ficus-indica fruits that grow in Northwest Argentina[J]. LWT Food Science & Technology, 2017. |
| [36] |
Won S M, Chen S, Park K W, et al. Isolation of lactic acid bacteria from kimchi and screening of Lactobacillus sakei ADM14 with anti-adipogenic effect and potential probiotic properties[J]. LWT- Food Science and Technology, 2020, 126:109296.
DOI URL |
| [37] | 王璐, 王伟伟, 王艳霞, 等. 果蔬发酵乳酸菌的筛选、鉴定及发酵性能分析[J]. 食品科学, 2020, 41(10):166-171. |
| WANG Lu, WANG Weiwei, WANG Yanxia, et al. Screening,Identification and Fermentation Characteristics of Lactic Acid Bacteria for Fermentation of Fruits and Vegetables[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(10):166-171. |
| [1] | 何齐, 冯倩, 李雪, 易鸳鸯, 顾美英, 朱静, 孙建, 张志东. 赛里木酸奶中乳酸菌的分离鉴定及特性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2323-2330. |
| [2] | 贺婷婷, 王旭哲, 宋磊, 马春晖. 不同添加剂对油莎豆青贮品质及有氧稳定性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(7): 1767-1775. |
| [3] | 罗影;关永强;贾培松;努尔孜亚·亚力买买提;郝敬喆;贾文捷;魏鹏. 新疆阿魏菇细菌性斑点病病原菌的鉴定[J]. , 2017, 54(3): 513-519. |
| [4] | 魏志奎;王子荣;王琴;臧长??杨开伦. 五种发酵剂发酵酸奶品质比较研究[J]. , 2015, 52(3): 566-571. |
| [5] | 刘晓蓉;向廷建;逄焕明;古丽娜孜;李瑾瑜;王子荣. 乌昌地区传统酸牛奶中乳酸菌的分离鉴定[J]. , 2013, 50(8): 1434-1441. |
| [6] | 唐血梅;李海英;赵芳;姚新奎;董婷;车驰;祝春梅;刘婷婷;曾亚琦;韩煜茹;曹丽萍;王建文;刘志安;孟军;李智军. 新疆酸马奶中高产胞外多糖乳酸菌筛选鉴定及培养条件优化研究[J]. , 2012, 49(8): 1540-1545. |
| [7] | 任志娟;李轶杰;马正海. 乳酸乳球菌质粒提取方法的改进与优化[J]. , 2011, 48(4): 734-738. |
| [8] | 陈阳;姚新奎;潘道东;曾小群. 一株酸马奶乳酸菌分子生物学鉴定及降解胆固醇试验研究[J]. , 2009, 46(5): 1121-1125. |
| [9] | 张晓琳;王炜;张广敏;常玮;孔健. 类开菲尔粒的发酵特性及强产酸乳酸菌的分离鉴定[J]. , 2009, 46(4): 856-860. |
| [10] | 傅力;葛钰瑛;李焕荣;朱正兰;桑昆. 发酵羊肉乳酸菌发酵剂的筛选及发酵性能研究[J]. , 2009, 46(3): 630-634. |
| [11] | 熊素玉;姚新奎;谭小海;刘珩;张积荣;陈潇;许鹏;熊伟. 酸马奶中乳酸菌的分离、纯化与鉴定[J]. , 2007, 44(5): 696-701. |
| [12] | 熊素玉;姚新奎;谭小海;刘珩;张积荣;曾波;许鹏;熊伟;吴津蓉. 不同温度及pH条件对乳酸菌生长影响的研究[J]. , 2006, 43(6): 533-538. |
| [13] | 黄玲. 对番茄酱中乳酸菌培养基的筛选研究[J]. , 2004, 41(z1): 90-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||