

Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (7): 1766-1771.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.07.024
• Plant Protection·Soil Fertilizer • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHEN Hongfei1,2( ), JIA Fenglian1, LIU Yi2, WU Yan2, YANG Ruwei2(
), JIA Fenglian1, LIU Yi2, WU Yan2, YANG Ruwei2( ), SUN Hui2, LI Guangyue1(
), SUN Hui2, LI Guangyue1( )
)
Received:2024-01-05
Online:2024-07-20
Published:2024-09-04
Correspondence author:
YANG Ruwei, LI Guangyue
Supported by:
洪飞1,2( ), 贾丰莲1, 刘易2, 吴燕2, 杨茹薇2(
), 贾丰莲1, 刘易2, 吴燕2, 杨茹薇2( ), 孙慧2, 李广悦1(
), 孙慧2, 李广悦1( )
)
通讯作者:
杨茹薇,李广悦
作者简介:沈洪飞(1989-),男,云南昆明人,助理研究员,研究方向为马铃薯育种及病害防治,(E-mail)hongfeiscience@163.com
基金资助:CLC Number:
SHEN Hongfei, JIA Fenglian, LIU Yi, WU Yan, YANG Ruwei, SUN Hui, LI Guangyue. Isolation and identification of the pathogen for potato black scurf in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(7): 1766-1771.
洪飞, 贾丰莲, 刘易, 吴燕, 杨茹薇, 孙慧, 李广悦. 新疆马铃薯黑痣病病原菌的分离及定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(7): 1766-1771.
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| ITS1 | TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
| AG-2-1-F | CAAAGGCAATGGGTTATTGGAC |
| AG-2-1-R | CCTGATTTGAGATCAGATCATAAAG |
| Rs1F2 | TTGGTTGTAGCTGGTCTATTT |
| AG-3PR2 | ACACTGAGATCCAGCTAATA |
Tab.1 Primers for pathogen identification
| 引物名称 Primer name | 引物序列(5'-3') Primer sequence(5'-3') |
|---|---|
| ITS1 | TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG |
| ITS4 | TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC |
| AG-2-1-F | CAAAGGCAATGGGTTATTGGAC |
| AG-2-1-R | CCTGATTTGAGATCAGATCATAAAG |
| Rs1F2 | TTGGTTGTAGCTGGTCTATTT |
| AG-3PR2 | ACACTGAGATCCAGCTAATA |
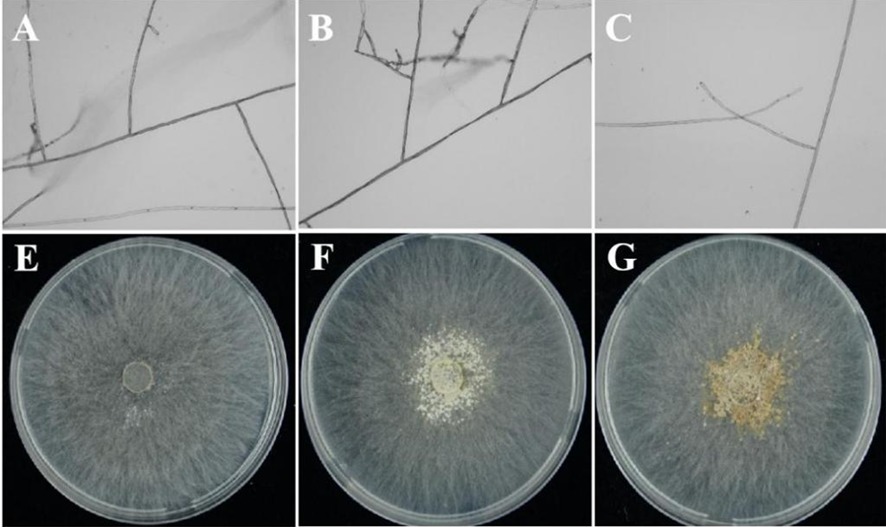
Fig.1 Changes of morphological characteristics of pathogen isolated from potato sample infected with R.solani Note: A-C is the hyphal growth characteristic; E is the colony of pathogen incubatedon in PDA media for 72 hours, F is the colony of pathogen incubatedon in PDA media for 96 hours, and G is the colony of pathogen incubatedon in PDA media for 168 hours

Fig.2 Verification of pathogenicity of the isolated strains Note: CK is harvested tuber from soil without tuber; XJ1-4 was a tieback strain isolated from tuber and harvested tuber
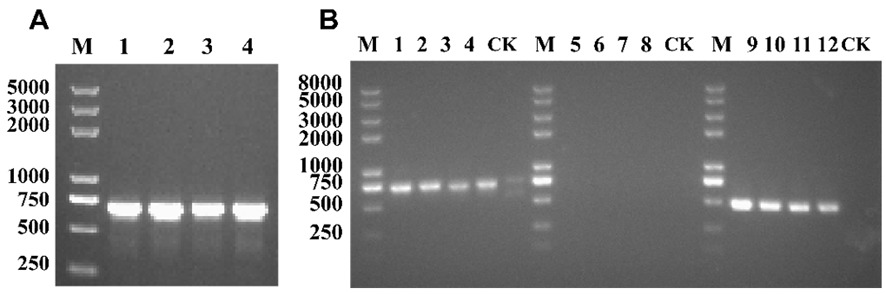
Fig.3 Gel electrophoresis of the PCR amplification with specific primer Note: A is the electrophoretic PCR amplification of universal primer ITS1/IT4 in ITS region of the original pathogen, M is Star Marker D2000 PlusⅡ, 1-4 is strain XJ1-4 isolated from Xinjiang potato.The B diagram is an electrophoretic diagram of PCR amplification verification of pathogens reisolated after tieback.1-4 are universal primers ITS1/IT4.5-8 is the specific primer AG-2-1-F/R, and 9-12 is the specific primer Rs1F2/AG-3PR2
| [1] |
Liu B B, Gu W Y, Yang Y, et al. Promoting potato as staple food can reduce the carbon-land-water impacts of crops in China[J]. Nature Food, 2021, 2(8): 570-577.
DOI PMID |
| [2] | Kȓíkovská B, Viktorová J, Lipov J. Approved genetically modified potatoes (Solanum tuberosum) for improved stress resistance and food safety[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2022, 70(38): 11833-11843. |
| [3] |
高勇刚, 高海峰, 吕卓, 等. 新疆北部沿天山主要种植区马铃薯病害分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(1): 170-178.
DOI |
|
GAO Yonggang, GAO Haifeng, LYU Zhuo, et al. Investigation into the diseases of the potato in different producing areas in Xinjiang[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 170-178.
DOI |
|
| [4] | 王利红, 姜华, 王艳丽, 等. 立枯丝核菌遗传多样性的研究方法[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2013, 29(3): 226-233. |
| WANG Lihong, JIANG Hua, WANG Yanli, et al. Methodology in researching of genetic variance ofRhizoctonia solani[J]. Chinese Journal of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2013, 29(3): 226-233. | |
| [5] | 夏善勇, 牛志敏, 李庆全, 等. 马铃薯黑痣病立枯丝核菌及其综合防控研究进展[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2022, 50(12): 28-34. |
| XIA Shanyong, NIU Zhimin, LI Qingquan, et al. Research progress on Rhizoctonia solani causing potato black scurf and its comprehensive control[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 50(12): 28-34. | |
| [6] | Iradukunda L, Wang Y, Nkurikiyimfura O, et al. Establishment and Application of a Multiplex PCR Assay for the Rapid Detection of Rhizoctonia solani Anastomosis Group (AG)-3PT, the Pathogen Causing Potato Black Scurf and Stem Canker[J]. 2022, 11(6): 627. |
| [7] | 李磊, 陈利达, 黄艺烁, 等. 马铃薯黑痣病菌实时荧光定量PCR检测体系的建立及应用[J]. 农业生物技术学报, 2021, 29(7): 1417-1425. |
| LI Lei, CHEN Lida, HUANG Yishuo, et al. Establishment and application of real-time quantitative PCR detection system for black scurf pathogen in potato(Solanum tuberosum)[J]. Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2021, 29(7): 1417-1425. | |
| [8] |
李晓妮, 徐娜娜, 于金凤. 中国北方马铃薯黑痣病立枯丝核菌的融合群鉴定[J]. 菌物学报, 2014, 33(3): 584-593.
DOI |
|
LI Xiaoni, XU Nana, YU Jinfeng. Anastomosis groups ofRhizoctonia solanifrom black scurf of potato in Northern China[J]. Mycosystema, 2014, 33(3): 584-593.
DOI |
|
| [9] | 刘霞, 冯蕊, 高达芳, 等. 云南省马铃薯黑痣病病原菌融合群鉴定及8种药剂对其的毒力[J]. 植物保护, 2016, 42(2): 165-170. |
| LIU Xia, FENG Rui, GAO Dafang, et al. Anastomosis groups ofRhizoctonia solani and toxicity of eight fungicides against R.solani from black scurf of potato[J]. Plant Protection, 2016, 42(2): 165-170. | |
| [10] | 杨帅, 郭梅, 王文重, 等. 黑龙江省马铃薯黑痣病菌融合群类型分析[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2022, 36(3): 228-235. |
| YANG Shuai, GUO Mei, WANG Wenzhong, et al. Identity of the anastomosis group of potato black scurf in Heilongjiang Province[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2022, 36(3): 228-235. | |
| [11] | 刘宝玉, 胡俊, 蒙美莲, 等. 马铃薯黑痣病病原菌分子鉴定及其生物学特性[J]. 植物保护学报, 2011, 38(4): 379-380. |
| LIU Baoyu, HU Jun, MENG Meilian, et al. Molecular identification and biological characters of the pathogen causing black scurf disease in potato[J]. Journal of Plant Protection, 2011, 38(4): 379-380. | |
| [12] | 杨帅, 闵凡祥, 高云飞, 等. 环境因子对马铃薯致病立枯丝核菌AG-3融合群生长的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学, 2016, 44(24): 151-154. |
| YANG Shuai, MIN Fanxiang, GAO Yunfei, et al. Influence of environmental factors on growth status of AG-3 for potato pathogenicRhizoctonia solani[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2016, 44(24): 151-154. | |
| [13] | 戴启洲. 马铃薯黑痣病发病规律及综合防治[J]. 中国蔬菜, 2012,(15): 31-32. |
| DAI Qizhou. Incidence and comprehensive control of potato black scurf[J]. China Vegetables, 2012,(15): 31-32. | |
| [14] | 曹春梅, 王晓娇, 许飞, 等. 内蒙古地区马铃薯黑痣病立枯丝核菌融合群及致病性研究[J]. 中国马铃薯. 2018, 32(5): 293-302. |
| CAO Chunmei, WANG Xiaojiao, XU Fei, et al. Anastomosis Groups of Rhizoctonia solani from Potato and Pathogenicities in Inner Mongolia[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2018, 32(5): 293-302. | |
| [15] | Yang Y G, Zhao C, Guo Z J, et al. Anastomosis group and pathogenicity ofRhizoctonia solani associated with stem canker and black scurf of potato in China[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2015, 143(1): 99-111. |
| [16] | 田晓燕, 蒙美莲, 张笑宇, 等. 马铃薯黑痣病菌菌丝融合群的鉴定[J]. 中国马铃薯, 2011, 25(5): 298-301. |
| TIAN Xiaoyan, MENG Meilian, ZHANG Xiaoyu, et al. Identification of anastomosis groups ofRhizoctonia solanion potato plant[J]. Chinese Potato Journal, 2011, 25(5): 298-301. | |
| [17] | Djébali N, Elkahoui S, Taamalli W, et al. TunisianRhizoctonia solaniAG3 strains affect potato shoot macronutrients content, infect faba bean plants and showin vitroresistance to azoxystrobin[J]. Australasian Plant Pathology, 2014, 43(3): 347-358. |
| [18] | López-Corrales R, Michereff S J, Garcia-Estrada R S, et al. First confirmed report ofRhizoctonia solani AG-7 causing potato stem canker inMexico[J]. Plant Disease, 2023. |
| [19] |
Moliszewska E, Nabrdalik M, Ziembik Z. Rhizoctonia solaniAG 11 isolated for the first time from sugar beet in Poland[J]. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 2020, 27(7): 1863-1870.
DOI PMID |
| [20] | Yang Y G, Zhao C, Guo Z J, et al. Anastomosis group and pathogenicity ofRhizoctonia solani associated with stem canker and black scurf of potato in China[J]. European Journal of Plant Pathology, 2015, 143(1): 99-111. |
| [21] | Chen W R, Chen J D, Zeb A, et al. Mobile convolution neural network for the recognition of potato leaf disease images[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2022, 81(15): 20797-20816. |
| [22] | Iradukunda L, Wang Y P, Nkurikiyimfura O, et al. Establishment and application of a multiplex PCR assay for the rapid detection ofRhizoctonia solani anastomosis group (AG)-3PT, the pathogen causing potato black scurf and stem canker[J]. Pathogens, 2022, 11(6): 627. |
| [1] | YU Lyujian, YANG Jin, DING Yu, LI Xiaoman, LIU Fengjuan, FAN Yingying, LIANG Hongyu, JIAO Ziwei, WANG Cheng. Isolation,identification and pathogenicity of fungi on the surface of pomegranate fruit [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(1): 148-155. |
| [2] | XU Lijuan, CHEN Yong, WANG Zeyu, WANG Bo, Ainijiang Ersiman, GUO Rui, LI Kemei, SONG Suqin. Isolation, identification and biological characteristics of potato scab pathogen in Baicheng, Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 60(9): 2258-2265. |
| [3] | SONG Suqin, GAO Haifeng, LV Zhuo, TANG Qiyong, GU Meiying, ZHANG Zhidong, CHU Min, ZHU Jing, WANG Wei. Isolation and Identification of Pathogen of Potato Scab and Its Growth Characteristics from Zepu Area in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(8): 1999-2006. |
| [4] | GAO Yonggang, GAO Haifeng, LÜ Zhuo, XU lijuan, , TANG Qiyong, GU Meiying, ZHANG Lijuan, ZHU Jinquan, SONG Suqin. Investigation into the Diseases of the Potato in Different Producing Areas in Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(1): 170-178. |
| [5] | LÜ Zhuo, GAO Yonggang, TANG Qiyong, CHU Min, GU Meiying, ZHU Jing, CHENG Siqi, MA Xiaoxue, SONG Suqin, WANG Jing. Preliminary Identification of the Pathogen of Potato Disease in Qitai [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2020, 57(5): 902-909. |
| [6] | HAN Meng-li, ZHANG Xing-xing, WU Tong-zhong, GUO Qiang-qiang, HUANG Xin, ZHONG Fa-gang. Isolation and Identification of Pasteurella multocida Rabbits [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2018, 55(7): 1333-1342. |
| [7] | DAI Jing, PENG Bin, LEI Chen-hong, Aray Hayrat. Isolation,Identification and Drug Resistance Detection of Campylobacter Jejuni from Cattle in Partial Areas of Xinjiang [J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2017, 54(9): 1730-1736. |
| [8] | YANG Xue-yun;LI Jian-jun;WANG Shuo;WU Jian-yong;WANG Deng-feng;WANG Zhi-cai. Evaluation of the Modified Granada Medium for Detection of Streptococcus agalactiae from Mastitis Samples [J]. , 2014, 51(11): 2093-2098. |
| [9] | LIU Xiao-rong;XIANG Ting-jian;PANG Huan-ming;Gulinazi;LI Jin-yu;WANG Zi-rong. Isolation and Identification of Lactic Acid Bacteria from Tradional Yogurt in Urumqi and Changji Region [J]. , 2013, 50(8): 1434-1441. |
| [10] | ZHANG Xiang-feng;Ainiwaer·Aishan;Mairemunisha·Wufuer;YAN Jing-yang;Yusufu·Rexiti. Isolation and Identification of Lactobacillus from Xinjiang Small Reed Silage [J]. , 2009, 46(6): 1327-1331. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||