

新疆农业科学 ›› 2024, Vol. 61 ›› Issue (11): 2844-2852.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2024.11.026
陆桂丽( ), 苗书魁(
), 苗书魁( ), 魏婕, 魏玉荣, 米晓云, 海力且木·买买提依明
), 魏婕, 魏玉荣, 米晓云, 海力且木·买买提依明
收稿日期:2024-04-11
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2025-01-08
通信作者:
苗书魁(1983- ),男,甘肃人,正高级实验师,硕士,研究方向为动物病毒病原学及免疫学,(E-mail)903076760@qq.com作者简介:陆桂丽(1977-),女,江苏人,研究员,博士,研究方向为动物传染病防控,(E-mail)66498744@qq.com
基金资助:
LU Guili( ), MIAO Shukui(
), MIAO Shukui( ), WEI Jie, WEI Yurong, MI Xiaoyun, Hailiqiemu Maimaitiyiming
), WEI Jie, WEI Yurong, MI Xiaoyun, Hailiqiemu Maimaitiyiming
Received:2024-04-11
Published:2024-11-20
Online:2025-01-08
Supported by:摘要:
【目的】研究新疆牛冠状病毒(Bovine coronavirus,BCoV)流行株的遗传变异规律,分析纤突(Spike,S)蛋白结构与功能特征。【方法】对新疆巴楚县某牛场BCoV阳性的犊牛粪便,提取病毒RNA,采用RT-PCR方法扩增S基因,通过序列测定和拼接,获得BCoV S基因全长序列,对其开展生物信息学分析和遗传进化分析。【结果】获得BCoV S基因核苷酸序列(GenBank索引号:OR136878.1)。S基因全长4 092核苷酸(nucleotide,nt),编码1 363氨基酸(amino acid,aa)。BCoV S蛋白分子量为150.67 Ku,等电点为5.29,有1个跨膜螺旋区,亲水性较弱,疏水性略强。S蛋白主要分布于宿主细胞的内质网膜和高尔基体,具有信号肽的概率为0.984 2,是分泌型蛋白,含有14个潜在的N-糖基化位点和132个磷酸化位点。S蛋白具有3个结构域,其中受体结合结构域(Receptor binding domain,RBD)共含有215 aa,无规则卷曲(Coiled coil, Cc)占比最高(62.79%),其次为延伸链(Extended strand, Es)(20.47%)和α-螺旋(α-helix, Hh)(12.56%),β-转角(β-turn, Tt)占比最少(4.19%)。筛选出S蛋白15个优势B细胞表位和11个T细胞表位。S蛋白能与SWISS-MODEL数据库中模板(SMTL ID:7sbw.1.C)同源建模,二者序列相似性为92.00%,模型GMQE值为0.76,QMEAN值为0.82,符合率较高,拉氏图(Ramachandran plots)的Ramachandran favored值为96.14%,表明空间构象合理,模型准确可靠。遗传进化试验扩增的BCoVS基因序列,与2016年我国新疆的BCV-Aks-01株处于同一小分支,两者S基因核苷酸序列同源性为99.1%。【结论】BCoV S蛋白存在多个抗原表位。RBD在病毒进入宿主细胞时具有重要作用,可针对RBD序列设计疫苗靶点,阻止病毒与宿主受体结合。采用生物信息学方法首次分析BCoV S蛋白理化性质、信号肽和亚细胞定位、磷酸化位点、糖基化位点、结构域、抗原表位、三级结构和RBD二级结构等特征,为BCoV S基因遗传进化、结构与功能研究、疫苗研发、靶向药物设计提供参考。
中图分类号:
陆桂丽, 苗书魁, 魏婕, 魏玉荣, 米晓云, 海力且木·买买提依明. 牛冠状病毒纤突蛋白的结构与功能分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2024, 61(11): 2844-2852.
LU Guili, MIAO Shukui, WEI Jie, WEI Yurong, MI Xiaoyun, Hailiqiemu Maimaitiyiming. Structure and function analysis of spike protein of bovine coronavirus[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 61(11): 2844-2852.
| 引物 Primer | 序列(5'-3') Sequence (5'-3') | 产物长度 Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| BCoV S1F | TACCTATTTGTGTGTATG | 923 |
| BCoV S1R | ATTCTAAAGTCATAGCAC | |
| BCoV S2F | GGTGTTGTTTCCTGTTTA | 919 |
| BCoV S2R | AAGACCCATCCAATTTAC | |
| BCoV S3F | ATTTACCTGCTGCTAATGT | 911 |
| BCoV S3R | GACAACACAACCAAGATAG | |
| BCoV S4F | CTACGGTTTTAGAGATTAC | 876 |
| BCoV S4R | AACACCTTGATACCATTAT | |
| BCoV S5F | TGTATTAGGTTGTTTAGGA | 908 |
| BCoV S5R | CAGTGAACATCCAAGTATT | |
| BCoV S6F | TTTTGTGGTAATGGTAATC | 904 |
| BCoV S6R | GAACAGTAATAGGCATAAT |
表1 牛冠状病毒S基因引物
Tab.1 Primers of S gene of bovine coronavirus
| 引物 Primer | 序列(5'-3') Sequence (5'-3') | 产物长度 Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| BCoV S1F | TACCTATTTGTGTGTATG | 923 |
| BCoV S1R | ATTCTAAAGTCATAGCAC | |
| BCoV S2F | GGTGTTGTTTCCTGTTTA | 919 |
| BCoV S2R | AAGACCCATCCAATTTAC | |
| BCoV S3F | ATTTACCTGCTGCTAATGT | 911 |
| BCoV S3R | GACAACACAACCAAGATAG | |
| BCoV S4F | CTACGGTTTTAGAGATTAC | 876 |
| BCoV S4R | AACACCTTGATACCATTAT | |
| BCoV S5F | TGTATTAGGTTGTTTAGGA | 908 |
| BCoV S5R | CAGTGAACATCCAAGTATT | |
| BCoV S6F | TTTTGTGGTAATGGTAATC | 904 |
| BCoV S6R | GAACAGTAATAGGCATAAT |
| 分析项目 Items analyzed | 工具 Tools | 网址/软件 Website/Software |
|---|---|---|
| 理化性质分析 Analysis of physico chemical properties | Expasy-ProtScale | https://web.expasy.org/protparam |
| 跨膜结构 Transmembrane structure | TMHMM Server v2.0 | https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?DeepTMHMM |
| 测亲/疏水性 Test for kin ship/hydrophobicity | ExPAsy | https://web.expasy.org/protscale |
| 信号肽Signal peptide | SignalP | https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?SignalP-5.0 |
| 亚细胞定位Subcellular localization | PSORT Ⅱ | https://psort.hgc.jp/form2.html |
| 糖基化位点Glycosy lation site | NetNGlyc-1.0 | https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetNGlyc |
| 磷酸化位点Phosphorylation site | NetPhos-3.1 | http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos |
| 结构域Domain | SMART | http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/set_mode.cgi?NORM |
| 受体结合结构域 Receptor binding domain | NPS@SOPMA | https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html |
| B细胞抗原表位B cell antigenic | ABCpred | https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/abcpred/index.html |
| T细胞抗原表位T cell antigenic | SYFPEITHI | http://www.syfpeithi.de/bin/mhcserver.dll/epitopeprediction.htm |
| 二级结构Seconclary structure | PRABI | https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html |
| 三级结构Tertiary structure | SWISS-MODEL | https://swissmodel.expasy.org/interactive |
| 遗传进化分析Genetic evolution analysis | Mega | Mega 5.0 |
表2 预测网址及软件
Tab.2 Prediction website and software
| 分析项目 Items analyzed | 工具 Tools | 网址/软件 Website/Software |
|---|---|---|
| 理化性质分析 Analysis of physico chemical properties | Expasy-ProtScale | https://web.expasy.org/protparam |
| 跨膜结构 Transmembrane structure | TMHMM Server v2.0 | https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?DeepTMHMM |
| 测亲/疏水性 Test for kin ship/hydrophobicity | ExPAsy | https://web.expasy.org/protscale |
| 信号肽Signal peptide | SignalP | https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?SignalP-5.0 |
| 亚细胞定位Subcellular localization | PSORT Ⅱ | https://psort.hgc.jp/form2.html |
| 糖基化位点Glycosy lation site | NetNGlyc-1.0 | https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetNGlyc |
| 磷酸化位点Phosphorylation site | NetPhos-3.1 | http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos |
| 结构域Domain | SMART | http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/smart/set_mode.cgi?NORM |
| 受体结合结构域 Receptor binding domain | NPS@SOPMA | https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=/NPSA/npsa_sopma.html |
| B细胞抗原表位B cell antigenic | ABCpred | https://webs.iiitd.edu.in/raghava/abcpred/index.html |
| T细胞抗原表位T cell antigenic | SYFPEITHI | http://www.syfpeithi.de/bin/mhcserver.dll/epitopeprediction.htm |
| 二级结构Seconclary structure | PRABI | https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa_sopma.html |
| 三级结构Tertiary structure | SWISS-MODEL | https://swissmodel.expasy.org/interactive |
| 遗传进化分析Genetic evolution analysis | Mega | Mega 5.0 |

图1 BCoV S基因扩增结果 注:M: GeneRuler 1kb Plus DNA Ladder;1~6:分别为BCoV-S1(923 bp)、BCoV-S2(919 bp)、BCoV-S3(911 bp)、BCoV-S4(876 bp)、BCoV-S5(908 bp)、BCoV-S6(904 bp)片段扩增产物
Fig.1 Amplification results of S gene of BCoV Note:M: GeneRuler 1kb Plus DNA Ladder;1~6:Amplified products of BCoV-S1(923 bp), BCoV-S2(919 bp), BCoV-S3(911 bp), BCoV-S4(876 bp), BCoV-S5(908 bp) and BCoV-S6(904 bp), respectively
| 排序 Rank | 抗原表位序列 Sequence | 氨基酸 起始位置 Start position | 评分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TGSGYYYPEPITGNNV | 1 200 | 0.97 |
| 2 | HTGIGTCPAGTNYLTC | 509 | 0.96 |
| 3 | LYEIQIPSEFTIGNME | 797 | 0.92 |
| 3 | RRSITTGYRFTNFEPF | 767 | 0.92 |
| 3 | YPTSGSTYRNMALKGT | 68 | 0.92 |
| 3 | PVTCNSAMTLEYWVTP | 249 | 0.92 |
| 4 | CDNINATLTEVNELLD | 848 | 0.91 |
| 4 | FHFYQEGGTFYAYFTD | 210 | 0.91 |
| 5 | ANSSEPALLFRNIKCN | 695 | 0.9 |
| 5 | NGLGTYYVLDRVYLNT | 45 | 0.9 |
| 5 | PSISTDTVDVTNGLGT | 34 | 0.9 |
| 5 | KTLSIAPSTGVYELNG | 297 | 0.9 |
| 5 | SHYYVMPVTCNSAMTL | 243 | 0.9 |
| 5 | CCTGCGTSCFKKCGGC | 1 330 | 0.9 |
| 5 | TCAVNYTKAPDVMLNI | 1 220 | 0.9 |
表3 S蛋白B细胞表位预测
Tab.3 Prediction of B cell epitopes of S protein
| 排序 Rank | 抗原表位序列 Sequence | 氨基酸 起始位置 Start position | 评分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | TGSGYYYPEPITGNNV | 1 200 | 0.97 |
| 2 | HTGIGTCPAGTNYLTC | 509 | 0.96 |
| 3 | LYEIQIPSEFTIGNME | 797 | 0.92 |
| 3 | RRSITTGYRFTNFEPF | 767 | 0.92 |
| 3 | YPTSGSTYRNMALKGT | 68 | 0.92 |
| 3 | PVTCNSAMTLEYWVTP | 249 | 0.92 |
| 4 | CDNINATLTEVNELLD | 848 | 0.91 |
| 4 | FHFYQEGGTFYAYFTD | 210 | 0.91 |
| 5 | ANSSEPALLFRNIKCN | 695 | 0.9 |
| 5 | NGLGTYYVLDRVYLNT | 45 | 0.9 |
| 5 | PSISTDTVDVTNGLGT | 34 | 0.9 |
| 5 | KTLSIAPSTGVYELNG | 297 | 0.9 |
| 5 | SHYYVMPVTCNSAMTL | 243 | 0.9 |
| 5 | CCTGCGTSCFKKCGGC | 1 330 | 0.9 |
| 5 | TCAVNYTKAPDVMLNI | 1 220 | 0.9 |
| 排序 Rank | 抗原表位序列 Sequence | 氨基酸起始位置 Start position | 评分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 052 | ALNNLLQQL | 28 |
| 2 | 1 070 | SLQEILSRL | 28 |
| 3 | 1 090 | LINGRLTAL | 28 |
| 4 | 1 311 | WLLIGFAGV | 27 |
| 5 | 972 | TLAATSASL | 26 |
| 6 | 4 | ILLISLPTT | 25 |
| 7 | 95 | FLSDFTNGI | 25 |
| 8 | 850 | NINATLTEV | 25 |
| 9 | 853 | ATLTEVNEL | 25 |
| 10 | 1 279 | RLQEAIKVL | 25 |
| 11 | 1 320 | AMLVLLFFI | 25 |
表4 S蛋白T细胞表位预测
Tab.4 Prediction of T cell epitopes of S protein
| 排序 Rank | 抗原表位序列 Sequence | 氨基酸起始位置 Start position | 评分 Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 052 | ALNNLLQQL | 28 |
| 2 | 1 070 | SLQEILSRL | 28 |
| 3 | 1 090 | LINGRLTAL | 28 |
| 4 | 1 311 | WLLIGFAGV | 27 |
| 5 | 972 | TLAATSASL | 26 |
| 6 | 4 | ILLISLPTT | 25 |
| 7 | 95 | FLSDFTNGI | 25 |
| 8 | 850 | NINATLTEV | 25 |
| 9 | 853 | ATLTEVNEL | 25 |
| 10 | 1 279 | RLQEAIKVL | 25 |
| 11 | 1 320 | AMLVLLFFI | 25 |
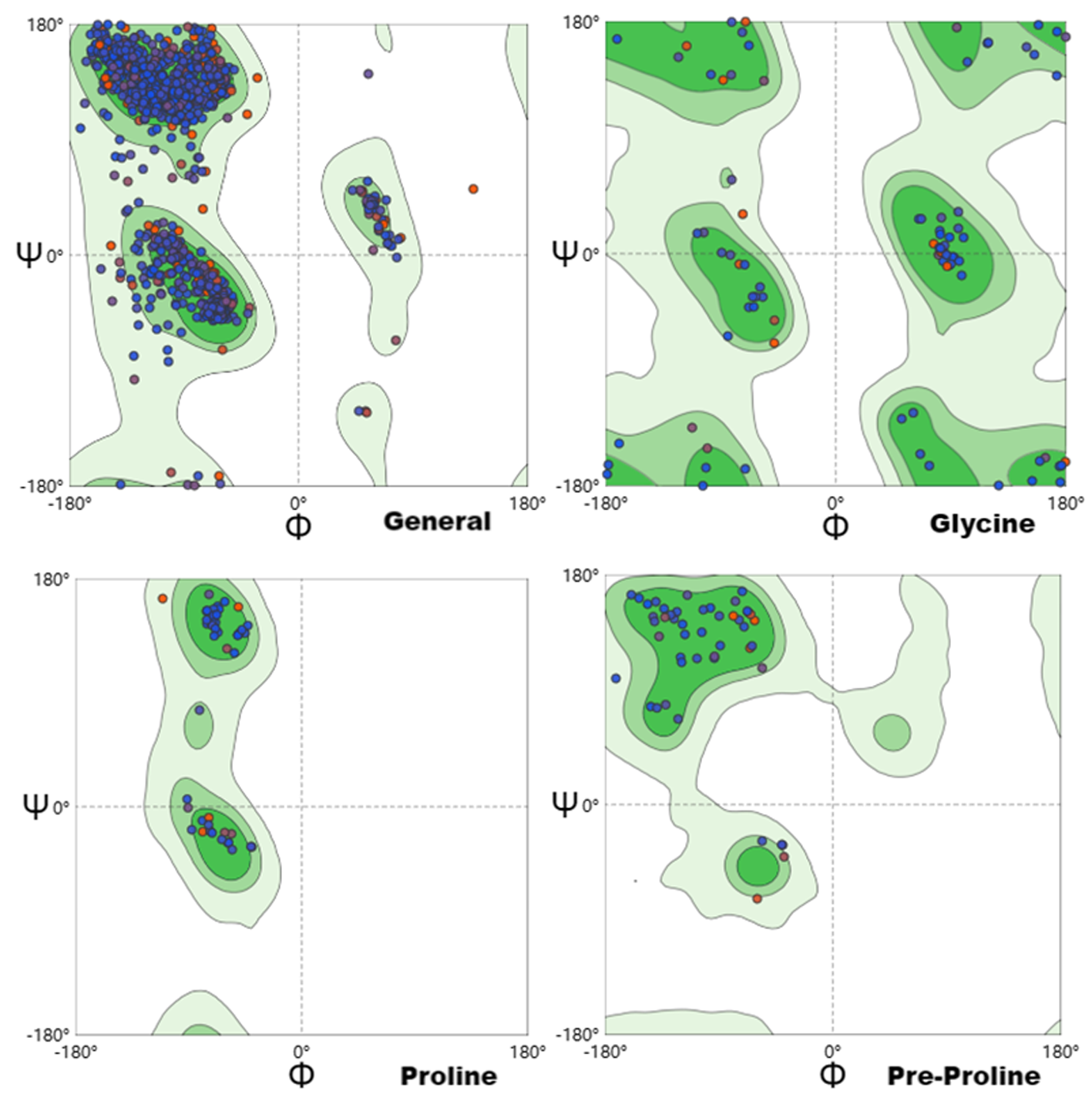
图10 BCoV S基因编码蛋白的拉氏图 注:深绿色:最适区域;绿色:允许区域;浅绿色:最大允许区域;白色:不允许区域
Fig.10 Ramachandran plots of protein encoded by BCoV S gene Note: Dark green: the optimum area; Green: the allowed area; Light green: the maximum allowable area; White: area not allowed
| [1] | Maier G U, Breitenbuecher J, Gomez J P, et al. Vaccination for the prevention of neonatal calf diarrhea in cow-calf operations: a scoping review[J]. Veterinary and Animal Science, 2022, 15: 100238. |
| [2] | Woode G N, Bridger J C, Meyling A. Significance of bovine coronavirus infection[J]. The Veterinary Record, 1978, 102(1): 15-16. |
| [3] |
Benfield D A, Saif L J. Cell culture propagation of a coronavirus isolated from cows with winter dysentery[J]. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 1990, 28(6): 1454-1457.
DOI PMID |
| [4] | Geng HL, Meng XZ, Yan WL. et al. Prevalence of bovine coronavirus in cattle in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Microbial Pathogenesis[J]. Microb Pathog, 2023, 176:106009. |
| [5] | Saif L J. Bovine respiratory coronavirus[J]. The Veterinary Clinics of North America Food Animal Practice, 2010, 26(2): 349-364. |
| [6] | Lotfollahzadeh S, Madadgar O, Reza Mohebbi M, et al. Bovine coronavirus in neonatal calf diarrhoea in Iran[J]. Veterinary Medicine and Science, 2020, 6(4): 686-694. |
| [7] | Zhu Q H, Su M J, Li Z J, et al. Epidemiological survey and genetic diversity of bovine coronavirus in Northeast China[J]. Virus Research, 2022, 308: 198632. |
| [8] | 寇美玲, 谢佳芮, 杨佳萍, 等. 牛冠状病毒的全基因组测序及遗传进化分析[J]. 动物医学进展, 2022, 43(10): 1-7. |
| KOU Meiling, XIE Jiarui, YANG Jiaping, et al. Whole genome sequencing and Genetic Evolution Analysis of Bovine Coronavirus[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2022, 43(10): 1-7. | |
| [9] | 张莹钰, 张迎春, 王青青, 等. 新疆南疆牛冠状病毒BCV-Aks-01株分离及基因型鉴定[J]. 中国兽医杂志, 2018, 54(2): 12-14, 18, 2. |
| ZHANG Yingyu, ZHANG Yingchun, WANG Qingqing, et al. Isolation and genotype identification of bovine coronavirus BCV-aks-01 strain in southern Xinjiang[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 54(2): 12-14, 18, 2. | |
| [10] | 张坤. 新疆北疆地区规模化奶牛场犊牛病毒性腹泻相关病原的调查研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2016. |
| ZHANG Kun. Investigation of Calves Viral Diarrhea Related Pathogen of Large-scale Dairy Farm in Northern Xin Jiang Region[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2016. | |
| [11] |
Masters P S. The molecular biology of coronaviruses[J]. Advances in Virus Research, 2006, 66: 193-292.
PMID |
| [12] |
Gunn L, Collins P J, O’Connell M J, et al. Phylogenetic investigation of enteric bovine coronavirus in Ireland reveals partitioning between European and global strains[J]. Irish Veterinary Journal, 2015, 68: 31.
DOI PMID |
| [13] | Franzo G, Drigo M, Legnardi M, et al. Bovine coronavirus: variability, evolution, and dispersal patterns of a No longer neglected betacoronavirus[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(11): 1285. |
| [14] | Singh S, Singh R, Singh K P, et al. Immunohistochemical and molecular detection of natural cases of bovine rotavirus and coronavirus infection causing enteritis in dairy calves[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis, 2020, 138: 103814. |
| [15] |
Abraham S, Kienzle T E, Lapps W, et al. Deduced sequence of the bovine coronavirus spike protein and identification of the internal proteolytic cleavage site[J]. Virology, 1990, 176(1): 296-301.
DOI PMID |
| [16] | Boileau M J, Kapil S. Bovine coronavirus associated syndromes[J]. The Veterinary Clinics of North America Food Animal Practice, 2010, 26(1): 123-146. |
| [17] |
Toftaker I, Holmøy I, Nødtvedt A, et al. A cohort study of the effect of winter dysentery on herd-level milk production[J]. Journal of Dairy Science, 2017, 100(8): 6483-6493.
DOI PMID |
| [18] | Yoshizawa N, Ishihara R, Omiya D, et al. Application of a photocatalyst as an inactivator of bovine coronavirus[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(12): 1372. |
| [19] | Salem E, Dhanasekaran V, Cassard H, et al. Global transmission, spatial segregation, and recombination determine the long-term evolution and epidemiology of bovine coronaviruses[J]. Viruses, 2020, 12(5): 534. |
| [20] |
Wrapp D, Wang N S, Corbett K S, et al. Cryo-EM structure of the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation[J]. Science, 2020, 367(6483): 1260-1263.
DOI PMID |
| [21] |
Yuan M, Wu N C, Zhu X Y, et al. A highly conserved cryptic epitope in the receptor binding domains of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6491): 630-633.
DOI PMID |
| [22] | 闫静静, 迟晓妍, 卢佳琪, 等. SARS-CoV-2结构蛋白S和N的生物信息学比较分析及应用研究[J]. 中国病原生物学杂志, 2023, 18(4): 377-384. |
| YAN Jingjing, CHI Xiaoyan, LU Jiaqi, et al. Comparative bioinformatics analysis of structural proteins s and N of SARS-CoV-2 and their application[J]. Journal of Pathogen Biology, 2023, 18(4): 377-384. | |
| [23] | Parker M D, Yoo D, Cox G J, et al. Primary structure of the S peplomer gene of bovine coronavirus and surface expression in insect cells[J]. The Journal of General Virology, 1990, 71 ( Pt 2): 263-270. |
| [24] | St Cyr-Coats K S, Storz J, Hussain K A, et al. Structural proteins of bovine coronavirus strain L 9: effects of the host cell and trypsin treatment[J]. Archives of Virology, 1988, 103(1/2): 35-45. |
| [25] | 向田, 章晓联. 病毒与宿主细胞的糖基化修饰及相关功能[J]. 生物化学与生物物理进展, 2017, 44(10): 898-907. |
| XIANG Tian, ZHANG Xiaolian. Glycosylation modification and related functions of virus and host cells[J]. Progress in Biochemistry and Biophysics, 2017, 44(10): 898-907. |
| [1] | 李敏, 马英, 呼尔查, 何文文, 史倩云, 阿力木江·加帕尔, 蒋倩, 巴音查汗. 边缘革蜱Dm 86基因表达及免疫原性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2022, 59(9): 2324-2332. |
| [2] | 陆亚冬, 刘贤侠, 陈创夫. 牛冠状病毒核衣壳蛋白原核表达及鉴定[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(6): 1154-1165. |
| [3] | 王玉凯, 赵欢, 牛建新. 库尔勒香梨kfpSPL及其启动子克隆分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2018, 55(6): 1017-1026. |
| [4] | 冯亚宁;姜志强;马晓玲;李江伟. 新疆双峰驼纳米抗体噬菌体展示文库多样性的生物信息学分析[J]. , 2016, 53(8): 1533-1538. |
| [5] | 郭春苗;杨波;吐迪·麦麦提;李宁;唐亚萍;龚鹏;王继勋. 8个新疆扁桃S-基因多态性与生物信息学研究[J]. , 2016, 53(6): 1067-1073. |
| [6] | 李宁;王柏柯;杨生保;唐亚萍;王强;杨涛;帕提古丽;余庆辉. 21种植物八氢番茄红素合成酶的生物信息学分析[J]. , 2015, 52(12): 2157-2165. |
| [7] | 苏立波;艾力扎提·艾力;刘柳;彭丹;杨艺;张富春. 盐穗木Hc2a1基因的克隆及与表达分析[J]. , 2014, 51(9): 1686-1691. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 13
|
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||