

新疆农业科学 ›› 2021, Vol. 58 ›› Issue (12): 2236-2243.DOI: 10.6048/j.issn.1001-4330.2021.12.010
靳一南1,2( ), 董合林1, 李鹏程1, 孙淼1, 邵晶晶1, 冯卫娜1, 徐文修2, 郑苍松1(
), 董合林1, 李鹏程1, 孙淼1, 邵晶晶1, 冯卫娜1, 徐文修2, 郑苍松1( )
)
收稿日期:2021-05-18
出版日期:2021-12-20
发布日期:2021-12-31
通信作者:
郑苍松
作者简介:靳一南(1995-),女,河北人,硕士研究生,研究方向为棉花高产栽培,(E-mail) 30663858839@qq.com
基金资助:
JIN Yinan1,2( ), DONG Helin1, LI Pengcheng1, SUN Miao1, SHAO Jingjing1, FENG Weina1, XU Wenxiu2, ZHENG Cangsong1(
), DONG Helin1, LI Pengcheng1, SUN Miao1, SHAO Jingjing1, FENG Weina1, XU Wenxiu2, ZHENG Cangsong1( )
)
Received:2021-05-18
Online:2021-12-20
Published:2021-12-31
Correspondence author:
ZHENG Cangsong
Supported by:摘要: 目的 田间小区下研究不同钾水平对棉花前期生长及光合作用的影响,为棉田钾素管理提供理论支撑。方法 采用随机区组试验设计,设置6个土壤速效钾浓度,k1(99.77 mg/kg)、k2(110.90 mg/kg)、k3(123.48 mg/kg)、k4(140.13 mg/kg)、k5(154.43 mg/kg)、k6(165.77 mg/kg)。于棉花子叶期选择10株测定干物重和全钾含量,苗期和蕾期分别选择10株和5株棉花测定干物重、叶面积、叶片净光合速率、胞间二氧化碳浓度、蒸腾速率、气孔导度、SPAD值、全钾含量。结果 棉花株高和茎粗在苗期的范围分别为5.10~6.37 cm和2.43~3.01 mm,均随土壤速效钾水平增加而增加,而苗期至蕾期的单日增长量差异不显著,分别在0.63和0.12 mm/d。k6处理的棉株干物重、果枝数、现蕾数、棉花叶面积及叶面积单日增长量均显著高于k1。在苗期和蕾期,不同土壤钾水平处理间棉花功能叶净光合速率、胞间二氧化碳浓度、蒸腾速率、气孔导度和叶绿素SPAD值均无显著差异,但各处理的棉株全钾含量和主茎叶钾含量均随土壤速效钾水平增加而显著增加。结论 土壤速效钾水平在100~160 mg/kg时,对棉株前期光合特性无显著影响,但高钾(>150 mg/kg)水平处理能够增加棉株叶面积和果枝数以保障产量结构。
中图分类号:
靳一南, 董合林, 李鹏程, 孙淼, 邵晶晶, 冯卫娜, 徐文修, 郑苍松. 土壤钾水平对棉花前期生长及光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2021, 58(12): 2236-2243.
JIN Yinan, DONG Helin, LI Pengcheng, SUN Miao, SHAO Jingjing, FENG Weina, XU Wenxiu, ZHENG Cangsong. Effects of soil potassium level on growth and photosynthetic characteristics of early cotton[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(12): 2236-2243.
| 钾浓度(处理编号) Potassium concentration (Treatment no.) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g/kg) | 速效磷 Quick-acting phosphorus (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Quick-acting potassium (mg/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 水溶性盐 Water-soluble salts (g/kg) | pH值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 0.57±0.02 | 18.75±6.76 | 99.77±3.94 | 11.20±1.33 | 0.48±0.01 | 7.52±0.34 |
| k2 | 0.58±0.02 | 23.67±4.99 | 110.90±6.74 | 10.72±0.61 | 0.48±0.02 | 7.67±0.27 |
| k3 | 0.57±0.02 | 14.25±2.28 | 123.48±13.35 | 10.81±0.40 | 0.51±0.04 | 7.58±0.23 |
| k4 | 0.58±0.02 | 15.33±2.87 | 140.13±6.11 | 10.53±0.24 | 0.50±0.03 | 7.70±0.28 |
| k5 | 0.57±0.02 | 17.67±4.92 | 154.43±19.74 | 10.28±0.39 | 0.49±0.02 | 7.51±0.26 |
| k6 | 0.57±0.03 | 17.67±4.50 | 165.77±13.04 | 11.62±1.17 | 0.51±0.04 | 7.54±0.23 |
表1 小区耕层土壤养分状况
Table 1 Micro area arable layer soil nutrient status
| 钾浓度(处理编号) Potassium concentration (Treatment no.) | 全氮 Total nitrogen (g/kg) | 速效磷 Quick-acting phosphorus (mg/kg) | 速效钾 Quick-acting potassium (mg/kg) | 有机质 Organic matter (g/kg) | 水溶性盐 Water-soluble salts (g/kg) | pH值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 0.57±0.02 | 18.75±6.76 | 99.77±3.94 | 11.20±1.33 | 0.48±0.01 | 7.52±0.34 |
| k2 | 0.58±0.02 | 23.67±4.99 | 110.90±6.74 | 10.72±0.61 | 0.48±0.02 | 7.67±0.27 |
| k3 | 0.57±0.02 | 14.25±2.28 | 123.48±13.35 | 10.81±0.40 | 0.51±0.04 | 7.58±0.23 |
| k4 | 0.58±0.02 | 15.33±2.87 | 140.13±6.11 | 10.53±0.24 | 0.50±0.03 | 7.70±0.28 |
| k5 | 0.57±0.02 | 17.67±4.92 | 154.43±19.74 | 10.28±0.39 | 0.49±0.02 | 7.51±0.26 |
| k6 | 0.57±0.03 | 17.67±4.50 | 165.77±13.04 | 11.62±1.17 | 0.51±0.04 | 7.54±0.23 |
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 苗期 Seedling stage (cm) | 蕾期 Bud stage (cm) | 日增长量 Daily growth (cm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 5.10b | 17.97a | 0.61a |
| k2 | 5.43ab | 18.83a | 0.64a |
| k3 | 5.80ab | 18.74a | 0.62a |
| k4 | 5.73ab | 18.59a | 0.61a |
| k5 | 6.17ab | 19.05a | 0.61a |
| k6 | 6.37a | 20.79a | 0.69a |
表2 棉株株高及日增长量变化
Table 2 Cotton plant height and daily growth
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 苗期 Seedling stage (cm) | 蕾期 Bud stage (cm) | 日增长量 Daily growth (cm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 5.10b | 17.97a | 0.61a |
| k2 | 5.43ab | 18.83a | 0.64a |
| k3 | 5.80ab | 18.74a | 0.62a |
| k4 | 5.73ab | 18.59a | 0.61a |
| k5 | 6.17ab | 19.05a | 0.61a |
| k6 | 6.37a | 20.79a | 0.69a |
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 苗期 Seedling stage (mm) | 蕾期 Bud stage (mm) | 日增长量 Daily growth (mm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 2.43c | 4.78b | 0.11a |
| k2 | 2.58bc | 5.13ab | 0.12a |
| k3 | 2.74abc | 5.24ab | 0.12a |
| k4 | 2.73abc | 5.25ab | 0.12a |
| k5 | 2.91ab | 5.50ab | 0.12a |
| k6 | 3.01a | 5.89a | 0.14a |
表3 棉株茎粗及日增长量变化
Table 3 Cotton plant stem diameter and daily growth
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 苗期 Seedling stage (mm) | 蕾期 Bud stage (mm) | 日增长量 Daily growth (mm/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 2.43c | 4.78b | 0.11a |
| k2 | 2.58bc | 5.13ab | 0.12a |
| k3 | 2.74abc | 5.24ab | 0.12a |
| k4 | 2.73abc | 5.25ab | 0.12a |
| k5 | 2.91ab | 5.50ab | 0.12a |
| k6 | 3.01a | 5.89a | 0.14a |
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 苗期 Seedling stage (cm2) | 蕾期 Bud stage (cm2) | 日增长量 Daily growth (cm2/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 37.53b | 510.71b | 22.53b |
| k2 | 47.42ab | 595.45ab | 26.10ab |
| k3 | 46.17ab | 583.86ab | 25.60ab |
| k4 | 43.42ab | 574.85ab | 25.31ab |
| k5 | 45.41ab | 591.66ab | 26.01ab |
| k6 | 52.34a | 731.67a | 32.35a |
表4 棉株叶面积及日增长量变化
Table 4 Leaf area and daily growth of cotton plant
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 苗期 Seedling stage (cm2) | 蕾期 Bud stage (cm2) | 日增长量 Daily growth (cm2/d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 37.53b | 510.71b | 22.53b |
| k2 | 47.42ab | 595.45ab | 26.10ab |
| k3 | 46.17ab | 583.86ab | 25.60ab |
| k4 | 43.42ab | 574.85ab | 25.31ab |
| k5 | 45.41ab | 591.66ab | 26.01ab |
| k6 | 52.34a | 731.67a | 32.35a |
| 处理 Deal with | 果枝始节 Node of the first fruiting branch | 果枝数 Branch number (个/株) | 现蕾数 Budding number (个/株) | 果枝始节 高度 Height of the first fruiting branch (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 6.7a | 3.2c | 3.3b | 12.5a |
| k2 | 6.2ab | 4.3abc | 4.9ab | 12.4a |
| k3 | 6.1ab | 4.8abc | 5.7ab | 11.6a |
| k4 | 5.9b | 3.6bc | 4.2b | 11.8a |
| k5 | 5.6b | 5.1ab | 5.9ab | 11.4a |
| k6 | 5.5b | 5.7a | 7.1a | 11.9a |
表5 蕾期棉株生育性状变化
Table 5 Growth traits of cotton plant at bud stage
| 处理 Deal with | 果枝始节 Node of the first fruiting branch | 果枝数 Branch number (个/株) | 现蕾数 Budding number (个/株) | 果枝始节 高度 Height of the first fruiting branch (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1 | 6.7a | 3.2c | 3.3b | 12.5a |
| k2 | 6.2ab | 4.3abc | 4.9ab | 12.4a |
| k3 | 6.1ab | 4.8abc | 5.7ab | 11.6a |
| k4 | 5.9b | 3.6bc | 4.2b | 11.8a |
| k5 | 5.6b | 5.1ab | 5.9ab | 11.4a |
| k6 | 5.5b | 5.7a | 7.1a | 11.9a |
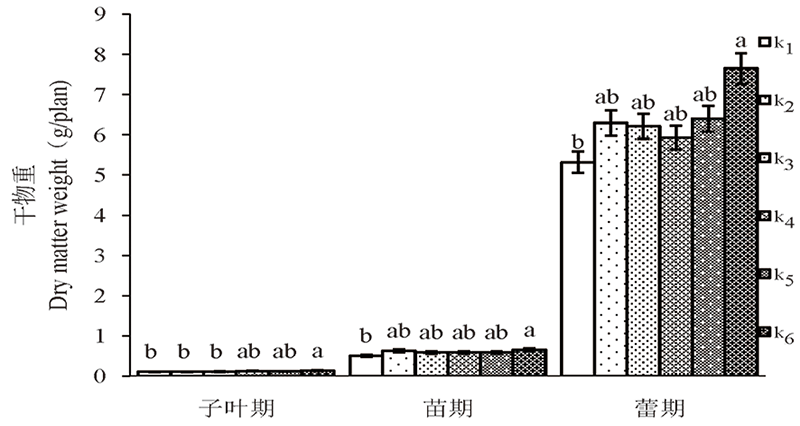
图1 棉株干物重变化 注:不同字母表示达到显著差异(P < 0.05)
Fig.1 Dry matter weight of cotton plant Note: Different letters in the chart indicate significant differences (P < 0.05)
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 净光合速率 Pn (umol/(m2·s)) | 胞间二氧化碳浓度 Ci (umol/mol) | 蒸腾速率 E (mmol/(m2·s)) | 气孔导度 Gs (mol/(m2·s)) | SPAD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | |
| k1 | 23.60a | 33.93a | 155.89a | 151.16a | 5.69a | 6.87a | 0.22a | 0.33a | 47.39a | 57.75a |
| k2 | 23.62a | 33.35a | 173.07a | 154.79a | 6.42a | 6.98a | 0.24a | 0.32a | 50.46a | 58.10a |
| k3 | 24.89a | 35.09a | 152.98a | 152.97a | 5.83a | 7.04a | 0.23a | 0.34a | 49.43a | 56.00a |
| k4 | 24.62a | 35.54a | 164.25a | 153.80a | 6.22a | 7.46a | 0.24a | 0.36a | 49.54a | 55.37a |
| k5 | 26.42a | 33.67a | 179.63a | 148.69a | 6.75a | 6.86a | 0.23a | 0.32a | 50.19a | 56.37a |
| k6 | 26.61a | 33.90a | 168.94a | 139.87a | 6.64a | 6.95a | 0.24a | 0.31a | 49.24a | 57.33a |
表6 棉花功能叶光合特性变化
Table 6 Photosynthetic characteristics of functional leaves of cotton
| 处理编号 Treatment no | 净光合速率 Pn (umol/(m2·s)) | 胞间二氧化碳浓度 Ci (umol/mol) | 蒸腾速率 E (mmol/(m2·s)) | 气孔导度 Gs (mol/(m2·s)) | SPAD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | 苗期 Seedling stage | 蕾期 Bud stage | |
| k1 | 23.60a | 33.93a | 155.89a | 151.16a | 5.69a | 6.87a | 0.22a | 0.33a | 47.39a | 57.75a |
| k2 | 23.62a | 33.35a | 173.07a | 154.79a | 6.42a | 6.98a | 0.24a | 0.32a | 50.46a | 58.10a |
| k3 | 24.89a | 35.09a | 152.98a | 152.97a | 5.83a | 7.04a | 0.23a | 0.34a | 49.43a | 56.00a |
| k4 | 24.62a | 35.54a | 164.25a | 153.80a | 6.22a | 7.46a | 0.24a | 0.36a | 49.54a | 55.37a |
| k5 | 26.42a | 33.67a | 179.63a | 148.69a | 6.75a | 6.86a | 0.23a | 0.32a | 50.19a | 56.37a |
| k6 | 26.61a | 33.90a | 168.94a | 139.87a | 6.64a | 6.95a | 0.24a | 0.31a | 49.24a | 57.33a |
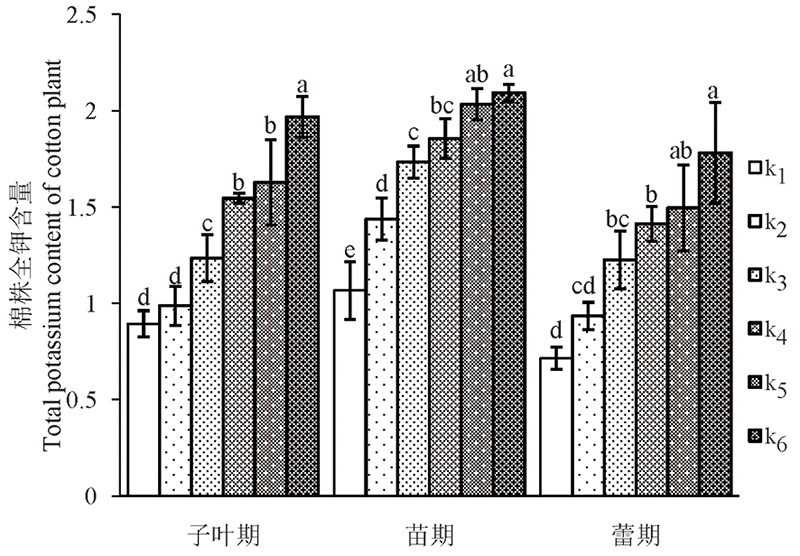
图2 棉株全钾含量变化 注:不同字母表示达到显著差异(P < 0.05)
Fig. 2 Total potassium content of cotton plant Note: Different letters in the chart indicate significant differences (P < 0.05)

图3 棉花叶片全钾含量变化 注:不同字母表示达到显著差异(P < 0.05)
Fig.3 Total potassium content in cotton leaves Note: Different letters in the chart indicate significant differences (P < 0.05)
| [1] | 白由路, 杨俐苹. 我国农业中的测土配方施肥[J]. 土壤肥料, 2006,(2):3-7. |
| BAI Youlu, YANG Liping. Soil test and formula fertilization in agriculture of our country[J]. Soil and Fertilizer, 2006,(2):3-7. | |
| [2] | 李鹏程, 郑苍松, 孙淼, 等. 国内棉花氮营养诊断和推荐施氮研究进展[J]. 中国棉花, 2019,46(6):1-4, 15. |
| LI Pengcheng, ZHENG Cangsong, SUN Miao, et al. Research progress of nitrogen nutrition diagnosis and recommended nitrogen application in cotton in China[J]. China Cotton, 2019,46(6):1-4, 15. | |
| [3] | 哈丽哈什·依巴提, 张炎, 李青军, 等. 施肥对棉花养分吸收、分配、利用和产量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2018,(2):61-66. |
| Hariharsh Yibadi, ZHANG Yan, LI Qingjun, et al. Effects of fertilization on nutrient uptake, distribution, utilization and yield of cotton[J]. Soil and Fertilizer in China, 2018,(2):61-66. | |
| [4] | 陆志峰, 鲁剑巍, 潘勇辉, 等. 钾素调控植物光合作用的生理机制[J]. 植物生理学报, 2016,52(12):1773-1784. |
| LU Zhifeng, LU Jianwei, PAN Yonghui, et al. Physiological mechanism of potassium regulating plant photosynjournal[J]. Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology, 2016,52(12):1773-1784. | |
| [5] | 耿计彪, 马强, 张民, 等. 包膜氯化钾一次基施对棉花生长周期钾素供应, 产量及品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016,(4):1064-1070. |
| GENG Jibiao, MA Qiang, ZHANG Min, et al. Effect of primary potassium chloride application on potassium supply, yield and quality in cotton growth cycle[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016,(4):1064-1070. | |
| [6] | 付小勤, 原保忠, 张献龙, 等. 钾肥分期施用对棉花产量及构成因素影响[J]. 中国农学通报, 2014,30(18):95-103. |
| FU Xiaoqin, YUAN Baozhong, ZHANG Xianlong, et al. Effect of potassium fertilizer application in stages on cotton yield and its components[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2014,30(18):95-103. | |
| [7] | Tariq M, Afzal M N, Muhammad D, et al. Relationship of tissue potassium content with yield and fiber quality components of Bt cotton as influenced by potassium application methods[J]. Field Crops Research, 2018, (229):37-43. |
| [8] | Fontana J E, Wang G, Sun R, et al. Impact of potassium deficiency on cotton growth, development and potential MicroRNA-mediated mechanism[J]. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry, 2020, (153):72-80. |
| [9] | 刘爱忠, 洪德成, 董合林, 等. 不同供钾水平和氮素形态对棉花功能叶质体色素、碳氮代谢及钾含量的影响[J]. 河南农业科学, 2018,47(4):31-37. |
| LIU Aizhong, HONG Decheng, DONG Helin, et al. Effects of different potassium supply levels and nitrogen forms on pigment, carbon and nitrogen metabolism and potassium content of functional leaf plastids in cotton[J]. Henan Agricultural Sciences, 2018,47(4):31-37. | |
| [10] | Yang F Q, Du M W, Tian X L, et al. Cotton yield and potassium use efficiency as affected by potassium fertilizer management with stalks returned to field[J]. Crop Science, 2016,56(2):740-746. |
| [11] | 齐海坤, 李芳军, 孟璐, 等. 氮、钾肥运筹对棉花熟性、产量和肥料利用率的影响[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2020,43(4):1-9. |
| QI Haikun, LI Fangjun, MENG Lu, et al. Effects of nitrogen and potash fertilizer operation on cotton ripness, yield and fertilizer utilization rate[J]. Journal of Hebei Agricultural University, 2020,43(4):1-9. | |
| [12] | 李书田, 邢素丽, 张炎, 等. 钾肥用量和施用时期对棉花产量品质和棉田钾素平衡的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2016,(1):111-121. |
| LI Shutian, XING Suli, ZHANG Yan, et al. Effect of potassium fertilizer amount and application period on cotton yield and quality and cotton field potassium balance[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2016,(1):111-121. | |
| [13] | 陈世耕. 棉花早期生长与产量品质的关系的研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 1952,(6):14-15. |
| CHEN Shigeng. Study on the relationship between early growth and yield and quality of cotton[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1952,(6):14-15. | |
| [14] | 李宗泰, 陈二影, 张美玲, 等. 施钾方式对棉花叶片抗氧化酶活性、产量及钾肥利用效率的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2012,38(3):487-494. |
| LI Zongtai, CHEN Erying, ZHANG Meiling, et al. Effect of potassium application on antioxidant enzyme activity, yield and utilization efficiency of potash fertilizer in cotton leaves[J]. Acta Agronomica, 2012,38(3):487-494. | |
| [15] | 许晓龙, 李宗泰, 姬红, 等. 钾素营养对不同棉花品种苗期生长和叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 华北农学报, 2013,28(S1):303-307. |
| XU Xiaolong, LI Zongtai, JI Hong, et al. Effects of potassium nutrition on growth and leaf physiological characteristics of different cotton cultivars at seedling stage[J]. North China Journal of Agronomy, 2013,28(S1):303-307. | |
| [16] | 胡伟. 钾对棉铃对位叶碳氮代谢及抗氧化代谢的影响[D]. 南京农业大学, 2017. |
| HU Wei. Effects of potassium on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and antioxidant metabolism of cotton boll counterleaves[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2017. | |
| [17] | 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 中国农业出版社, 2000. |
| BAO Shidan. Soil agrochemical analysis [M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2000. | |
| [18] | 庞念厂, 魏晓文, 贵会平, 等. 棉花株式图APP田间记录系统与初步统计[J]. 中国棉花, 2017,44(9):16-18, 21. |
| PANG Nianchang, WEI Xiaowen, GUI Huiping, et al. Field Record System and Preliminary statistics of Cotton plant type chart APP[J]. China Cotton, 2017,44(9):16-18, 21. | |
| [19] | 许晓龙. 钾肥运筹对不同基因型棉花品种生长发育及产量品质的影响[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2013. |
| XU Xiaolong. Effects of potash fertilizer operation on growth and development and yield and quality of cotton varieties with different genotypes[D]. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2013. | |
| [20] | 秦宇坤, 陈俊英, 王玉萍, 等. 施钾量对油后直播棉干物质分配及产量的影响[J]. 棉花科学, 2020,42(4):3-7. |
| QIN Yukun, CHEN Junying, WANG Yuping, et al. Effect of potassium application amount on dry matter distribution and yield of direct seeding cotton after oil application[J]. Cotton Sciences, 2020,42(4):3-7. | |
| [21] | 李伶俐, 房卫平, 马宗斌, 等. 氮钾配合施用对短季棉光合特性和产量品质的影响[J]. 棉花学报, 2008,20(5):379-383. |
| LI Lingli, FANG Weiping, MA Zongbin, et al. Effects of combined application of nitrogen and potassium on photosynthetic characteristics and yield and quality of short-season cotton[J]. Cotton Science, 2008,20(5):379-383. | |
| [22] | 杜海岩, 柳新伟, 徐双, 等. 钾素营养对盐碱地棉花中后期生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 江苏农业科学, 2016,44(3):114-117. |
| DU Haiyan, LIU Xinwei, XU Shuang, et al. Effects of potassium nutrition on growth and physiological characteristics of cotton in saline and alkaline land in middle and late stage[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2016,44(3):114-117. | |
| [23] | 耿计彪, 张民, 马强, 等. 控释氮肥对棉花叶片生理特性和产量的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2015,29(4):267-271. |
| GENG Jibiao, ZHNG Min, MA Qiang, et al. Effects of controlled release nitrogen fertilizer on physiological characteristics and yield of cotton leaves[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2015,29(4):267-271. | |
| [24] | 马宗斌, 李伶俐, 朱伟, 等. 施钾对不同基因型棉花光合特性及产量和品质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2007,13(6):1129-1134. |
| MA Zongbin, LI Lingli, ZHU Wei, et al. Effects of potassium fertilization on photosynthetic characteristics, yield and quality of cotton with different genotypes[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2007,13(6):1129-1134. | |
| [25] | 郭英, 孙学振, 宋宪亮, 等. 钾营养对棉花苗期生长和叶片生理特性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2006,12(3):363-368. |
| GUO Ying, SUN Xuezhen, SONG Xianliang, et al. Effect of potassium nutrition on growth and leaf physiological characteristics of cotton at seedling stage[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer, 2006,12(3):363-368. | |
| [26] | 刘伟华, 詹学武, 向凤玲, 等. 光照和施钾对棉苗生长发育和钾效率的影响[J]. 棉花科学, 2015,37(4):12-16. |
| LIU Weihua, ZHAN Xuewu, XIANG Fengling, et al. Effects of light and potassium application on growth and potassium efficiency of cotton seedlings[J]. Cotton Science, 2015,37(4):12-16. | |
| [27] | 董合忠, 唐薇, 李振怀, 等. 棉花缺钾引起的形态和生理异常(英文)[J]. 西北植物学报, 2005, (3):615-624. |
| DONG Hezhong, TANG Wei, LI Zhenhuai, et al. Morphological and physiological abnormalities caused by potassium deficiency in cotton (English)[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-West, 2005,(3):615-624. |
| [1] | 王朋, 郑凯, 赵杰银, 高文举, 龙遗磊, 陈全家, 曲延英. 陆地棉种质资源材料的耐热性评价及指标筛选[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2081-2090. |
| [2] | 王辉, 郭金成, 宋佳, 张庭军, 何良荣. 高温胁迫下陆地棉GhCIPK6转基因后代生理生化分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2109-2119. |
| [3] | 陈传信, 张永强, 聂石辉, 孔德鹏, 赛力汗·赛, 徐其江, 雷钧杰. 生物质炭施用量对滴灌冬小麦生长发育和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2146-2151. |
| [4] | 宋冰梅, 姜岩, 陈鑫, 张宇, 程宛楠, 潘洪生. 新型转基因高产棉花萌发期和苗期耐盐性与耐碱性评价[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(9): 2239-2247. |
| [5] | 马青山, 杜霄, 陶志鑫, 韩万里, 龙遗磊, 艾先涛, 胡守林. 陆地棉种质材料机采农艺性状鉴定分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1830-1839. |
| [6] | 肖乐乐, 李志强, 冶军, 蒲敏, 阮向阳, 刘怀金. 肽肥与镁配施对森田尼无核葡萄品质和产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 1904-1912. |
| [7] | 魏迎凤, 张全成, 查慧, 王小丽, 王俊刚. 二甲戊灵对龙葵苗期主要生长发育和生理指标的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(8): 2013-2021. |
| [8] | 杨晓娟, 靳娟, 樊丁宇, 郝庆, 杨磊, 耿文娟. 极端高温环境对骏枣和伏脆蜜枣光合特性的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(7): 1679-1688. |
| [9] | 耿翡翡, 孟超敏, 卿桂霞, 周佳敏, 张富厚, 刘逢举. 陆地棉磷高效基因GhMYB4的克隆与表达分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(6): 1406-1412. |
| [10] | 田文强, 郭飞, 聂凌帆, 孙刚刚, 王泓懿, 史永清, 尚艳明, 吴利, 石书兵, 张金汕. 超晚播对冬小麦光合特性、干物质积累及产量的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1059-1066. |
| [11] | 李家辉, 赵晓钰, 李海英, 张俐华, 张杰, 魏彦, 周军, 赵全庄, 李宗福. 也迷离鸡生长发育规律及体重体尺的相关性分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(5): 1281-1291. |
| [12] | 彭增莹, 张巨松, 卡地力亚·阿不都克力木, 贺宏伟, 刘群, 郭仁松. 氮肥与缩节胺对机采棉生长发育及氮素分布的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 781-789. |
| [13] | 陈丽靓, 鲁倩君, 马媛媛, 刘迎, 赵宝龙, 孙军利. 不同葡萄品种的耐盐性比较分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(4): 880-888. |
| [14] | 郝曦煜, 杨涛, 张俊杰, 李雪, 张仲鹃, 武晨清, 宗绪晓, 冷友斌, 陈博, 郭来春. 不同氮磷钾处理对鹰嘴豆产量、农艺性状及经济效益的影响[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(3): 555-566. |
| [15] | 陈亮亮, 张梦, 郭立平, 戚廷香, 张学贤, 唐会妮, 王海林, 乔秀琴, 吴建勇, 邢朝柱. 陆地棉杂交组合F1、F2苗期优势表现及亲本配合力分析[J]. 新疆农业科学, 2023, 60(2): 261-271. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||